Contents
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- What's new
- About Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal
- Distribution kit
- Hardware and software requirements
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Compatibility of KUMA versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Compatibility of XDR versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Compatibility of KPSN versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Compatibility of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with VK Cloud
- Restrictions
- Data provision
- Service data of the application
- Data of the Central Node and Sensor components
- Sandbox component data
- Data transmitted between application components
- Data contained in application trace files
- Data of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows data
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux data
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac data
- Application licensing
- About the End User License Agreement
- About the license
- About the license certificate
- About the key
- About the key file
- Viewing information about the license and added keys in the web interface of the Central Node
- Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of the Central Node
- Viewing the text of the Privacy Policy in the web interface of the Central Node
- Viewing information about the third-party code used in the application
- Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of the Sandbox
- Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement for the Endpoint Agent component
- Adding a key
- Replacing a key
- Removing a key
- Application modes based on the license
- Architecture of the application
- Operating principle of the application
- Distributed solution and multitenancy
- Distributed solution and multitenancy mode transition scenario
- Modifications of application settings for the distributed solution and multitenancy mode
- Assigning the PCN role to a server
- Assigning the SCN role to a server
- Processing SCN to PCN connection requests
- Viewing information about tenants, PCN and SCN servers
- Adding a tenant to the PCN server
- Deleting a tenant from the PCN server
- Renaming a tenant on the PCN server
- Disconnecting an SCN from PCN
- Modifications of application settings for disconnecting an SCN from PCN
- Decommissioning an SCN server
- Sizing Guide
- Installing and performing initial configuration of the application
- Preparing for installing application components
- Preparing the IT infrastructure for installing application components
- Preparing the IT infrastructure for integration with a mail server used for receiving messages via POP3
- Preparing the IT infrastructure for integration with a mail server used for receiving messages via SMTP
- Preparing the virtual machine for installing the Sandbox component
- Preparing an installation disk image with the Central Node, Sensor, and Sandbox components
- Procedure for installing and configuring application components
- Installing the Sandbox component
- Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting a disk for installing the Sandbox component
- Step 3. Assigning the host name
- Step 4. Selecting the controlling network interface in the list
- Step 5. Assigning the address and network mask of the controlling interface
- Step 6. Adding DNS server addresses
- Step 7. Configuring a static network route
- Step 8. Configuring the minimum password length for the Sandbox administrator password
- Step 9. Creating the Sandbox administrator account
- Deploying the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster
- Deploying a storage server
- Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting a server role
- Step 3. Selecting the deployment mode
- Step 4. Selecting a disk for installing the component
- Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
- Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
- Step 7. Selecting the cluster network interface
- Step 8. Selecting the external network interface
- Step 9. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
- Step 10. Creating an administrator account and authenticating the server in the cluster
- Step 11. Adding DNS server addresses
- Step 12. Selecting disks for the Ceph storage
- Deploying the processing server
- Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting a server role
- Step 3. Selecting the deployment mode
- Step 4. Selecting a disk for installing the component
- Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
- Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
- Step 7. Selecting the cluster network interface
- Step 8. Selecting the external network interface
- Step 9. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
- Step 10. Authenticating the server in the cluster
- Step 11. Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
- Step 12. Adding DNS server addresses
- Deploying a storage server
- Installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the server
- Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting a server role
- Step 3. Selecting a disk for installing the component
- Step 4. Allocating the disk for the Targeted Attack Analyzer component's database
- Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
- Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
- Step 7. Selecting the external network interface
- Step 8. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
- Step 9. Creating the administrator account
- Step 10. Adding DNS server addresses
- Step 11. Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
- Step 12. Configuring time synchronization with an NTP server
- Installing the Sensor component on a standalone server
- Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
- Step 2. Selecting a server role
- Step 3. Selecting a disk for installing the component
- Step 4. Selecting the external network interface
- Step 5. Connecting to the server with the Central Node component
- Step 6. Creating the administrator account
- Configuring Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system
- Optimization of network interface settings for the Sensor component
- Connecting and configuring external storage for the Sensor component
- Purging hard drives on storage servers
- Preparing for installing application components
- Configuring the sizing settings of the application
- Configuring the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
- Configuring the trusted connection of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server
- Generating a TLS certificate for the Central Node server in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Central Node server using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Uploading a TLS certificate of the Central Node server or Sensor to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Enabling the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Generating a TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and downloading a cryptographic container
- Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Viewing the table of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Filtering and searching Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Deleting Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Configuring the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate by the Central Node server and uploading a cryptographic container to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Configuring traffic redirection from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to the Sensor server
- Generating a TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
- Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to your computer
- Configuring the integration and trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side
- Configuring the trusted connection of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application
- Getting started with the application
- Managing accounts of application administrators and users
- Creating an administrator account for the application web interface
- Creating a user account for the application web interface
- Configuring user account table display
- Viewing the user account table
- Filtering user accounts
- Clearing the account filter
- Changing access rights of an application web interface user account
- Enabling and disabling an administrator account or user account of the application web interface
- Changing the password of an application administrator or user account
- Changing the password of your account
- Authentication using domain accounts
- Participation in Kaspersky Security Network and use of Kaspersky Private Security Network
- Managing the Sandbox component through the web interface
- Updating the Sandbox component databases
- Configuring connection between the Sandbox and Central Node components
- Configuring the Sandbox component network interfaces
- Setting the Sandbox system date and time
- Installing and configuring images of operating systems and applications required for the operation of the Sandbox component
- Managing operating system and application images in the Sandbox Storage
- Managing virtual machine templates
- Managing virtual machines
- Setting the maximum number of simultaneously running virtual machines
- Changing the number of license keys for a virtual machine with a custom operating system image
- Downloading the Sandbox system log to the hard drive
- Exporting Sandbox settings
- Importing Sandbox settings
- Restarting the Sandbox server
- Powering off the Sandbox server
- Changing the Sandbox administrator account password
- For administrators: Getting started with the application web interface
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Interface
- Monitoring the performance of the application
- About widgets and layouts
- Selecting a tenant and a server to manage in the Dashboard section
- Adding a widget to the current layout
- Moving a widget in the current layout
- Removing a widget from the current layout
- Saving a layout to PDF
- Configuring the data display period in widgets
- Monitoring the receipt and processing of incoming data
- Monitoring the queues for data processing by application modules and components
- Monitoring the processing of data by the Sandbox component
- Viewing the working condition of modules and components of the application
- Managing Central Node, PCN, or SCN servers using the application web interface
- Configuring the date and time on the server
- Generating or uploading a TLS certificate of the server
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the server
- Assigning a server DNS name
- Configuring DNS settings
- Configuring settings of the network interface
- Configuring the default network route
- Configuring proxy server connection settings
- Configuring the mail server connection
- Selecting operating systems to use when scanning objects in Sandbox
- Managing the Sensor component
- Viewing the table of servers with the Sensor component
- Processing a connection request from the Sensor component
- Configuring the maximum size of a scanned file
- Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
- Selecting network protocols for receiving mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
- Configuring integration with a mail server via SMTP
- Configuring TLS encryption of connections with a mail server via SMTP
- Configuring integration with a proxy server via ICAP
- Configuring raw network traffic recording
- Configuring integration with a mail server via POP3
- Managing the cluster
- Notifications about the maximum allowed CPU and RAM load for the Central Node and Sensor servers
- Configuring the SNMP protocol connection
- Managing Endpoint Agent host information
- Selecting a tenant to manage in the Endpoint Agents section
- Viewing the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component on a standalone Central Node server
- Viewing information about a host
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that have been isolated from the network
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by PCN and SCN server names
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by computer IP address
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by operating system version on the computer
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity
- Quickly creating a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Resetting the filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Configuring activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component
- Removing hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Automatic removal of inactive hosts
- Supported interpreters and processes
- Configuring integration with the Sandbox component
- Configuring integration with external systems
- Configuring integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response
- Configuring integration with an SIEM system
- Managing the activity log
- Updating application databases
- Creating a list of passwords for archives
- Configuring integration with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1
- For security officers: Getting started with the application web interface
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Interface
- Selecting a tenant to manage in the web interface of the application
- Monitoring the performance of the application
- About widgets and layouts
- Adding a widget to the current layout
- Moving a widget in the current layout
- Removing a widget from the current layout
- Saving a layout to PDF
- Configuring the data display period in widgets
- Configuring the widget display scale
- Basics of managing "Alerts" type widgets
- Viewing the working condition of modules and components of the application
- Viewing the alert table
- Configuring the alert table display
- Filtering, sorting, and searching alerts
- Filtering alerts by VIP status
- Filtering and searching alerts by time
- Filtering alerts by level of importance
- Filtering and searching alerts by categories of objects detected
- Filtering and searching alerts by obtained information
- Filtering and searching alerts by source address
- Filtering and searching alerts by destination address
- Filtering and searching alerts by server name
- Filtering and searching alerts by technology name
- Filtering and searching alerts by the status of their processing by the user
- Sorting alerts in the table
- Quickly creating an alert filter
- Clearing an alert filter
- Recommendations for processing alerts
- Viewing alerts
- Viewing alert details
- General information about an alert of any type
- Information in the Object information section
- Information in the Alert information section
- Information in the Scan results section
- Information in the IDS rule section
- Information in the Network event section
- Scan results in Sandbox
- IOC scan results
- Information in the Hosts section
- Information in the Change log section
- Sending alert data
- Viewing alert details
- User actions performed on alerts
- Events database threat hunting
- Searching events in design mode
- Searching events in source code mode
- Sorting events in the table
- Changing the event search conditions
- Searching events by processing results in EPP applications
- Uploading an IOC file and searching for events based on conditions defined in the IOC file
- Creating a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions
- Event information
- Recommendations for processing events
- Information about events in the tree of events
- Viewing the table of events
- Configuring the event table display
- Viewing information about an event
- Information about the "Process started" event
- Information about the "Process terminated" event
- Information about the "Module loaded" event
- Information about the "Remote connection" event
- Information about the "Prevention rule" event
- Information about the "Document blocked" event
- Information about the "File modified" event
- Information about the "System event log" event
- Information about the "Changes in the registry" event
- Information about the "Port listened" event
- Information about the "Driver loaded" event
- Information about the "Alert" event
- Information about the "Alert processing result" event
- Information about the "Interpreted file run" event
- Information about the "AMSI scan" event
- Information about the "Interactive command input at the console" event
- Managing Endpoint Agent host information
- Viewing the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Configuring the display of the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Viewing information about a host
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that have been isolated from the network
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by PCN and SCN server names
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by computer IP address
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by operating system version on the computer
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version
- Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity
- Quickly creating a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Resetting the filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Removing hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Configuring activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component
- Supported interpreters and processes
- Network isolation of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Automatically sending files from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts to be scanned by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules
- Selecting operating systems to use when scanning objects in Sandbox
- Managing tasks
- Viewing the task table
- Viewing information about a task
- Creating a get file task
- Creating a forensic collection task
- Creating a registry key retrieval task
- Creating an NTFS metafile retrieval task
- Creating a process memory dump retrieval task
- Creating a disk image retrieval task
- Creating a RAM dump retrieval task
- Creating a process termination task
- Creating a task to scan hosts using YARA rules
- Creating a service management task
- Creating an application execution task
- Creating a file deletion task
- Creating a file quarantine task
- Creating a quarantined file recovery task
- Creating a copy of a task
- Deleting tasks
- Filtering tasks by creation time
- Filtering tasks by type
- Filtering tasks by name
- Filtering tasks by file name and path
- Filtering tasks by description
- Filtering tasks by server name
- Filtering tasks based on the name of the user that created the task
- Filtering tasks by processing status
- Clearing a task filter
- Managing policies (prevention rules)
- Viewing the prevention rule table
- Configuring prevention rule table display
- Viewing a prevention rule
- Creating a prevention rule
- Importing prevention rules
- Enabling and disabling a prevention rule
- Enabling and disabling presets
- Deleting prevention rules
- Filtering prevention rules by name
- Filtering prevention rules by type
- Filtering prevention rules by file hash
- Filtering prevention rules by server name
- Clearing a prevention rule filter
- Managing user-defined rules
- Using indicators of compromise (IOC) and attack (IOA) for Threat Hunting
- Managing user-defined TAA (IOA) rules
- Viewing the TAA (IOA) rule table
- Creating a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions
- Importing a TAA (IOA) rule
- Viewing custom TAA (IOA) rule details
- Searching for alerts and events in which TAA (IOA) rules were triggered
- Filtering and searching TAA (IOA) rules
- Resetting the TAA (IOA) rule filter
- Enabling and disabling TAA (IOA) rules
- Modifying a TAA (IOA) rule
- Deleting TAA (IOA) rules
- Managing user-defined IOC rules
- Viewing the table of IOC files
- Viewing information about an IOC file
- Uploading an IOC file
- Downloading an IOC file to a computer
- Enabling and disabling the automatic use of an IOC file when scanning hosts
- Deleting an IOC file
- Searching for alerts in IOC scan results
- Searching for events using an IOC file
- Filtering and searching IOC files
- Clearing an IOC file filter
- Configuring an IOC scan schedule
- Managing user-defined IDS rules
- Importing a user-defined IDS rule
- Viewing the information of a user-defined IDS rule
- Enabling and disabling the use of an IDS rule when scanning events
- Configuring the importance of alerts generated by the user-defined IDS rule
- Replacing a user-defined IDS rule
- Exporting a user-defined IDS rule file to the computer
- Deleting a user-defined IDS rule
- Managing user-defined YARA rules
- Managing objects in Storage and quarantine
- Viewing the table of objects that were placed in Storage
- Viewing information about an object manually placed in Storage using the web interface
- Viewing information about an object placed in Storage by a get file task
- Viewing information about an object placed in Storage by a get data task
- Downloading objects from Storage
- Uploading objects to Storage
- Sending objects in Storage for scanning
- Deleting objects from Storage
- Filtering objects in Storage by object type
- Filtering objects in Storage by object description
- Filtering objects in Storage based on scan results
- Filtering objects in Storage based on the name of Central Node, PCN, or SCN server
- Filtering objects in Storage by object source
- Filtering objects based on the time they were placed in Storage
- Clearing a Storage objects filter
- Viewing the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
- Viewing information about a quarantined object
- Restoring an object from Quarantine
- Obtaining a copy of a quarantined object on a Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
- Removing information about the quarantined object from the table
- Filtering information about quarantined objects by object type
- Filtering information about quarantined objects by object description
- Filtering information about quarantined objects by host name
- Filtering information about quarantined objects by time
- Resetting the filter for information about quarantined objects
- Managing reports
- Viewing the table of templates and reports
- Creating a template
- Creating a report based on a template
- Viewing a report
- Downloading a report to a local computer
- Editing a template
- Filtering templates by name
- Filtering templates based on the name of the user that created the template
- Filtering templates by creation time
- Clearing a template filter
- Deleting a template
- Filtering reports by creation time
- Filtering reports by name
- Filtering reports by the name of the server with the Central Node component
- Filtering reports based on the name of the user that created the report
- Clearing a report filter
- Deleting a report
- Managing rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts
- Viewing the table of VIP status assignment rules
- Creating a VIP status assignment rule
- Deleting a VIP status assignment rule
- Modifying a VIP status assignment rule
- Importing a list of VIP status assignment rules
- Exporting the list of data excluded from the scan
- Filtering and searching by type of VIP status assignment rule
- Filtering and searching by value of VIP status assignment rule
- Filtering and searching by description of VIP status assignment rule
- Clearing a VIP status assignment rule filter
- Managing the list of scan exclusions
- Viewing the table of data excluded from the scan
- Adding a scan exclusion rule
- Deleting a scan exclusion rule
- Editing a rule added to scan exclusions
- Exporting the list of data excluded from the scan
- Filtering rules in the scan exclusion list by criterion
- Searching rules in the scan exclusion list by value
- Resetting the rule filter in the scan exclusion list
- Managing IDS exclusions
- Managing TAA exclusions
- Managing ICAP exclusions
- Viewing the ICAP exclusion table
- Adding a rule to ICAP exclusions
- Removing rules from ICAP exclusions
- Editing or disabling a rule in the ICAP exclusion list
- Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by criterion
- Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by value
- Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by state
- Clearing rule filter conditions in the ICAP exclusion list
- Creating a list of passwords for archives
- Viewing server settings
- Viewing the table of servers with the Sandbox component
- Viewing the settings of the set of operating systems used for scanning objects in Sandbox
- Viewing the table of servers with the Sensor component
- Managing raw network traffic
- Viewing the table of external systems
- Managing user-defined Sandbox rules
- Viewing the table of user-defined Sandbox rules
- Configuring the Sandbox rule table display
- Filtering and searching Sandbox rules
- Clearing a Sandbox rule filter
- Viewing the information of a user-defined Sandbox rule
- Creating a user-defined Sandbox rule for scanning files
- Creating a user-defined Sandbox rule for URL scanning
- Copying a user-defined Sandbox rule
- Importing user-defined Sandbox rules for file scanning
- Editing a user-defined Sandbox rule
- Enabling or disabling user-disabling Sandbox rules
- Exporting user-defined Sandbox rules for file scanning
- Deleting user-defined Sandbox rules
- List of extensions for file categories
- Sending notifications
- Viewing the table of rules for sending notifications
- Creating a rule for sending notifications about alerts
- Creating a rule for sending notifications about the operation of application components
- Enabling and disabling a rule for sending notifications
- Modifying a rule for sending notifications
- Deleting a rule for sending notifications
- Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules by rule type
- Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules based on the notification subject
- Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules by email address
- Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules based on their status
- Clearing a notification forwarding rule filter
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
- Creating a backup copy and restoring the application from backup
- Creating a backup copy of Central Node server settings from the application administrator menu
- Downloading a file containing a backup copy of server settings from the Central Node or PCN server to the hard drive of the computer
- Uploading a file containing a backup copy of server settings from your computer to the Central Node server
- Restoring server settings from a backup copy using the application administrator menu
- Creating a backup copy of the application in Technical Support Mode
- Restoring the application from a backup copy in Technical Support Mode
- Upgrading Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Upgrading the Central Node component installed on a server
- Upgrading the Central Node component installed as a cluster
- Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.1
- Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.2
- Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.4
- Contents and amount of information kept when upgrading the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Interaction with external systems via API
- Integrating an external system with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- API for scanning objects of external systems
- API that external systems can use to receive information about application alerts
- API that external systems can use to receive information about application events
- API for managing Threat Response actions
- Request for getting the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Request for information about network isolation and the existence of prevention rules for hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
- Host network isolation management
- Managing prevention rules
- Managing the application run task
- Sources of information about the application
- Contacting the Technical Support Service
- Glossary
- Advanced persistent threat (APT)
- Alternate data stream
- Anti-Malware Engine
- Backdoor program
- Central Node
- Communication channel bandwidth
- CSRF attack
- Distributed solution
- Dump
- End User License Agreement
- Endpoint Agent component
- ICAP client
- ICAP data
- Intrusion Detection System
- IOA
- IOC
- IOC file
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Kaspersky Private Security Network
- Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
- Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal
- KATA
- KEDR
- Kerberos authentication
- Keytab file
- Local reputation database of KPSN
- Malicious web addresses
- MIB (Management Information Base)
- Mirrored traffic
- MITM attack
- MITRE technique
- Multitenancy
- New generation threats
- NTP server
- OpenIOC
- Phishing URL addresses
- Sandbox
- Sensor
- Service principal name (SPN)
- SIEM system
- Signature
- SPAN
- Syslog
- TAA (IOA) rule
- Targeted attack
- Targeted Attack Analyzer
- Tenant
- TLS encryption
- Tracing
- VIP status
- YARA
- YARA rules
- Zero-day attack
- Zero-day vulnerability
- Information about third-party code
- Trademark notices
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Help
 New functions
New functions
 Hardware and software requirements
Hardware and software requirements
- Hardware and software requirements
- Compatibility of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
- Compatibility of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Linux, and Mac
 Licensing
Licensing
 Getting started
Getting started
- Distributed solution and multitenancy
- Sizing the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Installation and initial configuration of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Configuring the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
 Getting started in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface
Getting started in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface
- Getting started with the application web interface — For administrators
- Getting started with the application web interface — For security officers
 Additional features
Additional features
 Update
Update
 Contacting the Technical Support Service
Contacting the Technical Support Service
Page top
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform (hereinafter also referred to as "the application") is a solution designed for the protection of a corporate IT infrastructure and timely detection of threats such as zero-day attacks, targeted attacks, and complex targeted attacks known as advanced persistent threats (hereinafter also referred to as "APT"). The solution is developed for corporate users.
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution includes three functional blocks:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (hereinafter also referred to as "KATA"), which provides perimeter security for the enterprise IT infrastructure.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "KEDR"), which provides protection for the local area network of the organization.
- Network Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "NDR"), which provides protection of the corporate LAN.
The solution can receive and process data in the following ways:
- Integrate into the local area network, receive and process mirrored , and extract objects and metadata from the HTTP, HTTP2, FTP, SMTP, DNS, SMB, and NFS protocols.
- Connect to the proxy server via the ICAP protocol, receive and process data of HTTP, HTTP2, and FTP traffic, as well as HTTPS traffic if the administrator has configured SSL certificate replacement on the proxy server.
- Connect to the mail server via the POP3 (S) and SMTP protocols, receive and process copies of e-mail messages.
- Integrate with Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway and Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server, receive, and process copies of email messages.
For detailed information on Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway and Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server, please refer to the documentation of these applications.
- Integrate with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security and receive data (events) from individual computers running Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems in the corporate IT infrastructure. These applications continuously monitor processes running on those computers, active network connections, and files that are modified.
- Integrate with external systems with the use of the REST API interface and scan files on these systems.
The solution uses the following means of Threat Intelligence:
- Infrastructure of Kaspersky Security Network (also referred to as "KSN") cloud services that provides access to the online Knowledge Base of Kaspersky, which contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false alarms.
- Integration with Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) to access the reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network and other statistical data without sending data from user computers to Kaspersky Security Network.
- Integration with the Kaspersky information system known as Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal, which contains and displays information about the reputation of files and URLs.
- The Kaspersky Threats database.
The solution can detect the following events that occur within the corporate IT infrastructure:
- A file has been downloaded or an attempt was made to download a file to a corporate LAN computer.
- A file has been sent to the email address of a user on the corporate LAN.
- A website link was opened on a corporate LAN computer.
- Network activity has occurred in which the IP address or domain name of a corporate LAN computer was detected.
- Processes have been started on a corporate LAN computer.
The application can provide the results of its operation and Threat Intelligence to the user in the following ways:
- Display the results of work done in the web interface of the Central Node, Primary Central Node (hereinafter also PCN) or Secondary Central Node (hereinafter also SCN) servers.
- Publish alerts to a SIEM system already being used in your organization via the Syslog protocol.
- Integrate with external systems via the REST API and send information on alerts generated by the solution to external systems on demand.
- Publish information on Sandbox component alerts in the local reputation database of Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Users with the Senior security officer or Security officer role can perform the following actions in the application:
- Monitor the components of the solution.
- View the table of detected signs of targeted attacks and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure, filter and search alerts, view and manage each alert, and follow recommendations for evaluating and investigating incidents.
- Look through the table of events occurring on computers and servers of the corporate IT infrastructure, search for threats, filter, view and manage each event, follow recommendations for evaluating and investigating incidents.
- Run tasks on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security: run applications and stop processes, download and delete files, quarantine objects on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security, place copies of files in Storage of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and restore files from quarantine.
- Set up policies for preventing the running of files and processes that they consider to be unsafe on selected computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- Isolate individual computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Endpoint Security from the network.
- Work with TAA (IOA) rules to classify and analyze events.
- Manage user-defined Targeted Attack Analyzer TAA (IOA), Intrusion Detection System (IDS), and YARA rules — upload rules to be used for scanning events and creating alerts.
- Work with OpenIOC compliant files (IOC files) to search for signs of targeted attacks, infected and probably infected objects on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component and in the Alerts database.
- Exclude TAA (IOA) rules and IDS rules defined by Kaspersky from scanning.
- Manage objects in quarantine and copies of objects in Storage.
- Manage reports about application performance and alerts.
- Configure the sending of notifications about alerts and problems encountered by the application to email addresses of users.
- Manage the list of VIP alerts and the list of data excluded from the scan, and populate the local reputation database of KPSN.
- Store and download copies of raw network traffic for analysis in external systems.
Users with the Security auditor role can perform the following actions in the application:
- Monitor the components of the solution.
- View the table of detected signs of targeted attacks and intrusions into the enterprise IT infrastructure, filter and search alerts, and view the data of each alert.
- Look through the table of events occurring on the computers and servers of the enterprise IT infrastructure, search for threats, filter and view each event.
- View the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component and information about selected hosts.
- View user-defined rules for Targeted Attack Analyzer TAA (IOA), Intrusion Detection System (IDS), and YARA.
- View the scan-excluded TAA (IOA) rules and IDS rules defined by Kaspersky experts.
- View reports about application performance and alerts.
- View the list of VIP alerts and the list of data excluded from the scan.
- View all settings made in the application web interface.
- Store and download copies of raw network traffic for analysis in external systems.
Users with the Local administrator or Administrator role can perform the following actions in the application:
- Edit application settings.
- Configure servers for the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Set up the integration of the application with other applications and systems.
- Manage TLS certificates and set up trusted connections between the Central Node server and the Sandbox server, between Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers and the Endpoint Agent component, and with external systems.
- Manage accounts of application users.
- Monitor application health.
What's new
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.4 now has the following new features:
- Fixed vulnerabilities in the Suricata module.
- The time zone for servers with Central Node and Sandbox components can only be selected from the drop-down list. Selecting the time zone on the map is no longer supported.
- Selecting a country when setting the date and time for the Sandbox component is not supported.
- Fixed an error that occurred when updating anti-virus databases.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.2 now has the following new features:
Fixed vulnerabilities in the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) application module.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0 now has the following new features:
- A distribution kit of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application based on the Astra Linux operating system is now provided.
- Added support for KVM virtualization for a limited number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Added ICAP integration with feedback. ICAP integration with feedback can work in two modes:
- Standard scan. In standard scan mode, the object is scanned by all supported technologies. While being scanned by the Sandbox component, the object remains available. If a threat is detected, the object is blocked.
- Advanced scan. In the advanced scan mode, objects are scanned by all supported technologies. While being scanned by the Sandbox component, the object is not available. If a threat is detected, the object is blocked.
- Threats can now be detected in the SMB, NFS, HTTP2 protocols.
- Scanning mirrored encrypted traffic is now possible thanks to integration with the ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1 application.
- Traffic capture and analysis at speeds up to 10 Gbps is now supported for the Sensor component.
- Copies of raw network traffic can now be recorded, stored, and downloaded.
- Now you can configure automatic removal of inactive hosts displayed in the Endpoint Agents list on the server with the Central Node component.
- In the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can now use the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac application with built-in support for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Deploying on the VK Cloud platform is now possible.
- Expanded functionality for hosts that have Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux 12 as the Endpoint Agent component:
- Added the 'Delete file' task.
- Added the 'Kill process' task.
- Individual hosts can now be isolated from the network.
- Added support for files conforming to the OpenIOC open standard for the description of indicators of compromise (IOC files).
- The Sandbox component no longer supports the Windows XP SP3 operating system in preset form.
Changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.16 for Windows:
You can view the list of changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.16 for Windows in the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows Online Help.
Changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.5 for Windows:
You can view the list of changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.5 for Windows in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help.
Changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux:
You can view the list of changes in Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Online Help.
About Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal
For additional information about files that you consider to be suspicious, you can go to the website of the Kaspersky application Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal, which analyzes each file for malicious code and shows information about the reputation of the file.
Access to the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence application is provided for a fee. Authorization on the application website requires that an application access certificate is installed in the certificate storage on your computer. In addition, you must have a user name and password for access to the application.
For more details about the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal, please visit the Kaspersky website.
Distribution kit
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform distribution kit includes the following files:
- Disk image (file with the iso extension) containing the installation files for the Ubuntu Server 22.04.2 operating system and for the Sensor and Central Node components.
- Disk image (file with the iso extension) containing the installation files for the CentOS 7.9 operating system and for the Sandbox component.
- Archive (.tar.gz file) of the Sensor, Central Node components for creating an iso image based on Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4. UU1 operating system.
- Archive (.tar.gz file) of the Sandbox component for creating an iso image based on Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4. UU1 operating system.
- Disk images (.iso files) of operating systems in which the Sandbox component runs files.
- Utility (.tar file) for creating an iso image based on Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4. UU1 operating system.
- Upgrade package (upgrade.tar.gz) for the Central Node component.
- Upgrade package for the Central Node and Sensor components, kata-cn-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz.
- Upgrade package for the Sandbox component, kata-sb-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz.
- Upgrade package for the Central Node, Sensor, Sandbox components, upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz.
- File with information about third-party code used in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution kit includes the following files:
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent distribution kit
File |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installation package. |
|
File for creating Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installation package using Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
Installation package for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent Management administration plug-in for Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
Configuration file required for creating installation package for English version of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
Configuration file required for creating installation package for Russian version of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using Kaspersky Security Center. |
|
File with the text of the terms of participation in Kaspersky Security Network in English. |
|
File with the text of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy in English. |
|
File with the text of the Release Notes for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in English. |
|
File with the text of the terms of participation in Kaspersky Security Network in Russian. |
|
File with the text of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy in Russian. |
|
File with the text of the Release Notes for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Russian. |
Hardware and software requirements
Hardware and software requirements for servers for installing Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Deploying the application on a virtual platform requires installing the VMware ESXi hypervisor version 6.7.0 or 7.0.
For the application to work correctly in a virtual environment, you must install an up-to-date upgrade package for the hypervisor.
For the Central Node, Sensor and Sandbox hardware requirements see the Sizing Guide.
Hardware and software requirements for installing the Endpoint Agent component
The hardware and software requirements of the Endpoint Agent component reflect the hardware and software requirements of the applications that act as the Endpoint Agent component, and are described in the documentation of these applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
Hardware and software requirements for using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
One of the following browsers must be installed on the computers in order to configure and manage the application using the web interface:
- Mozilla Firefox for Linux.
- Mozilla Firefox for Windows.
- Google Chrome for Windows.
- Google Chrome for Linux.
- Edge (Windows).
- Safari (Mac).
Minimum screen resolution to use web interface: 1366х768.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application uses predefined settings that determine the impact that it has on the performance of the local computer under scenarios of information retrieval and interaction with the Central Node component.
If the version of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform installed on Central Node servers is incompatible with the version of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed on computers on the corporate LAN, the functionality of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform may be limited.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
Version of |
Type |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
Yes |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
There are limitations |
Yes |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Endpoint Agent |
Standalone installation |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Limited compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.12 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 4.1.
The amount of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is limited:
- Scanning autorun points using the Start YARA scan task is not supported.
- The tasks Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get registry key are not supported.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.12 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 5.0–6.0.
The amount of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is limited:
- Scanning autorun points using the Start YARA scan task is not supported.
- The tasks Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get registry key, Get disk image, Get memory dump are not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the Process terminated event.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.13 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 4.0.
A server of this Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version can receive a limited scope of data from the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application: Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get registry key tasks cannot be created in the web interface of the application.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.13 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 4.1–6.0.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent does not support the creation of the following tasks: Get disk image, Get memory dump.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 4.0.
The server of this Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version can receive a limited scope of data from the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application: creation of Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get registry key, Get disk image, Get memory dump tasks is not available in the web interface of the application.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 4.1.
A server of this Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version can receive a limited scope of data from the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application: the tasks Get disk image and Get memory dump cannot be created in the web interface of the application.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications
If you want to use the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application as the Endpoint Agent component, you can install just the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, or configure the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with workstation protection applications (Endpoint Protection Platform, hereinafter also "EPP"), Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Security for Windows Server, and Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent. If the integration of applications is configured, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent also sends the information about threats detected by EPP applications and their processing results to the Central Node server.
The integration scenarios described above do not work when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is installed on a virtual desktop in Virtual Desktop Infrastructure.
Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and Kaspersky Security for Windows Server requires installing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as part of those applications.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with versions of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
You can install the following versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as part of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.9 as part of Kaspersky Security 11 for Windows Server.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10 as part of Kaspersky Security 11.0.1 for Windows Server.
When you install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as part of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server, the standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Agent of the same or earlier version is removed. If Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installed as part of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server has an earlier version, it will not be installed. In this case, you must first remove the standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application.
If necessary, you can upgrade the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application that is already installed as part of Kaspersky Security for Windows Server. Integration between compatible versions of the applications is maintained both when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is upgraded and when Kaspersky Security for Windows Server is upgraded.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server versions
Kaspersky Security for Windows Server version |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.11, 3.12 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.13, 3.14, 3.15, 3.16 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
There are limitations |
When integrating with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.13–3.16, Kaspersky Security for Windows Server does not transmit event information of the AMSI scan event.
For more details about installing Kaspersky Security for Windows Server, see Kaspersky Security for Windows Server Help.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
You can install the following versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (Endpoint Sensors) as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.7 or Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (Endpoint Sensors) 3.6.1 as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.2, 11.3 for Windows.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent (Endpoint Sensors) 3.6.1 is not compatible with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version 4.1 or higher.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.7 is not compatible with all versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.9 as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4, 11.5.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10 as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.6.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.11 as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.7, 11.8.
When you install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10 or later as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, the standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application of the same or earlier version is removed. If the separately installed Kaspersky Endpoint Agent has a later version, the application bundled with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not installed. In this case, you must first remove the standalone Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application.
If necessary, you can upgrade the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application that is already installed as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. Integration between compatible versions of the applications is maintained both when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is upgraded and when Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is upgraded. You can upgrade a previous version of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to version 3.14 only for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent version 3.7 or higher.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.8, 3.9 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.10, 3.12 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.11 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.13, 3.14, 3.15, 3.16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
No |
No |
For more details about installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with versions of Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent
You can configure the integration of separately installed Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions and Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent versions
Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent version |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.12 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.11, 3.13, 3.14 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.15 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent installed on a virtual machine generate the same load on the Central Node server as Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent installed on the host.
For more details about enabling the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent, see Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent Help.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with versions of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes
You can install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent on a device with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes installed. The applications are integrated automatically.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent versions with versions of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes version |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.11, 3.12 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.13, 3.14, 3.15 |
Compatibility with Endpoint Agent 3.16 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
Yes |
To integrate with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes, the corresponding license key must be installed in the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
For detailed information, you can contact your account manager.
Page top
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
You can use Kaspersky Endpoint Security as the Endpoint Agent component.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
To integrate Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 or later with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you do not need to install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
When integrating Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.7, 12.8 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 5.0-6.0, the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server receives a limited amount of data from Kaspersky Endpoint Security:
- Information about the following events is not processed: Named pipe, WMI, LDAP, DNS, Code injection.
- For the File modified event, information about the following subtypes is not processed: File read, Hard link created, Symbolic link created.
- For the Registry modified event, information about the following subtypes is not processed: Registry key renamed, Registry key saved.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
You can use Kaspersky Endpoint Security as the Endpoint Agent component.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
There are limitations |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
To integrate Kaspersky Endpoint Security with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you do not need to install the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
Starting from version 12, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux can be used as the Light Agent for Linux component for the Kaspersky Security for Virtualization application. For more details about the integration, see Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent Help.
When Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is used as the Light Agent for Linux component, the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is retained.
Limited compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 5.1, 6.0.
The scope of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is limited:
- Creation of network isolation rules is not supported.
- Creation of prevention rules is not supported.
- Searching for indicators of compromise on computers using IOC files is not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Get forensics, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get disk image, Get memory dump, Kill process, Start YARA scan, Service management, Delete file, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine, Delete file, Kill process.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 5.0, 5.1.
The scope of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is limited:
- Creation of network isolation rules is not supported.
- Creation of prevention rules is not supported.
- Searching for indicators of compromise on computers using IOC files is not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Get forensics, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get disk image, Get memory dump, Kill process, Start YARA scan, Service management, Delete file, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine, Delete file, Kill process.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Optimum 5.1.
The scope of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is limited:
- Creation of prevention rules is not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Get forensics, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get disk image, Get memory dump, Kill process, Start YARA scan, Service management, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12–12.1 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.
The scope of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is limited:
- Creation of prevention rules is not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Get forensics, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get disk image, Get memory dump, Kill process, Start YARA scan, Service management, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine.
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.2 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.
The scope of data sent by Kaspersky Endpoint Security is limited:
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Get forensics, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles, Get process memory dump, Get disk image, Get memory dump, Kill process, Start YARA scan, Service management, Restore file from quarantine.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
You can use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac as the Endpoint Agent component.
Information about the compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
Kaspersky Endpoint Security version |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security |
No |
No |
No |
No |
There are limitations |
Limited compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions
- Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12–12.1 with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.
- Creation of network isolation rules is not supported.
- Creation of prevention rules is not supported.
- Searching for indicators of compromise on computers using IOC files is not supported.
- Event information is not transmitted for the following events: Process terminated, Module loaded, Connection to remote host, Blocked application (prevention rule), Document blocked, Registry modified, Port listened, Driver loaded, Process: interpreted file run, Process: console interactive input, AMSI scan.
- Creation of the following tasks is not supported: Kill process, Get forensics, Start YARA scan, Delete file, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine, Service management, Get disk image, Get memory dump.
Compatibility of KUMA versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can use KUMA as a SIEM system.
Information about the compatibility of KUMA versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of KUMA versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
KUMA |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
KUMA |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
KUMA |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
KUMA |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Compatibility of XDR versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can use XDR as a SIEM system.
Information about the compatibility of XDR versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of XDR versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
XDR |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XDR |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
XDR |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Compatibility of KPSN versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can use Kaspersky Private Security Network (KPSN) instead of Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) to avoid sending your organization's data beyond the corporate LAN.
Information about the compatibility of KPSN versions with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform versions is listed in the table below.
Compatibility of KPSN versions with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
KPSN |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
KPSN |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
KPSN |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
KPSN |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Compatibility of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with VK Cloud
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform supports deployment on the VK Cloud platform.
When deploying the application, you can connect Sandbox components to the Central Node component.
The following restrictions apply when deploying Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform for integration with VK Cloud:
- Only the KATA functional block is supported.
- Only the certified version of the application based on Astra Linux is supported.
- Only the non-high-availability version of the application is supported.
- You can configure integration only with an external KSMG system. For more details on integration, see KSMG Help.
- You can use the distributed solution mode only if you are using the KSMG integration.
For the Sandbox component to work, the following requirements must be met:
- Nested virtualization must be enabled for the virtual machine.
- The network interface settings must be correctly configured to provide Internet access to objects being processed.
Windows images can only be activated if the network interface is configured correctly.
- The network interface used for Internet access of processed objects must be isolated from the local network of your organization.
- The network interface used by processed objects for Internet access must be connected to a subnet that is not the same as the subnet to which the control interface is connected.
- We do not recommend using a static public IP address for the network interface that handles Internet access of the objects being processed.
Restrictions
Limitations that apply when deploying the Central Node component as a cluster:
- A Central Node cluster must include at least 4 servers: 2 storage servers and 2 processing servers. You can scale the cluster to increase the amount of traffic handled or the number of connected hosts in accordance with the Sizing Guide.
- It is recommended to add servers with the same hardware configuration to the cluster. Otherwise, a proportional increase in performance is not guaranteed.
- Adding an extra server to the cluster does not speed up the processing of objects that are already in the scan queue.
- The web interface of the application can be temporarily unavailable if the server on which it is hosted fails.
- If the processing server fails, you may lose ICAP, POP3, and SMTP traffic data as well as the copies of emails that are waiting to be processed and the detections associated with them.
- If the processing server is configured to receive mirrored traffic from SPAN ports, then SPAN traffic is not processed if this server fails.
- If one of the cluster servers fails or the connection between the server and the Endpoint Agent component is temporarily lost, data in the event database can temporarily become desynchronized.
- If the configuration of the cluster servers is changed, processing of traffic and events from computers with the Endpoint Agent component may be temporarily slowed down.
Limitations that apply to the Sensor component:
- Only Sensor components installed on standalone servers can be used to capture network traffic at the maximum speed of 10 Gbps.
- Capturing FTP traffic at the maximum speed of 10 Gbps can result in a high level of loss.
- Real-time ICAP traffic scanning on standalone servers with the Sensor component can only be configured in Technical Support Mode.
Limitations that apply to the Sandbox component:
- The following versions of operating systems are supported for custom images:
- Windows XP SP3 or later
- Windows 7
- Windows 8.1 64-bit
- Windows 10 64-bit (up to version 1909)
- Only English and Russian localizations are fully supported for custom operating system images.
- License keys for activating the operating systems and software are not provided.
- If some of the operating systems selected in the set of operating systems on the Central Node server are not installed on the Sandbox server, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not send objects to the Sandbox component for scanning. If multiple servers with the Sandbox component are connected to the server with the Central Node component, the application sends objects to those servers whose installed operating systems match the set selected on the Central Node.
Limitations that apply when integrating with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows:
- Tasks for getting RAM dumps and disk images can only be assigned to computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 or later for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 or later for Windows.
- Tasks for getting process memory dumps, NTFS metafiles, and registry keys can only be assigned to computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 or later for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 or later for Windows.
- The task of scanning hosts using YARA rules can only be assigned to computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 or later for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 or later for Windows. If you simultaneously assign a task to computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent version 3.14 or later, and to computers with earlier versions of that application, the task runs only on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 or later.
- If autorun points are selected as the scan scope, the task runs only on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.14 or later and Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.1 or later for Windows.
Limitations that apply when integrating with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux:
- The following functionality is not available for computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux 11.4:
- Network isolation of a host.
- Creating a prevention rule.
No notifications are created about the unsuccessful application of a prevention rule on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux applications.
- Finding indicators of compromise on computers using IOC files.
No notifications are created about the unsuccessful search of indicators of compromise on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux applications.
- The following functionality is not available for computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux 12:
- Creating a prevention rule.
No notifications are created about the unsuccessful application of a prevention rule on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux applications.
- Creating a prevention rule.
- The list of events that Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 or 12 for Linux logs in the event database is limited to the following types:
- The list of tasks that you can create on computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux is limited to the following types:
- Get file
When you create the task, the application does not attempt to verify the path to the executable file or the file that you want to retrieve.
- Run application
- Get file
- The list of tasks that you can create on computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux is limited to the following types:
- Get file
When you create the task, the application does not attempt to verify the path to the executable file or the file that you want to retrieve.
- Run application
- Delete file
- Kill process
- Get file
- In information about events registered in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 or 12 for Linux, the Time created field displays file modification time.
Limitations that apply when integrating with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac:
- The following functionality is not available for computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac:
- Network isolation of a host.
- Creating a prevention rule.
No notifications are created about the unsuccessful application of a prevention rule on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac applications.
- Finding indicators of compromise on computers using IOC files.
No notifications are created about the unsuccessful search of indicators of compromise on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac applications.
- The list of events that Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac logs in the event database is limited to the following types:
- The list of tasks that you can create on computers running Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac is limited to the following types:
- Get file
When you create the task, the application does not attempt to verify the path to the executable file or the file that you want to retrieve.
- Run application
- Get file
- In information about events registered in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac, the Time created field displays file modification time.
Limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.16 for Windows:
You can view the list of limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.16 for Windows in the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows Online Help.
Limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.5 for Windows:
You can view the list of limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12.5 for Windows in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Online Help.
Limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux:
You can view the list of limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux Release Notes.
Limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac:
You can view the list of limitations of Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Mac in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac Online Help.
Data provision
The operation of certain components of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform requires data processing on the Kaspersky side. Components do not send data without the consent of the administrator of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
You can view the list of data and the terms on which it is used as well as give consent to data processing in the following agreements between your organization and Kaspersky:
- In the End User License Agreement (for example, during installation of the application).
According to the terms of the End User License Agreement, you agree to automatically send Kaspersky the information listed in the End User License Agreement under Data Provision. The End User License Agreement is included in the application distribution kit.
- In the KSN Statement (for example, during installation of the application or in the administrator menu after installation).
When you participate in Kaspersky Security Network, information obtained as a result of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform operation is automatically sent to Kaspersky. The list of transmitted data is specified in the KSN Statement. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user independently decides on his/her participation in KSN. The KSN Statement is included in the application distribution kit.
Before KSN statistics are sent to Kaspersky, they are accumulated in the cache on servers hosting Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform components.
Kaspersky protects any information received in this way as prescribed by law and applicable rules of Kaspersky. Data is sent over encrypted communication channels.
When using Kaspersky Private Security Network, Kaspersky is not sent information about the operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. However, KSN statistical data is accumulated in the cache on servers hosting Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform components to the same extent as when using Kaspersky Security Network. This accumulated KSN statistical data may be transmitted beyond the perimeter of your organization if a server with the Kaspersky Private Security Network application is located outside of your organization.
The Kaspersky Private Security Network administrator must personally ensure the security of such data.
Service data of the application
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
Service data of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform include:
- Data on user accounts.
- Information about computers connected to the Central Node component on which the Endpoint Agent component is installed.
- Data about presets and prevention rules.
- Information about tasks assigned to computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Data about TAA (IOA) user-defined rules.
- Data about user IDS user-defined rules.
- Data about IOC user-defined rules.
- Data on network isolation rules.
- Data about scan exclusions.
- Data on report templates.
- Information about Endpoint Agent component certificates.
The above data is stored indefinitely on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/ datadirectory if the Central Node component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers indefinitely. - System event log
OS log files are stored indefinitely in the
/var/logdirectory on the server hosting the Central Node component. - Log with information about the application operation.
The log file is stored indefinitely in the
/datadirectory on the server hosting the Central Node component, if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers indefinitely. - File scan queue.
Files are stored on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers. The data is retained until the scan is completed. - Files received from computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
Files are stored on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers. Data is rotated when disk space becomes full. - Files with YARA and IDS rules (user-defined and from Kaspersky).
Files are stored indefinitely in the
/datadirectory on the server hosting the Central Node component, if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers indefinitely. - Files with data about alerts sent to external systems.
Files are stored indefinitely on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers indefinitely. - Artifacts of the Sandbox component.
Files are stored on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers. Data is rotated when disk space becomes full. - Files for which alerts were created by the Sandbox component.
Files are stored on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers. Data is rotated when disk space becomes full. - Certificate files used for the authentication of application components.
Files are stored indefinitely in the
/datadirectory on the server hosting the Central Node, PCN, SCN, Sensor component or on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component. - Encryption keys that are transmitted between application components.
Files are stored indefinitely in the
/datadirectory on the server hosting the Central Node, PCN, SCN, Sensor component or on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component. - Copies of raw network traffic.
Files are stored in storage mounted on the server with the Sensor component. Data is deleted as disk space becomes full.
- ICAP exclusion filters
Files are stored indefinitely on the server hosting the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory if the component is installed on the server. When the Central Node component is installed on a cluster, data is stored on storage servers indefinitely.
The application stores the following information about user accounts:
- Account ID.
- Account name.
- The hash and salt of the account password.
- Domain name of the user.
- Account role.
- Account status.
- Access rights to tenants in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- ID of the tenant in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
The application stores the following information about computers connected to the Central Node component on which the Endpoint Agent component is installed:
- ID of the computer assigned by Kaspersky Security Center.
- Computer name.
- IP address of the computer.
- The operating system used on the computer.
- The version of the application that fills the role of the component.
- Self-Defense status.
- Date and time when the first and last telemetry packet were sent to the Central Node component.
- Date and time of the last IOC scan run.
- Result of the last IOC scan run.
- Status of the license on the host.
The application stores the following information about the prevention rules:
- MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file that is prevented from running.
- The account name of the user who created the prevention rule.
- The account name of the user who changed the prevention rule.
- List of computers on which the file is prevented from running.
- Prevention rules change log.
- Prevention rule creation date and time.
- Date and time of prevention rule modification.
- Name of the prevention rule.
- Attribute indicating whether the user must be notified about file start being blocked.
The application stores the following information about tasks assigned to computers with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Task type.
- Computer name.
- IP address of the computer.
- Task creation date and time.
- Task expiration date.
- Name of the user account that created the task.
- Task settings data.
- Task report data.
- Task comments.
The application stores the following information about TAA (IOA) user-defined rules:
- Rule name.
- Source code of the request being scanned.
- Rule ID.
- Rule status.
- Rule creation date and time.
- The importance that was specified when the rule was added.
- Level of confidence that depends on the likelihood of false alarms as defined by the user when the rule was added.
The application stores the following information about IDS user-defined rules:
- Account name of the user who uploaded the rules file.
- Date and time when the rule file was uploaded.
- Status of the rule.
- Importance specified in the rule file.
The application stores the following information about IOC user-defined rules:
- Account name of the user who uploaded the rules file.
- Name of the IOC file.
- Contents of the IOC file.
- Date and time when the IOC file was uploaded.
- Status of the IOC rule.
- Importance as specified in the IOC file.
- Description of the IOC rule.
The application stores the following information about YARA user-defined rules:
- Account name of the user who uploaded the rules file.
- Contents of the YARA file.
- Date and time when the YARA file was uploaded.
- Name of the file containing YARA rules.
- Importance.
- Status of the YARA rule.
The application stores the following information about network isolation rules:
- Account name of the user that enabled network isolation.
- ID of the isolated computer.
- Rule name.
- Rule status.
- List of resources excluded from network isolation.
- Date and time when the network isolation rule was modified.
- State of the rule.
- Expiration date of the network isolation rule.
The application stores the following information about scan exclusions:
- Account name of the user that added the exception.
- List of objects excluded from the scan.
- Rule exception ID.
- Name of the exclusion.
- Date and time when the exclusion was created.
The application stores the following information about report templates:
- ID of the user account that created or modified the template.
- Template creation date.
- Date of last modification of the template.
- Text of the template as HTML code.
- Name of the template.
The application stores the following information about Endpoint Agent component certificates:
- Account name of the user who uploaded the certificate file.
- Digest of the certificate.
- Serial number of the certificate.
- Public key.
- Expiration date of the certificate.
The application stores the following information about Sandbox scan rules:
- State of the rule
- Type of the rule
- Masks of included objects
- Masks of excluded objects
- Size of scanned files
- Rule creation date and time
- ID of the virtual machine where the rule is assigned
The application stores the following information about the virtual machine configuration:
- IP address of the server hosting the Sandbox component
- List of virtual machines
Data of the Central Node and Sensor components
This section contains the following information about user data that is stored on the server with the Central Node component and on the server with the Sensor component:
- Contents of stored data
- Storage location
- Storage duration
- User access to data
Traffic data of the Sensor component
Traffic data of the Sensor component is stored on the server with the Sensor component or on the server with Sensor and Central Node components if Sensor and Central Node are installed on the same server or deployed as a cluster.
Traffic data is recorded and stored in sequentially created files. The application stops recording data in one file and starts logging data in the next file if:
- The maximum file size is reached (you can configure this setting)
- The configured time interval has elapsed (you can configure this setting)
- The traffic saving service or the entire Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application is restarted
As traffic data accrues, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform filters data and keeps only the following information:
- Information related to alerts generated by the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology
- PCAP files in which:
- Source or destination IP address matches an IP address from the alert
- Traffic data belongs to the time period within 15 minutes from the alert time
Filtered traffic data is moved to a separate section. The rest of the traffic data (that do not satisfy filtering criteria) is deleted.
Filtered traffic data is saved in sequentially created files. The application stops recording data in one file and starts logging data in the next file if:
- The maximum file size is reached
- The configured time interval has elapsed
Filtered data traffic is stored for the last 24 hours. Older data is deleted.
Data in alerts
Alerts may contain user data. If Central Node is installed on a server, information about alerts and files that caused an alert when scanned is stored on the Central Node server in the /data directory. If Central Node is installed as a cluster, information about alerts and files that caused an alert when scanned is stored in ceph storage.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
The following information is stored in all alerts:
- Date and time of detection.
- Date and time of alert modification.
- Category of the detected object.
- Name of the detected file.
- Alert source.
- Detected URL.
- MD5 and SHA256 hash of the detected file.
- User comments added to the alert information.
- ID of the TAA (IOA) rule by which the alert was generated.
- IP address and name of the computer on which the alert was generated.
- ID of the computer on which the alert was generated.
- User agent.
- The user account to which the alert was assigned.
- List of files.
When an alert is changed, the following information is stored on the server:
- The user account that modified the alert.
- The user account to which the alert was assigned.
- Date and time of alert modification.
- Alert status.
- User comment.
If an email message was detected, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Email addresses of the sender and recipients of the message, including the recipients of copies and blind carbon copies of the message.
- Subject of the email message.
- Date and time when the message was received by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, with precision up to the second.
- All service headers of the message (as they appear in the message).
If the alert was generated by URL Reputation technology, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Name of the computer from which the data was sent.
- Name of the computer that received the data.
- The IP address of the computer from which the data was sent.
- The IP address of the computer that received the data.
- The URI of the transferred resource.
- Information about the proxy server.
- Unique ID of the email message.
- Email addresses of the sender and recipients of the message (including the recipients of copies and blind carbon copies of the message).
- Subject of the email message.
- Date and time when the message was received by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, with precision up to the second.
- List of detected objects.
- Time of network connection.
- URL of network connection.
- User agent.
If the alert was generated by Intrusion Detection System technology, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Name of the computer from which the data was sent.
- Name of the computer that received the data.
- The IP address of the computer from which the data was sent.
- The IP address of the computer that received the data.
- Transmitted data.
- Data transfer time.
- URL extracted from the file containing the traffic, User Agent, and method.
- File containing the traffic where the alert occurred.
- Object category based on the IDS database.
- Name of the custom IDS rule that was used to generate the alert.
- HTTP request body.
- List of alerts.
If the alert was generated using YARA rules, the following information can be stored on the server:
- Version of YARA rules that was used to generate the alert.
- Category of the detected object.
- Name of the detected object.
- MD5 hash of the detected object.
- Date and time when the object was detected.
- Additional information about the alert.
If the alert was generated using the Sandbox component, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Version of the application databases used to generate the alert.
- Category of the detected object.
- Names of detected objects.
- MD5 hashes of detected objects.
- Information about detected objects.
If the alert was generated by IOC or TAA (IOA) user rules, the following information can be stored on the server:
- Date and time of scan completion.
- IDs of the computers on which the alert was generated.
- Name of TAA (IOA) rule.
- Name of the IOC file.
- Information about detected objects.
- List of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
If the alert was generated by Anti-Malware Engine technology, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Versions of databases of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform components that were used to generate the alert.
- Category of the detected object.
- List of detected objects.
- MD5 hash of detected objects.
- Additional information about the alert.
If the alert was generated as a result of a rescan, the following information may be stored on the server:
- File name.
If the alert was generated as a result of scanning a file, the following information may be stored on the server:
- Full name of the detected file.
- MD5 and SHA256 hash of the detected file.
- Size of the detected file.
- Information about the signature of the file.
If the alert was generated as a result of scanning FTP traffic, the following information may be stored on the server:
- URI of the FTP request.
If the alert was generated as a result of scanning HTTP traffic, the following information may be stored on the server:
- URI of the HTTP request.
- URI of the request source.
- User agent.
- Information about the proxy server.
Data in events
Events may contain user data. If Central Node is installed on a server, information about occurred events is stored in the /data directory. If Central Node is installed as a cluster, the information is stored in ceph storage.
Data is rotated as the disk becomes full.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
Event data can contain information related to the following:
- Name of the computer where the event occurred.
- Unique ID of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Name of the user account under which the event occurred.
- Name of the group that the user belongs to.
- Event type.
- Event time.
- Information about the file for which the event was logged: name, path, full name.
- MD5 and SHA256 hash of the file.
- File creation time.
- File modification time.
- File access rights.
- Environment variables of the process.
- Command-line parameters.
- Text of the command entered into the command line.
- Local IP address of the adapter.
- Local port.
- Remote host name.
- Remote host IP address.
- Port on the remote host.
- URLs and IP addresses of visited websites, and links from these websites.
- Network connection protocol.
- HTTP request method.
- HTTP request header.
- Information about Windows registry variables: path to the variable, variable name, variable value.
- Contents of a script or binary file sent for AMSI scanning.
- Information about the event in the Windows log: event type, event type ID, event ID, user account under which the event was logged, full text of the event from the Windows Event Log in XML format.
Data in reports
Reports may contain user data. If the Central Node component is installed on a server, information about occurred events is stored in the /data directory indefinitely. If Central Node is installed as a cluster, the information is stored in ceph storage indefinitely.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
Reports may contain the following information:
- Report creation date.
- Time period covered in the report.
- ID of the user account that generated the report.
- Report status.
- Text of the report as HTML code.
- Description.
- Name of the template that the report was generated from.
Data on objects in Storage and Quarantine
Objects in Storage and quarantine may contain user data. If the Central Node component is installed on a server, information about objects in Storage and copies of objects quarantined on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, which were saved on the server using the Get file task, is stored in the /data directory. If the Central Node component is installed as a cluster, information about objects in Storage and copies of objects quarantined on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, which were saved on the server using the Get file task, is stored in ceph storage.
Data is rotated as the disk becomes full.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
Data on objects in Storage and quarantine may contain the following information:
- Name of the object.
- Path to the object on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- MD5 and SHA256 hash of the file.
- ID of the user who quarantined the object on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- ID of the user who placed the object in Storage.
- IP address of the computer on which the quarantined object is stored.
- Name of the computer on which the quarantined object is stored.
- Unique ID of the computer on which the quarantined object is stored in Storage.
- ID of the TAA (IOA) rule by which the alert was generated.
- Category of the detected object.
- Results for the object scanned using individual modules and technologies of the application.
- File download time.
- Metadata of scanned files and their sources.
- Resulting status of the object in Storage.
Sandbox component data
For the processing time, the body of the file sent by the Central Node component is saved in open form on the server hosting the Sandbox component. During processing, the server administrator can access the sent file in Technical Support Mode. The scanned file is deleted by a special script according to the schedule. Once every 60 minutes by default.
Information about the data stored on the server with the Sandbox component is provided in the table below.
Data stored on the server with the Sandbox component
Scope of data |
Storage location |
Storage duration |
Access to data |
|---|---|---|---|
Scanned files |
|
After the Central Node component receives the scan results or until automatic deletion, but no more than 24 hours. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
File scan results |
|
After the Central Node component receives the scan results or until automatic deletion, but no more than 24 hours. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
Task settings |
|
After the Central Node component receives the scan results or until automatic deletion, but no more than 24 hours in the directory Up to 90 days in the Sandbox component database. |
User access to the directory A password is required for user authentication in the database. Access to database files is granted only to users who started database processes and users with root privileges. Access is provided only over an encrypted IPSec channel. |
Trace files |
|
Up to 21 days. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. Only authorized users can perform actions with trace files. Information about actions with trace files is saved in the application event log. |
Settings of the update source |
|
Until modified or deleted. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
Minimum password length settings |
|
Until modified or deleted. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
Virtual machines |
|
Until modified or deleted. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
Downloaded images of operating systems and applications in iso format |
|
Until modified or deleted. |
User access is defined by the administrator using operating system tools. |
Data transmitted between application components
Central Node, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows applications send the following to the Central Node component: reports about running tasks, information about events and alerts that occurred on computers running these applications, and information about terminal sessions.
If there is no connection with the Central Node component, all data to be sent is accumulated until it is sent to the Central Node component, or until Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is removed from the computer, but no longer than 21 days.
If an event occurred on the user's computer, the applications send the following data to the events database:
- General information for all events:
- Event type.
- Event time.
- User account for which the event was generated.
- Name of the host where the event occurred.
- IP address of the host.
- Type of the operating system installed on the host.
- File creation event.
- Details of the process that created the file: process file name, and MD5- and SHA256 hash of the process file.
- File name.
- Path to the file.
- Full name of the file.
- MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file.
- Date of file creation and modification.
- File size.
- Registry monitoring event.
- Details of the process that modified the registry: Process ID, process file name, and MD5- and SHA256 hash of the process file.
- Path to the registry key.
- Registry value name.
- Registry value data.
- Registry value type.
- Previous path to the registry key.
- Previous registry value data.
- Previous registry value type.
- Driver loading event.
- File name.
- Path to the file.
- Full name of the file.
- MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file.
- File size.
- Date of file creation and modification.
- Listening port opening event.
- Details of the process that opened the listening port: process file name, and MD5- and SHA256 hash of the process file.
- Port number.
- Adapter IP address.
- Event in the operating system log.
- Time of the event, host on which the event occurred, and user account name.
- Event ID.
- Channel/log name.
- Event ID in the log.
- Provider name.
- Authentication event subtype.
- Domain name.
- Remote IP address.
- Event header fields: ProviderName, EventId, Version, Level, Task, Opcode, Keywords, TimeCreatedSystemTime, EventRecordId, CorellationActivityId, ExecutionProcessID, ThreadID, Channel, Computer.
- Event body fields: AccessList, AccessFiles mask, AccountExpires, AllowedToDelegateTo, Application, AuditPolicyChanges, AuthenticationPackageName, CategoryId, CommandLine, DisplayName, Dummy, ElevatedToken, EventCode, EventProcessingFailure, FailureReason, FilterRTID, HandleId, HomeDirectory, HomePath, ImpersonationLevel, IpAddress, IpPort, KeyLength, LayerName, LayerRTID, LmPackageName, LogonGuid, LogonHours, LogonProcessName, LogonType, MandatoryLabel, MemberName, MemberSid, NewProcessId, NewProcessName, NewUacValue, NewValue, NewValueType, ObjectName, ObjectServer, ObjectType, ObjectValueName, OldUacValue, OldValue, OldValueType, OperationType, PackageName, ParentProcessName, PasswordLastSet, PrimaryGroupId, PriviledgeList, ProcessId, ProcessName, ProfileChanged, ProfilePath, Protocol, PublisherId, ResourceAttributes, RestrictedAdminMode, SamAccountName, ScriptPath, ServiceAccount, ServiceFileName, ServiceName, ServiceStartType, ServiceType, SettingType, SettingValue, ShareLocalPath, ShareName, SidHistory, SourceAddress, SourcePort, Status, SubcategoryGuid, SubcategoryId, SubjectDomainName, SubjectLogonId, SubjectUserName, SubjectUserSid, SubStatus, TargetDomainName, TargetLinkedLogonId, TargetLogonId, TargetOutboundDomainName, TargetOutboundUserName, TargetUserName, TargetUserSid, TaskContent, TaskName, TokenElevationType, TransmittedServices, UserAccountControl, UserParameters, UserPrincipalName, UserWorkstations, VirtualAccount, Workstation, WorkstationName.
- Process start event.
- Information about the process file: file name, file path, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, file size, creation and modification date, name of the organization that issued the digital certificate of the file, digital signature verification result.
- UniquePID.
- Process start options.
- Process start time.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, process start options.
- Process stop event.
- Information about the file of the process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, file size, and process end time.
- UniquePID.
- Process start options.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, process start options.
- Module loading event.
- Details of the file that loaded the module: UniquePID, file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file, and file size.
- DLL name.
- Path to DLL.
- DLL full name.
- MD5 or SHA256 hash of the DLL.
- DLL size.
- Date of DLL creation and modification.
- Name of the organization that issued the digital certificate of the DLL.
- DLL digital signature verification result.
- Process startup blocking event.
- Details of the file that attempted to run: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file, file size, and date of file creation and modification.
- Command-line parameters.
- File startup blocking event.
- Details of the file that attempted to open: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file, type of checksum used for file size blocking (0 – MD5, !=0 – SHA256, not used for search).
- Details of the executable file: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file, file size, and date of file creation and modification.
- Details of the parent process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file, PID, and UniquePID.
- Event of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Scan result.
- Name of the detected object.
- ID of the record in application databases.
- Release time of the application databases with which the alert was generated.
- Object processing mode.
- Category of the detected object (for example, name of a virus).
- MD5 hash of the detected object.
- SHA256 hash of the detected object.
- Unique ID of the process.
- Process PID displayed in the Windows Task Manager.
- Process start command line.
- Reason for the error when processing the object.
- Contents of the script scanned using AMSI.
- AMSI scan event.
- Contents of the script scanned using AMSI.
Central Node, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux sends the following to the Central Node component: task completion reports, information on events and alerts that occurred on computers with this application, and information about terminal sessions.
If there is no connection with the Central Node component, all pending information is accumulated until it is sent to the Central Node component, or until Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is removed from the computer, but no longer than 21 days.
If an event occurs on the user's computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux sends the following data to the events database:
- General information for all events:
- Event type.
- Event time.
- User account for which the event was generated.
- Name of the host where the event occurred.
- IP address of the host.
- Type and version of the operating system that is installed on the host.
- Name of the host that was used to remotely log in to the system.
- Name of the user assigned when registering in the system.
- Group to which the user belongs.
- User name that was used to log in to the system.
- Group of the user whose name was used to log in to the system.
- Name of the user who created the file.
- Name of the group whose users can modify or delete the file.
- Permissions that can be used to gain access to the file.
- Inherited privileges of the file.
- Process start event.
- Information about the file of the process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, and file size.
- UniquePID.
- Command that was used to start the process.
- Process type.
- Environment variables of the process.
- Process start time.
- Process end time.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, command that was used to start the process.
- File creation event.
- Details of the process that created the file: process file name, and MD5- and SHA256 hash of the process file.
- File name.
- Path to the file.
- Full name of the file.
- File type.
- MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file.
- Date of file creation and modification.
- File size.
- Event in the operating system log.
- Event time.
- Event type.
- Result of the operation.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, command that was used to start the process.
- Process stop event.
- Information about the file of the process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, file size, and process end time.
- UniquePID.
- Process start options.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, process start options.
- Event of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
- Scan result.
- Name of the detected object.
- ID of the record in application databases.
- Release time of the application databases with which the alert was generated.
- Object processing mode.
- Category of the detected object (for example, name of a virus).
- MD5 hash of the detected object.
- SHA256 hash of the detected object.
- Unique ID of the process.
- PID of the process.
- Process start command line.
- Reason for the error when processing the object.
Central Node, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac sends the following to the Central Node component: task completion reports, information on events and alerts that occurred on computers with this application.
If there is no connection with the Central Node component, all pending information is accumulated until it is sent to the Central Node component, or until Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac is removed from the computer, but no longer than 21 days.
If an event occurs on the user's computer, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac sends the following data to the events database:
- General information for all events:
- Event type.
- Event time.
- User account for which the event was generated.
- Name of the host where the event occurred.
- IP address of the host.
- Type and version of the operating system that is installed on the host.
- Name of the host that was used to remotely log in to the system.
- Name of the user assigned when registering in the system.
- Group to which the user belongs.
- User name that was used to log in to the system.
- Group of the user whose name was used to log in to the system.
- Name of the user who created the file.
- Name of the group whose users can modify or delete the file.
- Permissions that can be used to gain access to the file.
- Process start event.
- Information about the file of the process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, and file size.
- UniquePID.
- Command that was used to start the process.
- Process type.
- Environment variables of the process.
- Process start time.
- Process end time.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, command that was used to start the process.
- File creation event.
- Details of the process that created the file: process file name, and MD5- and SHA256 hash of the process file.
- File name.
- Path to the file.
- Full name of the file.
- File type.
- MD5- and SHA256 hash of the file.
- Date of file creation and modification.
- File size.
- Process stop event.
- Information about the file of the process: file name, file path, full name of the file, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file, file size, and process end time.
- UniquePID.
- Process start options.
- Information about the parent process: file path, UniquePID, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the process file, process start options.
- Event of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- Scan result.
- Name of the detected object.
- ID of the record in application databases.
- Release time of the application databases with which the alert was generated.
- Object processing mode.
- Category of the detected object (for example, name of a virus).
- MD5 hash of the detected object.
- SHA256 hash of the detected object.
- Unique ID of the process.
- PID of the process.
- Process start command line.
- Reason for the error when processing the object.
Central Node and Sandbox
The Central Node component sends to the Sandbox component files and URLs extracted from the network and email traffic. The files are not changed in any way prior to sending. The Sandbox component sends scan results to the Central Node component.
Central Node and Sensor
The application may transmit the following data between Central Node and Sensor components:
- Files and email messages.
- Data on alerts generated by the Intrusion Detection System and URL Reputation technologies.
- License information.
- List of data excluded from the scan.
- Data of the Endpoint Sensors application, if integration with a proxy server has been configured.
- Application databases, if receiving database updates from the Central Node component is configured.
Servers with PCN and SCN roles
If the application is running in distributed solution mode, the following data is transmitted between the PCN and connected SCNs:
- Data on alerts.
- Data on events.
- Data on tasks.
- Data on policies.
- Data on scans using IOC, TAA (IOA), IDS, YARA user rules.
- Data on files in Storage.
- Data on user accounts.
- About the license.
- The list of computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Objects placed in Storage.
- Objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Files attached to alerts.
- IOC and YARA files.
Data contained in application trace files
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform resources provide no capability to restrict the rights of the users of servers and operating systems to which the Central Node component is installed. The administrator is advised to use any system resources at their own discretion to control how the users of servers and operating systems with the application installed may be granted access to the personal data of other users.
Trace files can include any personal data of the user or confidential data of your organization. Files are stored in the /data/var/log/kaspersky directory indefinitely.
Data of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
You can view detailed information about Kaspersky Endpoint Agent data that is stored and processed locally in the Online Help of the application:
- Data in requests to the KATA Central Node component.
- Service data.
- Data contained in trace files and dumps.
- Information about acceptance of the KSN Statement.
- Windows Event Log event data.
Data received from the Central Node component
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent saves the values of settings received from the Central Node component on the hard disk of the computer. Data is saved in open non-encrypted form in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\data.
By default, only users with System and Administrator permissions have read-access to files when Self-Defense is enabled. When Self-Defense is disabled, users with System and Administrator permissions can also delete the files, modify their contents, and modify the access rights to them. The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application does not manage access permissions to this folder or any files in it. It is the system administrator who determines access permissions.
The data is deleted when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is removed.
Data received from the Central Node component may contain the following information:
- Data on network connections.
- Data on the operating system that is installed on the server with the Central Node component.
- Data on operating system user accounts.
- Data on user sessions in the operating system.
- Data on Windows event log.
- About a RT_VERSION resource.
- About the contents of a PE file.
- About operating system services.
- Certificate of the server with the Central Node component.
- URL- and IP addresses of visited websites.
- HTTP protocol headers.
- Computer name.
- MD5 hashes of files.
- Unique ID of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Names and values of Windows registry keys.
- Paths to Windows registry keys.
- Names of Windows registry variables.
- Name of the local DNS cache entry.
- Address from the local DNS cache entry in IPv4 format.
- IP address or name of the requested host from the local DNS cache.
- Host of the local DNS cache element.
- Domain name of the local DNS cache element.
- Address of the ARP cache element in IPv4 format.
- Physical address of the ARP cache element.
- Serial number of the logical drive.
- Home folder of the local user.
- Name of the user account that started the process.
- Path to the script that is run when the user logs in to the system.
- Name of the user account under which the event occurred.
- Name of the computer where the event occurred.
- Full paths to files on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Names of files on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Masks of files on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Full names of folders on computers with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Comments of the file publisher.
- Mask of the process file image.
- Path to the process file image that opened the port.
- Name of the process that opened the port.
- Local IP address of the port.
- Trusted public key of the digital signature of executable modules.
- Process name.
- Process segment name.
- Command-line parameters.
Data in alerts and events
Event data is saved in binary form in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\kata in open non-encrypted form.
By default, only users with System and Administrator permissions have read-access to files when Self-Defense is enabled. When Self-Defense is disabled, users with System and Administrator permissions can also delete the files, modify their contents, and modify the access rights to them. The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application does not manage access permissions to this folder or any files in it. It is the system administrator who determines access permissions.
Event data can contain information related to the following:
- Data on executable modules.
- Data on network connections.
- About the operating system that is installed on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Data on user sessions in the operating system.
- Data on operating system user accounts.
- Data on Windows event log.
- About alerts of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- About organizational units (OU) of Active Directory.
- HTTP protocol headers.
- Fully qualified domain name of the computer.
- MD5- and SHA256 hash of files and their fragments.
- Unique ID of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Unique IDs of certificates.
- Certificate publisher.
- Certificate subject.
- Name of the algorithm used to generate the certificate fingerprint.
- Address and port of the local network interface.
- Address and port of the remote network interface.
- Application vendor.
- Application name.
- Name of the Windows registry variable.
- Path to the Windows registry key.
- Windows registry variable data.
- Name of the detected object.
- Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent ID.
- Contents of the hosts file.
- Process start command line.
Data contained in task completion reports
Prior to being sent to the Central Node component, the reports and relevant files are temporarily saved on the hard disk of the computer with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application. The task completion reports are saved in archived non-encrypted form in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\kata\data_queue.
By default, only users with System and Administrator permissions have read-access to files when Self-Defense is enabled. When Self-Defense is disabled, users with System and Administrator permissions can also delete the files, modify their contents, and modify the access rights to them. The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application does not manage access permissions to this folder or any files in it. It is the system administrator who determines access permissions.
Task completion reports contain the following information:
- Data on task output.
- Data on executable modules.
- Data on operating system processes.
- Data on user accounts.
- Data on user sessions.
- Fully qualified domain name of the computer.
- Unique ID of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Files of the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Names of .
- Full paths to files on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Full names of folders on the computer with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
- Content of the process standard output.
- Content of the process standard error stream.
Data contained in an install log
The administrator can enable the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent installation log (using the msiexec standard procedure) during installation using the command line. The administrator shows the path to the file where the install log will be saved.
The log records installation process steps and the msiexec command line containing the address of the server hosting the Central Node component and the path to the install log file.
Data on files that are blocked from starting
Data on files that are blocked from starting is stored in open non-encrypted form in the folder C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\kata.
By default, only users with System and Administrator permissions have read-access to files when Self-Defense is enabled. When Self-Defense is disabled, users with System and Administrator permissions can also delete the files, modify their contents, and modify the access rights to them. The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application does not manage access permissions to this folder or any files in it. It is the system administrator who determines access permissions.
Data on files that are blocked from starting may contain the following information:
- Full path to the blocked file.
- MD5 hash of the file.
- SHA256 hash of the file.
- Process start command.
Data related to the performance of tasks
When performing a task for placing a file in quarantine, the archive containing this file is temporarily saved in one of the following folders:
- C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\kata\temp for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent that is installed as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.
- C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\data\kata\temp for Kaspersky Endpoint Agent that is installed from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform distribution kit.
When performing an application run task on a host, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent locally stores the contents of standard output streams and errors of the running process in plain unencrypted form until the task completion report is sent to the Central Node component. Files are stored in one of the following folders:
C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\kata\tempfor Kaspersky Endpoint Agent that is installed as part of Kaspersky Endpoint Security.C:\ProgramData\Kaspersky Lab\Endpoint Agent\protected\data\kata\tempfor Kaspersky Endpoint Agent that is installed from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform distribution kit.
By default, only users with System and Administrator permissions have read-access to files when Self-Defense is enabled. When Self-Defense is disabled, users with System and Administrator permissions can also delete the files, modify their contents, and modify the access rights to them. The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application does not manage access permissions to this folder or any files in it. It is the system administrator who determines access permissions.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows data
For detailed information about data transmitted by Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the Online Help of the application:
- Provision of data under the End User License Agreement.
- Provision of data when Kaspersky Security Network is used.
- Compliance with European Union law (GDPR).
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux data
For detailed information about data transmitted by Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the Online Help of the application.
Page top
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac data
For detailed information about data transmitted by Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the Online Help of the application.
Page top
Application licensing
This section covers the main aspects of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform licensing.
About the End User License Agreement
The End User License Agreement (EULA) is a binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab, stipulating the terms on which you may use the application.
Read through the terms of the End User License Agreement carefully before you start using the application.
You can view the terms of the End User License Agreement (EULA) in the following ways:
- During installation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- By reading the text named /EULA/License.<language>.
This file is included in the application distribution kit.
- In the application web interface, in the Settings section, License subsection, by clicking the License agreement button.
- In the web interface of the Sandbox component, in the
 menu, by clicking the End User License Agreement link.
menu, by clicking the End User License Agreement link.
By confirming that you agree with the End User License Agreement when installing the application, you signify your acceptance of the terms of the EULA. If you do not accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, you must abort application installation and must not use the application.
Page top
About the license
A license is a limited-time right to use Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform granted under the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement (EULA).
The list of available functionality and the period for which you can use the application depend on the license under which you are using the application.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides the following types of licenses:
- NFR (not for resale) is a free license for a set period, intended to familiarize the user with the application and to carry out test deployments.
- Commercial—Paid license that is provided when you buy the application.
When the license expires, the application continues to work but with limited functionality. To use the application full functionality, you must purchase a commercial license or renew a commercial license.
In the current version of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, the available functionality of the application also depends on the type of key installed.
The update functionality (including anti-virus signature updates and code base updates), as well as the KSN functionality may be unavailable in the territory of the USA.
Page top
About the license certificate
The License Certificate is a document provided with the key file or activation code.
The License Certificate contains the following license information:
- License key or order number.
- Details of the license holder.
- Information about the application that can be activated using the license.
- Limitation on the number of licensing units (devices on which the application can be used under the license).
- License start date.
- License expiration date or license validity period.
- License type.
About the key
A license key is a sequence of bits used to activate and use the application in accordance with the End User License Agreement. A license key is generated by Kaspersky.
To add a key to the application, upload the key file.
Kaspersky can block a key over violations of the End User License Agreement. If the key has been blocked, you have to add a different key to continue using the application.
In the current version of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, the available functionality of the application depends on the type of the added license key:
- KATA and KEDR keys. Full functionality of the application.
- KEDR key. Receiving and processing of data from network traffic and mail traffic is limited.
- KATA key. The web interface sections Threat Hunting, Tasks, Prevention, Custom rules, Storage, and Endpoint Agents have limited functionality.
About the key file
A key file is a file with the .key extension that you receive from Kaspersky. Key files are designed to activate the application by adding a license key.
After purchasing the application or ordering the trial version of the application, you receive a key file at the email address you specified.
You do not need to connect to Kaspersky activation servers in order to activate the application with a key file.
You can recover a key file if it is accidentally deleted. You may need a key file to register with Kaspersky CompanyAccount.
To restore a key file, contact the vendor of the license.
Page top
Viewing information about the license and added keys in the web interface of the Central Node
In
and , you can view information about the license and added keys in the web interface of PCN servers and all connected SCNs under the account of a local administrator, administrator, or users of the application web interface.To view information about the license and added keys,
In the web interface of the server hosting the Central Node component, select the Settings section, License subsection.
The web interface shows the following information about the license and added keys:
- License serial number.
- Application activation date.
- License expiration date.
- Number of days until license expiration.
During the period within 30 days of license expiration, the Dashboard section displays a notification about the need to renew the license. This notification is displayed on all servers with the Central Node component (in distributed solution and multitenancy mode – on PCNs and all connected SCNs) for all users, regardless of their role.
Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of the Central Node
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can view the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of PCN servers and all connected SCNs under the account of a local administrator, administrator, or users of the application web interface.
To view the text of the End User License Agreement, perform the following steps in the web interface of the server hosting the Central Node component:
- Select section Settings, subsection License.
- Click the License agreement button in the upper-right corner of the workspace.
- In the opened window, carefully read the text of the End User License Agreement.
- When you are done, click the Close button.
Viewing the text of the Privacy Policy in the web interface of the Central Node
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can view the text of the Privacy Policy in the web interface of PCN servers and all connected SCNs under the account of a local administrator, administrator, or users of the application web interface.
To view the text of the Privacy Policy, perform the following steps in the web interface of the server hosting the Central Node component:
- Select section Settings, subsection License.
- Click the Privacy Policy button in the upper-right corner of the workspace.
- In the opened window, carefully read the text of the Privacy Policy.
- When you are done, click the Close button.
Viewing information about the third-party code used in the application
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can view information about third-party code used in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform in the web interface of PCN servers and all connected SCNs under the account of a local administrator, administrator, or users of the application web interface.
To view information about third-party code, perform the following steps in the web interface of the server hosting the Central Node component:
- Select section Settings, subsection License.
- Click the Third-party code button in the upper-right corner of the workspace.
- In the opened window, view the information about third-party code.
- When you are done, click the Close button.
Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of the Sandbox
To view the text of the End User License Agreement in the web interface of the Sandbox server:
- Sign in to the Sandbox web interface using the account credentials that you specified during installation of the Sandbox component.
- Click the
 button in the lower-left part of the web interface window.
button in the lower-left part of the web interface window. - This opens a window containing information about the Sandbox component.
- Click the End User License Agreement link to open the window containing the text of the End User License Agreement for the application.
- Carefully read the text of the End User License Agreement.
- When you are done, click the
 button.
button.
Viewing the text of the End User License Agreement for the Endpoint Agent component
You can view the text of the End User License Agreement for the application that is being used as the Endpoint Agent component. For details on how to view the text of the End User License Agreement, see the Online Help for the relevant application.
About the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows End User License Agreement
About the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows End User License Agreement
About the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux End User License Agreement
About the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac End User License Agreement
Adding a key
In distributed solution mode, a key can be added only on the PCN server.
To add a key:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, License subsection.
- Select the type of key: or .
- In the section with the selected key type, click the Upload button.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a key file to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The key is added to the application.
Replacing a key
In distributed solution mode, a key can be replaced only on the PCN server.
To replace the active application key with a different key:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, License subsection.
- Select the type of key: KATA or KEDR.
- In the section with the selected key type, click the Replace button.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a key file you want to use to replace the active key and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The loaded key replaces the active key of the application.
Removing a key
In distributed solution mode, a key can be removed only on the PCN server.
To remove a key:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, License subsection.
- Select the type of key: KATA or KEDR.
- In the section with the selected key type, click Delete.
This opens the key removal confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The key removal confirmation window closes.
The key is removed.
Application modes based on the license
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides various operating modes depending on the added keys.
No license
After the application is installed and the web interface is started, the application operates in this mode until you add a key.
Unlicensed mode has the following limitations:
- Application databases are not updated.
- There is no connection to the Kaspersky Security Network Knowledge Base.
- Receiving and processing of data from network traffic and mail traffic is limited.
- The web interface sections Threat Hunting, Tasks, Prevention, Custom rules, Storage, and Endpoint Agents have limited functionality.
Commercial license
In this operating mode, the application connects to the Kaspersky Security Network Knowledge Base and updates its databases.
When the key for commercial license expires, the application stops updating its databases and does not connect to the Knowledge Base of Kaspersky Security Network.
To resume the operation of the application, you must replace the key or add a new commercial license key.
In the current version of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, the available functionality of the application also depends on the type of the added license key:
- KATA and KEDR keys. Full functionality of the application.
- KEDR key. Receiving and processing of data from network traffic and mail traffic is limited.
- KATA key. The web interface sections Threat Hunting, Tasks, Prevention, Custom rules, Storage, and Endpoint Agents have limited functionality.
Architecture of the application
The application includes the following main components:
- Sensor. Receives and scans data, can also be used as a proxy server during data exchange between Endpoint Agent and Central Node.
- Central Node. Receives and scans data, analyzes the behavior of objects, and publishes analysis results in the web interface of the application.
- Sandbox. Starts virtual images of operating systems. Starts files in these operating systems and tracks the behavior of files in each operating system to detect malicious activity and signs of targeted attacks to the corporate IT infrastructure.
- Endpoint Agent. Installed on workstations and servers in the IT infrastructure of the organization. Continuously monitors processes running on those computers, active network connections, and files that are modified.
Sensor component
The following modules of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform run on each server hosting the Sensor component:
- Sensor. Receives data from network and mail traffic and sends the data for processing to the server with the Central Node component.
- Intrusion Detection System (hereinafter also referred to as IDS). Scans the Internet traffic for signs of intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
- KSN. Checks the reputation of files and URL addresses in the Knowledge Base of Kaspersky Security Network on behalf of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and provides information about categories of websites (for example, malicious website, phishing website).
Kaspersky Security Network (hereinafter also "KSN") is an infrastructure of online services that provides access to Kaspersky's online Knowledge Base with information on the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false alarms.
If you do not want to participate in KSN, you can use Kaspersky Private Security Network (hereinafter also referred to as KPSN). KPSN is a solution that allows users to access the reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network and other statistical data without actually sending data from their own computers to Kaspersky Security Network.
- URL Reputation. Detects malicious and phishing URL addresses, and URL addresses that were previously used by hackers in targeted attacks against and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
You can also use a mail sensor as a Sensor component, which is a server or virtual machine on which Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway (KSMG) or Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server (KLMS) is installed. These applications send email messages to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform for processing. Based on the results of processing of email messages in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, KSMG and KLMS may block the transfer of messages.
The Sensor component can also be used as a proxy server for outgoing connections from the Endpoint Agent component.
If KSMG or KLMS is being used as a Sensor component, scan exclusion lists configured for message recipients and MD5 checksums of files are not transmitted to KSMG and KLMS and are not applied when messages are processed by KSMG and KLMS.
Central Node component
The component can be deployed on one server or as a high availability cluster that consists of 2 roles: storage servers and processing servers.
High availability is achieved through duplication of data between the storage servers and the redundancy of computing resources: if one server fails, its functions are performed by another server with the same role. Meanwhile, the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform continues to work.
Only one failure of a server in a cluster is tolerated. If multiple servers fail, the cluster becomes inoperable.
The following application modules, kernels and technologies run on each server or cluster with the Central Node component:
- Anti-Malware Engine (hereinafter also referred to as AM or AM Engine). Scans files and objects for viruses and other threats to the corporate IT infrastructure using anti-virus databases.
- Mobile Attack Analyzer (also referred to as MAA). Scans executable files in the APK format in the cloud infrastructure using a machine learning technology. As a result of the scan, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives information about detected threats or absence of threats.
- YARA. Scans files and objects for signs of targeted attacks on the corporate IT infrastructure using YARA Rules databases created by users of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Targeted Attack Analyzer (hereinafter also referred to as TAA or TA Analyzer). Analyzes and monitors network activity of software installed on computers of the corporate LAN using TAA (IOA) rules. Searches for signs of network activity that the user of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is advised to direct his/her attention, as well as signs of targeted attacks to the corporate IT infrastructure.
- KSN. Checks the reputation of files and URL addresses in the Knowledge Base of Kaspersky Security Network on behalf of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and provides information about categories of websites (for example, malicious website, phishing website).
Sandbox component
Servers hosting the Sandbox component run virtual machines with images of operating systems.
The Sandbox component starts objects in these operating systems and analyzes the behavior of the objects to detect malicious activity and signs of targeted attacks to the corporate IT infrastructure.
By default, the maximum file size scanned by the Sandbox module is 100 MB. You can configure scan settings in the administrator menu of the application management console.
The maximum level of nesting for scanned archives is 32.
The maximum number of objects that can be in queue to be scanned by the Sandbox component per day is 20,000 objects. When this limit is reached, the application deletes 10% of the objects that have been queued for scanning the longest and replaces them with new objects queued for scanning. The deleted objects are saved in the application with the NOT_SCANNED status.
Endpoint Agent component
Software component. It can be represented by the following applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
The applications are installed on workstations and servers in the IT infrastructure of the organization (hereinafter also referred to as "computers"). On these computers, the applications continually monitor processes, active network connections, and files being modified, and send this monitoring data to the Central Node server.
Computers intended for installation of applications must meet hardware and software requirements.
Operating principle of the application
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application includes three functional blocks:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (hereinafter also referred to as "KATA"), which detects threats on the perimeter of the enterprise IT infrastructure.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "KEDR"), which provides protection for the local area network of the organization.
- Network Detection and Response (hereinafter also referred to as "NDR"), which provides protection of the corporate LAN.
You can use the full functionality of the application (KATA key and KEDR key) or partial functionality (only KATA key or only KEDR key).
Principle of operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack includes the following components:
- Sensor.
- Central Node.
- Sandbox.
Sensor, Central Node and Sandbox interoperate as follows:
- The Sensor component receives mirrored SPAN, ERSPAN, RSPAN traffic, objects metadata of HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS protocols, HTTP and FTP traffic data, as well as HTTPS traffic (if the administrator has configured SSL certificate replacement on the proxy server), copies of email messages, and does the following with the gathered data:
- Scans Internet traffic for signs of intrusion into the corporate IT infrastructure using the Intrusion Detection System technology (hereinafter also referred to as IDS).
IDS technology can recognize and detect network activity in 80 protocols, particularly in 53 application layer protocols of the TCP/IP model, detecting suspicious traffic and network attacks. Supported protocols include TCP, UDP, FTP, TFTP, SSH, SMTP, SMB, CIF, SSL, HTTP, HTTP/2, HTTPS, TLS, ICMPv4, ICMPv6, IPv4, IPv6, IRC, LDAP, NFS, DNS, RDP, DCERPC, MS-RPC, WebSocket, Citrix and others.
- Checks the reputation of files and URLs against the Kaspersky Security Network database (hereinafter also referred to as "KSN") or Kaspersky Private Security Network (hereinafter also referred to as "KPSN").
- Sends objects and files to be scanned by the Central Node component.
You can also use a mail sensor as a Sensor component, which is a server or virtual machine on which Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway (KSMG) or Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server (KLMS) is installed.
- Scans Internet traffic for signs of intrusion into the corporate IT infrastructure using the Intrusion Detection System technology (hereinafter also referred to as IDS).
- The Central Node component scans files and objects using anti-virus databases, YARA rule databases created by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack users, and if necessary, sends files and objects to be scanned by the Sandbox component.
- The Sandbox component analyzes the behavior of objects in virtual operating systems to detect malicious activity and signs of targeted attacks on corporate IT infrastructure, and sends scan results to the Central Node server.
If any threats are detected, the Central Node server records relevant information in the alert database. You can view the alert table in the Alerts section of the application web interface or by generating an alert report.
Alert information can also be published to a SIEM system that is used in your organization, as well as external systems. Information on Sandbox component alerts can be published in the local reputation database of Kaspersky Private Security Network.
Principle of operation of Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response includes the following components:
- Central Node.
- Endpoint Agent.
The component may be represented by any of the following applications: Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- Sandbox.
Optional component.
The Sensor component can be used as a proxy server for outgoing connections from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
The Endpoint Agent and Central Node components interoperate as follows:
One of the applications that represents the Endpoint Agent component is installed on individual computers within the corporate IT infrastructure and continuously monitors processes, open network connections, and files being modified. The monitoring data are sent to the server with the Central Node component. Events are generated based on these data.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows transmit data about the following events to the Central Node server:
- Process started
- Process terminated
- Module loaded
- Connection to remote host
- Blocked application (prevention rule)
- Document blocked
- File changed
- System event log
- Registry modified
- Port listened
- Driver loaded
- Process: interpreted file run
- Process: console interactive input
- Scan: detection
- Scan: detection processing result
- AMSI scan
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux sends information about the following events to the Central Node server:
- Process started
- Process terminated
- File changed
- System event log
- Scan: detection
- Scan: detection processing result
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac sends information about the following events to the Central Node server:
- Process started
- Process terminated
- File changed
- Scan: detection
- Scan: detection processing result
The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows can be integrated with Endpoint Protection Platform (hereinafter also "EPP") applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent for Windows.
Information about compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications is provided in the Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications section.
In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent also sends information about threats detected by the EPP applications and results of threat processing by these applications to the Central Node server.
EPP applications, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, and Central Node components interoperate as follows:
- EPP applications send information about detected threats and results of threat processing to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows can also supply Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with information about third-party applications with Antimalware Scan Interface support (hereinafter also referred to as "AMSI") sending objects (for example, PowerShell scripts) to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows for additional scanning.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent sends data gathered while monitoring processes, open network connections, and files being modified, as well as data received from EPP applications, to the Central Node server.
The Central Node server processes received data and displays the corresponding events in the application web interface.
EPP application data processing generates Scan: detection, Scan: detection processing result, AMSI scan events (when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows).
Events arriving at the Central Node server are marked by TAA (IOA) rules. As a result of this markup, alerts can be generated for events that require user attention. If you have the Sandbox component, you can also automatically send files from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts to be scanned by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules.
When the Central Node server is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you can do the following to react to detected threats:
- Manage files and applications by running the following tasks on Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts: Kill process, Get forensics, Start YARA scan, Run application, Get file, Delete file, Quarantine file, Restore file from quarantine, Service management, Get disk image, Get memory dump.
- Configure policies for preventing the running of files and processes on selected hosts.
- Isolate individual hosts from the network.
- Work with TAA (IOA) rules to classify and analyze events.
- Work with OpenIOC compliant files (IOC files) to search for signs of targeted attacks, infected and probably infected objects on hosts and in the Alerts database.
- Perform Threat Response actions using the API.
When the Central Node server is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, you can do the following to react to detected threats:
- Manage files and applications by running Get file, Run application tasks.
- Work with TAA (IOA) rules to classify and analyze events.
- Perform the following Threat Response actions using the API: Managing the application run task.
When the Central Node server is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux, you can do the following to react to detected threats:
- Manage files and applications by running Get file, Run application, Delete file, Kill process tasks.
- Isolate individual hosts from the network.
- Work with OpenIOC compliant files (IOC files) to search for signs of targeted attacks, infected and probably infected objects on hosts and in the Alerts database.
- Perform the following Threat Response actions using the API: Host network isolation management, Managing the application run task.
The principle of operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is shown in the following picture.

Principle of operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can configure settings of each Central Node component individually or manage several components in a centralized way in distributed solution mode.
A distributed solution is a two-tier hierarchy of Central Node servers. This structure sets apart a primary control server known as the Primary Central Node (PCN) and secondary servers known as Secondary Central Nodes (SCN).
The principle of operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform in distributed solution mode is shown in the following picture.

Principle of operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform in distributed solution mode
Distributed solution and multitenancy
You can configure settings of each Central Node component individually or manage several components in a centralized way in distributed solution mode.
The distributed solution is a two-tier hierarchy of servers with Central Node components installed. This structure sets apart a primary control server known as the Primary Central Node (PCN) and secondary servers known as Secondary Central Nodes (SCN). Interaction of servers requires connecting SCN to PCN.
If you have deployed the Central Node component as a cluster, the entire cluster takes on the role of a PCN or SCN.
PCN and SCN scan files and objects using the same technology as the individually managed Central Node component.
The distributed solution allows centralized management of the following functional areas of the application:
- Users.
- Alerts.
- Threat Hunting.
- Tasks.
- Prevention.
- Custom rules.
- Storage.
- Endpoint Agents, including network isolation of hosts.
- Reports.
If you are supporting multiple organizations or branch offices of the same organization, you can use the application in multitenancy mode.
Multitenancy mode lets you use the application to simultaneously protect the infrastructure of multiple organizations or branch offices of the same organization (hereinafter also referred to as "
"). You can install Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on one or more Central Node for each tenant. Each tenant can manage the application independently from other tenants. The service provider can manage the data of multiple tenants.For each user account, the number of simultaneous application management sessions is limited to one IP address. If the same user name is used to log in to the application from a different IP address, the earlier session is terminated.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the limit is enforced for each PCN and SCN server separately.

Operation of the application in distributed solution mode
You can use the distributed solution and multitenancy mode in the following cases:
- To protect more than 10,000 hosts of a tenant
- For centralized management of the application in different business units of the tenant
- For centralized management of the application on servers of multiple tenants
- For processing network traffic at a maximum rate of 10 Gbps if your network includes more than one 10 Gbps segment and if you want to process traffic traffic in these segments
When the application switches to the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, all previously added license keys are deleted from servers with the SCN role. Each connected SCN receives a key from the PCN. If full functionality of the application is used for the PCN (KATA and KEDR key), and partial functionality is used for the SCN (only KATA key or only KEDR key), the SCN server load limit may be exceeded because of the increased volume of data. If partial application functionality is used for the PCN (only KATA key or only KEDR key), and full functionality is used for the SCN (KATA and KEDR key), the application functionality is partially unavailable.
License keys can be managed only on the PCN.
You can use the following scenarios to deploy the application in distributed solution and multitenancy mode:
- Install the Central Node component on new servers and assign PCN and SCN roles to those servers.
- Assign PCN and SCN roles to servers that already have the Central Node component installed.
In this case, you must upgrade the Central Node component to version 6.0.
Before you switch servers with Central Node components installed to distributed solution mode, you should review the changes that will be applied to the system after the operating mode is changed. Assigning the PCN role to a server is irreversible.
Distributed solution and multitenancy mode transition scenario
Switching the application to the distributed solution and multitenancy mode involves the following steps:
- Installing the Central Node components.
- Assigning the PCN role to one of the servers.
- Assigning the SCN role to the rest of the servers and sending requests to connect to the PCN.
- Processing a SCN to PCN connection request.
Modifications of application settings for the distributed solution and multitenancy mode
Modifications of application settings for the distributed solution and multitenancy mode are listed in the following table.
Modifications of application settings when switching to the distributed solution and multitenancy mode
Functional area |
PCN |
SCN |
|---|---|---|
Users |
Users and roles assigned to them are preserved. Additionally, PCN users are granted access rights to work with PCN and all connected SCNs. |
All users are deleted except the user that was created while Central Node was deployed. After that, the SCN requests a list of users from the PCN and uses that list to create local users with the same parameters:
Users that do not have rights to access the SCN, are not displayed in the list of users. |
Alerts |
Information about all alerts from all connected SCNs is added to the PCN database. |
The user name is no longer displayed in existing alert information. User data are deleted from alert operation history. |
Dashboard |
On the Alerts tab, you can now select the SCNs whose information must be displayed in the widget. On the System health tab, the status of connection of the PCN with connected SCNs is now displayed. |
On the System health tab, the status of connection with the PCN is now displayed. |
Tasks |
Tasks created on the Central Node server before it was assigned the PCN role, as well as tasks created on the PCN after switching to distributed solution mode, apply to all connected SCNs. Tasks created on SCNs are also displayed in the task list. Settings of these tasks cannot be changed on the PCN. |
Tasks created on the PCN are displayed, as well as tasks created on this SCN. Settings of tasks created on the PCN cannot be changed. |
Reports |
Templates and reports created before the switch to distributed solution mode are preserved. A Servers column is added to the report table, containing information about the relevant SCN for the alert. After switching to distributed solution mode, only reports created on a PCN are displayed. |
Templates and reports created before the switch to distributed solution mode are preserved. Information about the user who created the report is preserved if the PCN has a user with the same ID (guid). In other cases user information is deleted. After switching to distributed solution mode, only reports created on an SCN are displayed. |
Prevention |
Policies created on the Central Node server before it was assigned the PCN role, as well as policies created on the PCN after switching to distributed solution mode, apply to all connected SCNs. Policies created on SCNs are also displayed in the policy list. Settings of these policies cannot be changed on the PCN. |
Policies created on the PCN are displayed, as well as policies created on this SCN. Settings of policies created on the PCN cannot be changed. |
Storage |
All files and metadata that were stored on PCNs before the switch to distributed solution mode are preserved. The name of the PCN is displayed for them in the Central Node column. The PCN also keeps the contents of the Storage of all connected SCNs. |
All files and metadata that were stored on SCNs before the switch to distributed solution mode are preserved. |
TAA exclusions |
No changes. |
No changes. |
VIP status |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Notification rules |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Integration with mail sensors |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Threat Hunting |
During threat hunting in the database, the PCN sends a request to all connected SCNs. After the search query is processed, a list of PCN and SCN events of the selected tenant is displayed. |
No changes. |
Custom rules ‑ TAA |
IOC files added on the Central Node server before it was assigned the PCN role are applied to the PCN. TAA (IOA) rules that were added on the Central Node server before it was assigned the PCN role are applied to the PCN. |
IOC files and TAA (IOA) rules added on the PCN, as well as IOC files and TAA (IOA) rules added on this SCN before and after switching to distributed solution mode are displayed. |
Backup of the application |
Backup of the application is only available on a PCN that does not have SCNs connected. To back up the application on a PCN, disconnect all SCNs from the PCN. |
Backup of the application on an SCN is not available. To back up the application on an SCN, disconnect that server from the PCN by switching it to standalone server mode. |
Assigning the PCN role to a server
Assigning the PCN role to a server is irreversible. After changing the server role to PCN, you will not be able to change the role of that server to SCN or standalone server. To change the role of that server you will have to reinstall the application.
To assign the PCN role to the server:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You need to log in to the web interface of the server to which you want to assign the PCN role.
- Select the Operation mode section.
- Click Distributed solution.
- In the Server role drop-down list, select Primary Central Node.
- In the Tenant name field, enter the name of the tenant to which this Central Node server belongs.
- Click Assign the PCN role.
This opens the action confirmation window.
After confirming the action, log in to the application web interface again.
- Click Yes.
The server is assigned the PCN role and the name of the tenant.
After logging in to the application web interface with administrator credentials, the Operation mode section of the application web interface displays the following information:
- Current mode – Distributed solution.
- Server role – Primary Central Node.
- Certificate fingerprint – the fingerprint of the server's certificate required for authentication when establishing connection with an SCN.
- Tenants – information about tenants to which this server and connected SCN servers belong:
- IP – Primary Central Node for this server and IP addresses of SCN servers (after they connect).
- Server – name of this server and names of SCN servers (after they connect).
This name is not related to name of the host where the application is installed. You can change it.
- Certificate fingerprint – blank value for this server and certificate fingerprints of SCN servers (after they connect).
- Status – connection state of SCN servers (after they connect) and the number of servers connected to tenants.
- The Servers pending authorization table contains information about connected SCN.
Assigning the SCN role to a server
To assign the SCN role to the server:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You need to log in to the web interface of the server to which you want to assign the SCN role.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- Click Distributed solution.
- In the Server role drop-down list, select Secondary Central Node.
- In the PCN IP field, enter the IP address of the server that has the PCN role, to which you want to connect the SCN.
- Click Get certificate fingerprint.
A fingerprint of the certificate of the server that has the PCN role is displayed in the workspace.
- Contact the administrator of the PCN and compare the certificate fingerprint you received with the fingerprint displayed on the PCN in the Certificate fingerprint field of the Operation mode section.
- If certificate fingerprints on the SCN and the PCN match, click Send connection request.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The server is assigned the SCN role after the PCN administrator accepts the connection request. The SCN server is assigned to the tenant specified by the PCN administrator.
Processing SCN to PCN connection requests
To process a SCN to PCN connection request:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You need to log in to the web interface of the PCN server that you want to use to process connection requests from other servers.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
The workspace displays the Servers pending authorization table.
- Contact the SCN administrator who sent the connection request and verify the certificate fingerprint in the Servers pending authorization table. It must match the fingerprint displayed on the SCN in the Certificate fingerprint from request field of the Operation mode section.
- If certificate fingerprints on the PCN and the SCN match, do one of the following:
- If you want to reject the connection request from the SCN, click Reject.
- If you want to accept the connection request from the SCN:
- Click Accept.
This opens the Accept connection request window.
- In the Tenant list, select the tenant to which you want to assign this SCN server. The list includes previously added tenants.
- Click Accept.
- Click Accept.
Accepting connection requests is not recommended if certificate fingerprints do not match. Make sure the data you entered is correct.
While the SCN server is connected to the PCN, all buttons in the Operation mode window are locked. After the connection is completed, the buttons are unlocked.
If you reject the connection request, the SCN will continue to operate as a standalone Central Node server.
Viewing information about tenants, PCN and SCN servers
In the web interface of the PCN server, you can view information about this server and about all SCN servers that are connected to it.
To view information about PCN and SCN servers in multitenancy mode:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You need to log in to the web interface of the PCN server.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
The workspace displays the following information about servers:
- Current mode – Distributed solution.
- Server role – Primary Central Node.
- Certificate fingerprint – certificate fingerprint of the PCN server.
- Tenants – information about tenants to which the server belongs, as well as all SCN servers connected to the PCN.
- IP – Primary Central Node for the PCN server and IP addresses of SCN servers connected to the PCN.
- Server – name of the server and names of SCN servers that connect to the PCN.
This name is not related to name of the host where the application is installed. You can change it.
- Certificate fingerprint – blank value for the PCN server and certificate fingerprints of SCN servers waiting to connect to the PCN.
- Status – connection status of SCN servers and the number of servers connected to the tenant.
- The Servers pending authorization table contains the following information:
- IP – IP address or domain name of the SCN server.
- Server is the name of the SCN server that is displayed in the application web interface.
This name is not related to name of the host where the application is installed. You can change it.
- Certificate fingerprint – certificate fingerprint of the SCN server that is sent to the PCN with the connection request.
- Status – status of the SCN to PCN connection.
Adding a tenant to the PCN server
To add a tenant in the PCN server web interface:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You must log in to the web interface of the PCN server for which you want to add a tenant.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the right part of the Tenants workspace, click Add.
- In the Name field, enter the name of the tenant that you want to add.
- Click Add.
The tenant is added and is displayed in the list.
Deleting a tenant from the PCN server
To delete a tenant in the PCN server web interface:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You must log in to the web interface of the PCN server for which you want to delete a tenant.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the Tenants workspace, select the tenant that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
The action is irreversible. All global objects as well as reports and report templates of this tenant are lost.
- Click Yes.
The tenant is deleted.
Renaming a tenant on the PCN server
To rename a tenant in the web interface of the PCN server:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
You must log in to the web interface of the PCN server for which you want to rename a tenant.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the Tenants list, click
 next to the tenant that you want to rename.
next to the tenant that you want to rename.This opens a window in which you can rename the tenant.
- In the Name field, enter the new name of the tenant.
- Click Save.
The tenant is renamed.
Disconnecting an SCN from PCN
The SCN can be disconnected from the PCN unilaterally.
If you disconnect an SCN using the SCN web interface, changed settings are only applied to the SCN. The PCN continues to display information about that server.
If you disconnect the SCN using the PCN web interface, information about that server is deleted at the PCN. However, the server with the SCN role will keep trying to connect to the PCN to synchronize settings.
To complete a bilateral disconnect, you must follow both instructions presented below. In this case, the SCN keeps working as a standalone Central Node server, and information about the disconnected SCN is displayed on the PCN.
The administrator of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is responsible for the confidentiality of data on PCN, SCN, and Central Node servers. If you plan to move an SCN server from one tenant to another, you must delete all data remaining on the server after using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform before handing over the server to the different tenant.
To disconnect the SCN from the PCN through the PCN web interface:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
Log in to the web interface of the PCN server that you want to disconnect the SCN from.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the server list, select the SCN that you want to disconnect.
- Click Disconnect.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The SCN will attempt to connect to the PCN to synchronize settings.
To disconnecting the SCN from the PCN through the SCN web interface:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
Log in to the web interface of the SCN server that you want to disconnect from the PCN.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- Click Disconnect.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The SCN is disconnected from the PCN and continues working as a standalone Central Node server.
Modifications of application settings for disconnecting an SCN from PCN
Modifications of application settings after an SCN is disconnected from the PCN are listed in the following table.
Modifications of application settings after disconnecting an SCN from PCN
Functional area |
PCN |
SCN |
|---|---|---|
Users |
The disconnected SCN is not removed from the list of servers to which user rights apply. Information about changes of the user account that has rights on the disconnected SCN is not sent to the SCN. |
User accounts received from the PCN are not deleted. You can create new user accounts again, as well as disable and change passwords for existing user accounts. |
Alerts |
Alert information on the disconnected SCN is deleted. |
Operation history and all alert information is preserved. |
Tasks |
Tasks created on the disconnected SCN are deleted. |
Tasks created on the PCN are deleted. Information about users who created tasks on the SCN is preserved. |
Reports |
All reports created earlier concerning the disconnected SCN are preserved, as well as the ability to filter the report list by this server. |
Templates and reports are not modified. |
Prevention |
Policies created on the disconnected SCN are deleted. |
Policies created on the PCN are deleted. Information about users who created policies on the SCN is preserved. |
Storage |
All objects related to the disconnected SCN are deleted from Storage. |
All objects in the Storage are preserved. The link to the task stops working in information about objects received as part of tasks created on the PCN. |
TAA exclusions |
No changes. |
No changes. |
VIP status |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Notification rules |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Integration with mail sensors |
No changes. |
No changes. |
Threat Hunting |
After the search query is processed, events related to the disconnected SCN are not displayed. |
No changes. |
Custom rules ‑ TAA and IOC |
IOC and TAA (IOA) rules of a disconnected SCN are deleted. |
IOC and TAA (IOA) rules created on the PCN are deleted. |
Backup of the application |
Backup of the application remains unavailable. |
Backup of the application becomes available. |
Decommissioning an SCN server
If you are not planning to subsequently use an SCN server, you can decommission the SCN server by removing it on the PCN.
The administrator of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is responsible for the confidentiality of data on PCN, SCN, and Central Node servers. If you plan to move an SCN server from one tenant to another, you must delete all data remaining on the server after using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform before handing over the server to the different tenant.
Decommissioning an SCN server involves the following steps:
- Deleting all data on the SCN
- Disconnecting the SCN from the PCN through the PCN web interface
- Disconnecting the SCN from the PCN through the SCN web interface
- Deleting the SCN through the PCN web interface
To delete the SCN through the PCN web interface:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
Log in to the web interface of the PCN server from which you want to delete the SCN.
- Select the Operation mode section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the server list, select the SCN that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The SCN will be deleted. Information about the deleted SCN will no longer be displayed on the PCN.
Sizing Guide
To obtain and maintain optimum performance under varying operational conditions of the application, you must take into account the number of networked devices, network topology, and the set of application features that you need.
Selection of the optimal application configuration consists of the following steps:
Common scenarios for deployment and installation of application components
The scenario for deployment and installation of application components is determined by the planned load on the application servers.
The Endpoint Agent component can be installed on any computers that belong to the organization's IT infrastructure and run the Windows operating system. Outbound connections from computers with the Endpoint Agent component to the server hosting the Central Node component must be allowed directly, without a proxy server.
You can install one or multiple Central Node components. If you install multiple Central Node components, you can use them independently of each other or combine them for centralized management in distributed solution mode.
The deployment scenario selection depends on the utilized application functionality. All scenarios listed in this manual also apply to the deployment of the application on a virtual platform.
Full functionality (KATA and KEDR)
When using KATA and KEDR functionality, you can scan network traffic, mail traffic, and data on corporate LAN computers.
If more than 5000 hosts with the Endpoint Agent component are used within the organization, it is not recommended to use the Central Node component to process traffic.
You can use the Sensor component as a proxy server for connecting hosts to the Endpoint Agent component and the Central Node. One Sensor component supports the connection of up to 1000 hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
The criteria for selecting a deployment scenario when using KATA and KEDR functionality are presented in the table below. The selection algorithm is as follows:
- In each row of the table, select the cell containing the value of the criterion corresponding to your IT infrastructure.
If a row contains two cells with identical values, you must select the cell on the left.
- Select the right-most column in which there are marked cells.
Selecting a deployment scenario when using KATA and KEDR functionality
Criterion
Network traffic and mail traffic cannot be received on the same device.
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Number of Endpoint Agent hosts
No
From 5000 to 10,000
From 5000 to 10,000
Over 10,000
1 Gbps
From 1 to 2 Gbps
Over 2 Gbps
Over 2 Gbps
The number of remote infrastructures in which traffic needs to be analyzed.
No
One
Two or more
Two or more
The capacities of one Sandbox component are insufficient to analyze all objects within acceptable time frames.
No
No
Yes
Yes
In distributed solution mode, each application component must meet the hardware requirements specified in the sizing calculator.
Processing of network traffic, mail traffic, and web traffic (KATA)
It is recommended to use KATA functionality if the organization does not need to process data on corporate LAN computers. If this is the case, only network traffic and mail traffic are processed.
The criteria for selecting a deployment scenario when using KATA functionality are presented in the table below. The selection algorithm is as follows:
- In each row of the table, select the cell containing the value of the criterion corresponding to your IT infrastructure.
If a row contains two cells with identical values, you must select the cell on the left.
- Select the right-most column in which there are marked cells.
Selecting a deployment scenario when using KATA functionality
Criterion
Network traffic and mail traffic cannot be received on the same device.
No
Yes
Yes
1 Gbps
From 1 to 2 Gbps
Over 2 Gbps
The number of remote infrastructures in which traffic needs to be analyzed.
No
One
Two or more
The capacities of one Sandbox component are insufficient to analyze all objects within acceptable time frames.
No
No
Yes
Processing of data from corporate LAN computers (KEDR)
It is recommended to use KEDR functionality if the organization does not need to process traffic. If this is the case, only data on corporate LAN computers is processed.
Depending on the presence of a third-party Sandbox solution within the organization, you can use one of the following deployment scenarios:
Two-server deployment scenario
When using KATA and KEDR functionality, you can install the Endpoint Agent component on corporate LAN computers. When using KATA functionality, the Endpoint Agent component is not installed.
When using this deployment scenario, the Central Node and Sensor components are installed on the same server or cluster. This server or cluster receives traffic, performs an initial analysis of traffic and a deeper analysis of extracted files. Based on the scan results, components detect signs of targeted attacks on the organization's IT infrastructure.
The Sandbox component is installed on the other server.
The scenario for application operation when deployed on two servers is presented in the figure below.

Application operating scenario when deployed on two servers
Three-server deployment scenario.
When using KATA and KEDR functionality, you can install the Endpoint Agent component on corporate LAN computers. When using KATA functionality, the Endpoint Agent component is not installed.
When using this deployment scenario, the Sensor, Central Node and Sandbox components are installed on separate servers. The Central Node component can also be deployed as a cluster. The server with the Sensor component receives traffic, performs an initial analysis, extracts files and forwards them to the Central Node component for a deeper analysis.
Using this deployment scenario, the Central Node component can receive traffic and perform an initial analysis of data in the main infrastructure. In this case, you can install the Sensor component on a server of a remote infrastructure whose traffic needs to be analyzed. If the channel bandwidth in the main infrastructure is more than 2 Gbps, you are advised to install the server with the Sensor component in the main infrastructure.
The traffic exchanged between the Central Node and Sensor components comprises up to 20% of traffic received by the Sensor component.
The application operating scenario when deployed on three servers is presented in the figure below.

Application operating scenario when deployed on three servers
Scenario of deployment on four or more servers.
When using KATA and KEDR functionality, you can install the Endpoint Agent component on corporate LAN computers. When using KATA functionality, the Endpoint Agent component is not installed.
If there is a large volume of traffic, you can install multiple Sensor components or multiple Sandbox components on different servers. This scenario is recommended for deployment in large organizations.
You can also use one Sandbox component to connect to multiple Central Node components.
The operating schematic of the application when deployed on four or more servers is presented in the figure below.

Application operating scenario when deployed on four or more servers
Scenario for deploying KEDR functionality with a Sandbox component
Using this deployment scenario, you need to install the Central Node component separately from the Sensor component.
The application operating scenario when deploying KEDR functionality with the Sandbox component is presented in the figure below.

Application operating scenario when deploying KEDR functionality with the Sandbox component
Scenario for deploying KEDR functionality without a Sandbox component
You do not need to install the Sandbox component and can use the Central Node component only for managing the Endpoint Agent component and data analysis.
Using this deployment scenario, you need to install the Central Node component separately from the Sensor component.
The application operating scenario when deploying KEDR functionality without the Sandbox component is presented in the figure below.
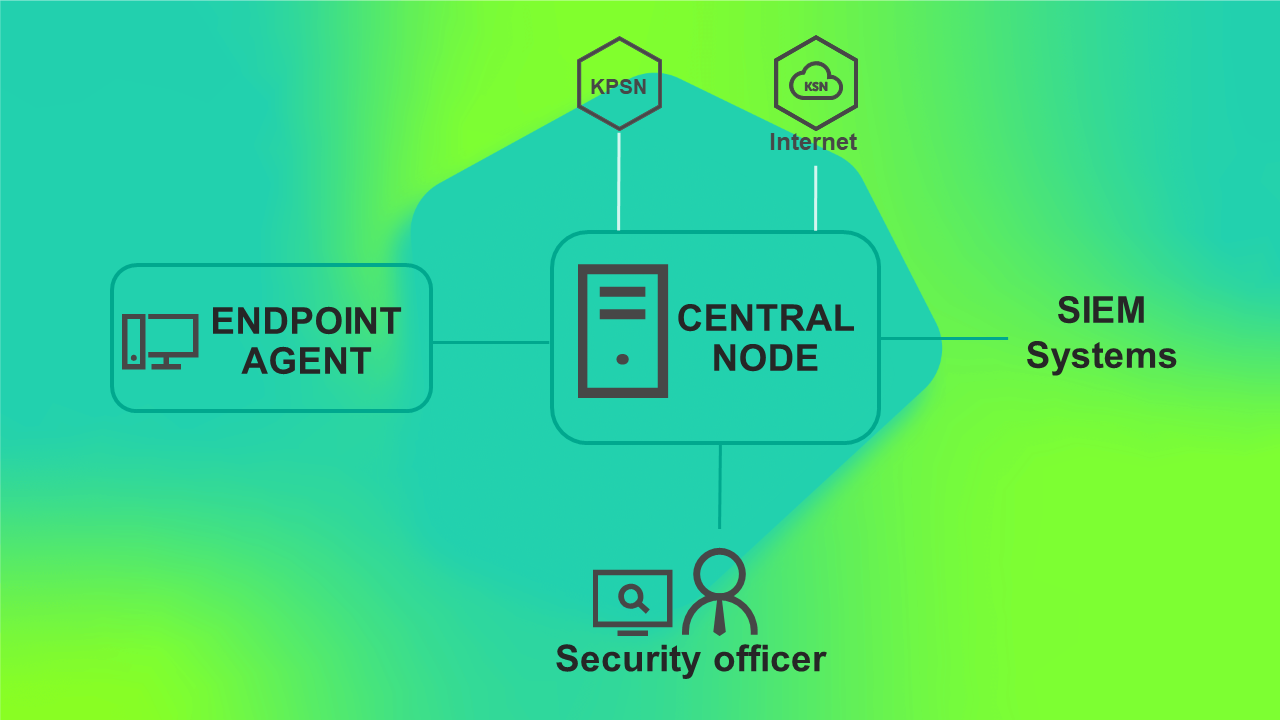
Application operating scenario when deploying KEDR functionality without the Sandbox component
Sizing calculator
After you have selected the deployment scenario that is most appropriate for your IT infrastructure, you must calculate the hardware requirements for servers used for installing application components.
Calculations for the Sensor component
These calculations also apply when the application is deployed on a virtual platform.
When calculating the hardware requirements for the Sensor component, consider that the maximum traffic volume that can be processed is 10 Gbps. This maximum traffic volume can be processed on one Sensor installed on a standalone server or on multiple Sensors installed on standalone servers which are connected to one Central Node. The total traffic volume from all Sensors connected to one Central Node may not exceed 10 Gbps.
If the network includes more than one 10 Gbps segment and you need to process traffic in these segments, you must use the distributed solution mode.
You can use a server hosting the Sensor as a proxy server during data exchange between workstations with Endpoint Agent and the Central Node to simplify configuration of network rules. For example, if workstations with Endpoint Agent are in a separate segment of the network, it is sufficient to configure a connection between Central Node and Sensor servers.
When using the Sensor as a proxy server for communication between Endpoint Agent components and the Central Node component, consider the following limitations:
- A maximum of 15,000 workstations with the Endpoint Agent component can connect to a single Central Node component.
- The maximum allowed packet loss between Sensor servers and the Central Node is 10% with a packet delay of up to 100 ms.
The required bandwidth of the link between Central Node and Sensor servers depends on the traffic volume that must be processed and is calculated as follows:
10% SPAN port traffic at typical load or 20% of the SPAN port traffic at peak load + email traffic + ICAP traffic + requirement for the link between the Central Node and the Endpoint Agent
Hardware requirements for the Sensor server
The Sensor component can be integrated with the IT infrastructure of an organization as follows:
- Receive mirrored traffic from network devices from SPAN ports.
- Connect to a mail server over the POP3 protocol.
- Connect to a mail server over the SMTP protocol.
- Receive traffic from a proxy server over the ICAP protocol.
The hardware requirements for the Sensor server are listed in the table below. The calculations are provided for a case in which the Sensor processes email messages and mirrored traffic from SPAN ports. If the Sensor is used as a proxy server for communication between Endpoint Agent workstations and the Central Node, you must also take into account the link requirements.
Hardware requirements for the Sensor server depending on the volume of processed traffic from SPAN ports
Number of Endpoint Agent components |
Volume of processed traffic (Mbps) |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores |
|---|---|---|---|
10000 |
100 |
16 |
4 |
15000 |
500 |
24 |
8 |
15000 |
1000 |
32 |
12 |
15000 |
2000 |
64 |
20 |
15000 |
4000 |
92 |
32 |
15000 |
7000 |
128 |
52 |
15000 |
10000 |
160 |
72 |
The CPU must support the BMI2, AVX, and AVX2 instruction sets.
If you want to process only email messages, but not mirrored traffic from SPAN ports, we recommend using a Sensor installed on the same server as the Central Node. For more details about the hardware requirements, see the Calculations for the Central Node component section → Hardware requirements for the Central Node and Sensor server.
If one Sensor server processes traffic via multiple protocols, to calculate the server hardware, you must consider that mail server or mail sensor integration requires disabling SMTP traffic processing.
Disk space requirements on a Sensor server
It is recommended to use a RAID 1 disk array. The total disk space must be at least 500 GB.
Hardware requirements of the Sensor when saving raw network traffic
If you are saving raw network traffic, the hardware requirements of the Sensor server are higher:
- 0.5 CPU for each 1 Gbps of network traffic.
- 6 GB of RAM for under 2 Gbps of network traffic, or 12 GB of RAM for over 2 Gbps of network traffic.
- Install separate disk storage in the form of a RAID array or DAS pool with the maximum bandwidth calculated using the following formula:
<disk storage bandwidth> = 3 * <maximum throughput of recorded traffic> - The capacity of disk storage is determined by the expected storage duration and the maximum throughput of traffic being saved, with filters taken into account. According to approximate calculations, to store recorded traffic with a maximum throughput of 10 Gbps for 7 days, you need 750 TiB of disk storage.
Calculations for the Central Node component
Deploying the application on a virtual platform requires 10 percent more CPU resources than deploying the application on a physical server. In virtual disk settings, a Thick Provision disk type must be selected.
To avoid possible performance degradation when deploying the application on a virtual platform, we recommend to:
- Set Latency Sensitivity to High.
- Reserve all memory.
- Reserve all CPU.
Hardware requirements for a server with the Central Node and Sensor components
The hardware requirements for a server on which the Central Node and Sensor components are installed depend on the following conditions:
- Volume of processed traffic
To determine the volume of processed decrypted traffic for calculating the load on the server, use the following formula:
<volume of decrypted traffic transmitted by ArtX TLSProxy 1.9.1> = 5 * <volume of unencrypted traffic>To determine the volume of traffic processed on the ICAP server for calculating the load on the server, use the following formula:
<volume of traffic processed on the ICAP server> = 5 * <volume of traffic that is not processed on the ICAP server> - Number of email messages processed per second
- Number of Endpoint Agent hosts
The Endpoint Agent component can be installed on a workstation, terminal server, file server, or network attached storage (NAS).
Information about the compatibility of versions of applications that represent the Endpoint Agent component with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is provided in the following Help sections: Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows can also be installed on a SCADA server.
To determine the effective number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for calculating the server load, you can use the following formula:
K = A+3*B+20*Cwhere
- 'K' is the maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- 'A' is the number of workstations and users of terminal servers running a Windows operating system with the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- 'B' is the number of workstations and users of terminal servers running a Linux or macOS operating system with the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- "C" is the number of servers.
If the volume of processed traffic is greater than 1 Gbps, you must install Central Node and Sensor components on standalone servers.
The hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component depending on the utilized functionality are presented in the table below.
To run Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on Astra Linux, you must configure the application.
Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using KEDR functionality
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores at 3 GHz |
First disk subsystem (RAID 1 or RAID 10) |
Second disk subsystem (RAID 10) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ROPS (read operations per second) |
WOPS (write operations per second) |
Disk array size (TB) |
The number of disks in the array |
ROPS (read operations per second) |
WOPS (write operations per second) |
Disk array size (TB) |
|||
1000 |
64 |
8 |
100 |
1000 |
1 |
4 |
300 |
200 |
Up to 7.2 TB |
3000 |
80 |
12 |
100 |
1000 |
1 |
4 |
700 |
500 |
|
5000 |
96 |
16 |
100 |
1000 |
1 |
4 |
1000 |
600 |
|
10,000 |
144 |
24 |
100 |
1000 |
1 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
|
15,000 |
192 |
32 |
100 |
1000 |
1 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
|
Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using KATA and KEDR functionality
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Maximum number of email messages per second |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on the server with the Central Node component |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on servers with the Sensor component (Mbps) |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores at 3 GHz |
First disk subsystem (RAID 1 or RAID 10) |
Second disk subsystem (RAID 10) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ROPS (read operations per second) |
WOPS (write operations per second) |
Disk array size (TB) |
The number of disks in the array |
ROPS (read operations per second) |
WOPS (write operations per second) |
||||||
1000 |
1 |
200 |
Not processed |
96 |
16 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
300 |
300 |
2000 |
2 |
500 |
Not processed |
128 |
24 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
500 |
500 |
5000 |
1 |
1000 |
Not processed |
160 |
36 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
1000 |
600 |
10,000 |
2 |
1000 |
Not processed |
224 |
48 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
5000 |
5 |
Not processed |
2000 |
144 |
32 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
1000 |
600 |
10,000 |
20 |
Not processed |
4000 |
224 |
56 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
15,000 |
20 |
Not processed |
4000 |
256 |
64 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
15,000 |
20 |
Not processed |
7000 |
320 |
104 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
15,000 |
20 |
Not processed |
10,000 |
320 |
144 |
100 |
1000 |
1.9 |
4 |
2000 |
800 |
Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using КАТА functionality
Maximum number of email messages per second |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on the server with the Central Node component |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on servers with the Sensor component (Mbps) |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores at 3 GHz |
First disk subsystem (RAID 1 or RAID 10) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ROPS (read operations per second) |
WOPS (write operations per second) |
Disk array size (TB) |
The number of disks in the array |
|||||
2 |
500 |
Not processed |
64 |
20 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
1000 |
Not processed |
80 |
28 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
5 |
Not processed |
2000 |
64 |
20 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
4 |
20 |
Not processed |
4000 |
80 |
40 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
Not processed |
7000 |
128 |
72 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
Not processed |
10,000 |
128 |
112 |
100 |
1000 |
2 |
2 |
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not support operation with software RAID array.
The CPU must support the BMI2 instruction set.
Example calculations of required server configuration for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform components If you want to:
you need two servers with the following hardware:
The above calculation is also valid for an infrastructure with 5000 hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or a combination of components (for example, 9000 hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows and 2000 hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux). |
Disk space requirements on the Central Node server
The server with the Central Node component must have at least 2000 GB of free space on the first disk subsystem and at least 2400 GB on the second disk subsystem. The amount of space required on the second disk subsystem depends on the preferred storage policy and can be calculated using the following formula:
150 GB + <number of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows hosts>/15,000 * (400 GB + 240 GB * <number of days to store data>)/0.65, but no more than 12 TB.
This formula can be used to roughly estimate the required disk space. The actual amount of stored data depends on the traffic profile of the organization and may differ from the calculated result.
If you did not install the Central Node and Sensor component as a high availability cluster, you must calculate the disk space for the Events database, GB and Storage, GB settings using the following formula:
A = F - R, GB.
where
- 'A' is the space used by the events database and the Storage.
- 'F' is the size of the hard drive on which the Central Node component is installed.
- 'R' is the reserved amount of free space (GB) corresponding to the number of connected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component; this parameter is taken from the table below.
If the number of hosts connected to the Central Node component is in between the listed values, use the larger number in your calculations.
Reserved amount of free space depending on the number of Endpoint Agent hosts
Number of Endpoint Agent hosts |
Reserved amount of free space (GB) |
|---|---|
1000 |
1000 |
3000 |
1200 |
5000 |
1400 |
10,000 |
1900 |
15,000 |
2400 |
If you have configured integration for scanning external system objects using the REST API, the hardware requirements of the Central Node server must be increased. Additional hardware requirements are presented in the table below.
Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component with integrated external systems
Maximum number of processed objects per second |
Number of additional logical cores |
The number of additional servers with the Sandbox component |
|---|---|---|
8 |
2 |
1 |
16 |
4 |
2 |
24 |
7 |
3 |
If you configured integration to send events to an external system using the REST API, you must increase the hardware requirements of the Central Node server by 1 logical core and 6 GB of RAM.
If you are saving network traffic, the hardware requirements of the Central Node server must be increased. For more details on hardware requirements, see Calculations for the Sensor component → Hardware requirements of the Sensor when saving raw network traffic.
Requirements for the PCN server in distributed solution mode
If you are using distributed solution mode, to calculate the hardware requirements, you must take into account that the hardware requirements of the PCN server are 10% higher in terms of RAM and the number of logical cores than the hardware requirements of the server with the Central Node component. The hardware requirements of the server with the Central Node component are listed in the following tables: Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using KEDR functionality; Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using KATA+KEDR functionality; Hardware requirements for the server with the Central Node component when using КАТА functionality (see above).
You can connect up to 30 SCN servers to one PCN server.
Communication channel requirements
You must make sure that sufficient communication channel bandwidth is available between the server with the Central Node component and each network segment, depending on the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component in the segment. The bandwidth requirements depending on the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is listed in the table below.
Communication channel bandwidth depending on the number of Endpoint Agent hosts
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Required bandwidth of the communication channel reserved for Endpoint Agent components (Mbps) |
|---|---|
10 |
1 |
50 |
2 |
100 |
3 |
1000 |
20 |
10,000 |
200 |
Minimum requirements for the communication channel between the PCN and SCN servers in distributed solution mode are listed in the table below.
Minimum requirements for the communication channel between the PCN and SCN servers
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Maximum number of email messages per second |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports (Mbps) |
Required communication channel bandwidth (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|
5000 |
5 |
2000 |
20 |
10,000 |
20 |
4000 |
30 |
Hardware requirements for Central Node cluster servers
A cluster must include at least 4 servers: 2 storage servers and 2 processing servers. If you have up to 15,000 connected hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component, you need at least 2 storage servers and 2 processing servers. If you have from 15,000 to 30,000 connected hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component, you need at least 2 storage servers and 3 processing servers.
Each cluster server must have two network adapters to configure cluster and external subnet. The cluster subnet must be capable of up to 10 Gbps.
The cluster subnet must also meet the following requirements:
- A cluster subnet must include only the cluster servers and network switches.
- The cluster subnet must be isolated.
- The cluster servers must all be in the same L1 or L2 segment. To do this, you can connect all the servers in the cluster to a single network switch or use software tunneling. For example, L2TPv3 or Overlay Transport Virtualization (OTV).
- The "network latency" value must meet the "single digit latency" requirement, that is, the value must be less than 10 milliseconds.
The hardware requirements for cluster servers when using KEDR functionality are listed in the table below.
Hardware requirements for processing servers when using KEDR functionality
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores |
RAID disk array type |
The number of disks in a RAID disk array |
Single HDD volume (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
256 |
48 |
RAID 1 |
2 |
1200 |
Hardware requirements for storage servers when using KEDR functionality
Minimum RAM (GB) |
Minimum number of logical cores |
First disk subsystem |
Second disk subsystem |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RAID disk array type |
The number of disks in a RAID disk array |
Single HDD volume (GB) |
Number of disks |
Single HDD volume (GB) |
||
128 |
16 |
RAID 1 |
2 |
1200 |
at least 6 |
at least 1200 |
We recommend using disks of the same size for the two disk subsystems. For the second disk subsystem, you must use disks that are not combined into a RAID array.
The performance requirements for disk subsystems are equivalent to those specified in the table Hardware requirements for a server with the Central Node component when using KEDR functionality (see above).
Calculations for the Sandbox component
The hardware requirements for a server with the Sandbox component depend on the type and volume of processed traffic and on the permissible object scan time.
By default, the permissible object scan time is 1 hour. To reduce this time, you need a more powerful server or more servers with the Sandbox component.
It is recommended to calculate the configuration of the Sandbox component as follows:
- Install the Central Node and Sensor components on one server and the Sandbox component on a different server for pilot operation of the application.
To receive sufficient statistical data, the application must process traffic of the organization for a week.
- Run the data recording script by executing the following commands:
sudo kata-run.sh kata-collect --output-dir path-to-folder--output-dir <path to directory>When the script finishes running, the collect.tar.gz archive will be moved to the specified directory.
- Forward this archive to Kaspersky Lab staff for analysis.
If multiple virtual machines are started simultaneously, the speed of processing objects from the queue is increased.
The Sandbox component is not supported on AMD processors.
Hardware requirements for the server hosting the Sandbox component
The calculation of the number of servers with the Sandbox component when using preset images of operating systems is shown in the table below.
Hardware requirements for the Sandbox component when using preset images of operating systems
Maximum number of email messages per second |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports (Mbps) |
Maximum number of computers with the Endpoint Agent component |
Number of physical servers with the Sandbox component |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
When using |
When using |
|||
1 |
200 |
1000 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
500 |
3000 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1000 |
5000 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
2000 |
5000 |
1 |
1 |
20 |
4000 |
10,000 |
2 |
1 |
20 |
7000 |
15,000 |
4 |
2 |
20 |
10,000 |
15,000 |
5 |
2 |
If you want to install the Sandbox component on a virtual server, you need 3 to 4 times more virtual servers to get the same performance you would get from a physical server.
Additional capacity may be required when using custom images for servers with the Sandbox component. To calculate the number of physical Sandbox servers required when using custom operating system images, you can use the following formula:
<number of files that need to be processed per hour in accordance with to user-defined Sandbox rules> * <number of custom operating system images> / 1000
To calculate the number of virtual Sandbox servers required when using custom operating system images, you can use the following formula:
<number of files that need to be processed per hour in accordance with to user-defined Sandbox rules> * <number of custom operating system images> / 280
The estimation of the number of Sandbox servers is listed for servers with the following configuration:
- When installing the Sandbox component on a physical server:
- 2 CPUs: Intel Xeon 8 Core (HT) at 2.6 GHz or higher.
- 80 GB of RAM
- 2 HDDs, 300 GB each, combined into a RAID 1 array.
- When installing the Sandbox component on a VMware ESXi virtual machine:
- Intel Xeon 15 Core (HT) CPU at 2.1 GHz or higher.
- 32 GB of RAM
- 300 GB HDD
On the virtual machine:
- Nested virtualization enabled.
- Latency Sensitivity option set to High.
- Entire RAM is reserved.
- Entire CPU frequency is reserved.
When installing the Sandbox component on a VMware ESXi virtual machine, you must set the limit for simultaneously running virtual machines to 12.
If you plan to use custom operating system images, we recommend increasing the disk space to 600 GB or more.
Calculations for the Central Node component deployed on the KVM virtualization platform
To deploy the Central Node component in a virtual infrastructure, you must install the KVM hypervisor based on the Debian GNU/Linux 12 operating system using the QEMU 8.0.2 emulator.
When deploying the Central Node component in a virtual infrastructure, you must keep in mind the following limitations:
- It is possible to install the application with the installation files of the Ubuntu operating system only.
- Only the non-high-availability version of the application can be installed.
- You can only use the Sensor component deployed on the same server as the Central Node component.
- You can only connect a Sandbox component deployed outside the KVM virtualization platform on a physical server or on another supported virtualization platform.
- For each Central Node server deployed in a virtual infrastructure, a separate network interface must be used for receiving mirrored SPAN traffic.
- You cannot use the API to inform external systems about alerts generated by the application or the API for informing external systems about application events.
- Support for KVM virtualizations used in cloud solutions is not guaranteed.
- In the virtual machine settings, the host value must be set for the type parameter in the CPU settings and the VMware vmxnet3 value for the model parameter in the network adapter settings.
The hardware requirements for the Central Node server depending on the functionality being used are listed in the table below.
Hardware requirements of the Central Node server when using KEDR functionality
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Maximum number of email messages per minute |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on the server with the Central Node component (Mbps) |
Minimum number of logical cores at 3 GHz |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
50 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
20 |
100 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
20 |
150 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
20 |
250 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
22 |
500 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
24 |
750 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
26 |
Hardware requirements of the Central Node server when using KATA and KEDR functionality
Maximum number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component |
Maximum number of email messages per minute |
Maximum volume of traffic from SPAN ports on the server with the Central Node component (Mbps) |
Minimum number of logical cores at 3 GHz |
Minimum RAM (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
100 |
1 |
20 |
6 |
26 |
250 |
5 |
50 |
6 |
28 |
500 |
30 |
100 |
10 |
31 |
750 |
30 |
100 |
12 |
31 |
Installing and performing initial configuration of the application
This section contains instructions on installation and initial configuration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Preparing for installing application components
This section provides information on how to prepare your corporate IT infrastructure for the installation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform components.
Preparing the IT infrastructure for installing application components
Before installing the application, prepare your corporate IT infrastructure for the installation of components of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Ensure that the servers, the computer intended for working with the application web interface, and the computers to be installed with the Endpoint Agent component all satisfy the hardware and software requirements.
- Perform the following preliminary preparations of the corporate IT infrastructure for installation of the Sandbox component:
- For both network interfaces, block access of the server hosting the Sandbox component to the corporate LAN in order to keep the network safe from the objects being analyzed.
- For the first network interface, allow Internet access for the server hosting the Sandbox component for the purpose of analysis of the behavior of objects.
- For the second network interface, allow inbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Sandbox component:
- TCP 22 for connection to the server over the SSH protocol.
- TCP 443 for receiving objects to scan from the Central Node component.
- TCP 8443 for using the application web interface.
- For the second network interface, allow outbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Sandbox component:
- TCP 80, 443 for communication with Kaspersky update servers.
- Perform the following preliminary preparations of the corporate IT infrastructure for installation of the Central Node component:
- Allow inbound connections to the server hosting the Central Node component on the following ports:
- TCP 22 for connection to the server via SSH.
- TCP 443 for receiving data from computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- TCP 8443 for viewing scan results in the application web interface.
- UDP 53 for communication with the server with the Sensor component.
- TCP 9081 for receiving data from Sensor components installed on standalone servers.
- Allow outbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Central Node component:
- TCP 80, 443 and 1443 for communication with servers of the KSN service and Kaspersky update servers.
- TCP 443 for sending objects to the Sandbox component so that they can be scanned.
- TCP 601 for sending messages to a SIEM system.
- UDP 53 for communication with the server with the Sensor component.
- Allow inbound connections to the server hosting the Central Node component on the following ports:
- Perform the following preliminary preparations of the corporate IT infrastructure for installation of the Sensor component:
- For the network interface used for integration with a proxy server and mail server, allow inbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Sensor component:
- TCP 22 for connection to the server via SSH.
- TCP 1344 for receiving traffic from a proxy server.
- TCP 25 for receiving SMTP traffic from a mail server.
- TCP 443 when forwarding traffic from computers with the Endpoint Agent component to the server with the Central Node component.
- UDP 53 for communication with the server with the Central Node component.
- Allow outbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Sensor component:
- TCP 80 and 443 for communication with servers of the KSN service and Kaspersky update servers.
- TCP 995 (or TCP 110 for unprotected connections) for integration with a mail server.
- TCP 9081 for forwarding traffic to the server with the Central Node component.
- UDP 53 for communication with the server with the Central Node component.
If you install an additional network interface that receives only mirrored traffic in a VMware ESXi virtual environment, use the E1000 network adapter or disable the LRO (large receive offload) option on a VMXNET3 network adapter.
- For the network interface used for integration with a proxy server and mail server, allow inbound connections to the following ports for the server hosting the Sensor component:
- On network equipment, allow an encrypted communication channel between servers that have the Central Node and Sensor components.
The connection between servers that have the Central Node and Sensor components is established within the encrypted communication channel based on IPSec using the ESP, AH, IKEv1, and IKEv2 protocols.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, prepare the corporate IT infrastructure for installation of the Central Node components as follows:
- Allow inbound connection to port 8443 for the server with the PCN role.
- Configure your network equipment to allow the establishment of an encrypted communication channel between the PCN and SCN servers.
The connection between servers that have the PCN and SCN role is established within the encrypted communication channel based on IPSec using the ESP protocol.
If needed, you can designate other ports for the application components to use in the administrator menu of the server with the Central Node component. If you change the ports in the administrator menu, you need to allow connections to these ports in your corporate IT infrastructure.
Preparing the IT infrastructure for integration with a mail server used for receiving messages via POP3
If you are using a Microsoft Exchange mail server as your mail server and an email sender configured a request for read receipt notification, you must disable read receipt notifications. Otherwise, read receipt notifications will be sent from the email address that you have configured as the email address used for receiving messages of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. You must also disable automatic processing of meeting requests to prevent filling of the mailbox used for receiving messages of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
To disable sending read receipt notifications from the email address used for receiving messages of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- On the Microsoft Exchange server, check whether or not notifications are enabled. To do so, execute the command:
Get-MailboxMessageConfiguration -Identity <email address for receiving messages by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform> | fl - If notifications are enabled, run the following command:
Set-MailboxMessageConfiguration -Identity <email address for receiving messages by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform> -ReadReceiptResponse NeverSend
This will disable read receipt notifications from the email address used for receiving messages of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
To disable automatic processing of meeting requests:
- On the Microsoft Exchange server, check whether or not notifications are enabled. To do so, execute the command:
Get-CalendarProcessing -Identity <email address for receiving messages by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform> | fl - If automatic processing of meeting requests is enabled, run the following command:
Set-CalendarProcessing -Identity <email address for receiving messages by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform> -AutomateProcessing:None
Automatic processing of meeting requests will be disabled.
Preparing the IT infrastructure for integration with a mail server used for receiving messages via SMTP
To prepare your corporate IT infrastructure for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform integration with a mail server over the SMTP protocol:
- On the external mail server, configure rules for forwarding copies of the messages that you want to send for scanning by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to the addresses specified in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Specify the route for forwarding email messages to the server with the Sensor component.
It is recommended to specify a static route – IP address of the server with the Sensor component.
- In the firewall of your organization, allow inbound connections to port 25 of the server with the Sensor component from mail servers that are forwarding copies of email messages.
You can also improve the security of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform integration with a mail server over the SMTP protocol.
To improve the security of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform integration with a mail server over the SMTP protocol.
- Configure authentication of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server on the side of the mail servers forwarding email messages for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Configure mandatory encryption of traffic on mail servers that are forwarding email messages for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Configure authentication of mail servers forwarding email messages for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side.
Preparing the virtual machine for installing the Sandbox component
To prepare the virtual machine for installing the Sandbox component:
- Run the VMware ESXi hypervisor.
- Open the virtual machine management console.
- In the context menu of the virtual machine on which you want to install the Sandbox component, choose Edit Settings.
This opens the virtual machine properties window.
- On the Virtual Hardware tab, expand the CPU settings group and select the Expose hardware-assisted virtualization to guest OS check box.
- On the VM Options tab in the Latency Sensitivity drop-down list, select High.
- Click OK.
The virtual machine is ready for installing the Sandbox component.
Preparing an installation disk image with the Central Node, Sensor, and Sandbox components
Before installing the application, you must prepare an iso image of the installation disk with the Central Node, Sensor, and Sandbox components based on the Astra Linux operating system.
Minimum hardware requirements for a device that can be used to create the iso image:
- CPU: 4 cores, clock rate 2500 MHz or more.
- RAM: 8 GB.
- Available disk space: 100 GB.
Software requirements:
- Operating system based on an up-to-date Linux kernel.
- Docker 20 or later
- Availability of the iso image of the Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4 UU1 operating system.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not support other versions of the Astra Linux operating system.
To mount an iso image of the Central Node and Sensor or Sandbox components based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- From the distribution kit, download the Central Node and Sensor component distribution kit (kata-cn-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz), the Sandbox component distribution kit (kata-sb-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz) and the file named iso-builder-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.
- Create an iso_builder.sh file with the following content.
- Run the
mkdir /var/kata_buildercommand. - Put the files listed in step 1 in the newly created /var/kata_builder directory. Make sure that the Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4 UU1 iso image is named "installation-1.7.4.11-23.06.23_17.13.iso". If the name of the iso image is different, you must rename it.
- Run the following command:
- If you are preparing a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components:
sudo ./iso_builder.sh /var/kata_builder/installation-1.7.4.11-23.06.23_17.13.iso /var/kata_builder/kata-cn-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz /var/kata_builder/iso-builder-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar /var/kata_builder buildCNSensorAstra.iso - If you are preparing a disk image with the Sandbox component:
sudo ./iso_builder.sh /var/kata_builder/installation-1.7.4.11-23.06.23_17.13.iso /var/kata_builder/kata-sb-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz /var/kata_builder/iso-builder-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar /var/kata_builder buildSandboxAstra.iso
- If you are preparing a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components:
After running the commands, the installation disk images with the Central Node and Sensor components named buildCNSensorAstra.iso and buildSandboxAstra.iso are located in the /var/kata_builder directory.
If you use other directories for storing files, you can run the command as follows: sudo ./iso_builder.sh <source_iso_host_path> <distribution_host_path> <iso_builder_image_host_path> <build_host_path> <target_iso_name>, where:
- source_iso_host_path is the path to the distribution kit of the Astra Linux Special Edition 1.7.4 UU1 operating system.
- distribution_host_path is the path to the kata-cn-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz or kata-sb-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz distribution kit.
- iso_builder_image_host_path is the path to the iso-builder-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar file.
- build_host_path is the path where the mounted iso image must be located, without specifying the name being assigned to the iso image.
- target_iso_name is the name that is being assigned to the iso image.
Page top
Procedure for installing and configuring application components
Installing and configuring the application involves the following steps:
- Installing the disk image containing the Sandbox component
- Configuring the Sandbox component through the Sandbox web interface
- Installing the disk images of Microsoft Windows operating systems and applications for the Sandbox component
- Installing the Central Node and Sensor components
You can install the Central Node and Sensor components in one of the following configurations:
If there are multiple Central Node components, you can use the application in distributed solution mode.
- Installing the Sensor component
If there are multiple Sensor components, you can install and configure the Sensor component on the necessary number of servers.
- Configuring the Central Node and Sensor components
- Installing the Endpoint Agent component on computers of the corporate IT infrastructure.
As the Endpoint Agent component, you may use following applications: Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
Information about the compatibility of versions of applications that represent the Endpoint Agent component with versions of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is provided in the following Help sections: Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
The Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application can be used in the following configurations:
- Without integration with the EPP application.
In this case, you only need to install Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows.
- With integration with the EPP application.
In this case, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent also sends information about threats detected by the EPP application and results of threat processing by this application to the Central Node server.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows can integrate with the following EPP applications:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Security for Windows Server.
Integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server
- Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent for Windows.
- Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Nodes.
Information about compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications is provided in the Compatibility of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows versions with EPP applications section.
For details about installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the Online Help of the application:
- Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
- Installing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
If your hosts have earlier versions of applications installed, you can upgrade them. For details, see the following sections.
Installing the Sandbox component
This section provides step-by-step instructions on installing the Sandbox component.
To begin the installation of the Sandbox component:
- Run the disk image containing the Sandbox component.
The Setup Wizard starts.
- Click Ok.
Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
To continue installation, please read the End User License Agreement (EULA) and accept its terms and conditions. Installation will not continue until you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
You must also read the Privacy Policy and accept its terms and conditions. If the Privacy Policy is not accepted, the installation cannot proceed.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the Sandbox component based on the CentOS operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window showing the End User License Agreement text.
- Please read the End User License Agreement.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click I accept.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the Sandbox component based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list by pressing F1.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window with the text of the Astra Linux End User License Agreement.
- Read the End User License Agreement of the Astra Linux operating systems.
- If you accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement of Astra Linux operating systems, click Yes.
This opens a window with the text of the AO Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- Read the AO Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click I accept.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 2. Selecting a disk for installing the Sandbox component
Select a physical disk for installing the Sandbox component.
To select a disk for installing the Sandbox component:
- In the Select device window, in the list of disks, select the disk on which you want to install the Sandbox component and press ENTER.
If the disk is not empty, a window is displayed asking you to confirm that you want to format the disk and install the application.
- Click Install.
The archive with the installation files will be unpacked to the disk. The server is restarted.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 3. Assigning the host name
Assign a server host name to be used by DNS servers.
To assign the host name for a server:
- Enter the full domain name of the server into the Hostname field.
Specify the server name in FQDN format (for example: host.domain.com or host.domain.subdomain.com).
- Click Ok.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 4. Selecting the controlling network interface in the list
To ensure proper functioning of the Sandbox component, you must connect at least two network cards and configure the following network Interfaces:
- Management network interface. This interface is intended for providing access to the server with the Sandbox component via the SSH protocol, and the server with the Sandbox component will use this interface to receive objects from the server with the Central Node component.
- Network interface used for Internet access of processed objects. Objects that are processed by the Sandbox component can use this interface to attempt activities on the Internet, and the Sandbox component can analyze their behavior. If you block Internet access, the Sandbox component cannot analyze the behavior of objects on the Internet, and will therefore only analyze the behavior of objects without Internet access.
The network interface used for Internet access of processed objects must be isolated from the local network of your organization.
Select the network interface that you want to use as the controlling interface.
To select the management network interface:
- In the list of network interfaces, select the network interface that you want to use as the controlling interface.
- Press ENTER.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 5. Assigning the address and network mask of the controlling interface
To assign the IP address and network mask of the management network interface:
- In the Address field, enter the IP address that you want to assign to this network interface.
- In the Netmask field, enter the network mask in which you want to use this network interface.
- Click Ok.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 6. Adding DNS server addresses
To add DNS server addresses:
- In the DNS servers window, select New and press ENTER.
This opens the DNS server address entry window.
- In the DNS server text box, enter the IP address of the primary DNS server in IPv4 format.
- Click Ok.
The DNS server address entry window is closed.
- If you want to add the IP address of an additional DNS server, repeat the steps in the DNS servers window.
- When you are done adding DNS servers, in the DNS servers window, select Continue and press ENTER.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 7. Configuring a static network route
To configure a static network route:
- In the IPv4 Routes window, select New and press ENTER.
This opens the IPv4 Static Route window.
- In the Address/Mask field, enter the IP address and mask of the subnet for which you want to configure the network route.
- If you want to use the default network route, enter 0.0.0.0/0.
- In the Gateway field, enter the IP address of the gateway.
- Click Ok.
- If you want to add other network routes, repeat the steps in the IPv4 Static Route window.
- If you are done adding network routes, click Continue.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 8. Configuring the minimum password length for the Sandbox administrator password
To set the minimum length of the administrator password for the Sandbox component:
- In the Minimal length, enter the length in characters. Passwords 12 or more characters long are recommended.
- Click Ok.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Step 9. Creating the Sandbox administrator account
Create an administrator account for working in the Sandbox web interface in the administrator menu and in the management console of the server with the Sandbox component.
To create a Sandbox administrator account:
- In the Username field, enter the name of the administrator account. The 'admin' account is used by default.
- In the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
The password must satisfy the following requirements:
- Must contain at least 8 characters.
- Must contain at least three types of characters:
- Uppercase character (A-Z).
- Lowercase character (a-z).
- Number.
- Special character.
- Must not be the same as the user name.
- Enter the password again in the Confirm password field.
- Click Ok.
This opens a window with the IP address of the Sandbox server. You can enter this address in your web browser to open the Sandbox web interface. To log in, use the Sandbox administrator account that you have created.
The Sandbox server will restart.
Proceed to configuration of the Sandbox component through the web interface.
Deploying the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster
A cluster must include at least 4 servers: 2 storage servers and 2 processing servers. You can use the Sizing Guide determine the right number of servers for your organization.
Deployment of the Central Node and Sensor components in the form of a cluster includes the following steps:
- Deploying the first storage server
The first step is to deploy the storage server. After the storage server is deployed, you can add additional storage and processing servers to the cluster.
- Deploying processing servers and additional storage servers
You can deploy the servers in any order.
- Configuring the sizing settings of the application
At the final stage of cluster deployment, you need to configure the scaling settings of the application: specify the planned volume of SPAN traffic, email traffic, the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component, as well as the size of the Storage and event database.
The Central Node component is always installed together with the Sensor component. If you need to use the Central Node component separately, when deploying the processing server, turn off receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports at step 11.
If you have a cluster deployed on physical servers and want to add more hard drives to these servers or replace some of the existing drives and then reinstall the cluster, you must purge the drives previously allocated for the OSD (Object Storage Daemon) on the storage servers before installing components. Otherwise, the application is not guaranteed to work correctly. If you want to completely disconnect the drives and no longer plan to reconnect them to the server, purging the drives is not necessary.
Deploying a storage server
To deploy a data storage server, you need to run a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components.
If an error occurred while performing the steps of the Setup Wizard, contact Technical Support.
Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
To continue the installation, you must read the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy and accept their terms and conditions. Installation will not continue until you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Ubuntu operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window showing the End User License Agreement text.
- Please read the End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the End User License Agreement, select I accept and press Enter.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list by pressing F1.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window with the text of the Astra Linux End User License Agreement.
- Read the End User License Agreement of the Astra Linux operating systems.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement of Astra Linux operating systems, click Yes.
This opens a window with the text of the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- Read the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click Yes.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click Yes.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting a server role
To select a server role:
- Select one of the following options:
- storage.
This role is for installing a storage server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
- processing.
This role is for installing a processing server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
The role also includes the installation and configuration of the Sensor component.
- single.
This role is for installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the same server.
- sensor.
This role is for installing the Sensor component on a standalone server.
- storage.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting the deployment mode
To select a deployment mode:
- Select one of the following options:
- First node installation.
Select this value when deploying the first server in the cluster.
- Add extra node to the cluster.
Select this value when deploying a server that will be added to an existing cluster.
- First node installation.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 4. Selecting a disk for installing the component
You need at least 150 GB of disk space. If less than 150 GB of disk space is available, installation finishes with an error.
To select a disk for installing the component:
- Select one of the suggested drives for installing the component and press Enter.
The confirmation window is displayed.
- Select Yes and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
We recommend using the default value.
The netmask may not match netmasks used in the organization's infrastructure.
To specify the network mask for server addressing:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.18.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
We recommend using the default value.
The network for application component addressing must not overlap with the network for cluster server addressing.
To specify the network mask for addressing the main components of the application:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.19.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 7. Selecting the cluster network interface
The cluster network interface is used for communication between cluster servers.
To select the cluster network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the internal network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 8. Selecting the external network interface
The external network interface is used for SSH access to the server, managing the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and other external connections.
To select the external network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the external network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 9. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
To select a method for obtaining an IP address for network interfaces:
- Select the row containing the Configuration type: and press Enter.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the opened window, select one of the following options:
- dhcp.
- static.
- If you selected static:
- Select the row containing the parameter and press the Enter key.
- In the opened window, enter the required data and press Enter twice.
You need to specify a value for each parameter.
- Select the row containing Save.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 10. Creating an administrator account and authenticating the server in the cluster
During this step, you need to do one of the following:
- Create an administrator account if you are deploying the first server in the cluster.
- Authenticate a server in the cluster if you are deploying additional storage servers.
Creating the administrator account
An administrator account is only required when deploying the first server in the cluster. If you are deploying an additional storage server, instead of opening a window that prompts you to create an administrator account, the application prompts you to authenticate the server in the cluster.
When deploying the first server in the cluster, you need to create an administrator account. This account is used to work in the web interface for sizing management, the application administrator menu, and to work in Technical Support Mode.
By default, the user name of the administrator account is admin. You must enter a password for that user account.
To enter a password for the administrator user account:
- This opens a window; in that window, in the min length field, enter the minimum password length. You must enter a value of 8 or greater.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
This opens the password creation window.
- This opens a window; in that window, in the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the confirm field, enter the password again.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Authenticating the server in the cluster
Authenticating a server in the cluster is only required when deploying additional storage servers. If you are deploying the first server in the cluster, the application prompts you to create an administrator account instead of authenticating the server.
To authenticate a server in the cluster, you need to enter the admin account password that was set when the first server in the cluster was deployed.
To authenticate a server in the cluster:
- In the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
To select a button, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys.
The server in the cluster will be authenticated. The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 11. Adding DNS server addresses
Configure the DNS settings for the operation of servers with application components.
To add DNS server addresses:
- Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server in IPv4 format.
You must enter at least one DNS server address.
- If you want to add the IP address of an additional DNS server, press Enter and enter the address of the server.
- Having added all DNS servers, press Enter twice.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 12. Selecting disks for the Ceph storage
Select the disks for the Ceph storage. The number of drives is determined according to the scaling guide.
To select disks for the Ceph storage:
- Select the row containing the required drive.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
- Repeat steps 1-2 to select the following drives.
The configuration will take some time. Then the installation is complete. You can proceed to the configuration of cluster servers in the web interface for sizing management.
Page top
Deploying the processing server
To deploy a processing server, you need to run a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components.
If an error occurred while performing the steps of the Setup Wizard, contact Technical Support.
Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
To continue the installation, you must read the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy and accept their terms and conditions. Installation will not continue until you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Ubuntu operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window showing the End User License Agreement text.
- Please read the End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the End User License Agreement, select I accept and press Enter.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list by pressing F1.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window with the text of the Astra Linux End User License Agreement.
- Read the End User License Agreement of the Astra Linux operating systems.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement of Astra Linux operating systems, click Yes.
This opens a window with the text of the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- Read the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click Yes.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click Yes.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting a server role
To select a server role:
- Select one of the following options:
- storage.
This role is for installing a storage server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
- processing.
This role is for installing a processing server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
The role also includes the installation and configuration of the Sensor component.
- single.
This role is for installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the same server.
- sensor.
This role is for installing the Sensor component on a standalone server.
- storage.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting the deployment mode
To select a deployment mode:
- Select one of the following options:
- First node installation.
Select this value when deploying the first server in the cluster.
- Add extra node to the cluster.
Select this value when deploying a server that will be added to an existing cluster.
- First node installation.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 4. Selecting a disk for installing the component
You need at least 150 GB of disk space. If less than 150 GB of disk space is available, installation finishes with an error.
To select a disk for installing the component:
- Select one of the suggested drives for installing the component and press Enter.
The confirmation window is displayed.
- Select Yes and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
We recommend using the default value.
The netmask may not match netmasks used in the organization's infrastructure.
To specify the network mask for server addressing:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.18.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
We recommend using the default value.
The network for application component addressing must not overlap with the network for cluster server addressing.
To specify the network mask for addressing the main components of the application:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.19.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 7. Selecting the cluster network interface
The cluster network interface is used for communication between cluster servers.
To select the cluster network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the internal network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 8. Selecting the external network interface
The external network interface is used for SSH access to the server, managing the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and other external connections.
To select the external network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the external network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 9. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
To select a method for obtaining an IP address for network interfaces:
- Select the row containing the Configuration type: and press Enter.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the opened window, select one of the following options:
- dhcp.
- static.
- If you selected static:
- Select the row containing the parameter and press the Enter key.
- In the opened window, enter the required data and press Enter twice.
You need to specify a value for each parameter.
- Select the row containing Save.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 10. Authenticating the server in the cluster
To authenticate a server in the cluster, you need to enter the admin account password that was set when the first server in the cluster was deployed.
To authenticate a server in the cluster:
- In the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
To select a button, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys.
The server in the cluster will be authenticated. The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 11. Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
In this step, you can configure receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports.
To turn on receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Enter y.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To turn off receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Enter n.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 12. Adding DNS server addresses
Configure the DNS settings for the operation of servers with application components.
To add DNS server addresses:
- Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server in IPv4 format.
You must enter at least one DNS server address.
- If you want to add the IP address of an additional DNS server, press Enter and enter the address of the server.
- Having added all DNS servers, press Enter.
Installation is complete. You can proceed to the configuration of cluster servers in the web interface for sizing management.
Page top
Installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the server
Deployment of the Central Node and Sensor components on a single server includes the following steps:
- Installing the Central Node and Sensor components
To install the components on the physical server, you need to run a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components.
To install components on a virtual server, you need to connect the disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components to the selected virtual machine and run it. The installation starts immediately after the virtual machine is turned on. You can manage the installation process using the console of the virtual machine.
- Configuring the sizing settings of the application
At the final stage of cluster deployment, you need to configure the scaling settings of the application: specify the planned volume of SPAN traffic, email traffic, the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component, as well as the size of the Storage and event database.
The Central Node component is always installed together with the Sensor component. If you need to use the Central Node component separately, turn off receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports in step 10.
If an error occurred while performing the steps of the Setup Wizard, contact Technical Support.
Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
To continue the installation, you must read the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy and accept their terms and conditions. Installation will not continue until you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Ubuntu operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window showing the End User License Agreement text.
- Please read the End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the End User License Agreement, select I accept and press Enter.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list by pressing F1.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window with the text of the Astra Linux End User License Agreement.
- Read the End User License Agreement of the Astra Linux operating systems.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement of Astra Linux operating systems, click Yes.
This opens a window with the text of the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- Read the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click Yes.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click Yes.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting a server role
To select a server role:
- Select one of the following options:
- storage.
This role is for installing a storage server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
- processing.
This role is for installing a processing server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
The role also includes the installation and configuration of the Sensor component.
- single.
This role is for installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the same server.
- sensor.
This role is for installing the Sensor component on a standalone server.
- storage.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting a disk for installing the component
You need at least 150 GB of disk space. If less than 150 GB of disk space is available, installation finishes with an error.
To select a disk for installing the component:
- Select one of the suggested drives for installing the component and press Enter.
The confirmation window is displayed.
- Select Yes and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 4. Allocating the disk for the Targeted Attack Analyzer component's database
For optimal performance of the Targeted Attack Analyzer component, it is advised that you allocate on the server a physical disk of at least 1 TB for the component's database.
In this step, you can allocate a physical disk for the Targeted Attack Analyzer component's database or decline allocating a physical disk.
To allocate the disk for the Targeted Attack Analyzer component's database:
- Select one of the suggested drives for the Targeted Attack Analyzer component database.
If you do not need the Targeted Attack Analyzer component database, select the Don't want TAA line.
The confirmation window is displayed.
- Select Yes and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 5. Selecting a network mask for server addressing
We recommend using the default value.
The netmask may not match netmasks used in the organization's infrastructure.
To specify the network mask for server addressing:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.18.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 6. Selecting a network mask for addressing of application components
We recommend using the default value.
The network for application component addressing must not overlap with the network for server addressing.
To specify the network mask for addressing the application components:
- If you want to use the predefined value for the network mask, press Enter.
Default value: 198.19.0.0/16.
- If you want to specify a different network mask, enter the value and press Enter.
The mask must match the template: x.x.0.0/16.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 7. Selecting the external network interface
The external network interface is used for SSH access to the server, managing the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and other external connections.
To select the external network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the external network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 8. Selecting the method of obtaining IP addresses for network interfaces
To select a method for obtaining an IP address for network interfaces:
- Select the row containing the Configuration type: and press Enter.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the opened window, select one of the following options:
- dhcp.
- static.
- If you selected static:
- Select the row containing the parameter and press the Enter key.
- In the opened window, enter the required data and press Enter twice.
You need to specify a value for each parameter.
- Select the row containing Save.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 9. Creating the administrator account
The administrator account is used to work in the web interface for sizing management, the application administrator menu, and to work in Technical Support Mode.
By default, the user name of the administrator account is admin. You must enter a password for that user account.
To enter a password for the administrator user account:
- This opens a window; in that window, in the min length field, enter the minimum password length. You must enter a value of 8 or greater.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
This opens the password creation window.
- This opens a window; in that window, in the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the confirm field, enter the password again.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 10. Adding DNS server addresses
Configure the DNS settings for the operation of servers with application components.
To add DNS server addresses:
- Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server in IPv4 format.
You must enter at least one DNS server address.
- If you want to add the IP address of an additional DNS server, press Enter and enter the address of the server.
- Having added all DNS servers, press Enter twice.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 11. Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
In this step, you can configure receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports.
To turn on receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Enter y.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To turn off receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Enter n.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 12. Configuring time synchronization with an NTP server
Configure synchronization of the server time with the NTP server.
To configure time synchronization with an NTP server:
- Enter the IP address or name of the NTP server.
- If you want to add an additional NTP server, press Enter and enter the IP address or name of the NTP server.
- Having added all NTP servers, press Enter twice.
The configuration will take some time. Then the installation is complete. You can proceed to server configuration in the web interface for scaling management.
Page top
Installing the Sensor component on a standalone server
To install the Sensor component on a physical server, you need to run a disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components.
To install the Sensor component on a virtual server, you need to connect the disk image with the Central Node and Sensor components to the selected virtual machine and run it. The installation starts immediately after the virtual machine is turned on. You can manage the installation process using the console of the virtual machine.
Step 1. Viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy
To continue the installation, you must read the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy and accept their terms and conditions. Installation will not continue until you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Ubuntu operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window showing the End User License Agreement text.
- Please read the End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the End User License Agreement, select I accept and press Enter.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click I accept.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
To accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy when installing the components based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Select the language for viewing the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in the list by pressing F1.
For example, if you want to view the End User License Agreement and Privacy Policy in English, select English and press Enter.
This opens a window with the text of the Astra Linux End User License Agreement.
- Read the End User License Agreement of the Astra Linux operating systems.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms and conditions of the End User License Agreement of Astra Linux operating systems, click Yes.
This opens a window with the text of the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
- Read the Kaspersky Lab End User License Agreement.
To move up and down, you can use the keys: ↑, ↓, PageUp and PageDown, or Enter.
- If you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, click Yes.
This opens a window displaying the text of the Privacy Policy.
- Please carefully read the Privacy Policy.
- If you accept the terms of the Privacy Policy, click Yes.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 2. Selecting a server role
To select a server role:
- Select one of the following options:
- storage.
This role is for installing a storage server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
- processing.
This role is for installing a processing server for deploying the Central Node component as a cluster.
The role also includes the installation and configuration of the Sensor component.
- single.
This role is for installing the Central Node and Sensor components on the same server.
- sensor.
This role is for installing the Sensor component on a standalone server.
- storage.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 3. Selecting a disk for installing the component
To select a disk for installing the component:
- Select one of the suggested drives for installing the component and press Enter.
The confirmation window is displayed.
- Select Yes and press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 4. Selecting the external network interface
The external network interface is used for SSH access to the server, managing the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and other external connections.
To select the external network interface:
- Select the row containing the network interface that is used for the external network.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 5. Connecting to the server with the Central Node component
To connect to the server on which you installed the Central Node component:
- In the Central Node field, enter the IP address or URL of the server with the Central Node component.
If the Central Node component is deployed as a cluster, you can enter the IP address of any server in the cluster.
- Press Enter.
The Setup Wizard proceeds to the next step.
Page top
Step 6. Creating the administrator account
The administrator account is used to manage the Sensor component in the application administrator menu and in Technical Support Mode.
By default, the user name of the administrator account is admin. You must enter a password for that user account.
To enter a password for the administrator user account:
- This opens a window; in that window, in the min length field, enter the minimum password length. You must enter a value of 8 or greater.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
This opens the password creation window.
- This opens a window; in that window, in the password field, enter the password for the administrator account.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, PageUp, and PageDown keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- In the confirm field, enter the password again.
- Select Ok and press Enter.
The installation will be complete.
Page top
Configuring Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system
To achieve the calculated performance characteristics of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system, you must configure the application.
To configure Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system:
- Enter Technical Support Mode.
- Run the following commands:
sudo -sastra-modeswitch set 0mv /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/misc/parsec.ko ./parsec.ko.backupupdate-initramfs -u -k allcp /lib/systemd/system/docker.service /lib/systemd/system/docker.service.backup - Edit the docker.service file in the /lib/systemd/system/ directory as follows:
- Change the value of the following string:
After=network-online.target docker.socket firewalld.service \docker-parsec-init.serviceto
After=network-online.target docker.socket firewalld.service - Change the value of the
Requires=docker.socket docker-parsec-init.servicestring toRequires=docker.socket
- Change the value of the following string:
- Restart the server and enter Technical Support Mode again.
- Run the following command:
lsmod | grep parsecAn empty string is displayed on the console.
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application based on the Astra Linux operating system is configured.
The security functions of the Parsec module are not required or used by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application.
Page top
Optimization of network interface settings for the Sensor component
Follow these instructions if the application encounters network packet loss or performance issues when processing network traffic.
To reduce network packet loss and incomplete extraction of files from traffic:
- Specify the maximum number of RSS queues:
- If the data transfer rate on your network is less than 1 Gbps, set the number to 1.
- If the data transfer rate on your network is greater than 1 Gbps, set the number to 16.
If your network interface does not allow setting the maximum number of RSS queues to 16, set it to the maximum supported number.
- Configure symmetric RSS hashing for the network interface. For details on configuring RSS hashing, refer to the vendor documentation of your network adapter.
- Create an interrupts.sh file with the following content.
- Run the following command:
sudo bash interrupts.sh <dev> <min_cpu> <max_cpu> <step>, where<dev>is the network interface whose interrupts you want to distribute among cores.<min_cpu>is the first core in the range for network adapter interrupt distribution.<max_cpu>is the last core in the range for network adapter interrupt distribution.<step>is the increment for picking the next core to assign to interrupts.Example:
sudo bash interrupts.sh ens192 2 11 1
- If you are using NVIDIA Mellanox network adapters (mlx4), configure the number of RSS queues and RSS hashing by running the following commands:
ethtool -L $dev rx 16ethtool -X $dev equal 16ethtool -X $dev hfunc xor - If you are using Intel network adapters (i40e), configure the number of RSS queues and RSS hashing:
rmmod i40e && modprobe i40eifconfig $dev downethtool -L $dev combined 16ethtool -K $dev rxhash onethtool -K $dev ntuple onifconfig $dev upethtool -X $dev hkey 6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A:6D:5A equal 16ethtool -A $dev rx offethtool -C $dev adaptive-rx off adaptive-tx off rx-usecs 125ethtool -G $dev rx 1024ethtool -N $dev rx-flow-hash tcp4 sdfnethtool -N $dev rx-flow-hash tcp6 sdfnethtool -N $dev rx-flow-hash udp4 sdfnethtool -N $dev rx-flow-hash udp6 sdfn
The network interfaces are configured.
After restarting the application, you must reconfigure the network interfaces following the instructions.
Page top
Connecting and configuring external storage for the Sensor component
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform saves traffic received from network interfaces as network traffic dump files. If you want to ensure long-term storage of network traffic dump files, you can connect and configure external storage. You can use network traffic dump files in external storage to download network traffic as PCAP files.
To connect and configure external storage for network traffic dump files on a server with the Sensor and Central Node components installed:
- Connect a disk of at least 100 GB that you want to use as external storage.
- Enter Technical Support Mode.
- Run the following commands:
sudo -ifdisk -lMake sure that the disk that you connected for external storage is displayed in the console.
- Run the following commands:
mke2fs -t ext4 -L DATA -m 0 /dev/<name of the connected disk>sudo nano etc/fstabThis opens the fstab file in a text editor.
- Add the following line at the end of the file:
/dev/<name of the connected disk> /data/volumes/dumps/ ext4 defaults 0 0 - Close the text editor.
- Run the following commands:
mountrm -r /data/volumes/dumps/*These commands delete all data from the connected disk.
The connected disk will be configured for use as external storage.
- Run the following commands:
chown kluser:klusers /data/volumes/dumps/ls -lah /data/volumes/dumps/lsblkMake sure that in the
- Run the following commands:
docker stop $(docker ps | grep preprocessor_span | awk '{print $1}')docker ps | grep preprocessor_spanWait until the
- Run the following commands:
docker exec -it $(docker ps | grep preprocessor_span | awk '{print $1}') bashlsblkMake sure that in the
External storage for network traffic dump files on the server with Sensor and Central Node installed is connected and configured.
To connect and configure external storage for network traffic dump files on a standalone server with the Sensor component installed:
- Connect a disk of at least 100 GB that you want to use as external storage.
- Enter Technical Support Mode.
- Run the following commands:
sudo -ifdisk -lMake sure that the disk that you connected for external storage is displayed in the console.
- Run the following commands:
mke2fs -t ext4 -L DATA -m 0 /dev/<name of the connected disk>sudo nano etc/fstabThis opens the fstab file in a text editor.
- Add the following line at the end of the file:
/dev/<name of the connected disk> /data/volumes/dumps/ ext4 defaults 0 0 - Close the text editor.
- Run the following command:
rm -r /data/volumes/dumps/*These commands delete all data from the connected disk.
External storage for network traffic dump files on the standalone server with the Sensor component installed is connected and configured.
Page top
Purging hard drives on storage servers
If you have a cluster deployed on servers and want to add more hard drives to these servers or replace some of the existing drives and then reinstall the cluster, you must purge the drives previously allocated for the OSD (Object Storage Daemon) on the storage servers before installing components. Otherwise, the application is not guaranteed to work correctly.
To purge the disks allocated for OSD on a live storage server:
- Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to purge the disks over SSH or through the terminal.
- Stop the OSD starter service by running
sudosystemctl stop kata-osd-starter.service. - Stop OSD containers by running
sudodocker ps --filter name=osd -q | xargs docker stop. - Get a list of OSD disks by running
sudoceph-volume --cluster ceph lvm list | grep devices. - Purge these disks by running
sudoceph-volume lvm zap --destroy /dev/<disk name>.You must run this command for each drive that you got at step 4. For example:
sudoceph-volume lvm zap --destroy /dev/sda.
The OSD daemon is removed from the disks.
If the server is not live, you must delete the information about volume groups from each disk allocated for the OSD.
To delete the information about volume groups from each disk allocated for the OSD on a non-live server:
- Start the server with the alternative operating system.
- Get group IDs for each disk allocated for the OSD using the
sudopvscommand.This command outputs a table where
PVare physical volumes,VGindicates logical group membership,Fmtindicates the volume format, andSizeindicates the physical volume size. - Remove the relevant volume groups by running
sudovgremove <volume group ID>.
Information about volume groups on disks allocated for OSD is deleted.
Page top
Configuring the sizing settings of the application
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
You can change the operational load on the Central Node component. For example, you can connect additional hosts with the Endpoint Agent component or servers with the Sensor component to the Central Node component. To do this, you need to specify the planned volume of SPAN traffic, mail traffic, the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component, as well as the size of the Storage and event database. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will determine the optimal configuration of the Central Node servers taking into account the specified settings.
If the Central Node component is deployed as a cluster, the application determines the optimal configuration of all servers in the cluster.
To configure the Central Node servers:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the Central Node server has been allowed, enter the IP address of the server with the Central Node component into the browser's address bar.
If you are using the high availability version of the application, you can enter the IP address of any server of the Central Node cluster or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the cluster.
An input window for account credentials of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user opens.
- Enter the administrator user name "admin" and the password that was set during installation of the application.
- Select the Local administrator check box.
- Click Log in.
- If you are using the high availability version of the application, go to the Server configuration section.
For the non-high-availability version of the application, only this section is displayed.
- In the Number of Endpoint Agents field, specify the number of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that you plan on using.
If you are not using a KEDR license key, specify 0.
- In the Mail traffic, messages per second field, specify the planned number of emails per second.
If you are not using a KATA license key, specify 0.
- In the SPAN traffic, Mbps field, specify the planned amount of traffic from SPAN ports on servers with the Sensor component.
If you are not using a KATA license key, specify 0.
- In the Available disk space section, specify the size of the event database and Storage in one of the following ways:
- Move the slider separating the Events database and Storage to the left or right.
- Specify the values in the Events database, GB and Storage, GB fields.
If you are using the Central Node component that is not deployed as a high availability cluster, you must keep default settings for the events database and Storage. The application does not check if the entered values are valid.
Disk space is automatically reserved for the alert database when the Central Node component is installed.
- If necessary, you can leave free space on disk by moving the last slider on the right.
- Click Configure.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will determine the optimal server configuration in accordance with the specified settings and configure the cluster servers. If the configuration is completed successfully, the web interface login window will appear.
Page top
Configuring the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
This section contains information on how to configure the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows, if it is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
You must follow the steps both on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side using the web interface and application administrator menu and on the side of the application that is being used as the Endpoint Agent component using the Administration Console (MMC).
If in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac for more information about integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, and Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac sections.
Configuring the trusted connection of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application
Actions to configure a trusted connection are performed both on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side through the web interface and the application administrator menu, and on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side through the KSC Administration Console.
You can use one of the following options to configure a trusted connection:
- Without validating the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side.
- Configuring the connection with the Central Node server without validating the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Central Node server. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not validate the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
- Configuring the connection with the Sensor server without validating the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Traffic redirection to the Sensor server is configured in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Sensor server. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not validate the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
- Configuring the connection with the Central Node server without validating the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Validating the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side.
- Configuring the connection with the Central Node server with validation of the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Central Node server. Additional security of the connection is configured in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is uploaded. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform validates the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
- Configuring the connection with the Sensor server with validation of the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Traffic redirection to the Sensor server is configured in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Sensor server. Additional security of the connection is configured in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is uploaded. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform validates the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
- Configuring the connection with the Central Node server with validation of the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Configuring the connection with the Central Node server without validating the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Central Node server. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not validate the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
If you are using this alternative configuration for the trusted connection, the procedure is as follows:
- Generate or upload an independently prepared TLS certificate of the Central Node server in the web interface of Central Node (if the TLS certificate of the Central Node has not been previously created).
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
- Uploading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Administration Console (MMC).
Configuring the connection with the Central Node server with validation of the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Central Node server. Additional security of the connection is configured in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is uploaded. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform validates the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
If you are using this alternative configuration for the trusted connection, the procedure is as follows:
- Generate or upload an independently prepared TLS certificate of the Central Node server in the web interface of Central Node (if the TLS certificate of the Central Node has not been previously created).
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
- Uploading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Administration Console (MMC)
- Enabling the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Generating and downloading the cryptographic container with the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent or uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
If you want to prepare the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent on your own, you must create a PFX cryptographic container with your certificate. For details on managing TLS certificates, see the OpenSSL documentation.
- Uploading the cryptographic container with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Administration Console (MMC).
Configuring the connection with the Sensor server without validating the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Traffic redirection to the Sensor server is configured in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Sensor server. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not validate the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
If you are using this alternative configuration for the trusted connection, the procedure is as follows:
- Enabling traffic redirection from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to the Sensor server
- Authorizing the Sensor component on a Central Node server
- Generating or uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to your computer
- Uploading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Administration Console (MMC)
Configuring the connection with the Sensor server with validation of the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Traffic redirection to the Sensor server is configured in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. Kaspersky Endpoint Agent establishes a trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the TLS certificate of the Sensor server. Additional security of the connection is configured in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is uploaded. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform validates the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent tries to connect.
If you are using this alternative configuration for the trusted connection, the procedure is as follows:
- Enabling traffic redirection from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to the Sensor server
- Authorizing the Sensor component on a Central Node server
- Generating or uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
- Downloading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to your computer
- Uploading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Administration Console (MMC).
- Enabling the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
- Generating and downloading the cryptographic container with the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent or uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
If you want to prepare the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent on your own, you must create a PFX cryptographic container with your certificate. For details on managing TLS certificates, see the OpenSSL documentation.
- Uploading the cryptographic container with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the KSC Administration Console.
Downloading the TLS certificate of the Central Node server
To download the TLS certificate of the server:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Download.
The server certificate file will be saved in the downloads folder of the browser.
Generating a TLS certificate for the Central Node server in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
If you are already using a Central Node server TLS certificate, generating a new certificate causes the currently used certificate to be removed and replaced with the newly generated certificate.
You must enter the data of the new certificate everywhere the old certificate was used.
If you replace the TLS certificate, you will need to:
- Reauthorize mail sensors (KSMG, KLMS) on Central Node.
- Reconfigure the connection of Central Node, PCN, and SCN to Sandbox.
- Reconfigure traffic forwarding from Endpoint Agent to Sensor and trusted connection with Endpoint Agent.
- Upload a new certificate to Active Directory (if you are using Active Directory).
Make sure to delete all Endpoint Agent host isolation rules. Connection with isolated hosts will be lost and you will not be able to manage them.
To generate a TLS certificate for a Central Node server:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Generate.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform generates a new TLS certificate. The page is automatically refreshed.
Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Central Node server using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
You can choose to prepare the TLS certificate on your own and upload it using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
The TLS certificate file prepared for upload must satisfy the following requirements:
- The file must contain the certificate itself and a private encryption key for the connection.
- The file must be in PEM format.
The application does not support other formats of certificates.
If you have prepared a certificate in a different format, you must convert it to the PEM format.
- The private key length must be 2,048 bits or longer.
For more details on preparing TLS certificates for import, please refer to the documentation on Open SSL.
If you are already using a Central Node server TLS certificate, uploading a new certificate causes the currently used certificate to be removed and replaced with the uploaded certificate.
You must enter the data of the new certificate everywhere the old certificate was used.
If you replace the TLS certificate, you will need to:
- Reauthorize mail sensors (KSMG, KLMS) on Central Node.
- Reconfigure the connection of Central Node, PCN, and SCN to Sandbox.
- Reconfigure traffic forwarding from Endpoint Agent to Sensor and trusted connection with Endpoint Agent.
Delete all Endpoint Agent host isolation rules. The connection with isolated hosts is severed and you cannot manage them.
To upload an independently prepared TLS certificate using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Upload.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a TLS certificate file to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The TLS certificate is added to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Make sure to delete all Endpoint Agent host isolation rules. Connection with isolated hosts will be lost and you will not be able to manage them.
Uploading a TLS certificate of the Central Node server or Sensor to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
To upload a TLS certificate of the Central Node server or Sensor to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Open the KSC Console.
- In the console tree, open the Policies folder.
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy section, select the required policy and double-click it to open its properties.
The properties of the selected policy are displayed.
- In the KATA integration section, select the KATA integration settings subsection.
- Select the Enable KATA integration check box.
- In the Address field, enter the address of the Central Node server of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform program that you want to configure integration with, and select a port to use for the connection. Port 443 is used by default.
- Select the Use pinned certificate to secure connection check box.
- Click Add a TLS certificate....
This opens the Adding TLS certificate window.
- To add a TLS certificate previously created on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side and downloaded, do one of the following:
- Add a certificate file. To do so, click Browse...; in the window that is displayed, select a certificate file and click Open.
- Paste the content of the certificate file to the Paste TLS certificate data: field.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent can store only one TLS certificate for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. If you have added a TLS certificate before and are adding a TLS certificate again, only the last added certificate is used.
If you have configured traffic redirection to the server with the Sensor component, you must download the TLS certificate of the Sensor server and then upload it here.
- Click Add.
Information about the added TLS certificate is displayed in the section for integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Make sure the toggle switch in the upper right corner of the group of settings is in the Under policy position.
- Click OK.
The TLS certificate of the Central Node server is downloaded to Endpoint Agent.
Enabling the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
To enable trusted connection with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Endpoint Agent certificates section, turn on the Validate Endpoint Agent TLS certificates switch.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will check TLS certificate data when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent attempts to connect to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Generating a TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and downloading a cryptographic container
To generate a TLS certificate for the connection of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Endpoint Agent certificates section, click Generate.
The new TLS certificate is displayed in the TLS certificate table. The cryptographic container fine with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate in the PFX format is downloaded to the browser downloads folder on your local computer.
You can use the cryptographic container to configure the validation of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate by the Central Node server when attempting to connect to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
By default, the cryptographic container is not password-protected. You can protect the cryptographic container with a password. For details on managing TLS certificates, see the OpenSSL documentation.
The cryptographic container contains only the certificate file, but not the private key file. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not store private keys for the TLS encryption of the connection.
Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
You can choose to prepare the TLS certificate on your own and upload it using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
The TLS certificate file prepared for upload must satisfy the following requirements:
- The file must contain the certificate itself and a private encryption key for the connection.
- The file must be in PEM format.
- The private key length must be 2048 bits or longer.
For more details on preparing TLS certificates for import, please refer to the documentation on Open SSL.
If you want to prepare the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent on your own, you must create a PFX cryptographic container with your certificate and upload the cryptographic container to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent.
You can use the cryptographic container to configure the validation of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate by the Central Node server when attempting to connect to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
For details on managing TLS certificates, see the OpenSSL documentation.
The cryptographic container must contain only the certificate file, but not the private key file. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not store private keys for the TLS encryption of the connection.
To upload a manually prepared TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Endpoint Agent certificates section, click Upload.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a TLS certificate file to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The TLS certificate is added to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Viewing the table of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
To view the list of TLS certificates for connection with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- The Endpoint Agent certificates section displays a list of TLS certificate with the following details for each certificate:
- TLS certificate – Fingerprint of the certificate.
- Serial number —Serial number of the certificate.
- Expires —Expiration date of the certificate.
Filtering and searching Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can filter TLS certificate displayed in the table by one or both columns (TLS certificate and Serial number) or enter search criteria to search TLS certificates by these columns.
To filter and search TLS certificates in the table:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- The Endpoint Agent certificates section displays a list of TLS certificate with the following details for each certificate:
- TLS certificate – Fingerprint of the certificate.
- Serial number —Serial number of the certificate.
- Expires —Expiration date of the certificate.
- If you want to filter or search TLS certificates by certificate fingerprint:
- Click the TLS certificate link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the TLS certificate text box, enter a few characters of the certificate fingerprint.
- Click Apply.
- If you want to filter or search TLS certificates by serial number:
- Click the Serial number link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the Serial number text box, enter a few characters of the serial number.
- Click Apply.
The table displays only those TLS certificates that match the filter criteria you have set.
To clear the filter for one or more filtering criteria:
Click ![]() to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
Deleting Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificates in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
To delete one or more TLS certificates for connection with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface window, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agent certificates subsection.
The Endpoint Agent certificates section displays a list of TLS certificates.
- Select check boxes next to one or more TLS certificates that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected TLS certificates are deleted.
Configuring the validation of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate by the Central Node server and uploading a cryptographic container to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
To configure the validation of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent TLS certificate by the Central Node server and upload the cryptographic container with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent:
- Open the KSC Console.
- In the console tree, open the Policies folder.
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy section, select the required policy and double-click it to open its properties.
The properties of the selected policy are displayed.
- In the KATA integration section, select the KATA Central Node subsection.
- Click Configure additional security.
- In the window that opens, select the Secure the connection with client certificate check box.
- Click Upload.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the cryptographic container file of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate that was generated on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server and downloaded to the hard drive of your computer.
- Click OK.
The window closes.
- Make sure the toggle switch in the upper right corner of the group of settings is in the Under policy position.
- Click OK.
The cryptographic container with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate is uploaded to Kaspersky Endpoint Agent. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform now validates the TLS certificate of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent when it tries to connect.
Configuring traffic redirection from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to the Sensor server
You can use the server with the Sensor component as a proxy server for communication between the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application and the Central Node component to reduce the load on the Central Node component.
When configuring the traffic redirection, keep in mind the following limitations:
- The maximum incoming traffic volume for the Sensor component should not exceed 1 Gbit/s.
- The recommended channel capacity between servers hosting the Central Node and Sensor components should be 15% of the SPAN port traffic.
- The maximum allowed packet loss between servers hosting the Sensor and Central Node components should be 10% with a packet delay up to 100 ms.
You can only use the Sensor component as a proxy server if the Sensor and Central Node components are located on different servers.
If you are using the Sensor component as a proxy server, make sure to enter the IP address of the Sensor component instead of the IP address of Central Node when configuring the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side.
Enabling traffic redirection from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to the Sensor server
To enable or disable the use of the Sensor component as a proxy server for communication between Kaspersky Endpoint Agent and the Central Node component, do the following in the administrator menu of the server with the Sensor component:
- In the main window of the administrator menu, select Program settings.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the next window of the administrator menu.
- Select Configure Central Node.
- Press ENTER.
This opens a window with information about the current state of connection of the Sensor component to the Central Node component.
- Click Change.
- In the Input Central Node IP address window, enter the IP address of the server hosting the Central Node component.
- Click Ok.
This opens a window containing information on the Central Node component certificate.
- Make sure that the displayed certificate matches the Central Node component certificate.
- Click Ok.
This opens a window with information about the current state of connection of the Sensor component to the Central Node component.
- Click Cancel.
Using the Sensor component as a proxy server will be enabled after authorization confirmation on the server hosting the Central Node component.
Authorizing the Sensor component on a Central Node server
To authorize the Sensor component on the Central Node server, do the following in the web interface under the local administrator account:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table displays the already connected Sensor components, and connection requests.
- Select the IP address of the server hosting the Sensor component, the request for authorization of which you want to confirm or reject.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to authorize the selected server hosting the Sensor component, click Accept.
- If you want to reject the authorization of the selected server hosting the Sensor component, click Reject.
The authorization request will be accepted or rejected.
Generating a TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
To create a TLS certificate for the server with the Sensor component, do the following in the administrator menu of the Sensor server:
- In the main window of the administrator menu, select Program settings.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the next window of the administrator menu.
- Select Manage server certificate.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Certificate management window.
- In the lower part of the window, select New.
- Press ENTER.
This opens a window containing information about the new certificate.
- Click Continue.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Generate.
Creation of the certificate starts.
- After creation of the certificate is completed, press ENTER.
This opens a window containing information about the installed certificate.
- Click Continue.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Ok.
The certificate will be created. The data of previously installed certificates will be overwritten.
Uploading an independently prepared TLS certificate for the Sensor server in the administrator menu of the Sensor server
You can independently prepare a TLS certificate and upload it to the server with the Sensor component via the SCP protocol. For more details on the methods for uploading files via the SCP protocol, see the documentation for the operating system installed on the computer from which you want to upload the TLS certificate.
The TLS certificate file prepared for upload to the server must satisfy the following requirements:
- The file must contain the certificate itself and a private encryption key for the connection.
- The file must be in PEM format.
- The file name must be kata.pem.
- The private key length must be 2048 bits or longer.
For more details on preparing TLS certificates for import, please refer to the documentation on Open SSL.
To upload an independently prepared TLS certificate to the server with the Sensor component via the SCP protocol, perform the following actions in your computer's interface used for working over the SCP protocol (using the Linux operating system as an example):
- Run the following command:
scp kata.pem admin@<IP address of the server with the Sensor component>: - At the password prompt, enter the administrator password for working in the administrator menu of the server with the Sensor component that was set during installation.
The TLS certificate is uploaded to the server with the Sensor component.
To apply the uploaded TLS certificate on the server with the Sensor component, do the following in the administrator menu of the Sensor server:
- In the main window of the administrator menu, select Program settings.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the next window of the administrator menu.
- Select Manage server certificate.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Certificate management window.
- In the lower part of the window, select Install from file.
- Press ENTER.
The certificate will be applied. The data of previously installed certificates will be overwritten.
Downloading the TLS certificate of the Sensor server to your computer
You can download a TLS certificate from the Sensor server to any computer that can connect to the Sensor server over the SCP protocol. For more details on the methods for uploading files via the SCP protocol, see the documentation for the operating system installed on the computer to which you want to download the TLS certificate.
To download the TSL certificate from the server with the Sensor component over the SCP protocol, do the following in your computer's interface used for working over the SCP protocol (using the Linux operating system as an example):
- Run the following command:
scp admin@<IP address of the server with the Sensor component>:ssl/kata.crt. - At the password prompt, enter the administrator password for working in the administrator menu of the server with the Sensor component that was set during installation.
The TLS certificate is downloaded from the server with the Sensor component to the current directory.
Configuring the integration and trusted connection with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side
To configure integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side:
- Open the KSC Console.
- In the console tree, open the Policies folder.
- In the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent policy section, select the required policy and double-click it to open its properties.
The properties of the selected policy are displayed.
- In the KATA integration section, select the KATA integration settings subsection.
- Select the Enable KATA integration check box.
- In the Address field, enter the address of the Central Node server of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform program that you want to configure integration with, and select a port to use for the connection. Port 443 is used by default.
- Select the Use pinned certificate to secure connection check box.
- Click Add a TLS certificate....
This opens the Adding TLS certificate window.
- To add a TLS certificate previously created on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform side and downloaded, do one of the following:
- Add a certificate file. To do so, click Browse...; in the window that is displayed, select a certificate file and click Open.
- Paste the content of the certificate file to the Paste TLS certificate data: field.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent can store only one TLS certificate for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. If you have added a TLS certificate before and are adding a TLS certificate again, only the last added certificate is used.
If you have configured traffic redirection to the server with the Sensor component, you must download the TLS certificate of the Sensor server and then upload it here.
- Click Add.
Information about the added TLS certificate is displayed in the section for integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Click Add client certificate....
- In the window that is displayed, select the Secure with client certificate check box.
- Click Download.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the cryptographic container file of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent certificate that was generated on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server and downloaded to the hard drive of your computer.
- Click OK.
The window closes.
- In the Timeout period (sec.): field, enter the maximum response timeout of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Central Node server in seconds.
- In the Send sync request to KATA server every (min.) field, enter the period in minutes.
- If you do not want Kaspersky Endpoint Agent to send information about repeated running of processes to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server, select the Apply TTL period for events transmission check box. If the process is started after the next TTL period expires, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent does not consider this a repeated start of the process.
- If you have set the "Apply TTL period for events transmission" check box, specify the time in the TTL period (min.) field.
- Make sure the toggle switch in the upper right corner of the group of settings is in the Under policy position.
- Click OK.
The integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent side is configured.
Getting started with the application
This section contains information about how to begin managing the application in the web interface, in the administrator menu, and in Technical Support Mode.
Getting started with the application web interface with a local administrator account
The web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is protected against CSRF attacks and operates only if the browser used for managing the application web interface provides the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. Make sure that the browser that you are using to work with the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface does not modify the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. If the connection with the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is established through a proxy server of your organization, make sure that the proxy server does not modify the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request.
After installing Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you must configure the sizing settings of the application in the web interface for sizing management.
If the sizing settings of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform are not configured, it is not possible to log in to the web interface with a local administrator account.
To get started with the application web interface with a local administrator account:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the Central Node server has been allowed, enter the IP address of the server with the Central Node component into the browser's address bar.
If you are using the high availability version of the application, you can enter the IP address of any server of the Central Node cluster or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the cluster.
An input window for account credentials of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user opens.
- Enter 'Administrator' as the account name and 'Administrator' as the password.
The 'Administrator' password is used by default. We strongly recommend changing the password for this account after logging in to the application web interface.
- Select the Local administrator check box.
- Click Log in.
The Dashboard page of the application web interface is displayed.
You can start using the application with a local administrator account.
For each user account, the number of simultaneous application management sessions is limited to one IP address. If the same user name is used to sign in to the application from a different IP address, the earlier session is terminated.
Getting started with the web interface for sizing management
In the web interface for sizing management, you can do the following:
- Manage the servers of the Central Node cluster.
- Configure servers hosting the Central Node component.
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface for sizing management is protected against CSRF attacks and operates only if the browser used for managing the application web interface provides the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. Make sure that the browser that you are using to work with the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface does not modify the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. If the connection with the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is established through a proxy server of your organization, make sure that the proxy server does not modify the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request.
The web interface for sizing management is located on the server hosting the Central Node.
To get started in the web interface for sizing management:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the Central Node server has been allowed, enter the IP address of the server with the Central Node component into the browser's address bar.
If you are using the high availability version of the application, you can enter the IP address of any server of the Central Node cluster or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the cluster.
An input window for account credentials of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user opens.
- Enter the administrator user name "admin" and the password that was set during installation of the application.
- Select the Local administrator check box.
- Click Log in.
You can now start working in the web interface for sizing management.
For the high availability version of the application, the web interface displays the Cluster and Server configuration sections.
If you are using the non-high-availability version of the application only the Server configuration section is displayed in the web interface.
For each user account, the number of simultaneous application management sessions is limited to one IP address. If the same user name is used to sign in to the application from a different IP address, the earlier session is terminated.
Page top
Getting started with the application administrator menu
You can manage the settings of each of the application's Sensor, Central Node, and Sandbox components in the administrator menu in the management console of each server on which the application component is installed.
Make sure that access to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator menu and server management console is possible only from computers to which you have granted such access.
Make sure the computers to which you grant access are inside the secure perimeter of your network.
You can configure access to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator menu and server management console from certain computers using the iptables command-line utility. For detailed information about managing iptables, see the iptables documentation.
To start working in the Sandbox, Sensor or Central Node component administrator menu in the server management hosting the needed component:
- Sign in to the management console of the server whose settings you want to change via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
The application component administrator menu is displayed.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
The application component administrator menu is displayed.
You can begin working in the Sensor or Sandbox component administrator menu.
Getting started with the application in Technical Support Mode
Any actions in Technical Support Mode that are not approved and/or not recommended by Technical Support staff are prohibited and are grounds for withdrawing technical support.
You can manage the Sensor, Central Node and Sandbox components of the application in Technical Support Mode.
Technical Support Mode provides the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator with unrestricted access rights (root) to the application and all of its stored data (including personal information).
Working with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from the management console in Technical Support Mode with superuser account rights enables you to:
- Manage application operation settings using configuration files.
You can also modify the settings for data encryption when data is transferred between application nodes, and the settings for storing and processing objects being scanned.
In this case, data is transmitted in unencrypted form. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator must use this data independently to ensure protection of servers. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator is responsible for modifying the configuration files of the application.
- Manage settings.
Trace files may contain confidential data of the user. Such files are retained indefinitely and can be manually deleted by the administrator of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. The path for trace files is specified by the administrator of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
To start working with the Sandbox, Sensor or Central Node component in Technical Support Mode:
- Sign in to the management console of the server whose settings you want to change via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was specified during installation of the component.
The application component administrator menu is displayed.
- In the application administrator menu, select Technical Support Mode.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Technical Support Mode confirmation window.
- Confirm that you want to manage the application in Technical Support Mode. To do so, select Yes and press ENTER.
You can proceed to manage the Central Node, Sensor, or Sandbox component in Technical Support Mode.
Managing accounts of application administrators and users
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides accounts for servers with the following components:
- Sensor. Administrator account for working in the application administrator menu and in the server management console (in Technical Support Mode).
The 'admin' account is used by default.
- Sandbox. Administrator account for working in the application administrator menu, in the server management console (in Technical Support Mode) and in the Sandbox web interface.
The 'admin' account is used by default.
- Central Node. The following accounts:
- Administrator account for working in the application administrator menu and in the server management console (in Technical Support Mode).
The "admin" account that was created during application installation is used by default.
- Local administrator account of the application web interface.
The "Administrator" account that was created during application installation is used by default. You can create other administrator accounts for the application web interface after installation.
- Administrator account of the application web interface.
- Application web interface user accounts with the Security auditor, Security officer, and Senior security officer roles.
- Administrator account for working in the application administrator menu and in the server management console (in Technical Support Mode).
Data from each of these accounts is stored on the server hosting the application component to which the account belongs.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, data from each of these accounts is stored on the PCN and on the server hosting the application component to which the account belongs.
The administrator account used for working in the server management console has unlimited rights to manage the server hosting the application component to which the account belongs (superuser rights). Under this account, you can turn off or restart a server, or modify the settings of the application in Technical Support Mode in the server management console.
An administrator account for working in the management console of a server (admin) has unlimited access to data on that server. The password of the administrator account for working in the server management console must be strong. The administrator must take steps to ensure the security of the servers. The administrator bears responsibility for access to data stored on servers.
An account with the Administrator role can add, enable and disable application user accounts, and change the passwords of application administrator accounts and web interface user accounts. In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, user accounts are managed on the PCN.
The local administrator account of the application web interface is intended for employees of your organization who need to manage Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When signing in to the application under this account, you will see all sections of the web interface that are available to a user with the Administrator role.
The administrator account of the application web interface lets you manage the application, however, unlike the local administrator account of the application web interface, such accounts are not allowed to manage PCN and SCN servers or tenants in the Operation mode section.
An account with the Security auditor role can view all sections of the web interface available to the local administrator and security personnel. A user with the Security auditor role can view data but cannot edit this data.
The Senior security officer and Security officer roles are intended for employees of your organization whose job description involves managing events and tasks of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When signing in to the application under accounts with these roles, you will see all sections of the web interface that are available to security officers. Users with the Senior security officer role have access to all operations. The restrictions for users with the Security officer role are listed in the table below.
Access restrictions for application users with the Security officer role
Functional scope / Section of the web interface |
Restrictions |
|---|---|
Dashboard |
Widgets of VIP group events are not available. It is not possible to use a link in the widget to go to the Alerts section. |
Alerts |
The following actions are not available:
|
Threat Hunting |
Events that are associated with hosts from VIP group alerts are not available. |
Tasks |
No access. |
Prevention |
No access. |
Custom rules |
Read access. |
Storage |
There is no access to objects that are placed in Storage as a result of tasks. Full access to objects that were manually downloaded by the user. |
Endpoint Agents |
Access to viewing tables of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent computers; restrictions on viewing details of tasks, policies, and network isolation. |
Network isolation of hosts |
No access. |
Reports |
No access. |
Settings: IOC scanning schedule |
Read access. |
Settings: Endpoint Agents |
Read access. |
Settings: KPSN reputation database |
No access. |
Settings: Notification rules |
No access to rules for sending notifications about alerts. Full access to rules for sending notifications about problems in application operation. |
Settings: VIP status |
Read access. |
Custom rules: YARA |
Access only to export rules. |
Settings: TAA exclusions |
Access to read and export. |
Settings: Passwords for archives |
No access. |
Settings: License |
Read access. |
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, access to tenants and the web interface of the SCN server can be allowed or denied for each account.
Creating an administrator account for the application web interface
The administrator account of the application web interface lets you manage the application, however, unlike the local administrator account of the application web interface, such accounts are not allowed to manage PCN and SCN servers or tenants in the Operation mode section.
To create an application web interface administrator account:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- Click Add.
This opens the New user window.
- To enable an account, turn on the Status toggle switch.
By default, the account is enabled.
If the user account is enabled, the user is allowed to gain access to the application web interface. If the user account is disabled, the user is prohibited from gaining access to the application web interface.
- In the Role drop-down list, select Administrator.
- Under Authentication type, select one of the following options:
- KATA user account.
In this case, to connect to the application web interface, the user must enter the user name and password that were configured when the account was created.
- Domain user account.
In this case, to connect to the application web interface, the user does not have to enter the user name and password; the user is authenticated with the domain account.
The KATA user account and Domain user account fields are available if Active Directory integration is configured.
- KATA user account.
- If you selected KATA user account:
- In the User name field, enter a user name for the account you want to create.
The user name must meet the following requirements:
- Must be unique in the list of user names (case-sensitive).
- Must contain no more than 32 characters.
- Can contain letters A–Z, a–z, digits 0–9, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
- Must begin with a letter (A–Z or a–z).
- In the New password field, enter a user password that will be used to access the web interface.
The password must satisfy the following requirements:
- Must not be the same as the user name.
- Must not contain dictionary words, popular combinations of letters, or examples of a keyboard layout (for example, Qwerty or passw0rd).
- Must contain at least 8 characters.
- Must contain at least three types of characters:
- Uppercase character (A–Z).
- Lowercase character (a–z).
- Number.
- Special character.
- In the Confirm password field, re-enter the user password that will be used to access the web interface.
- In the User name field, enter a user name for the account you want to create.
- If you selected Domain user account, in the User name field, enter the user's domain name.
- Click Add.
This will create an administrator account for the application web interface.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the administrator account of the PCN server web interface has access to the data of all organizations associated with that server.
Creating a user account for the application web interface
You can create user accounts with the Senior security officer, Security officer, and Security auditor roles.
To create a user account for the application web interface:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- Click Add.
This opens the New user window.
- If necessary, disable the user account using the Status toggle switch.
By default, the account is enabled.
If the user account is enabled, the user is allowed to gain access to the application web interface. If the user account is disabled, the user is prohibited from gaining access to the application web interface.
- Under Authentication type, select one of the following options:
- KATA user account.
In this case, to connect to the application web interface, the user must enter the user name and password that were configured when the account was created.
- Domain user account.
In this case, to connect to the application web interface, the user does not have to enter the user name and password; the user is authenticated with the domain account.
If you have selected the Domain user account authentication type, note that the user will not be able to log in to the application web interface with a different user account.
The KATA user account and Domain user account fields are available if Active Directory integration is configured.
- KATA user account.
- In the Role drop-down list, select one of the following roles:
- Senior security officer
- Security officer
- Security auditor
- If you select KATA user account:
- In the User name field, enter a user name for the account you want to create.
The user name must meet the following requirements:
- Must be unique in the list of user names (case-sensitive).
- Must contain no more than 32 characters.
- Can contain letters A–Z, a–z, digits 0–9, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
- Must begin with a letter (A–Z or a–z).
- In the New password field, enter a user password that will be used to access the web interface.
The password must satisfy the following requirements:
- Must not be the same as the user name.
- Must not contain dictionary words, popular combinations of letters, or examples of a keyboard layout (for example, Qwerty or passw0rd).
- Must contain at least 8 characters.
- Must contain at least three types of characters:
- Uppercase character (A–Z).
- Lowercase character (a–z).
- Number.
- Special character.
- In the Confirm password field, re-enter the user password that will be used to access the web interface.
- In the User name field, enter a user name for the account you want to create.
- If you selected Domain user account, in the User name field, enter the user's domain name.
- In the Access section, configure access rights:
- Turn on the SCN web interface toggle switch to allow the user to access not only the web interface of this PCN server, but also to web interfaces of all available SCN servers.
- To the right of the Tenants setting title, select check boxes for one or more tenants to whose web interfaces you want to grant access.
You can use the Select all and Deselect all links to select or unselect all tenants.
- Click Add.
Configuring user account table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the table of user accounts.
To configure user account table display:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
User account table display is configured.
Page top
Viewing the user account table
The event table is displayed in the Settings section, Users subsection of the application web interface window. You can sort events in the table by the User name, Role, Tenants, and Status columns.
The table contains the following information:
- User name is the user name configured when creating the account.
- Authentication type is the authentication type of the user. Possible values:
- KATA user account.
In this authentication type is selected, to connect to the application web interface, the user must enter the user name and password that were configured when the account was created.
- Domain user account.
If this authentication type is selected, to connect to the application web interface, the user does not have to enter the user name and password; the user is authenticated with the domain account.
- KATA user account.
- Role is the role assigned to the user.
- Tenants is a list of tenants to which the user has access.
This column is displayed only in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Status is the status of the account. Can have the following values:
- Enabled
If the user account is enabled, the user is allowed to gain access to the application web interface.
- Disabled
If the user account is disabled, the user is prohibited from gaining access to the application web interface.
- Enabled
Filtering user accounts
To filter or search for user accounts by required criteria:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- Depending on the filtering criterion, do the following:
The table displays accounts that correspond to configured filter criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing the account filter
To clear the YARA rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Click
 to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.
to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
Changing access rights of an application web interface user account
You can change access rights of users with Senior security officer and Security officer roles to data of PCN and SCN servers as well as tenants to which those servers belong.
To change access rights of an application web interface user account, do the following in the web interface of the PCN:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection. Select the account whose access rights you want to change.
This opens the Edit user account window.
- If you want to enable or disable an account, move the Status toggle switch.
- In the Access section, move the SCN web interface toggle switch as necessary:
- Set the toggle switch to Enabled if you want to grant the user access to web interfaces of all available SCN servers in addition to the web interface of this PCN server.
- Set the toggle switch to Disabled if you want to grant the user access only to the web interface of this PCN server.
- To the right of the Tenants setting name, select or clear check boxes of one or more tenants for which you want to change the access rights of server web interfaces.
You can use the Select all and Deselect all links to select or unselect all tenants.
- Click Save.
The access rights of the account are changed.
Enabling and disabling an administrator account or user account of the application web interface
To enable or disable an administrator account or user account for the application web interface, do the following in the web interface of the PCN:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- In the list of accounts, select the user account that you want to enable or disable.
- In the Status column, do one of the following:
- Turn on the toggle switch next to the name of an account if you want to enable the account.
- Turn off the toggle switch next to the name of an account if you want to disable the account.
The action confirmation window is displayed.
- Click Yes.
The state of the account is modified.
Changing the password of an application administrator or user account
Only users with the KATA user account authentication type can change the password of their user account.
To change the password of an application administrator account or user account, do the following in the web interface of the PCN:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection. In the list of accounts, select the user account whose password you want to change.
This opens the Edit user account window.
- In the New password field, enter a new password for the application web interface.
The password must satisfy the following requirements:
- Must not be the same as the user name.
- Must not contain dictionary words, popular combinations of letters, or examples of a keyboard layout (for example, Qwerty or passw0rd).
- Must contain at least 8 characters.
- Must contain at least three types of characters:
- Uppercase character (A–Z).
- Lowercase character (a–z).
- Number.
- Special character.
- In the Confirm password field, enter the new password again.
- Click Save.
The password of the application administrator account or user account is changed.
Changing the password of your account
Only users with the KATA user account authentication type can change the password of their user account.
To change the password of your user account:
- Sign in to the web interface with your account.
- In the lower part of the program web interface window, click the link with the name of your account to expand the action list.
- Select the Change password action.
This opens the Change password window.
- In the Old password field, enter the current password for the application web interface.
- In the New password field, enter a new password for the application web interface.
The password must satisfy the following requirements:
- Must not be the same as the user name.
- Must not contain dictionary words, popular combinations of letters, or examples of a keyboard layout (for example, Qwerty or passw0rd).
- Must contain at least 8 characters.
- Must contain at least three types of characters:
- Uppercase character (A–Z).
- Lowercase character (a–z).
- Number.
- Special character.
- In the Confirm password field, enter the new password again.
- Click Change password.
The user account password for accessing the application web interface is changed.
Authentication using domain accounts
If authentication using domain accounts is configured, users do not have to enter Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform account credentials to connect to the application web interface.
To enable authentication using domain accounts:
- Configure integration with Active Directory.
To set up the Active Directory integration, you must create a keytab file containing the
for the Central Node server on which you want to set up the integration. - Select the Domain user account authentication type for the user when creating the account.
Creating a keytab file
You can create one user account to authenticate at multiple Central Node servers. Service principal name (SPN)To do so, you must create a
that contains service principal names (hereinafter also SPN) for each of these servers. When you create the keytab file, you must use an attribute to generate a salt (hash function input modifier).The generated salt must be saved in any convenient way for adding more SPNs to the keytab file in the future.
You can also create a separate Active Directory user account for each Central Node server for which you want to set up Kerberos authentication.
To create a keytab file using one user account:
- On the domain controller, in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, create a user account (for example, with
control-useras its name). - If you want to use the AES256-SHA1 encryption algorithm, in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in:
- Open the properties of the user account that you have created.
- On the Account tab, select the This account supports Kerberos AES 256 bit encryption check box.
- Use the ktpass utility to create a keytab file for the
control-useruser. To do so, run the following command on the command line:C:\Windows\system32\ktpass.exe -princ HTTP/<fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Central Node server>@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -mapuser control-user@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -pass * +dumpsalt -out <path to the file>\<file name>.keytabThe utility requests the
control-userpassword when executing the command.The SPN of the selected server is added to the created keytab file. The generated salt is displayed on screen:
Hashing password with salt "<hash value>". - Add an SPN record for each subsequent Central Node server to the keytab file. To do so, run the following command:
C:\Windows\system32\ktpass.exe -princ HTTP/<fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Central Node server>@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -mapuser control-user@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -pass * -in <path and name of the previously created file>.keytab -out <path and new name>.keytab -setupn -setpass -rawsalt "<hash value of the salt obtained when creating the keytab file at step 3>"The utility requests the
control-userpassword when executing the command.
The keytab file is created. This file contains all added SPNs of selected servers.
Example: For example, you need to create a keytab file containing SPN names of 3 servers: To create a
Let's say you got To add another SPN, run the following command:
To add a third SPN:
This creates a |
To create a keytab file using a separate account for each Central Node server:
- On the domain controller server, in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, create a separate user account for each server (for example,
control-user,secondary1-user,secondary2-user, etc). - If you want to use the AES256-SHA1 encryption algorithm, in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in:
- Open the properties of the user account that you have created.
- On the Account tab, select the This account supports Kerberos AES 256 bit encryption check box.
- Use the ktpass utility to create a keytab file for the
control-useruser. To do so, run the following command on the command line:C:\Windows\system32\ktpass.exe -princ HTTP/<fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Central Node server>@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -mapuser control-user@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -pass * -out <path to the file>\<file name>.keytabThe utility requests the
control-userpassword when executing the command.The SPN of the selected server is added to the created keytab file.
- Add an SPN record for each subsequent Central Node server to the keytab file. To do so, run the following command:
C:\Windows\system32\ktpass.exe -princ HTTP/<fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Central Node server>@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -mapuser secondary1-user@<realm name of the Active Directory domain in uppercase> -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -pass * -in <path and name of the previously created file>.keytab -out <path and new name>.keytabThe utility requests the
secondary1-userpassword when executing the command.
The keytab file is created. This file contains all added SPNs of selected servers.
Example: For example, you need to create a keytab file containing SPN names of 3 servers: To create a
To add another SPN, run the following command:
To add a third SPN:
This creates a |
Configuring integration with Active Directory
To configure integration with Active Directory:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- Go to the Active Directory integration tab.
- Select the Integration check box if you want to enable integration with Active Directory.
- Click Browse to upload the keytab file.
- Select the keytab file and click Open.
After you upload the file, the following fields are displayed:
- Keytab file status. Possible values:
- File contains SPN for this server means the uploaded keytab file contains the SPN for that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
- No SPN for this server means the uploaded keytab file does not contain the SPN for that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
- The file contains is the list of SPNs that the file contains.
- Keytab file status. Possible values:
- Click Apply.
Integration with Active Directory is configured.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, Active Directory integration settings configured on the PCN server are not applied to SCN servers connected to that PCN server. If you want to set up Active Directory integration on individual SCN servers, you must complete the steps above on each of the selected SCN servers.
Page top
Disabling integration with Active Directory.
When integration with Active Directory is disabled, user authentication with domain accounts is not available.
To disable integration with Active Directory:
- Log in to the web interface with the application administrator account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Users subsection.
- Go to the Active Directory integration tab.
- Clear the Integration check box.
- Click Apply.
Integration with Active Directory is disabled. The uploaded keytab file is permanently deleted.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, Active Directory integration settings configured on the PCN server are not applied to SCN servers connected to that PCN server. If you want to disable Active Directory integration on individual SCN servers, you must complete the steps above on each of the selected SCN servers.
Page top
Participation in Kaspersky Security Network and use of Kaspersky Private Security Network
To protect the user's computer more effectively, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses data that is obtained from users around the globe. Kaspersky Security Network is designed to obtain such data.
Kaspersky Security Network (hereinafter also "KSN") is an infrastructure of online services that provides users with access to the Kaspersky online knowledge base containing information on the reputation of files, web resources, and software. Use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform responds faster to new objects that have not yet been added to the anti-virus databases, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false alarms.
Thanks to users who participate in Kaspersky Security Network, Kaspersky is able to promptly receive information about the types and sources of objects that have not yet been added to the anti-virus databases, develop solutions for neutralizing them, and minimize the number of false alarms. User participation also helps other users of Kaspersky Security Network promptly receive information about threats to the IT infrastructure of their organizations.
When you participate in Kaspersky Security Network, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends Kaspersky Security Network requests about the reputation of files, web resources and software, and receives a response containing data about the reputation of those objects.
Personal information of the user is not collected, processed, or stored. For information about data that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends to Kaspersky Security Network, refer to the KSN Statement.
Participation in Kaspersky Security Network is voluntary. The decision to participate in Kaspersky Security Network is made during installation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and that decision can be changed at any time.
If you do not want to participate in KSN, you can use Kaspersky Private Security Network (hereinafter also referred to as "KPSN"). KPSN is a solution that allows users to access the reputation databases of Kaspersky Security Network and other statistical data without actually sending data from their own computers to Kaspersky Security Network.
If you want to purchase the Kaspersky Private Security Network application, please contact Kaspersky partners in your region.
Participation in KSN is configured on the Central Node server and is applied to all connected Sensor servers.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, participation in KSN is configured on the PCN server. Configured participation in KSN is applied to all SCN servers connected to the PCN.
Viewing the KSN Statement and configuring participation in KSN
To configure the participation in Kaspersky Security Network:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- On the right of the Connection type parameter name, click the KSN button.
- Carefully read the Kaspersky Security Network Statement and select one of the following options:
- I agree to participate in KSN, if you accept the terms of the KSN Statement and want to participate in KSN.
- I do not agree to participate in KSN, if you do not accept the terms of the KSN Statement and do not want to participate in KSN.
If you do not agree with the terms of the Statement, use of Kaspersky Security Network will not be enabled.
- Click Apply.
Participation in Kaspersky Security Network will be configured.
Enabling the use of KPSN
To enable the use of KPSN:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- On the right of the Connection type parameter name, click the KPSN button.
- In the KPSN configuration files section, upload the kc_private.xms, kh_private.xms and ksncli_private.dat files by clicking Browse.
- Click Apply.
Use of Kaspersky Private Security Network will be enabled.
Configuring a connection to a local reputation database of KPSN
The application can save information about Sandbox component alerts to the
. In this case, the Untrusted status is assigned to objects. Data of local reputation databases is available only to corporate LAN computers.If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the connection of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to a local KPSN reputation database:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KPSN reputation database subsection.
- In the Host field, specify the IP address of the KPSN server on which the local reputation database of KPSN is stored.
- Click Browse to the right of the TLS certificate field.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the certificate file for user authentication in KPSN and click the Open button.
- Click Browse to the right of the TLS encryption key field.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the file containing the private encryption key, and click the Open button.
The connection to the local reputation database of KPSN will be configured.
Configuring information to be saved to a local reputation database of KPSN
The application can save MD5 and SHA256 hashes of objects detected by the Sandbox component in the
. In this case, the Untrusted status is assigned to objects. Data of local reputation databases is available only to corporate LAN computers.To configure the saving of alert details to the local reputation database of KPSN:
- Log in to the application web interface under the senior security officer account.
- Select the Settings section, KPSN reputation database subsection.
- Do one of the following:
- Turn on the Assign the "Untrusted" status to objects switch if you want the application to set the status of alerts to Untrusted and save information about Sandbox component alerts in the local reputation database of KPSN.
- Turn off the Assign the "Untrusted" status to objects switch if you do not want to save information about Sandbox component alerts in the local reputation database of KPSN.
- Click Save.
The saving of information to the local reputation database of KPSN is configured.
Declining participation in KSN and use of KPSN
To decline participation in Kaspersky Security Network and the use of KPSN:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- On the right of the Connection type parameter name, click the Not connected button.
- Click Apply.
You will not participate in KSN and will not use KPSN.
Managing the Sandbox component through the web interface
The Sandbox web interface is located on the server hosting the Sandbox component.
The Sandbox web interface is protected against CSRF attacks and operates only if the web interface user's browser provides the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. Make sure that the browser that you are using to work with the Sandbox web interface does not modify the Referrer header of an HTTP POST request. If the connection with the web interface is established through a proxy server of your organization, check the settings and make sure that the proxy server does not modify the Referrer header for an HTTP POST request.
To get started with the web interface of the Sandbox application:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the server with the Sandbox component is allowed, enter the IP address of the server with the Sandbox component.
This opens the Sandbox component administrator credentials input window.
- Enter the Sandbox component administrator user name and password that you specified when installing the Sandbox component.
You can now start working in the Sandbox web interface.
If you use more than one servers with the Sandbox component, configure settings of each Sandbox component from the Sandbox web interface of such server.
Updating the Sandbox component databases
The Sandbox component databases are files with records that make it possible to detect a malicious code and signs of suspicious behavior in scanned objects.
Virus analysts at Kaspersky detect hundreds of new threats daily, create records to identify them, and include them in database upgrade packages (or upgrade packages). Upgrade packages consist of one or more files containing records to identify threats that were detected since the previous upgrade package was released. We recommend that you regularly receive upgrade packages.
During the license validity period, you can obtain update packages automatically once every hour or update the databases manually.
Updating databases manually
To start a database update manually:
- Select the Database update section in the Sandbox web interface window.
The Last update settings group will show time and status of the last Sandbox database update.
- Click Start.
Selecting a database update source
To select a database update source:
- Select the Database update section in the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Update source settings group, select a source from which you want to receive upgrade packages:
- Kaspersky update server.
The program connects to Kaspersky update server over HTTP and downloads up-to-date databases.
- Kaspersky update server (secure connection).
The program connects to Kaspersky update server over HTTPS and downloads up-to-date databases. It is recommended to use HTTPS for database updates.
- Custom server.
The program connects to your FTP or HTTP server or to the folder with program databases on your computer to download up-to-date databases.
- Kaspersky update server.
- If you select Custom server, in the field under the name of the setting, enter the full path to the folder that contains the application database update package.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Enabling and disabling a proxy server for database update
To enable or disable a proxy server for updating the Sandbox component databases:
- Select the Database update section in the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the workspace, do one of the following:
- Enable the switch next to the Proxy server settings group name if you want to use the proxy server for the Sandbox component database update.
- Disable the switch next to the Proxy server settings group name if you do not want to use the proxy server for the Sandbox component database update.
Configuring proxy server connection settings for database update
To configure the proxy server connection for updating Sandbox component databases:
- Select the Database update section in the Sandbox web interface window.
- Enable the switch next to the Proxy server settings group name.
- In the Address field, enter the proxy server address.
- In the Port field, enter the proxy server port number.
- In the User name field, enter the proxy server user name.
- In the Password field, enter the password to obtain connection to the proxy server.
- Do one of the following:
- Select the check box Bypass proxy server for local addresses, if you do not want to use the proxy server for internal emails of your organization.
- Clear the Bypass proxy server for local addresses check box if you want to use the proxy server irrespective of email affiliations to your organization.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Configuring connection between the Sandbox and Central Node components
The following procedure is used to configure the Sandbox component connection with the Central Node component:
- A request for connection to the Sandbox component is created in the application web interface.
- The Sandbox web interface shows connection requests.
You can accept or reject the request.
After configuring the connection, the Sandbox server needs 5 to 10 minutes to get ready for operation. During this time, the System health window of the application web interface display a warning: Default configuration error. When the server is ready for operation, the warning disappears.
Processing connection requests from the Central Node servers in the Sandbox web interface
You can accept, reject, or revoke a previously accepted connection request from the Central Node servers in the Sandbox web interface.
To accept, reject, or revoke a connection request from Central Node servers:
- Select the Authorization section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
The Central Node connection requests section will show a list of connection requests from the Central Node components.
Each connection request contains the following information:
- IP—IP address of the Central Node server.
- Certificate fingerprint—Thumbprint of the Central Node TLS certificate used to establish an encrypted connection between servers.
- State—Status of the connection request.
May have the values Pending or Accepted.
- Make sure that the Central Node certificate thumbprint matches the certificate thumbprint configured for the Central Node.
You can check the Central Node certificate thumbprint from the Central Node server administrator menu in the Manage Server Certificate section.
- Click one of the following buttons in the line containing the connection request from the Central Node component:
- Accept if you want to accept the connection request.
- Reject if you want to reject the connection request.
- Revoke if you want to revoke a previously accepted connection request.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Configuring the Sandbox component network interfaces
This section describes configuration of the Sandbox component network interfaces.
Configuring DNS settings
To configure DNS:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Host name field, enter the name of the server on which you are installing the Sandbox component in FQDN format (for example, sandbox).
- To the right of the DNS servers parameter name, click the Add button.
This will add an empty field for the DNS server IP address input.
- Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server in IPv4 format.
- Click the
 button to the right of the entry field.
button to the right of the entry field.The DNS server will be added.
- If you want to add an additional DNS server, repeat steps 2-5.
- If you want to remove a previously added DNS server, click the
 button to the right of the line containing the DNS server IP address.
button to the right of the line containing the DNS server IP address.You can only remove additional DNS servers. You cannot remove the primary DNS server. If you added 2 and more DNS servers, you can remove any of them, and the remaining DNS server will be used as the primary server.
Configuring settings of the management network interface
A management network interface is intended for providing access to the server with the Sandbox component via the SSH protocol, and the Sandbox component will also receive objects from the Central Node component via this interface.
You can configure a management network interface during installation of the Sandbox component.
You can also configure a management network interface from the Sandbox web interface.
To configure a management network interface from the Sandbox web interface:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Management interface settings group from the Interface drop-down list, select a network interface, which you want to use as a management interface.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address that you want to assign to this network interface if no IP address is assigned.
- In the Mask field, enter the network mask in which you want to use this network interface.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Configuring settings of a network interface used for Internet access of processed objects
Objects processed by the Sandbox component may attempt activities on the Internet via the network interface used for Internet access of processed objects. The Sandbox component can analyze the behavior of these objects.
If you block Internet access, the Sandbox component cannot analyze the behavior of objects on the Internet, and will therefore only analyze the behavior of objects without Internet access.
The network interface used for Internet access of processed objects must be isolated from the local network of your organization.
If the security policy of your organization denies access to the Internet from computers of local network users, and you have configured the Sandbox network interface for Internet access of processed objects, there is a risk of the following scenario:
A hacker can attach a malicious application to a random file and initiate a Sandbox scan of this file from the computer of a local network user. This file will be taken over outside the local network through the network interface used for Internet access of processed objects in the course of scanning the file by the Sandbox component.
Unavailability of the Sandbox network interface for Internet access of processed objects eliminates any risk of such data transfer but compromises the quality of alerts.
To configure the network interface used for Internet access of processed objects:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Internet interface settings group from the Interface list, select a network interface that you want to use for Internet access of processed objects.
The management network interface that you configured previously cannot be selected from this list of network interfaces.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address that you want to assign to this network interface.
- In the Mask field, enter the network mask in which you want to use this network interface.
- In the Default gateway field, enter the gateway address of the network in which you want to use this network interface.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Adding, changing and removing static network routes
You can configure static network routes during installation of the Sandbox component.
You can also add, remove or change static network routes from the Sandbox web interface.
To add a static network route:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Static routes settings group, click the Add button.
A line with empty fields will be added in the list of static network routes.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address of the server for which you want to configure a static network route.
- In the Mask field, enter the subnet mask.
- In the Gateway field, enter the IP address of the gateway.
- From the Interface list, select a network interface for which you want to add a static network route.
- Click
 .
. - Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
To remove a static network route, proceed as follows:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Static routes settings group in the line containing the static network route that you want to remove, click the
 button.
button. - Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
To modify a static network route:
- Select the Network interfaces section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Static routes settings group in the line containing the static network route that you want to change, click the
 button.
button.The static network route line will become editable. You can change one or more parameters of a static network route.
- In the IP field, change the IP address of the server for which you want to configure a static network route.
- In the Mask field, change the subnet mask.
- In the Gateway field, change the IP address of the gateway.
- From the Interface list, select the network interface for which you are editing the network route.
- Click
 .
. - Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Setting the Sandbox system date and time
To set the date and time on the server hosting the Sandbox component:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select Date and time.
- In the Country drop-down list, select the relevant country.
- In the Time zone drop-down list, select the relevant time zone.
- If you prefer to synchronize the time with the NTP server, select Synchronization with NTP servers.
- If you prefer to set the date and time manually, do not enable the switch to the right of the Synchronization with NTP servers parameter name and proceed as follows:
- In the Date field, enter the current date or click the
 button and select a date in the calendar.
button and select a date in the calendar. - In the Time field, enter the current time.
- In the Date field, enter the current date or click the
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Selecting a country from the Country drop-down list is not available in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.4.
Installing and configuring images of operating systems and applications required for the operation of the Sandbox component
To scan objects, you can use your own (hereinafter also referred to as "custom") images of operating systems as well as preset images from the distribution kit. If you are using custom images, you can install any applications on these operating systems. The selection of applications for the preset images from the distribution kit cannot be modified.
The distribution kit includes preset ISO images of operating systems and applications required for the Sandbox component to work. Some operating systems and applications require activation.
The Sandbox component runs objects in selected operating systems and analyzes the behavior of these objects to detect malicious activity and indicators of targeted attacks and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
You can use custom and preset operating system images at the same time.
To use an operating system image for scanning objects by the Sandbox component, you must create a virtual machine for that image.
We strongly recommend that you use all of the necessary and available preset operating system images from the distribution kit on each Sandbox server. If only some of the images from the distribution kit or only custom images are used, objects may be scanned with a reduced quality. |
Creating virtual machines with preset images of operating systems from the distribution kit
Creating virtual machines with preset images of operating systems involves the following steps:
Creating virtual machines with custom images of operating systems
Creating virtual machines with custom images of operating systems involves the following steps:
- Uploading the image of the operating system and applications that you want to install on the operating system to the Sandbox Storage.
You can skip this step and upload the images while creating and editing a template.
- Create or import a custom template.
- Creating a virtual machine
- Installing the virtual machine
In case of problems with activation of operating systems or applications, the web interface of the Sandbox component displays an error message. If this happens, please contact Kaspersky Technical Support.
Page top
Managing operating system and application images in the Sandbox Storage
Custom images of operating systems and applications that you want to install on these operating systems are placed in Sandbox Storage.
You can upload the following custom operating system images to Storage:
- Windows XP SP3 or later
- Windows 7
- Windows 8.1 64-bit
- Windows 10 64-bit (up to version 1909)
Uploaded files must have the .ISO extension.
Uploading custom images of Linux operating systems is not supported.
If you want to use custom operating system images in a template, you must configure those operating systems.
Page top
Viewing the table of operating system and application images in Sandbox Storage
To view the table of operating system and application images in Sandbox Storage:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Storage section.
The table of operating system and application images in Sandbox Storage is displayed.
The table contains the following information:
- Uploaded is the image upload time.
- Name is the name of the image.
- Size is the size of the image.
- Actions are operations available for the image. Possible values: Create VM, Export, Delete.
Uploading operating system and application images to Storage
To upload to Storage the custom images of operating systems and applications that you want to install on these operating systems:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Storage section.
- Click Upload.
- This opens the file upload window.
- Select the .ISO file that you want to upload to Storage.
- Click Open.
If you want to upload multiple images, repeat steps 1 to 6 for each image.
The image is uploaded to Storage and displayed in the table of objects.
Page top
Activating operating system and application images in Sandbox Storage
You can create a virtual machine with non-activated images of Windows 7 (64-bit), Windows 10 (64-bit) and applications required by the Sandbox component and activate them using your own license code after installing the virtual machine.
Windows images and the Microsoft Office suite can be activated using the kata_images.py file. This file is part of the distribution kit.
Correct activation of Windows images and the Microsoft Office suite requires Internet access. Make sure Internet access is configured correctly.
During the activation procedure in the Dashboard section, the Central Node component alerts you to a self-diagnostics error of the Sandbox component. After successful activation, the self-diagnostics error of the Sandbox component is no longer displayed. During activation, objects are not sent to the Sandbox component for scanning.
To activate Windows images and the Microsoft Office suite:
- Make sure that virtual machines with non-activated images of Windows 7 (64-bit), Windows 10 (64-bit) and the Microsoft Office suite are created and installed.
- Use SSH to place the kata_images.py file on the server with the Central Node component:
scp ./kata_images.py admin@<IP address of the Sandbox server>: - Log in to the management console of the server with the Sandbox component via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was specified during installation of the application.
The Sandbox component administrator menu is displayed.
- In the application administrator menu, select Technical Support Mode.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Technical Support Mode confirmation window.
- Select Yes and press ENTER.
- Activate the Windows images and the Microsoft Office suite by running the following sequence of commands:
cd /var/opt/kaspersky/apt/filessudo -s./kata_images.py activate --vm_id Win7_x64 --component Win7 --key <Windows 7 64 bit activation code>./kata_images.py activate --vm_id Win7_x64 --component Office2010 --key <Microsoft Office 2010 activation code>./kata_images.py activate --vm_id Win10_x64 --component Win10 --key <Windows 10 64 bit activation code>./kata_images.py activate --vm_id Win10_x64 --component Office2016 --key <Microsoft Office 2016 activation code>
The activation code has the following format: XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX.
- Create recovery points for virtual machines with added license keys:
./kata_images.py snapshot --vm_ids Win7_x64,Win10_x64The process may take some time.
- Make sure the Dashboard section of the application web interface does not display any warnings about the Sandbox component not working.
Windows images and the Microsoft Office suite are activated. Images of Windows operating systems and Microsoft Office application suite must be activated on all servers with the Sandbox component.
Deleting operating system and application images from Sandbox Storage
To remove an operating system or application image from Sandbox Storage:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Storage section.
- In the Action column next to the relevant image, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The image is deleted.
Page top
Managing virtual machine templates
Virtual machines are created from templates. To create a virtual machine, you must first import or create a template for it. Multiple virtual machines can be created based on the same template.
You can perform the following operations with templates: view the table of templates, enable or disable templates, edit, export, or delete templates.
Operations with the template are not available if a virtual machine with a custom operating system image is being created or installed from this template. After the virtual machine creation and installation process is complete, you can again perform operations with the template.
Page top
Creating a virtual machine template
To create a virtual machine with the selected operating system, you must first create a template for it.
To create a template for a virtual machine:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- From the Add drop-down list, select Create template.
This opens the template creation window.
- At the Preparing the image step:
- In the Name field, type the name of the template.
- In the Description field, enter the template description. This field is optional.
- In the OS image drop-down list, do one of the following:
- Select the operating system image that you want to use for the template from the list of available images.
For an image to be displayed in the list, you must first upload it to Storage.
- To upload the operating system image, click the Upload link, select the relevant file, and click Open.
The uploaded file must have the ISO extension.
- Select the operating system image that you want to use for the template from the list of available images.
- Click Proceed.
- At the Customizing the template step, do one of the following:
- In the Mount ISO drop-down list, select the image of the application that you want to install in the operating system.
For the image to be displayed in the list, do one of the following:
- Upload the image to Storage.
- In the Mount ISO drop-down list, click the Upload link, select the relevant file, and click Open.
The uploaded file must have the ISO extension.
- If you want to unmount the installed image, in the Mount ISO drop-down list, click the
 icon next this image.
icon next this image. - Configure the operating system and installed software.
- In the Shut down drop-down list, you can do one of the following:
- Shut down if you want to shut down the system while saving the results of running applications.
- Power off if you want to shut down the system without saving the results.
If a template is enabled, you cannot create a virtual machine from it, and you cannot export the template. If you want to continue configuring the template, enable it.
- In the Mount ISO drop-down list, select the image of the application that you want to install in the operating system.
The virtual machine template is created. You can create a virtual machine based on it.
Page top
Viewing the table of templates
To view the table of templates:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
The table of templates is displayed.
The table contains the following information:
- Created is the template creation time.
- Type is the type of operating system: custom or preset.
- Name is the name of the template.
- Status is the status of the template, for example, Power on or Powered off.
- Size is the size of the template.
- OS is the version of the operating system used for the template.
- VMs is the virtual machine created based on this template.
- Actions are operations available for the template. The following operations are available: Create VM, Export (
 ), Delete (
), Delete ( ).
). - Description is the description specified when creating a template.
Turning a template on or off
If the template is turned off, you can perform the following operations with it: create a virtual machine based on the template, export, or delete it. If a template is turned on, you can edit it.
To turn a template on or off:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- In the Customizing the template section, do one of the following:
- If you want to turn on the template, click Power on in the template management console.
- If you want to turn off the template, select one of the options in the Shut down drop-down list in the template management console:
- Shut down if you want to shut down the system while saving the results of running applications.
- Power off if you want to shut down the system without saving the results.
The template is turned on or off.
Page top
Editing a template
To edit a template:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- If the template is turned off, turn it on by clicking Power on.
- If you want to install an application on the operating system that is used for the template, select the relevant application image from the Mount ISO drop-down list.
For an image to be displayed in the list, you must first upload the image to Storage.
- If you want to unmount the installed image, in the Mount ISO drop-down list, click the Unmount
 icon next to that image.
icon next to that image. - Configure the operating system and installed software.
The template is edited.
Page top
Configuring the operating system and software
Preparing operating systems for use
When installing Windows XP, 7, 8.1, or 10 operating systems, you must satisfy the following requirements:
- Disable the screen saver.
- Select the Always On power plan.
- Disable automatic updates.
- Disable Windows Firewall.
If you are using Windows 7, support of the SHA-2 hash algorithm is required. To make sure this hash algorithm is supported, install the Security Update for Windows 7 for x64-based Systems (KB3033929). For 32-bit Windows 7 operating systems, update KB3033929 must also be installed.
Do not install update KB4474419. This update may cause a crash during virtual machine deployment.
To use Windows 7, you must enable TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 in the operating system settings. To do this, in Windows 7, in the Control Panel → Internet Options → Advanced section, select the Use TLS 1.1 and Use TLS 1.2 check boxes.
When using Windows 8.1 and 10 operating systems, you must disable fast startup and enable autologon.
Configuring operating systems
When the operating system is installed:
- Make sure the default command shell is configured.
- Activate the operating system and other licensed software.
You can do the following with the installed operating system:
- Assign a static name to the computer.
- Create user accounts.
In this case, you need to configure automatic logon.
- Select a localization.
Russian and English localizations are fully supported. If you select a different localization, the quality of object scanning is diminished.
- Install software.
Limitations on software installation:
- Only one image at a time can be connected to one template. After the template has been saved, you can disconnect one image and mount another.
- Versions of Microsoft Office later than 2016 are not supported.
- Installing the following types of software is strongly discouraged:
- Software that injects its code into another running process
- Drivers for protection
- Anti-virus applications including Windows Defender
- Detection of malicious activity of files that rely on highly specialized software to run is not guaranteed.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not notify about problems with software installed on the operating system.
Page top
Exporting a template
You can export a template in one of the following ways:
- In the table of templates.
- When viewing a template.
The template must be turned off.
To export a template in the table of templates:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- In the Action column next to the relevant image, click
 .
.
The template is exported. The file download starts automatically.
To export a template when viewing a template:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- In the Actions drop-down list, select Export.
The file download starts automatically. The file download starts automatically.
Page top
Importing a template
You can import a previously created template.
To import a template:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- In the Add drop-down list, select Import template.
- This opens the file upload window.
- Select the file that you want to import.
- Click Open.
The template appears in the list of templates.
You can edit a template, create a virtual machine from it, export, or delete it.
Page top
Deleting a template
When you delete a template, all virtual machines created based on that template are deleted.
You can delete a template in one of the following ways:
- In the table of templates.
- When viewing a template.
The template must be turned off.
To delete a template in the table of templates:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- In the Action column next to the relevant image, click
 .
.This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The template is deleted.
To delete a template when viewing a template:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- In the Actions drop-down list, select Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The template is deleted.
Page top
Managing virtual machines
You can create, install, or delete installed virtual machines and virtual machines pending installation. You can also view lists of virtual machines with preset and custom operating systems.
Page top
Creating a virtual machine
You can create a virtual machine in one of the following ways:
- In the Virtual machines section.
- In the table of templates.
- In the template view.
The virtual machine template must be turned off. After the virtual machines is created, it must be installed.
Internet access is required to create a virtual machine with a custom operating system image.
Page top
Creating a virtual machine in the Virtual machines section
To create a virtual machine with a preset operating system image in the Virtual machines section:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Virtual machines section.
- Click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- Some operating systems from the distribution kit require accepting the terms of the relevant end user license agreement. Read the text of the end user license agreement and click Accept.
The virtual machine with a preset operating system image is created.
To create a virtual machine with a custom operating system image in the Virtual machines section:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Virtual machines section.
- Click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
The name must consist of Latin characters.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- If internet access is not configured for the server on which you are creating the virtual machine, the No internet access error message is displayed in the Templates window. To complete the virtual machine creation process, you must download debug symbols.
The virtual machine with a custom operating system image is created.
Page top
Creating a virtual machine in the table of templates
To create a virtual machine with a preset operating system image in the template table:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
Go to the Templates section.
- In the Actions column next to the template, click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- Some operating systems from the distribution kit require accepting the terms of the relevant end user license agreement. Read the text of the end user license agreement and click Accept.
The virtual machine with a preset operating system image is created.
To create a virtual machine with a custom operating system image in the template table:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
Go to the Templates section.
- In the Actions column next to the template, click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
The name must consist of Latin characters.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- If internet access is not configured for the server on which you are creating the virtual machine, the No internet access error message is displayed in the Templates window. To complete the virtual machine creation process, you must download debug symbols.
The virtual machine with a custom operating system image is created.
Page top
Creating a virtual machine in the template view
To create a virtual machine with a preset operating system image in the template view:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- Click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- Some operating systems from the distribution kit require accepting the terms of the relevant end user license agreement. Read the text of the end user license agreement and click Accept.
The virtual machine with a preset operating system image is created.
To create a virtual machine with a custom operating system image in the template view:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- Click Create VM.
This opens the virtual machine creation window.
- In the Template drop-down list, select a template for the virtual machine.
If the list does not contain a suitable template, you can import or create a template in the Templates section of the Sandbox web interface window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the virtual machine.
The name must consist of Latin characters.
- In the Description field, enter the description of the virtual machine. This field is optional.
- Click Add.
- If internet access is not configured for the server on which you are creating the virtual machine, the No internet access error message is displayed in the Templates window. To complete the virtual machine creation process, you must download debug symbols.
The virtual machine with a custom operating system image is created.
Page top
Viewing the table of virtual machines with preset operating systems
To view the list of virtual machines with preset operating systems:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Preconfigured tab.
The table of virtual machines with preset operating systems is displayed.
The table contains the following information:
- Name is the name of the virtual machine.
- Status is the status of the virtual machine, for example, Enabled or Disabled.
- Actions are operations available for the virtual machine. The following operations may be available: Delete.
The Not installed virtual machines section displays virtual machines that are ready for installation but have not yet been installed.
Page top
Viewing the table of virtual machines with custom operating systems
To view the list of virtual machines with custom operating systems:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Custom tab.
The table of virtual machines with custom operating systems is displayed.
The table contains the following information:
- Created is the time when the virtual machine was created.
- Name is the name of the virtual machine.
- Status is the status of the virtual machine, for example, Enabled or Disabled.
- Actions are operations available for the virtual machine. The following operations may be available: Delete.
- Description is the description specified when creating the virtual machine.
Installing a virtual machine
After creating a virtual machine, it must be installed.
To install a virtual machine with a preset operating system image:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Preconfigured tab.
- In the Not installed virtual machines section, click Install ready VMs.
All virtual machines pending installation are installed.
To install a virtual machine with a custom operating system image:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Custom tab.
- Next to the relevant virtual machine in the Actions column, click the Install link.
- When the virtual machine is installed, in the Actions column, click the Enable link.
The virtual machine is installed and ready to use.
Page top
Deleting a virtual machine
To delete an installed virtual machine:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Preconfigured or Custom tab.
- In the Actions column next to the relevant virtual machine, click Delete.
The virtual machine is deleted.
To delete a non-installed virtual machine with a preset operating system image:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- In the Not installed virtual machines section, click Delete all pending VMs.
All virtual machines with preset operating system images that are pending installation are deleted.
To delete a non-installed virtual machine with a custom operating system image:
- Select the Virtual machines section in the window of the Sandbox web interface.
- Select the Custom tab.
- Next to the relevant virtual machine in the Actions column, click the Delete link.
The virtual machine with a custom operating system image that is pending installation is deleted.
Page top
Downloading debug symbols
If internet access is not configured for the server on which the virtual machine with the custom image is installed, you must download the Microsoft debug symbols to correctly complete the virtual machine installation.
You can download debug symbols during virtual machine installation in the Templates window or after the virtual machine receives the Failed status in the list of virtual machines.
For debug symbols to download correctly, the operating system used for the virtual machine template must have Windows Debug Tools installed and the name of the host connected to the network (hostname) must contain only Latin letters, numerals, and special characters.
To download debug symbols during virtual machine installation in the Templates window:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- In the window with the No internet access error, click Download manifesto.
The Download manifesto is not available until the virtual machine gets the Failed status.
An archive is downloaded to your computer.
- Unpack the downloaded archive.
- Run the sbsymtool.ps1 using Windows PowerShell.
The archive with debug symbols is downloaded to the folder where this file is located.
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the template for which you have downloaded debug symbols.
- In the Actions drop-down list, select Upload symbols.
- This opens a window; in that window, select the archive with the debug symbols and click Open.
Debug symbols are downloaded. The virtual machine is installed and displayed in the list of virtual machines running custom operating systems.
To download debug symbols after a virtual machine has received the Failed status in the list of virtual machines:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Templates & Storage section.
- Go to the Templates section.
- Select the relevant template.
- In the Actions drop-down list, select Download manifesto.
An archive is downloaded to your computer.
- Unpack the downloaded archive.
- Run the sbsymtool.ps1 using Windows PowerShell.
The archive with debug symbols is downloaded to the folder where this file is located.
- In the Templates window, expand the Actions list and select Upload symbols.
- This opens a window; in that window, select the archive with the debug symbols and click Open.
Debug symbols are downloaded. The virtual machine is installed and displayed in the list of virtual machines running custom operating systems.
Page top
Setting the maximum number of simultaneously running virtual machines
Set a limit on the number of simultaneously running virtual machines with operating systems in which the Sandbox component will process objects.
The number of simultaneously running virtual machines cannot exceed 200.
Calculate the number of simultaneously running virtual machines with images of operating systems as follows: multiply the number of logical cores by 1.5.
To set the maximum number of simultaneously running virtual machines:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the Guest virtual machines group of settings, in the Maximum simultaneous VMs field, enter the number of simultaneously running virtual machines.
You can enter a number ranging from 1 to 200.
- Click Save.
Changing the number of license keys for a virtual machine with a custom operating system image
When creating a virtual machine with a custom operating system image, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform specifies the number of license keys for software that is used inside that virtual machine. By default, the number of license keys is equal to the number of virtual machines running at the same time. Your license must cover this number. If necessary, you can change the number of license keys for the virtual machine.
If the number of license keys configured for a virtual machine is less than the number of simultaneously running virtual machines, the overall performance of the Sandbox server may be degraded.
It is not recommended to change the specified number of simultaneously running virtual machines.
To change the number of license keys for a virtual machine with a custom operating system image:
- Enter the management console of the Sandbox server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- Get a list of servers by running the
sb-custom-images list-vmcommand.The table of virtual machines is displayed, where
idis the ID of the virtual machine,nameis the name of the virtual machine, andlicensesis the number of license keys. - Set the number of license keys for the selected virtual machine by running the
sb-custom-images licenses -id <virtual machine ID> -ln <number of licenses>command.
The number of license keys is changed.
To get help for the script, run the sb-custom-images --help command.
Downloading the Sandbox system log to the hard drive
Log data in the Sandbox system is stored in open, non-encrypted form. The data is stored for the last 7 days.
To download the Sandbox system log to the hard drive:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the System log settings group, click the Download button.
- The Sandbox system log is downloaded to your computer's hard drive into the folder set as the file download folder in the settings of the browser that you use for working with the application.
Exporting Sandbox settings
To export the settings of a Sandbox system:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the Settings settings group, click the Export button.
This opens the Warning window containing a warning on specifics of exporting the system parameters.
The Sandbox system parameters are dependent on hardware and software parameters of the server, on which the Sandbox component is installed. The Sandbox system exported parameters are intended to be imported to the same or another server strictly identical in configuration. Any attempt to restore the configuration of the Sandbox system with parameter values saved to another Sandbox system may disrupt the Sandbox system.
- Click Save.
A tar.gz file is downloaded to your computer's hard drive into the folder set as the file download folder in the settings of the browser that you use for working with the application. The file contains all the Sandbox system current parameters.
Archives with backup copies of the system parameters can contain confidential information, such as passwords and privacy keys. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator must independently ensure the security of this data.
Importing Sandbox settings
To import Sandbox settings:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the Settings settings group, click the Import button.
This open the Warning window containing a warning on specifics of importing the system parameters.
The Sandbox component parameters are dependent on hardware and software parameters of the server, on which the Sandbox is installed. The Sandbox exported parameters are intended to be imported to the same or another server strictly identical in configuration. Any attempt to restore the configuration of one Sandbox system with parameter settings saved to another Sandbox system may disrupt the system.
- Click Restore.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a tar.gz file with the Sandbox parameters that you want to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
If the Sandbox parameters have been successfully imported, the Sandbox server will restart. A few minutes later, you need to refresh the browser window and log in again.
Archives with backup copies of the system configuration can contain confidential information, such as passwords and privacy keys. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator must independently ensure the storage security of this data.
Restarting the Sandbox server
To restart the Sandbox server:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the Power settings group, click the Restart button.
This opens the Sandbox server restart confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The Sandbox server will restart. In a few minutes, you will be able to log in to the system.
Powering off the Sandbox server
To power off the Sandbox server:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- In the Power settings group, click the Power off button.
This opens the Sandbox server shutdown confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The Sandbox server powers off.
Changing the Sandbox administrator account password
To change the Sandbox administrator account password:
- In the Sandbox web interface window, select the Administration section.
- The Change password settings group will show the Sandbox administrator account name that you set during installation of the Sandbox and the fields for changing the password.
- In the Current password field, enter the current password for the Sandbox administrator account.
- In the New password field, enter a new password for the Sandbox administrator account.
- In the Confirm password field, enter the new password for the Sandbox administrator account again.
- Click Change password.
The Sandbox administrator account password will be changed.
For administrators: Getting started with the application web interface
The intended audience of this section are personnel who install and administer Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and manage PCN and SCN servers and tenants in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Interface
The application is managed through the web interface. Sections of the application web interface differ depending on the role of the user: Administrator or Senior security officer / Security officer/Security auditor.
The window of the application web interface contains the following:
- Sections in the left part and in the lower part of the application web interface window.
- Tabs in the upper part of the application web interface window for certain sections of the application.
- The workspace in the lower part of the application web interface window.
Sections of the application web interface window
The application web interface for the Administrator role contains the following sections:
- Dashboard. Contains Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Monitoring data.
- Operation mode. Contains information about PCN and SCN servers and about tenants in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Endpoint Agents. Contains information about connected computers with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component and their settings.
- Reports: Activity log. Contains information about the logging settings for user activity in the application web interface.
- Settings. Contains the settings of the server with the Central Node component.
- Sensor servers. Contains information about connected Sensor components and their settings.
- Sandbox servers. Contains information about the connection of the Central Node component to Sandbox components.
- External systems. Contains information about application integration with mail sensors.
Workspace of the application web interface window
The workspace displays the information you choose to view in the sections and on the tabs of the application web interface window. It also contains control elements that you can use to configure how the information is displayed.
Users with the Security auditor role can also view these sections of the application web interface.
Monitoring the performance of the application
You can monitor application operation using the widgets in the Dashboard section of the application web interface window. You can add, delete, and move widgets, configure the display scale of widgets, and select the data display period.
About widgets and layouts
You can use widgets to monitor application operation.
A layout is the appearance of the workspace of the application web interface window in the Dashboard section. You can add, delete, and move widgets in the layout.
The following widgets are available in the application:
- Processed. Displays the processing status for traffic coming from the Sensor component and the Endpoint Agent component to the server with the Central Node component.
- Queues. Displays information on the number and volume of objects waiting to be scanned by application modules and components.
- Sandbox processing time. Displays the average time taken to receive the scan results after objects were scanned by the Sandbox component.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the section displays information about the tenant and server that you chose.
Selecting a tenant and a server to manage in the Dashboard section
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, before using the Dashboard section, you must select the tenant and server whose data you want to view.
To select a tenant and server for which you want to display data in the Dashboard section:
- In the upper right part of the application web interface window, click the arrow next to the server name.
- In the drop-down list, select the tenant and server from the list.
Data for the selected server is displayed. If you want to select a different tenant and server, repeat the steps to select a tenant and server.
Page top
Adding a widget to the current layout
To add a widget to the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Click Widgets.
- In the Manage widgets window that opens:
- If you want to add the Queues widget, turn on the toggle switch next to the name of this widget.
- If you want to add the Sandbox processing time widget, turn on the toggle switch next to the name of this widget.
- If you want to add the Processed widget, click
 next to the name of this widget.
next to the name of this widget.
The selected widget is added to the current layout.
Moving a widget in the current layout
To move a widget in the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Select the widget that you want to move within the layout.
- Left-click and hold the upper part of the widget to drag and drop the widget to a different place in the layout.
- Click Save.
The current layout is saved.
Removing a widget from the current layout
To remove a widget from the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Click the
 icon in the upper right corner of the widget that you want to remove from the layout.
icon in the upper right corner of the widget that you want to remove from the layout.The widget is removed from the workspace of the application web interface window.
- Click Save.
The widget is removed from the current layout.
Saving a layout to PDF
To save a layout to PDF:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Save as PDF.
This opens the Saving as PDF window.
- In the lower part of the window, in the Layout drop-down list, select the page orientation.
- Click Download.
The layout in PDF format is saved to the hard drive of your computer in the downloads folder of the browser.
- Click Close.
Configuring the data display period in widgets
You can configure the display of data in widgets for the following periods:
- Day
- Week
- Month
To configure the display of data in widgets for a day (from 00:00 a.m. to 11:59 p.m.):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Day.
- In the calendar to the right of the Day period name, select the date for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
To configure the display of data on widgets for a week (Monday through Sunday):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Week.
- In the calendar to the right of the Week period name, select the week for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
To display data display in widgets for a month (calendar month):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Month.
- In the calendar to the right of the Month period name, select the month for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
Monitoring the receipt and processing of incoming data
In the Processed widget, you can assess the processing status of data coming from the Sensor component and the Endpoint Agent component to the server with the Central Node component, and track data processing errors.
To select the component (Sensor or Endpoint Agent) for which you want to assess incoming data, use the drop-down list to the right of the Processed widget name.
You can select the type of data display in the drop-down list to the right of the component name (Sensor or Endpoint Agent):
- Current load—The last 5 minutes.
- Selected period. In this case, you can also configure the period for which data is displayed in widgets.
The left part of each widget displays the legend for colors used in the widget itself.
If the Current load data display type is selected, the average data processing rate over the past 5 minutes is displayed to the right of the key.
Example: The Processed widget has (SPAN) or (ICAP) Sensor type and Current load data display type selected and displays the data processing rate for SPAN and ICAP traffic coming from the Sensor component to the server with the Central Node component over a specific time period. The following data is displayed:
|
If the Selected period data display type is selected, to the right of the key you will see the average rate of incoming traffic to the server with the Central Node component and the number of objects processed during the selected period.
Example: The Processed widget with an (SPAN) or (ICAP) Sensor, Selected period data display type, and Month data display period selected, displaying the rate of SPAN and ICAP traffic coming to the server with the Central Node component, as well as the number of files and URLs extracted from mail traffic during the selected month. The following data is displayed:
|
Monitoring the queues for data processing by application modules and components
You can use the Queues widget to assess the status of data processing by the
and application modules and the and monitor the amount of unprocessed data.Data transfer in the queue is measured in messages.
You can select the type of data display in the drop-down list to the right of the Queues widget name:
- Current load—The last 5 minutes.
- Selected period. In this case, you can also configure the period of data display on widgets.
The left part of the widget displays the legend for colors used in the widget.
The Queues widget displays the following data:
- Number of messages and Data volume processed by application modules and components:
- YARA—blue.
- Sandbox—violet.
- AM Engine—green.
- Unprocessed – amount of unprocessed data indicated by vertical red lines.
When you hover the mouse cursor over a widget, you see a pop-up window that displays the status of data processing by the YARA and AM Engine application modules and the Sandbox component, as well as the amount of unprocessed data during a specific time period.
Monitoring the processing of data by the Sandbox component
The Sandbox processing time widget displays the average time elapsed from the moment data is sent to one or multiple Sandbox component servers (including the time spent in the queue before getting sent) to the moment when the Sandbox processing results are displayed in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform for the selected period.
Example: If Month is configured as the period of data display in widgets, the Sandbox processing time widget displays orange-colored bars for each day of the month. When you move the mouse cursor over each column, you will see a pop-up window that displays the average time that elapses from the moment data is sent to one or several servers with the Sandbox component until the results from data processing by the Sandbox component are displayed in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform during the selected day. |
You can increase the rate at which data is processed by the Sandbox component and the throughput of the Sandbox component by increasing the number of servers with the Sandbox component and by distributing the data to be processed among those servers.
Viewing the working condition of modules and components of the application
If modules or components of the application encounter errors that the administrator is advised to look at, a yellow warning box is displayed in the upper part of the Dashboard section of the application web interface.
Users with the Local administrator, Administrator, or Security auditor roles can gain access to information about the working condition of the Central Node, PCN, or SCN server that the user is currently managing.
Users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, or Security auditor roles can gain access to the following information about the working condition:
- If you are using a standalone Central Node server, the user can access information about the working condition of the Central Node server which the user is currently managing.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, and the user is managing an SCN server, the user can gain access to information about the working condition of that SCN server for tenants to whose data the user has access.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, and the user is managing the PCN server, the user can gain access to information about the working condition of the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that server, for tenants to whose data the user has access.
For details about the working condition of application modules and components,
click View details to open the System health window.
In the System health window, one of the following icons is displayed depending on the working condition of the application modules and components:
 if the modules and components of the application are working normally.
if the modules and components of the application are working normally.- An icon with the number of problems (for example,
 ) if problems are found that the administrator is recommended to pay attention to. In this case, detailed problem information is displayed in the right part of the System health window.
) if problems are found that the administrator is recommended to pay attention to. In this case, detailed problem information is displayed in the right part of the System health window.
The System health window contains the following sections:
- Component health contains information on the operational status of application modules and components, quarantine, and database update on all servers where the application is running.
Example:
If the databases of one or more application components have not been updated in 24 hours, the
 icon is displayed next to the name of the server on which the application modules and components are installed.
icon is displayed next to the name of the server on which the application modules and components are installed.To resolve the problem, make sure that update servers are accessible. If you are using a proxy server to connect to update servers, make sure the proxy server has no errors pertaining to the connection to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers.
- Processed—Status of receiving and processing incoming data. The status is generated based on the following criteria:
- State of receiving data from servers with the Sensor component, from the server or virtual machine with the mail sensor, from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Information about exceeding the maximum allowed time that objects wait in the queue to be scanned by application modules and components.
- Connection with servers—Status of the connection between the PCN server and connected SCN servers (displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode).
If problems are detected with the performance of application modules or components and you cannot resolve those problems on your own, please contact Kaspersky Technical Support.
Managing Central Node, PCN, or SCN servers using the application web interface
You can use the application web interface to perform the following actions with the server on which the Central Node component is installed:
- Configure the date and time on the server.
- Power off and restart the server.
- Generate or upload a server certificate that you can prepare on your own.
- Configure the network settings of the server.
- Monitor the disk space usage on the server.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
Configuring the date and time on the server
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the date and time on the server.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Date and time subsection.
- In the Time zone drop-down list, select the time zone of the physical location of the server with the Central Node component.
You can specify the country and time zone by selecting the relevant region on the map under the drop-down lists.
Selecting a region on the map is not available in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.4.
- In the NTP servers section:
- If you want to add a new :
- Click Add.
- In the field that opens, enter the IP address or domain name of the NTP server.
- Click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field.
- If you want to edit the IP address or domain name of the NTP server, click the
 button in the line containing the server.
button in the line containing the server. - If you want to delete an NTP server, click the
 button in the line containing the server.
button in the line containing the server.
- If you want to add a new :
- Click Apply.
The date and time of the server will be configured.
Page top
Generating or uploading a TLS certificate of the server
If you are already using a server TLS certificate, generating or uploading a new certificate causes the currently used certificate to be removed and replaced with the new certificate.
You must enter the data of the new certificate everywhere the old certificate was used.
If you replace the TLS certificate, you will need to:
- Reauthorize mail sensors (KSMG, KLMS) on Central Node.
- Reconfigure the connection of Central Node, PCN, and SCN to Sandbox.
- Reconfigure traffic forwarding from Endpoint Agent to Sensor and trusted connection with Endpoint Agent.
Make sure to delete all Endpoint Agent host isolation rules. Connection with isolated hosts will be lost and you will not be able to manage them.
You can generate a new certificate in the web interface: of the Central Node server or upload a certificate that you have created independently.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To generate a TLS certificate for a Central Node server:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Generate.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform generates a new TLS certificate. The page is automatically refreshed.
Communication with the mail sensors, the Sandbox component, and the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application is interrupted until reauthorization.
You can choose to prepare the TLS certificate on your own and upload it using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
The TLS certificate file prepared for upload must satisfy the following requirements:
- The file must contain the certificate itself and a private encryption key for the connection.
- The file must be in PEM format.
The application does not support other formats of certificates.
If you have prepared a certificate in a different format, you must convert it to the PEM format.
- The private key length must be 2,048 bits or longer.
For more details on preparing TLS certificates for import, please refer to the documentation on Open SSL.
Upload the TLS certificate in the web interface of the PCN or SCN server to which you want to upload the certificate.
To upload an independently prepared TLS certificate using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface:
- Sign in to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface with the administrator credentials.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Upload.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a TLS certificate file to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The TLS certificate is added to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Communication with the mail sensors, the Sandbox component, and the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application is interrupted until reauthorization.
Downloading the TLS certificate of the server
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To download the TLS certificate of the server:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Certificates subsection.
- In the Server certificate section, click Download.
The server certificate file will be saved in the downloads folder of the browser.
Assigning a server DNS name
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To assign the server name to be used by DNS servers:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Settings section, Network settings subsection.
- Enter the full domain name of the server into the Server name (FQDN) field.
Specify the server name in FQDN format (for example:
host.domain.comorhost.domain.subdomain.com). - Click Apply.
The server name will be assigned.
Page top
Configuring DNS settings
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure DNS:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Settings section, Network settings subsection.
- In the DNS settings group, enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers in the DNS servers field.
- Click Apply.
The DNS settings will be configured.
Page top
Configuring settings of the network interface
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the network interface:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Settings section, Network settings subsection.
- Select the network interface whose settings you want to configure.
This opens the Edit network interface window.
- In the State settings group, select one of the following options:
- Disabled.
- Enabled, using DHCP server if you want the settings received from the DHCP server to be used for the network interface.
- Enabled, manual configuration if you want the manually configured network interface to be used.
- If you selected Enabled, manual configuration, specify values for the following parameters:
- In the IP field, specify the IP address of the network interface.
- In the Subnet mask field, specify the subnet mask of the network interface.
- In the Gateway text box, enter the IP address of the gateway.
- Click Save.
The settings of the network interface will be configured.
Page top
Configuring the default network route
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the default network route:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Settings section, Network settings subsection.
- In the Network route settings group, in the Network interface drop-down list, select the network interface for which you want to configure the network route.
- In the Gateway text box, enter the IP address of the gateway.
- Click Apply.
The default network route will be configured.
Page top
Configuring proxy server connection settings
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the proxy server connection:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, General settings subsection.
- In the Proxy server settings group, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
- In the Host field, specify the URL of the proxy server.
- In the Port field, specify the port for connecting to the proxy server.
- In the User name field, specify the user name for authentication on the proxy server.
- In the Password field, specify the password for authentication on the proxy server.
- If you do not want to use a proxy server when connecting to local addresses, select the Bypass proxy server for local addresses check box.
- Click Apply.
The proxy server connection settings will be configured.
Page top
Configuring the mail server connection
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
The application can send notifications about alerts and system performance. To do so, you must configure the settings of the server used for sending notifications.
To configure the server for sending notifications:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Mail server configuration tab.
- In the Host field, specify the IP address of the mail server.
- In the Port field, specify the port for connecting to the mail server.
- In the Email from field, specify the email address from which the notifications will be sent.
- If you want to enable authentication on the mail server, select the Use SMTP authentication of message recipients check box.
- In the User name field, specify the user name for authentication on the server used for sending notifications.
- In the Password field, specify the password for authentication on the server used for sending notifications.
- If you want to use TLS encryption when sending notifications, select the Use TLS encryption check box.
- If you want to validate the certificate of the mail server, select the Validate TLS encryption check box.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the mail server certificate.
If the Validate TLS encryption check box is not selected, the application will consider any certificate of the mail server as trusted.
- Click Apply.
The settings of the server used for sending notifications will be configured.
Selecting operating systems to use when scanning objects in Sandbox
You can select a set of operating systems that will be used to generate tasks for scanning objects using the Sandbox component. On the Sandbox server, you must install virtual machines with operating systems that match the configured set.
To select the set of operating systems:
- Select the Sandbox servers section in the window of the application web interface.
- Go to the Settings tab.
- Under OS set, select one of the following options:
- Windows 7, Windows 10.
- CentOS 7.8, Windows 7, Windows 10.
- Astra Linux 1.7, Windows 7, Windows 10.
- Custom.
- If you selected Custom, under Set composition, select the check boxes next to the operating systems that you want to include in the set.
Custom operating systems are displayed in the list if virtual machines with these operating systems are installed on the Sandbox server. Preset operating systems are always displayed in the list, but if virtual machines running these operating systems are not deployed, the Unknown status is displayed next to the name of the operating system.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will create tasks for scanning objects in Sandbox in accordance with the selected set.
If the set of operating systems installed on the Sandbox server does not match the set selected on the Central Node server, objects are not sent to be scanned by that Sandbox server. If multiple Sandbox servers are connected to the Central Node server, the application sends objects to those Sandbox servers whose installed operating systems match the set selected on Central Node.
You can change the set of operating systems in the course of using the application. In this case, you need to make sure that the configuration of the Sandbox server satisfies hardware requirements.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the settings of the operating system set configured on the PCN server are not applied to SCN servers connected to that PCN server. You can select the set of operating systems for each PCN and SCN server individually.
Page top
Managing the Sensor component
The Sensor component receives data from network traffic and mail traffic.
You can install the Sensor and Central Node components on the same server or on separate servers. The Sensor component installed on a standalone server must be connected to the server with the Central Node component. A connection request is created during component installation.
If the Sensor component is installed on the same server as the Central Node component, you can configure the Sensor component in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. If the Sensor component is installed on a standalone server, in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you can only process connection requests from this component and view information about the component in the table of servers with the Sensor component. Other component settings can be edited in the administrator menu.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, perform the necessary actions to connect to PCN or SCN servers.
Viewing the table of servers with the Sensor component
The table of servers with the Sensor component is located in the Sensor servers section of the application web interface window.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
The Server list table contains the following information:
- IP/name—IP address or domain name of the server with the Sensor component.
- Type—Type of Sensor component. Possible values:
- Central Node—The Sensor component is installed on the same server as the Central Node component.
- Remote—The Sensor component is installed on a different server or a mail sensor is used as the Sensor component.
- Certificate fingerprint—Fingerprint of the TLS certificate used to establish an encrypted connection between servers with the Sensor and Central Node components.
- KSN/KPSN—Status of the connection to the KSN/KPSN reputation databases.
- SPAN—Status of SPAN traffic processing.
- SMTP—Status of integration with a mail server via SMTP.
- ICAP—Status of integration with a proxy server via ICAP.
- POP3—Status of integration with a mail server via POP3.
- State—Status of the connection request.
Processing a connection request from the Sensor component
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
You can accept, decline, or revoke a previously accepted connection request from the Sensor component.
To process a connection request from the Sensor component:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table displays the already connected Sensor components, and connection requests.
- In the line containing the connection request of the Sensor component, perform one of the following actions:
- If you want to connect the Sensor component, click the Accept button.
- If you do not want to connect the Sensor component, click the Reject button.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The connection request from the Sensor component will be processed.
Page top
Configuring the maximum size of a scanned file
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure the maximum size of a scanned file:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component for which you want to configure the maximum size of a scanned file.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the General settings section.
- If you want the application to scan files of any size, select the Unlimited check box.
- If you want to set a maximum size for files that the application will scan:
- Clear the Unlimited check box.
- In the field under the check box, enter the maximum allowed size of a file.
- In the drop-down list to the right of the field, select the unit of measurement.
- Click Apply.
The maximum size of a scanned file will be configured.
Page top
Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component for which you want to configure the receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the SPAN traffic processing section.
The Network interfaces table is displayed.
- In the row of the network interface from which you want to configure the receipt of mirrored traffic, set the toggle switch in the SPAN traffic scanning column to Enabled.
- In the Capture thread drop-down list, select the stream that will process this network interface.
- In the Select CPU drop-down list, select the processor that will process the network traffic.
- Click Apply.
The receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports will be configured.
Page top
Selecting network protocols for receiving mirrored traffic from SPAN ports
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform can receive and process mirrored traffic, and extract objects and protocol metadata. You can configure receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports.
To select network protocols for receiving mirrored traffic from SPAN ports:
- Enter the management console of the Sensor server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
This opens the settings menu for the Sensor component. If the menu does not open, enter the
kata-admin-menucommand andpress - Go to the Program settings → Configure traffic capture → Setup capture protocols section using the ↑, ↓, and ENTER keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
This opens a window where you can enable or disable receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports for the following network protocols:
- DNS
- FTP
- HTTP
- HTTP2
- SMTP
- SMB
- NFS
To analyze NFS traffic, you must mount the NFS partition and specify the version of the protocol.
Example:
for NFS v.4:
mount -t nfs -o vers=4 -O uid=1000,iocharset=utf-8 <address>:/from/dir /to/dirfor NFS v.3:
mount -t nfs -o vers=3 -O uid=1000,iocharset=utf-8 <address>:/from/dir /to/dir
If receipt of mirrored traffic from a SPAN port via a network protocol is enabled, [x] is displayed to the right of the network protocol name. If receiving mirrored traffic from a SPAN port is disabled for a particular network protocol, [ ] is displayed to the right of the name of that protocol.
By default, receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports is enabled for all network protocols except HTTP2.
- If you want to enable or disable the receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports for a particular network protocol, select that using the ↑, ↓ keys and press ENTER.
- Select the line containing Apply and Exit and press ENTER.
Network protocols for receiving mirrored traffic from SPAN ports are selected.
Page top
Configuring integration with a mail server via SMTP
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure integration with a mail server over SMTP:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component for which you want to configure integration with the mail server via SMTP.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the SMTP integration section.
- In the State field, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
- In the Destination domains field, specify the name of the mail domain or subdomain. The application will scan email messages sent to mailboxes of the specified domains.
To disable a domain or subdomain, enclose it in the
!domain.tldform.If you leave the mail domain name blank, the application will receive messages sent to any email address.
- In the Clients field, specify the IP addresses of hosts and/or masks of subnets (in CIDR notation) with which the application is allowed to interact over the SMTP protocol.
To disable a host or subnet, enclose the address in the
!hostform.If you leave this field blank, the application will receive the following messages:
- From any email addresses if you specified email domains in the Destination domains field.
- From a mail server in the same subnet as the server with the Sensor component if no domain is indicated in the Destination domains field.
- If you want the application to receive messages of any size, in the Message size limit settings group, select the Unlimited check box.
- If you want to set a maximum allowed size of incoming messages:
- Clear the Unlimited check box.
- In the field under the check box, enter the maximum allowed size of a message.
- In the drop-down list to the right of the field, select the unit of measurement.
- Click Apply.
Integration with a mail server via SMTP will be configured. The application will scan email messages received over the SMTP protocol according to the defined settings.
If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, you can configure fault-tolerant integration with the mail server.
To configure fault-tolerant integration with the mail server:
- Configure Round Robin on the DNS server for the domain name corresponding to the Central Node cluster.
- Specify this domain name in the mail server settings.
Integration with the mail server will be configured based on the domain name. The mail server will communicate with a random server in the cluster. If this server fails, the mail server will communicate with another healthy server in the cluster.
Page top
Configuring TLS encryption of connections with a mail server via SMTP
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure TLS encryption of connections with the mail server over SMTP:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component for which you want to configure TLS encryption of connections with the mail server over the SMTP protocol.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the SMTP integration section.
- In the State field, set the toggle switch to Enabled if it is disabled.
- In the Client TLS security level settings group, select one of the following options:
- No TLS encryption.
The application will not employ TLS encryption of connections with a mail server.
- Allow TLS encryption for incoming messages.
The application will support TLS encryption of the connection, but encryption will not be mandatory.
- Require TLS encryption for incoming messages.
The application will receive messages only over encrypted channels.
- No TLS encryption.
- Click the Download TLS certificate button to save the TLS certificate of the server with the Sensor component on the computer in the browser's downloads folder.
This certificate is required for authentication on the mail server.
- In the Requesting client TLS certificate settings group, select one of the following options:
- Do not request.
The application will not verify the TLS certificate of the mail server.
- Request.
The application will request a TLS certificate from the mail server, if one is available.
- Require.
The application will receive messages only from those mail servers that have a TLS certificate.
- Do not request.
- Click Apply.
TLS encryption of connections with the mail server over the SMTP protocol will be configured.
Page top
Configuring integration with a proxy server via ICAP
Integration with a proxy server over ICAP with feedback allows you to prevent malicious objects from entering the corporate LAN and prevent users of the host from visiting malicious or phishing websites. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform acts as an ICAP server, and your proxy server acts as an ICAP client. The proxy server sends ICAP requests to the ICAP server. The ICAP server runs a scan and returns the result to the proxy server. If any threats are detected, a notification HTML page is displayed to the user on the host.
Enabling and disabling integration with a proxy server via ICAP
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
When a standalone proxy server is used, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not provide encryption of ICAP traffic or authentication of ICAP clients by default. The application administrator must take steps to ensure a secure network connection between your proxy server and Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform by using traffic tunneling or iptables.
To enable or disable integration with a proxy server via ICAP on a server with the Central Node and Sensor components installed:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Click the localhost Sensor component.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the ICAP integration with proxy server section.
- In the Settings> <name of the server with the Sensor component> section, in the State field, do one of the following:
- If you want to enable integration with a proxy server via ICAP, move the toggle switch to Enabled.
By default, the toggle switch is in the Disabled position.
- If you want to disable integration with a proxy server via ICAP, move the toggle switch to Disabled.
- If you want to enable integration with a proxy server via ICAP, move the toggle switch to Enabled.
- The Host field displays the URL of the Response Modification (RESPMOD) service that processes inbound traffic; the URL has the following format:
icap://<host>:1344/av/respmod, where <host>is the IP address of the server where the Sensor component is installed.To configure integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, copy this URL and paste it in the settings of the proxy server that your organization used.
Integration with a proxy server via ICAP is enabled.
To enable or disable integration with a proxy server via ICAP on an individual server with the Sensor component:
- Enter the management console of the Sensor server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
This opens the settings menu for the Sensor component. If the menu does not open, enter the
kata-admin-menucommand andpress - Go to the Program settings → Configure ICAP integration section.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, and ENTER keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- This opens a window, in that window, select the Enabled line and press the ENTER key.
[x] is displayed to the right of the Enabled setting.
- In the settings of your proxy server, enter the URL from the RESPMOD field.
Integration with the proxy server and an individual server with the Sensor component via ICAP is configured.
If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, you can configure high availability integration with a proxy server.
To configure the high availability integration with the proxy server:
- Configure Round Robin on the DNS server for the domain name corresponding to the Central Node cluster.
- Specify this domain name in the proxy server settings.
Integration with the proxy server will be configured based on the domain name. The proxy server will communicate with a random server in the cluster. If this server fails, the proxy server will communicate with another healthy server in the cluster.
Page top
Enabling or disabling real-time scanning of ICAP traffic
You can enable or disable real-time scanning of ICAP traffic if integration with a proxy server via ICAP is enabled.
If real-time scanning of ICAP traffic is enabled, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends information about scanned objects to the ICAP client in real time. This helps prevent downloading malicious objects and clicking untrusted links.
To enable or disable real-time scanning of ICAP traffic on a server with the Central Node and Sensor components installed:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Click the localhost Sensor component.
- Select the ICAP integration with proxy server section.
When integration is enabled in the Settings > <Sensor server name>, the Real-time scanning section is displayed.
- Under Real-time scanning, select one of the following options:
- Disabled.
If you select this option, real-time scanning of ICAP traffic is disabled. This option is selected by default.
- Enabled, standard ICAP traffic scanning.
When this type of scan is enabled, the reputation of files and URLs is checked against the knowledge base of Kaspersky Security Network, and files are scanned by the Sandbox component and Anti-Malware Engine and YARA modules. The files remain available while they are being scanned by the Sandbox component.
- Enabled, advanced ICAP traffic scanning.
When this type of scan is enabled, the reputation of files and URLs is checked against the knowledge base of Kaspersky Security Network, and files are scanned by the Sandbox component and Anti-Malware Engine and YARA modules. The files are unavailable while they are being scanned by the Sandbox component.
- Disabled.
- Click Apply.
- If you enabled real-time scanning of ICAP traffic and enabled the advanced scanning mode or the standard scanning mode, the Host field displays the URL of the Request Modification (REQMOD) service that processes outbound traffic in the following format: icap://<host>:1344/av/reqmod,
where <host> isthe IP address of the server where the Sensor component is installed. To configure integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, copy this URL and paste it in the settings of the proxy server that your organization used.
Real-time scanning of ICAP traffic is enabled or disabled.
To enable or disable real-time scanning of ICAP traffic on an individual server with the Sensor component installed:
- Enter the management console of the Sensor server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
This opens the settings menu for the Sensor component. If the menu does not open, enter the
kata-admin-menucommand andpress - Go to the Program settings → Configure ICAP integration section.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, and ENTER keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- This opens a window; in that window, make sure that [x] is displayed to the right of the Enabled setting.
- Select one of the following options:
- Disable real-time scanning.
If you select this option, real-time scanning of ICAP traffic is disabled. This option is selected by default.
- Standard ICAP scanning.
When this type of scan is enabled, the reputation of files and URLs is checked against the knowledge base of Kaspersky Security Network, and files are scanned by the Anti-Malware Engine and YARA modules.
- Advanced ICAP scanning.
When this type of scan is enabled, the reputation of files and URLs is checked against the knowledge base of Kaspersky Security Network, and files are scanned by the Sandbox component and Anti-Malware Engine and YARA modules.
- Disable real-time scanning.
- Select an option and press ENTER. (O) is displayed to the right of the selected option.
To select a row, you can use the ↑ and ↓ keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- If you enabled real-time scanning of ICAP traffic and enabled the advanced scanning mode or the standard scanning mode, specify the URL from the REQMOD field in the settings of your proxy server.
Real-time scanning of ICAP traffic on an individual server with the Sensor component is enabled or disabled.
If you enabled real-time scanning of ICAP traffic, scanning does not work if integration with the proxy server is disabled. All ICAP traffic scanning settings are saved. When you re-enable integration with the proxy server, ICAP traffic scanning is also enabled.
Page top
Configuring real-time scanning of ICAP traffic
Real-time ICAP traffic scanning on standalone servers with the Sensor component can only be configured in Technical Support Mode. To perform actions in Technical Support Mode, we recommend contacting Technical Support.
You can configure real-time ICAP traffic scanning on a server with the Central Node and Sensor components for anti-virus scanning of data. Scan results are displayed to the user of the host on a notification HTML page.
To configure real-time ICAP traffic scanning:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, ICAP traffic scanning subsection.
The ICAP traffic scanning settings page is displayed.
By default, under Notifications, pages corresponding to the following events are loaded:
- The page uploaded in the Link blocked field is displayed if a threat is detected at the address requested by the user.
- The page uploaded in the File blocked field is displayed if a threat is detected in a scanned file.
- The page uploaded in the Scan file field is displayed if a file scan is started. If the file is safe, the user can click a link to download the file.
- The page uploaded in the File expired field is displayed if the file was scanned, but the storage duration for that file has expired.
By default, HTML pages from the distribution kit are loaded in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. You can upload your own notification pages and configure how they must be displayed. The size of a notification page must not exceed 1.5 MB. If the uploaded notification page is larger than 1.5 MB, an error is displayed.
- Under File block threshold, in the Sandbox detection severity field, select a value from the drop-down list. These values correspond to the possible impact of the alert on the security of a computer or your corporate network based on the expert opinion of Kaspersky.
This setting can take one of the following values:
- High
 for a high importance alert. This option is selected by default.
for a high importance alert. This option is selected by default. - Medium
 for a medium-importance alert.
for a medium-importance alert. - Low
 for a low-importance alert.
for a low-importance alert.
- High
- Under Scan timeout, in the Timeout field, specify the time after which the link to the scanned file is unblocked and downloading the scanned file becomes possible.
The default value is 10 minutes. You can set any value greater than 1 minute.
- Click Apply.
The scan is performed with the specified settings.
Page top
Configuring the display of notification pages
While scanning ICAP traffic in real time, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform can perform various operations with the scanned objects: block access to an URL, block a file download, prevent the file from being downloaded while it is being scanned, and offer to re-download the file if its storage duration has expired after scanning. While these operations are in progress, a HTML notification page is displayed to the user on the host on which a URL access attempt or a file download request was made. If you want to display your own pages instead of the default pages, you can upload your own customized HTML pages.
To upload a notification page:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, ICAP traffic scanning subsection.
- In the Notifications section, click Browse next to one of the fields you need.
- This opens a window; in that window, select your HTML page.
- Click Open.
Your page is uploaded.
The notification page of the Scan file event is different from other notification pages because it includes a link to download the file. If you want to upload a Scan file notification page, you must add a scanned file download link to the source code of the notification page.
Example: <html> <body> <p>The file is being scanned. When the scan is completed, you will be able to download it or you will receive a report about any detected threats.</p> <a href="{{ download_url }}">Download link...</a> </body> </html> |
Configuring raw network traffic recording
With Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you can save raw network traffic for investigation and detection of malicious activity within the perimeter of your corporate LAN. With raw network traffic recording, you can perform retrospective analysis of network events and investigate the actions of hackers. Raw network traffic is saved as dumps in PCAP format.
To save raw network traffic, you need to enable and configure raw network traffic recording.
Enabling and configuring raw network traffic recording on a server with the Sensor and Central Node components installed
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, follow the steps on the PCN or SCN server that you want to configure.
To enable and configure raw network traffic recording on a server with the Central Node and Sensor components installed:
- Connect and configure external storage.
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component with the name localhost.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the SPAN traffic processing section.
The Network interfaces table is displayed.
- Go to the Traffic recording tab.
- In the Record traffic field, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
By default, the toggle switch is in the Disabled position.
Raw network traffic recording on the server with the Central Node and Sensor components installed is enabled. Raw traffic recording settings are displayed.
By default, raw network traffic is saved to the /mnt/kaspersky/nta/dumps directory. You cannot change the directory for raw network traffic recording. You can view raw network traffic dumps in the /data/ volumes/dumps directory.
- If necessary, edit raw network traffic recording settings:
- Under Dump storage size, in the Maximum storage size field, specify the maximum size of raw traffic dumps to be stored in dump storage.
The minimum value is set to 100 GB by default. The maximum value is 1,000,000 TB. For correct operation of the application, the connected disk must have at least the amount of free disk space listed above.
If the size of dumps in dump storage exceeds the Maximum storage size value, the earliest dumps are deleted, the total size of which is equal to the size of the new dumps.
If you reduce the maximum dump storage size, the earliest dumps are deleted, the total size of which is equal to the Maximum storage size change.
- If you want to restrict data capture in raw network traffic, under Traffic filtering upon saving, in the State field, set the toggle switch to Enabled. Traffic filtering can reduce the size of dumps in dump storage and facilitate traffic analysis.
If you have set the toggle switch in the State field to Enabled, enter the filtering rule in the BPF filtering rule field. The BPF filtering rule is written in the libpcap format. For more details about the syntax, please refer to the pcap-filter manual page.
Example of a filtering expression:
tcp port 102 or tcp port 502 - If you want to set a storage duration for raw network traffic dumps, under Dump storage duration, in the State field, set the toggle switch to Enabled. In the Store for field, enter the raw network traffic dump storage duration in days. Raw network traffic dumps that are stored longer than the specified duration are deleted from the storage.
- Click Apply.
- Under Dump storage size, in the Maximum storage size field, specify the maximum size of raw traffic dumps to be stored in dump storage.
Raw network traffic recording on the server with the Sensor and Central Node components is performed in accordance with the specified settings.
The First saved dump field displays the date and time of the first saved raw network traffic dump, and the Last saved dump field displays the date and time of the last raw network traffic dump.
Page top
Enabling and configuring raw network traffic recording on a standalone server with the Sensor component
To enable raw network traffic recording on a standalone server with the Sensor component:
- Connect and configure external storage.
- Enter the management console of the Sensor server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
This opens the settings menu for the Sensor component. If the menu does not open, enter the
kata-admin-menucommand and press Enter. - Go to the Program settings → Configure traffic capture section.
To select a row, you can use the ↑, ↓, and Enter keys. The selected row is highlighted in red.
- This opens a window, in that window, select the Enabled traffic storage line and press Enter.
[x] is displayed to the right of the title of the line.
Raw network traffic recording on the standalone server with the Sensor component will be enabled.
- If necessary, edit raw network traffic recording settings:
- Select the Traffic storage size line and press Enter. This opens a window; in that window, specify the maximum total size of stored raw traffic dumps, in terabytes.
The minimum value is set to 100 GB by default. The maximum value is 1,000,000 TB. For correct operation of the application, the connected drive must have at least the specified amount of free disk space. If the number entered in this field exceeds the free disk space on the connected drive, an error is displayed.
- Select the OK button and press Enter.
- Select the Traffic capture BPF-filter line and press Enter. This opens a window; in that window, enter the filtering rule. The BPF filtering rule is written in the libpcap format. For more details about the syntax, please refer to the pcap-filter manual page.
Example of a filtering expression:
tcp port 102 or tcp port 502. - Select the OK button and press Enter.
- Select the Traffic storage duration (in days) line and press Enter. This opens a window; in that window, enter the storage duration for raw network traffic dumps in the storage, in days.
- Select the OK button and press Enter.
- Select the Traffic storage size line and press Enter. This opens a window; in that window, specify the maximum total size of stored raw traffic dumps, in terabytes.
Raw network traffic recording on the standalone server with the Sensor component is performed in accordance with the specified settings.
Page top
Configuring integration with a mail server via POP3
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
To configure integration with a mail server over POP3:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component for which you want to configure integration with the mail server via POP3.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the POP3 integration section.
- Set the toggle switch next to the State parameter to Enabled.
- In the Mail server field, specify the IP address of the mail server with which you want to configure integration.
- In the Port field, specify the port for connecting to the mail server.
- In the Receive every field, specify the mail server connection frequency (in seconds).
- If you want to use TLS encryption of connections with the mail server via POP3, select the Use TLS encryption check box.
- In the User name field, specify the account name used for accessing the mail server.
- In the Password field, specify the password for accessing the mail server.
The mail server must support Basic Authentication.
- In the TLS certificate drop-down list, select one of the following options:
- Accept any.
- Accept untrusted self-signed.
- Accept only trusted.
When establishing a connection with an external mail server, it is recommended to configure the acceptance of only trusted TLS certificates. If you accept untrusted TLS certificates, protection of the connection against
cannot be guaranteed. Even though the acceptance of trusted TLS certificates also cannot guarantee protection of the connection against MITM attacks, it is the most secure of the supported methods for integration with a mail server over the POP3 protocol. - If necessary, in the Cipher suite field, modify the OpenSSL settings used when establishing a connection with the mail server via POP3.
You can view reference information on OpenSSL by clicking the Help link.
- Click Apply.
Integration with the mail server via POP3 will be configured.
If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, you can configure high availability integration with the mail server.
To configure high availability integration with the mail server:
- Configure Round Robin on the DNS server for the domain name corresponding to the Central Node cluster.
- Specify this domain name in the mail server settings.
Integration with the mail server will be configured based on the domain name. The mail server will communicate with a random server in the cluster. If this server fails, the mail server will communicate with another healthy server in the cluster.
Page top
Viewing the table of servers of the cluster
To view the table of cluster servers:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the Central Node server has been allowed, enter the IP address of any server in the Central Node cluster or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the cluster into the the address bar of your browser.
An input window for account credentials of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user opens.
- Enter the administrator user name "admin" and the password that was set during installation of the application.
- Select the Local administrator check box.
- Click Log in.
This opens a web interface window in which you can manage application sizing.
- Go to the Cluster section.
A window with a table will open.
The table contains the following information:
- Server type—server type depending on its role in the cluster.
The following values can be displayed:
- Storage.
- Processing.
- Status—server status.
The following values can be displayed:
- Connected.
- Not connected.
- Host name—server name.
- IP— IP address of the server.
- RAM—RAM load level of the server.
- CPU—CPU load level of the server.
- Action—Actions that you can perform with the server.
The following action is available: Delete.
Adding a server to a cluster
To add a server to the cluster, you need to start the installation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on this server and follow the steps to install the components. The added server is displayed in the cluster server list.
Page top
Increasing the disk space on the storage server
You can increase the disk space on an operational storage server by installing an additional disk.
To increase the disk space of the storage server by means of an additional disk, you need to contact Technical Support.
The server is configured in Technical Support Mode.
Page top
Decommissioning servers
To decommission an operational server, you need to contact Technical Support.
If a server fails, you can decommission it on your own.
To decommission an inoperable processing server:
- Add a new processing server to the cluster.
- Remove the server from the cluster.
- Configure the sizing of the application for the new configuration.
The processing server will be decommissioned.
To decommission an inoperable storage server:
- Add a new storage server to the cluster.
- Contact Technical Support to remove the inoperable server from the cluster.
The storage server will be decommissioned.
Page top
Removing a server from a cluster
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
A removed server cannot be restored. Make sure that the selected server is not operational.
To remove a server from the cluster:
- Log in to the web interface for sizing management.
- Go to the Cluster section.
- In the Action column, click the Delete link opposite the server that you want to remove.
- Click Proceed.
The removal process will start. Removal may take about a day. Information about the removed server will not be displayed in the table of servers.
After removing the server, you can reconfigure the servers in the cluster or add a server with the same role to maintain the same level of application performance.
Page top
Starting up and shutting down the cluster
To shut down or start the cluster, we recommend contacting Technical Support. Do not shut down or start the cluster if you encounter problems with application health.
If you want to power off the healthy servers in the cluster, you must first shut down the cluster to avoid data loss.
To shut down a cluster:
- In a browser on any computer on which access to the Central Node server has been allowed, enter the IP address of the server with the Central Node component into the browser's address bar.
If you are using the high availability version of the application, you can enter the IP address of any server of the Central Node cluster or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the cluster.
An input window for account credentials of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user opens.
- Enter the administrator user name "admin" and the password that was set during installation of the application.
- Select the Local administrator check box.
- Click Log in.
This opens a web interface window in which you can manage application sizing.
- Go to the Cluster section.
- Click the Shut down button.
The main components of the application are stopped. You can now power off the cluster servers.
To start up the cluster servers:
- Disconnect power to the servers if it has not been previously disconnected.
- Power on the storage server.
- Power up the remaining servers.
The cluster servers will start up.
The scaling management web interface becomes available when more than half of the cluster servers are started. For example, if there are 7 servers in the cluster, the web interface will be available when 4 servers of the cluster are powered on.
Page top
Powering off servers in a cluster
If necessary, you can power off a server in the cluster in one of the following ways:
- End the session in the application menu.
- Power off the server over SSH or through the terminal.
To power off the server over SSH or through the terminal:
- Sign in to the management console of the server that you want to power off over SSH or through a terminal.
- Run the
shutdown -h nowcommand.
The server is powered off.
High availability of the application is not guaranteed when a server in the cluster is powered off.
The recommended interval between powering on a server and powering off another server is 6 hours.
Page top
Notifications about the maximum allowed CPU and RAM load for the Central Node and Sensor servers
Maintaining a high load on the CPU and RAM of the Central Node and Sensor servers may prevent application components from working.
You can configure maximum values for the CPU and RAM loads on Central Node and Sensor servers; if these are exceeded, the upper part of the Dashboard section of the application web interface for users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, Administrator, or Local administrator roles displays a yellow warning box. You can also configure notifications to be sent to one or more email addresses and an SNMP protocol connection for sending information about the CPU and RAM load to external systems that support this protocol.
If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, warnings are displayed separately for each server in the cluster.
Users with the Senior security officer or Security officer role can also create rules for sending notifications. In this case, sending notifications correctly requires configuring maximum allowed load values for the CPU and RAM of servers, as well as notification settings on the server.
In existing rules for sending notifications about application components, the CPU load and RAM load notifications are enabled automatically if the All check box is selected under Components when the rule is created.
Configuring the maximum allowable CPU and RAM load of the Central Node and Sensor servers
In the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you need to set the maximum allowed load values for the CPU and RAM load of each Central Node server from which you want to receive notifications. If you use a Central Node cluster, you can configure these settings on any cluster server.
To configure the maximum allowed load on the CPU and RAM of the Central Node and Sensor servers:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, General settings subsection.
- Under Monitoring:
- In the Warning of CPU usage above N % for M min field, enter the maximum allowed CPU usage and time period for which the maximum load can be maintained.
By default, the maximum CPU load is 95% for 5 minutes.
- In the Warning of RAM usage above N % for M min field, enter the maximum allowed RAM usage and time period for which the maximum usage can be maintained.
By default, the maximum RAM usage is 95% for 5 minutes.
- In the Warning of CPU usage above N % for M min field, enter the maximum allowed CPU usage and time period for which the maximum load can be maintained.
- Click Apply.
The maximum allowed load of server CPU and RAM will be configured. If one of the values is exceeded on the Central Node and/or Sensor server, in the upper part of the Dashboard section of the application web interface for users with Senior security officer, Security officer, Administrator, or Local administrator role, a yellow warning box is displayed.
Page top
Configuring the SNMP protocol connection
You can send information about the CPU and RAM load on Central Node and Sensor servers to external systems that support the SNMP protocol. To do so, you must configure the connection for the protocol.
If the Central Node component is deployed as a cluster, data about the CPU and RAM load of each server in the cluster is sent to external systems.
To configure the SNMP protocol connection on the Central Node server:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, General settings subsection.
- Under SNMP, select the Use SNMP check box.
- In the Protocol version field, select a protocol version:
- v2c.
- v3.
- If you selected the v2c protocol version, in the Community string field, enter the password that will be used for connecting to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- If you selected v3:
- In the Authentication protocol field, select one of the following options for checking the accuracy and integrity of data sent to the external system:
- MD5.
- SHA256.
- In the User name field, enter the user name.
- In the Password field, enter the password for authentication.
User name and password configured in the User name and Password fields must match the user name and password configured when creating the account in the external system. If the credentials do not match, the connection cannot be established.
- In the Privacy protocol field, select an encryption type:
- DES.
- AES.
- In the Password field, enter the encryption password.
The password configured in this field must match the password configured in the external system.
- In the Authentication protocol field, select one of the following options for checking the accuracy and integrity of data sent to the external system:
Protocol connection on the Central Node server is configured. If the request for data is successfully processed, the server of the external system displays information about CPU and RAM load of the Central Node server.
To configure the SNMP protocol connection on the Sensor server:
- Enter the management console of the Sensor server via the SSH protocol or through a terminal.
- When the system prompts you, enter the administrator user name and the password that was set during the installation of the application.
The application component administrator menu is displayed.
- Follow steps 2 through 5 of the instructions above.
Protocol connection on the Sensor server is configured. If the request is successfully processed, the server of the external system displays information about CPU and RAM load of the Sensor server.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, SNMP connection settings for each PCN, SCN, and Sensor server must be configured separately.
Description of MIB objects of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
The tables below provide information about
objects of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.Information about hard drive, CPU, and RAM load of Central Node and Sensor servers
Information about hard drive, CPU, and RAM load of Central Node and Sensor servers
Symbolic name |
Description |
Object identifier (OID) |
|---|---|---|
|
Total size of the disk or partition, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.6 |
|
Available space on the disk, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.7 |
|
Used space on the disk, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.8 |
|
Percentage of space used on disk, %. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.9 |
|
System load average for 1, 5 and 15 minutes. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3 |
|
Total RAM size, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5 |
|
Total RAM used, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.6 |
|
Total RAM free, KB. |
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.11 |
Managing Endpoint Agent host information
The application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component is installed on individual computers (hereinafter also referred to as "hosts") in the IT infrastructure of the organization. The application continuously monitors processes running on those hosts, active network connections, and files that are being modified.
Users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, Security auditor, Local administrator, or Administrator role can assess how regularly data is received from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component on the Endpoint Agents tab of the web interface window of the Central Node server for tenants to whose data the user has access. If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the web interface of the PCN server displays the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for the PCN and all connected SCNs.
Users with the Local administrator and Administrator roles can configure the display of how regularly data is received from hosts with Endpoint Agent for tenants to whose data they have access.
If suspicious network activity is detected, users with the Senior security officer role can isolate from the network any host with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, for tenants to whose data the user has access. In this case, the connection between the server with the Central Node component and a host with the Endpoint Agent component will not be interrupted.
In order to provide support in case of problems with the Endpoint Agent component, Technical Support staff may ask you to perform the following actions for debugging purposes (including in Technical Support Mode):
- Activate collection of extended diagnostic information.
- Modify the settings of individual application components.
- Modify the settings for storing and sending the obtained diagnostic information.
- Configure network traffic to be intercepted and saved to a file.
Technical Support staff will provide all the information needed to perform these operations (description of the sequence of steps, settings to be modified, configuration files, scripts, additional command line functionality, debugging modules, special-purpose utilities, and other resources) and inform you about the scope of data obtained for debugging purposes. The retrieved diagnostic information is saved on the user's computer. The retrieved data is not automatically sent to Kaspersky.
The operations listed above should be performed only when instructed by and under the supervision of Technical Support experts. Unsupervised changes to application settings performed in ways other than those described in this manual or according to the instructions of Technical Support experts can slow down or crash the operating system, reduce computer security, or compromise the availability and integrity of data being processed.
Selecting a tenant to manage in the Endpoint Agents section
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, prior to using the Endpoint Agents section, you must select the tenant whose data you want to view.
To select a tenant to manage in the Endpoint Agents section:
- In the upper part of the application web interface menu, click the arrow next to the name of the tenant.
- In the drop-down list, select a tenant.
Data for the selected tenant is displayed. If you want to select a different tenant, repeat the steps to select the tenant.
Page top
Viewing the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component on a standalone Central Node server
The table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is located in the Endpoint Agents section of the application web interface window.
The table can display the following data:
- Number of hosts and activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component:
- Critical inactivity is the number of hosts from which latest data was received a very long time ago.
- Warning is the number hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Normal activity is the number of hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Host—Name of the host with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Servers—Names of servers to which the host with the Endpoint Agent component is connected.
This field is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- IP—IP address of the computer where the Endpoint Agent component is installed.
- OS—Version of the operating system that is installed on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Version is the version of the application that is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
- Activity—Activity indicator of the Endpoint Agent component. Possible values:
- Normal activity for hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Warning for hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity for hosts from which latest data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Last connection for the date and time of the last connection of the Endpoint Agent component to the Central Node server.
Clicking a link in a column of the table opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Viewing information about a host
To view information about a host with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Select the host for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the host.
The window contains the following information:
- In the Host section:
- Name is the name of the host with the Endpoint Agent component.
- IP is the IP address of the host where the Endpoint Agent component is installed.
- OS is the version of the operating system on the host with the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- Server—Name of the SCN or PCN server. Only displayed in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- In the Endpoint Agent section:
- Version is the version of the application that is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
- Activity is the activity indicator of the Endpoint Agent component. Possible values:
- Normal activity for hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Warning for hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity for hosts from which latest data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Connected to server—Name of the Central Node, SCN, or PCN server to which the host is connected.
- Last connection—time of the last connection to the Central Node, SCN, or PCN server.
- License key status is the status of the license key of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component.
The following action is available by clicking the links with the host name and its IP address: Copy value to clipboard.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Host link to open the filter configuration window.
- If you want to display only isolated hosts, select the Show isolated Endpoint Agents only check box.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the host name.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that have been isolated from the network
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that are isolated from the network:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Host link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select the Show isolated Endpoint Agents only check box.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by PCN and SCN server names
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter or find hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component based on the names of PCN and SCN servers to which those hosts are connected.
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by the names of PCN and SCN servers:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Servers link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select check boxes next to names of servers by which you want to filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by computer IP address
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by IP address of the computer on which the application is installed:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the IP link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the computer IP address. You can enter the IP address or subnet mask in IPv4 format (for example,
192.0.0.1or192.0.0.0/16). - To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by operating system version on the computer
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by version of the operating system installed on the computer:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the OS link to open the filter settings window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the operating system version.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version
You can filter hosts by version of the application that is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Version link to open the filter settings window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the entry field, specify one or more characters of the version of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Activity link to open the filter configuration window.
Select check boxes next to one or multiple activity indicators:
- Normal activity, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was recently received.
- Warning, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Quickly creating a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To quickly create a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Do the following to quickly add filter conditions to the filter being created:
- Position the mouse cursor on the link containing the table column value that you want to add as a filter condition.
- Left-click it.
This opens a list of actions to perform on the value.
- In the list that opens, select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value, if you want to include this value in the filter condition.
- Exclude from filter, if you want to exclude the value from the filter condition.
- If you want to add several filter conditions to the filter being created, perform the actions to quickly add each filter condition to the filter being created.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
Resetting the filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To clear the Endpoint Agent host filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
Configuring activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component
Users with the Local administrator and Administrator roles can define what durations of inactivity of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component are to be considered normal, low, or very low activity, and can configure the activity indicators for the application. Users with the Security auditor role can only view the settings of application activity indicators. Users with the Senior security officer or Security officer role can see activity indicators that you configured for the Endpoint Agent component in the Activity field of the Endpoint Agent host table in the Endpoint Agents section of the application web interface.
To configure activity indicators for the Endpoint Agent component:
- Sign in to the application web interface under the Local administrator, Administrator or Senior security officer account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agents subsection.
- In the fields under the section name, enter the number of days of inactivity of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that you want to display as Warning and Critical inactivity.
- Click Apply.
Activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component are configured.
Removing hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To remove one or more hosts from the Endpoint Agents table:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Select check boxes next to one or more hosts that you want to remove. You can select all hosts by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Delete.
- This opens the action confirmation window; in that window, click Yes.
The selected hosts are removed from the Endpoint Agents table.
When hosts are removed the following changes are made in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- You cannot create a task, prevention rule, or network isolation rule for a removed host.
- If a prevention rule was previously created for a host, its name in the rule window (the Prevent on field) is hidden when the host is removed. The rule continues to apply.
If this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the host name is restored in the Prevent on field and the prevention rule is applied to it again.
- If a network isolation rule was previously created for a host, it continues to apply until the time specified in the rule expires.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node, the rule is reapplied to this host.
- The metadata of objects quarantined on the remote host are deleted from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Quarantine.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the metadata of objects in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Quarantine are not restored. You can avoid Quarantine filling up on a host by clearing it on command line or in Kaspersky Security Center. For details, see the Help of the application that you are using in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
- If an object was quarantined by the Quarantine file task on one host only and that host was removed, the Restore all button in task window is inactive because the file cannot be restored on a removed host.
Event search by the name of the removed host remains available.
Automatic removal of inactive hosts
You can enable or disable the automatic removal of inactive hosts from the Endpoint Agents table. Inactive hosts are hosts that have not connected to the Central Node server for the configured time.
To enable or disable the automatic removal of hosts from the Endpoint Agents table:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agents subsection.
- Under Delete inactive hosts automatically, do the following:
- If you want to enable this functionality, move the Delete hosts toggle switch to Enabled.
- If you want to enable this functionality, move the Delete hosts toggle switch to Disabled.
- If you have enabled this functionality, in the Delete after field, specify the number of days after which hosts that have not connected to the Central Node component must be considered inactive.
The minimum value is 1 and the maximum value is 365.
Automatic removal of inactive hosts is enabled or disabled.
If the value specified in the Delete after field is less than the values specified in the Warning and/or Critical inactivity fields under Activity indicators, hosts are removed earlier than an inactivity warning is displayed in the Dashboard section.
When hosts are removed the following changes are made in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- You cannot create a task, prevention rule, or network isolation rule for a removed host.
- If a prevention rule was previously created for a host, its name in the rule window (the Prevent on field) is hidden when the host is removed. The rule continues to apply.
If this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the host name is restored in the Prevent on field and the prevention rule is applied to it again.
- If a network isolation rule was previously created for a host, it continues to apply until the time specified in the rule expires.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node, the rule is reapplied to this host.
- The metadata of objects quarantined on the remote host are deleted from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform quarantine.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the metadata of objects in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform quarantine are not restored. You can avoid quarantine filling up on a host by clearing it on command line or in Kaspersky Security Center. For details, see the Help of the application that you are using in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
- If an object was quarantined by the Quarantine file task on one host only and that host was removed, the Restore all button in the task window is inactive because the file cannot be restored on a removed host.
Event search by the name of the removed host remains available.
Supported interpreters and processes
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application monitors the execution of scripts by the following interpreters:
- cmd.exe
- reg.exe
- regedit.exe
- regedt32.exe
- cscript.exe
- wscript.exe
- mmc.exe
- msiexec.exe
- mshta.exe
- rundll32.exe
- runlegacycplelevated.exe
- control.exe
- explorer.exe
- regsvr32.exe
- wwahost.exe
- powershell.exe
- java.exe and javaw.exe (only if started with the –jar option)
- InstallUtil.exe
- msdt.exe
- python.exe
- ruby.exe
- rubyw.exe
Information about the processes monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application is presented in the table below.
Processes and the file extensions that they open
Process |
File extensions |
|---|---|
winword.exe |
rtf doc dot docm docx dotx dotm docb |
excel.exe |
xls xlt xlm xlsx xlsm xltx xltm xlsb xla xlam xll xlw |
powerpnt.exe |
ppt pot pps pptx pptm potx potm ppam ppsx ppsm sldx sldm |
acrord32.exe |
|
wordpad.exe |
docx |
chrome.exe |
|
MicrosoftEdge.exe |
Configuring integration with the Sandbox component
You can connect one Sandbox component to multiple Central Node components.
The following procedure is used to configure the Sandbox component connection with the Central Node component:
- Creating a request to connect to the Sandbox component
You can create a request in the application web interface under an administrator account. If you have several Central Node components installed on the server, you need to create a request for each server with the Central Node component that you want to connect to the Sandbox component. If the Central Node component is deployed as a cluster, you can create a request for connection from any server in the cluster.
- Processing a connection request in the Sandbox web interface
You can accept or reject each request.
After configuring the connection, the Sandbox server needs 5 to 10 minutes to get ready for operation. During this time, the System health window of the application web interface display a warning: Default configuration error. When the server is ready for operation, the warning disappears.
Viewing the table of servers with the Sandbox component
Users with the Security auditor role can view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
The table of servers with the Sandbox component is located in the Sandbox servers section, on the Servers tab of the application web interface window.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
The Server list table contains the following information:
- IP and name—IP address or fully qualified domain name of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Certificate fingerprint—Certificate fingerprint of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Authorization—Status of the request to connect to the Sandbox component.
- Status—Status of the connection to the Sandbox component.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
Page top
Creating a request to connect to the server with the Sandbox component
To create a request to connect to the server with the Sandbox component through the application web interface:
- Select the Sandbox servers section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the upper-right corner of the window, click the Add button.
This opens the Sandbox server connection window.
- In the IP field, specify the IP address of the server with the Sandbox component to which you want to connect.
- Click Get certificate fingerprint.
The workspace displays the fingerprint of the certificate of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Compare the obtained certificate fingerprint with the fingerprint indicated in the Sandbox web interface in the KATA authorization section in the Certificate fingerprint field.
If the certificate fingerprints match, perform the next steps of the instructions.
If certificate fingerprints do not match, confirming the connection is not recommended. Make sure the data you entered is correct.
- In the Name field, specify the Sandbox component name that will be displayed in the web interface of the Central Node component.
This name is not related to the name of the host where the Sandbox is installed.
- If you want to activate a connection with Sandbox immediately after connecting, select the Enable check box.
- Click Add.
The connection request is displayed in the web interface of the Sandbox component.
Page top
Enabling and disabling a connection with the Sandbox component
To make a connection with the Sandbox component active or to disable it:
- Select the Sandbox servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The table of servers with Sandbox components is displayed.
- In the row containing the relevant server in the Status column, perform one of the following actions:
- If you want to activate a connection with the Sandbox component, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
- If you want to disable a connection with the Sandbox component, set the toggle switch to Disabled.
- Click Apply.
The connection with the Sandbox component will become active or will be disabled.
Page top
Deleting a connection with the Sandbox component
To delete a connection with the Sandbox component:
- Select the Sandbox servers section in the window of the application web interface.
This displays the table of computers on which the Sandbox component is installed.
- Select the check box in the line containing the Sandbox component whose connection you want to delete.
- In the upper-right corner of the window, click the Delete button.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The connection with the Sandbox component will be deleted.
Page top
Configuring integration with external systems
You can configure integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with external systems to scan files stored in those systems. Their scan results are displayed in the alerts table.
The role of an external system can be served by a mail sensor, such as Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway or Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server. The mail sensor sends email messages to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform for processing. Based on the results of processing of email messages in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, the mail sensor may block the transfer of messages.
Integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with external systems involves the following procedure:
- Enter the integration settings and create an integration request from the external system.
For more details about entering integration settings for the mail sensor, please refer to the Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway Help or the Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server Help.
To integrate other external systems, use the REST API.
- Confirm integration for Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
External systems must use unique certificates for authorization on the server with the Central Node component. If this is the case, a single integration request will be displayed in the interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. To connect multiple external systems that have the same IP address, you must use a unique certificate for each external system.
When using one certificate, you can configure integration with only one external system.
- Check the connection between the external system and Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Viewing the table of external systems
The table of external systems is in the External systems section of the application web interface window. The table contains the following information:
- Sensor—IP address or domain name of the external system server.
- Type—Type of external system (mail sensor or other system).
- Name—Name of the integrated external system that is not a mail sensor.
A dash is displayed in this column for a mail sensor.
- ID—ID of the external system.
- Certificate fingerprint—Fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the server with the external system used to establish an encrypted connection with the server hosting the Central Node component.
The certificate fingerprint of the server with the Central Node component is displayed in the upper part of the window in the Certificate fingerprint field.
- State—State of the integration request.
Processing a request from an external system
To process an integration request from an external system:
- Select the External systems section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table displays the already connected external systems, and requests for integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from external systems.
- In the line containing the integration request, perform one of the following actions:
- If you want to configure integration with the external system, click the Accept button.
- If you do not want to configure integration with the external system, click the Reject button.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The integration request from the external system will be processed.
Page top
Removing an external system from the list of those allowed to integrate
After you have accepted an integration request from an external system, you can remove it from the list of those allowed to integrate. If this is the case, the connection between Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform and the external system will be terminated.
To remove an external system from the list of systems allowed to integrate:
- Select the External systems section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list displays the already added external systems and the requests to integrate with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from external systems.
- Click the Delete button in the line containing the integration request from the external system that you want to remove.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The external system will be removed from the list of those allowed to integrate.
Page top
Configuring the priority for processing traffic from mail sensors
You can enable or disable the maximum priority for processing traffic from mail sensors.
To enable or disable the maximum priority for processing traffic from mail sensors:
- Select the External systems section in the window of the application web interface.
- Do one of the following:
- Turn on the toggle switch next to the name of the Maximum scan priority parameter if you want to enable the maximum priority for processing traffic from mail sensors.
- Turn off the toggle switch next to the name of the Maximum scan priority parameter if you want to disable the maximum priority for processing traffic from mail sensors.
The priority for processing traffic from mail sensors will be configured.
Page top
Configuring integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response
Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response (hereinafter also "MDR") detects and prevents fraud in the client's infrastructure. MDR provides continuous managed protection and allows organizations to automatically discover hard-to-detect threats while freeing up IT security personnel to work on issues requiring their participation.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform obtains data and sends it to Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response using a Kaspersky Security Network stream. Therefore, participation in KSN is necessary for configuring integration with MDR.
Integration with MDR is only available if at least one KATA or EDR license is active. If only one license key (only KATA or only EDR) is added in the application statistics is limited to the functionality provided by that license. If both license keys are added in the application, complete statistics is sent.
Before configuring the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with the MDR application, you must download an archive with the configuration file from the MDR portal.
Only the Local Administrator and the KATA Web Interface Administrator can configure the integration with MDR.
Enabling the MDR integration
Make sure that an active license key is added and participation in KSN is configured in the application. Otherwise the MDR integration is unavailable.
To enable integration with MDR:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- Under MDR integration, click Upload to upload the configuration file.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the archive you downloaded during registration at the MDR portal and click Open.
The following information about the MDR license is displayed in the window:
- Serial number.
- Expiration date.
- Days remaining.
Integration with MDR is enabled. Integration settings configured in the configuration file are applied to all connected Sensor components. MDR starts using alert statistics sent via the KSN stream.
Page top
Disabling the MDR integration
To disable integration with MDR:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- Under MDR integration, click Delete file.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The configuration file is deleted and the MDR integration is disabled. Statistics is still sent to KSN servers, but this information is not used by MDR.
Page top
Replacing the MDR configuration file
To replace the MDR configuration file:
- Log in to the application web interface with the administrator account.
- Select the Settings section, KSN/KPSN and MDR subsection.
- Under MDR integration, click Replace file.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a new archive containing a configuration file and click Open.
MDR license information is updated in the application web interface.
The configuration file is replaced. New integration settings are applied to all connected Sensor components.
Page top
Configuring integration with an SIEM system
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform can publish information about user actions in the application web interface as well as alerts to a already in use at your organization using the
protocol.You can use
for data transmission.If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, you can configure fault-tolerant integration with an external system using one of the following options:
- Using the Round Robin function.
- Configure the settings of the external system so that the external system switches between the IP addresses of the cluster servers if a network error occurs.
To configure fault-tolerant integration with an external system using the Round Robin function:
- Configure Round Robin on the DNS server for the domain name corresponding to the Central Node cluster.
- Specify this domain name in the mail server settings.
Integration with the mail server will be configured based on the domain name. The mail server will communicate with a random server in the cluster. If this server fails, the mail server will communicate with another healthy server in the cluster.
Enabling and disabling information logging to a remote log
You can configure the logging of information about user actions in the web interface and alerts to a remote log. The log file is stored on the server on which the SIEM system is installed. To write to the remote log, you must configure the integration with the SIEM system.
To enable or disable the logging of information about user actions in the web interface and alerts to the remote log:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, SIEM system subsection.
- If you want to enable / disable the recording of information about user actions in the web interface to the remote log, do one of the following:
- If you want to enable recording of information about user actions in the web interface, select the Activity log check box.
- If you want to disable the recording of information about user actions in the web interface, clear the Activity log check box.
- If you want to enable / disable the recording of information about alerts to the remote log, do one of the following:
- If you want to enable recording of alert information, select the Alerts check box.
- If you want to disable recording of alert information, clear the Alerts check box.
You can select both check boxes simultaneously.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
Information logging in the remote log is enabled or disabled.
Users with the Security auditor role can only view information about remote logging settings.
Page top
Configuring the main settings for SIEM system integration
To configure the main settings for SIEM system integration:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, SIEM system subsection.
- Select the Activity log and/or Alerts check boxes.
You can select one check box or both check boxes.
- In the Host/IP field, enter the IP address or host name of the server of your SIEM system.
- In the Port field, enter the port number used for connecting to your SIEM system.
- In the Protocol field, select TCP or UDP.
- In the Host ID field, enter the host ID. The host with that ID is specified as the alert source in the log of the SIEM system.
- In the Heartbeat field, enter the interval for sending messages to the SIEM system.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
The main settings of integration with the SIEM system will be configured.
Users with the Security auditor role can only view information about the SIEM system integration settings.
Page top
Uploading a TLS certificate
To upload a TLS certificate for encrypting the connection with the SIEM system:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, SIEM system subsection.
- In the TLS encryption section, click the Upload button.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a TLS certificate file to download and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window.
The TLS certificate is added to the application.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
The uploaded TLS certificate will be used to encrypt the connection with the SIEM system.
Page top
Enabling and disabling TLS encryption of the connection with the SIEM system
To enable or disable TLS encryption of the connection with the SIEM system:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, SIEM system subsection.
- Select the Activity log and/or Alerts check boxes.
You can select one check box or both check boxes.
- In the TLS encryption section, perform one of the following actions:
- Turn on the toggle switch next to the name of the TLS encryption parameter if you want to enable TLS encryption of the connection with the SIEM system.
- Turn off the toggle switch next to the name of the TLS encryption parameter if you want to disable TLS encryption of the connection with the SIEM system.
The toggle switch next to the name of the TLS encryption setting can be used only if a TLS certificate is loaded.
- Click Apply in the lower part of the window.
TLS encryption of the connection with the SIEM system will be enabled or disabled.
Page top
Content and properties of syslog messages about alerts
Information about each alert is transmitted in a separate syslog category (syslog facility) that is not used by the system to deliver messages from other sources. Information about each alert is transmitted as a separate syslog message in CEF format. If the alert was generated by the Targeted Attack Analyzer module, information about that alert is transmitted as multiple separate syslog messages in CEF format.
The default maximum size of a syslog message about an alert is 32 KB. Messages that exceed the maximum size are truncated at the end.
The header of each syslog message about an alert contains the following information:
- Format version.
Current version number:
0. Current field value:CEF:0. - Vendor.
Current field value:
AO Kaspersky Lab. - Application name.
Current field value:
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. - Application version
Current field value: 6.0.0-200.
- Alert type.
See the table below.
- Event name.
See the table below.
- Alert importance.
Allowed field values:
Low,Medium,Highor0(forheartbeatmessages). - Additional information.
Example:
CEF:0|AO Kaspersky Lab| Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform |6.0.0-200|url_web| URL from web detected|Low|
The body of a syslog message about an alert matches the information about the alert that is displayed in the application web interface. All fields are presented in the "<key>=<value>" format. Depending on whether the alert occurred in network traffic or mail traffic, and depending on the technology that generated the alert, various keys may be transmitted in the body of a syslog message. If the value is empty, the key is not transmitted.
The keys, as well as their values contained in a message, are presented in the table below.
Information about an alert in syslog messages
Alert type |
Alert name and description |
Key and description of its value |
|---|---|---|
|
A file was detected in network traffic. |
|
|
A file was detected in mail traffic. |
|
|
An alert was generated by the Intrusion Detection System module. |
|
|
An alert was generated by URL Reputation technology or Sandbox in network traffic. |
|
|
An alert was generated by URL Reputation technology or Sandbox in mail traffic. |
|
|
An alert was generated by URL Reputation technology in DNS traffic. |
|
|
The alert was generated by the Endpoint Agent component on the user's computer and contains a file. |
|
|
The alert was generated while carrying out an IOC scan of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for Windows. This type of alert is available if you are using KEDR functionality. |
|
|
Alert resulting from the IOA analysis of events. This type of alert is available if you are using KEDR functionality. |
|
|
The alert was generated while carrying out a YARA scan of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for Windows. This type of alert is available if you are using KEDR functionality. |
|
|
Periodic message containing the state of components. |
|
Managing the activity log
Some user actions in the application web interface can cause errors in the operation of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. You can enable logging of user action information in the application web interface and if necessary, view the information by downloading log files.
Enabling and disabling the recording of information in the activity log
To enable or disable the logging of information about user actions in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface to the activity log:
- Select the Reports section, Activity log subsection in the window of the application web interface.
- Do one of the following:
- Set the Activity log toggle switch to the Enabled position if you want to enable the logging of information about user actions in the application web interface.
- Set the Activity log toggle switch to the Disabled position if you want to disable the logging of information about user actions in the application web interface.
This function is enabled by default.
Information is logged for 30 days in the user_actions.log file. After 30 days, the user_actions.log file is saved on the Central Node server in the /var/log/kaspersky/apt-base/ directory with the name user_actions.log<month>. A new file named user_actions.log is created to record information for the current month. Each file is retained for 90 days and then deleted.
To view activity log files, you must download them.
You can configure the logging of information about user activity in the application web interface to a remote log. The remote log is saved on the server on which a SIEM system is installed. The settings of integration with the SIEM system must be configured to write to the remote log.
In distributed solution mode, information about user actions in the application web interface is recorded in the log of the same server for which the users are managing the web interface. Information about the actions of PCN server users that affect the settings of SCN servers is recorded in the PCN server log.
Users with the Security auditor role can only view the settings for logging information to the activity log.
Page top
Downloading the activity log file
To download the activity log file:
- Select the Reports section, Activity log subsection in the window of the application web interface.
- Click Download.
Log files are saved on your local computer in your browser's downloads folder. The files are downloaded as a ZIP archive.
In distributed solution mode, you can download log files only for the server for which you are managing the web interface.
Page top
Content and properties of CEF messages about user activity in the web interface
The header of each message contains the following information:
- Format version.
Current version number:
0. Current field value:CEF:0. - Vendor.
Current field value:
AO Kaspersky Lab. - Application name.
Current field value:
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. - Application version
Current field value: 6.0.0-200.
- Event type.
See the table below.
- Event name.
See the table below.
- Event importance.
Current field value:
Low.Example:
CEF:0|AO Kaspersky Lab|Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform|6.0.0-200|tasks|Managing tasks|Low|
All fields of the CEF message have the "<key>=<value>" format. The keys, as well as their values contained in a message, are presented in the table below.
Event information in CEF messages
Event type |
Event name and description |
Key and description of its value |
|---|---|---|
|
Connecting the Sensor component to the Central Node server, modifying component settings. |
|
|
Connecting the Sandbox component to the Central Node server. |
|
|
Configuring integration with external systems. |
|
|
Configuring participation in Kaspersky Security Network, enabling or disabling the usage of Kaspersky Private Security Network, and configuring integration with Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response. |
|
|
Operations with YARA rules. |
|
|
Operations with IOC rules. |
|
|
Operations with IDS rules. |
|
|
Operations with TAA (IOA) rules. |
|
|
Operations with Sandbox rules. |
|
|
Operations with prevention rules. |
|
|
Operations with scan exclusion rules. |
|
endpoint_agents |
Managing Endpoint Agent hosts Operations with hosts on which the Endpoint Agent component is installed. |
|
|
Operations with tasks. |
|
|
Network isolation of Endpoint Agent hosts. |
|
|
Modifying Central Node server settings. |
|
|
The set of virtual machine operating systems is changed to <version of the operating system set>. |
|
|
Modifying the settings of Primary Central Node and Secondary Central Node servers in distributed solution and multitenancy mode. |
|
|
Actions on user accounts. |
|
|
Configuring email notifications. |
|
|
Managing the license key. |
|
If an operation is performed on over 30 objects simultaneously, only one entry is logged for this operation. The entry includes the information about the operation and the number of objects on which it was performed.
Page top
Updating application databases
Application databases (hereinafter also referred to as "databases") are files with records used by the application components and modules to detect events occurring in your organization's IT infrastructure.
Virus analysts at Kaspersky detect hundreds of new threats daily (including "zero-day" exploits), create records to identify them, and include them in database updates packages ("update packages"). Update packages consist of one or more files containing records to identify threats that were detected since the previous update package was released. We recommend that you regularly receive update packages. When the application is installed, the database release date is the same as the application release date, and therefore you must update the databases immediately after installing the application.
The application automatically looks for new update packages on Kaspersky update servers once every 30 minutes. By default, if for some reason application databases are not updated for 24 hours, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform displays this information in the Dashboard section of the window of the application web interface.
If the version of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is not supported, databases are not updated. You can see which versions of the application are currently supported on the application lifecycle page.
The update functionality (including anti-virus signature updates and code base updates), as well as the KSN functionality may be unavailable in the territory of the USA.
Selecting a database update source
You can select the source from which the application will download database updates. The update source may be the Kaspersky server, or a network folder or local folder on one of the computers of your organization.
To select a database update source:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, General settings subsection.
- In the Database update section, in the Update source drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- Kaspersky update server.
The application connects to Kaspersky update server over HTTP and downloads up-to-date databases.
- Kaspersky update server (secure connection).
The application connects to Kaspersky update server over HTTPS and downloads up-to-date databases. It is recommended to use HTTPS for database updates.
- Custom server.
The application connects to your FTP or HTTP server or to the folder with application databases on your computer to download up-to-date databases.
- Kaspersky update server.
- If you have selected Custom server, in the field under the name of this setting, enter the URL of the update package on your HTTP server or the full path to the folder on your computer containing the application database update package.
- Click Apply.
The application database update source is applied.
Page top
Updating databases manually
To start the database update manually:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, General settings subsection.
- In the Database update section, click the Start button.
- Click Apply.
The application database update is started. The progress of the update will be displayed to the right of the button.
Page top
Creating a list of passwords for archives
The application does not scan password-protected archives. You can create a list of the most frequently encountered passwords for archives that are used when exchanging files within your organization. If you do so, the application will try passwords from the list when scanning an archive. If one of the passwords match, the archive will be unlocked and scanned.
The list of passwords set in application settings is also transmitted to the server with the Sandbox component.
To create a list of archive passwords:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Passwords for archives subsection.
- In the Passwords for archives field, enter the passwords that the application will use for password-protected archives.
Enter each password on a new line. You can enter up to 50 passwords.
- Click Apply.
The list of passwords for archives will be created. When scanning PDF files and files of Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint that are password protected, the application will use the passwords from the defined list.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of passwords for archives, but cannot edit it.
Page top
Configuring integration with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1
You can configure the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1 to unwrap encrypted SSL/TLS traffic. Integrating Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with ArtX TLSProxy 1.9.1 improves the security and performance of infrastructure.
To configure the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1:
- Specify and edit integration settings in ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1.
For more details on specifying and editing integration settings in ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1, see the ArtX TLSproxy User Manual on the ArtX website.
- Create the erspan.netdev file in the /etc/systemd/network directory with the following contents:
[NetDev]Name=<name of the ERSPAN interface>Kind=erspan[Tunnel]Independent=trueERSPANIndex=<index or port number associated with the ERSPAN traffic source port>Local = <local fixed IP address of the network interface on which you are configuring ERSPAN traffic transmission>Remote = <IP address of the server hosting the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application on which you want to process ERSPAN traffic>Key = <Sequential number or key of the GRE header>.If not used, enter 0 as the value.SerializeTunneledPackets=true - Create the erspan.network file in the /etc/systemd/network directory with the following contents:
[Match]Name=<name of the ERSPAN interface>[Network]Address = <local IP address of the network interface/network interface mask> - Restart the server with the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application on which you are configuring the integration with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1.
- Go to the ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1 application and specify the network interfaces that you configured.
The settings in the erspan.netdev and erspan.network files must match the settings that you specified in ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1.
Integration with ArtX TLSproxy 1.9.1 is configured.
Page top
For security officers: Getting started with the application web interface
This section is intended for specialists who are in charge of providing data security within an organization. It contains information and instructions on configuring resources for the security of a corporate IT infrastructure and timely detection of threats.
The application allows multiple security officers to work together.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Interface
The application is managed through the web interface. Sections of the application web interface differ depending on the role of the user: Administrator or Senior security officer / Security officer / Security auditor.
The window of the application web interface contains the following:
- Sections in the left part and in the lower part of the application web interface window.
- Tabs in the upper part of the application web interface window for certain sections of the application.
- The workspace in the lower part of the application web interface window.
Sections of the application web interface window
The application web interface provides the following sections for users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, and Security auditor roles:
- Dashboard. Contains Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Monitoring data.
- Alerts Contains information about alerts in the network of the tenant to which you have access.
- Threat Hunting. Contains information about events found on hosts of the tenant to which you have access.
- Tasks. Contains information about tasks that you can use to manage files and application on hosts.
- Prevention. Contains information about policies that you can use to manage preventions of files running on selected hosts.
- Custom rules: TAA, IDS, IOC, and YARA. Contains information for managing user-defined rules.
- Storage: Files, and Quarantine. Contains information for managing objects in quarantine and Storage.
- Endpoint Agents. Contains information about computers with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component and their settings.
- Reports: Generated reports and Templates. Contains a report builder and a list of generated reports about alerts.
- Settings: IOC scanning schedule, Endpoint Agents, KPSN reputation database, Notification rules, VIP status, Exclusions, Passwords for archives, and License. Contains information on the IOC scan schedule, and the settings for publishing objects in KPSN and assigning the VIP status to alerts based on information contained in alerts, the list of allowed objects, and IDS and TAA (IOA) rules excluded from scanning, passwords of archives, and added keys.
Workspace of the application web interface window
The workspace displays the information you choose to view in the sections and on the tabs of the application web interface window. It also contains control elements that you can use to configure how the information is displayed.
Selecting a tenant to manage in the web interface of the application
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode with a Senior security officer or Security officer account, before you begin using the web interface, you must select the tenant that you want to manage in the application web interface.
To select a tenant to manage in the web interface of the application:
- In the upper part of the application web interface menu, click the arrow next to the name of the tenant.
- In the Select tenant drop-down list, select a tenant.
You can also start typing the name of the tenant in the search box and select the tenant from the list of search results.
All actions in the application web interface are applied to the selected tenant. If you want to select a different tenant, repeat the steps to select the tenant.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot select a tenant to manage in the web interface.
Page top
Monitoring the performance of the application
You can monitor application operation using the widgets in the Dashboard section of the application web interface window. You can add, delete, and move widgets, configure the display scale of widgets, and select the data display period.
About widgets and layouts
You can use widgets to monitor application operation.
A layout is the appearance of the workspace of the application web interface window in the Dashboard section. You can add, delete, and move widgets in the layout, as well as configure the scale of widgets.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, this section displays information for the selected tenant.
By default, this section displays information only on alerts that were not processed by users. To also display information on processed alerts, turn on the Processed switch in the upper-right corner of the window.
The Dashboard section displays the following widgets:
- Alerts:
- Alerts by status. Displays the alert status depending on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user processing the alert and on whether or not this alert has been processed.
- Alerts by technology. Displays the names of the application modules or components that generated the alert.
- Alerts by attack vector. Displays detected objects based on the vector of the attack.
- VIP alerts by importance. Displays the importance of alerts with VIP status depending on the impact that these alerts may have on the security of computers or the corporate LAN based on Kaspersky experience.
- Alerts by importance. Displays the importance of alerts for users of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform depending on the impact that these alerts may have on the security of computers or the corporate LAN based on Kaspersky experience.
The left part of each widget lists attack vectors, alert importance levels, alert status, and technologies that generated the alerts. The right part of each widget displays the number of times the alerts were triggered during the selected period for data display in widgets.
To go to the Alerts section of the application web interface and view related alerts, click the link with the name of the attack vector, alert importance level, and technology that generated the alert. Alerts are filtered based on the selected element.
- Top 10:
- Domains. 10 domains most frequently seen in alerts.
- IP addresses. 10 IP addresses most frequently seen in alerts.
- Email senders. 10 email senders most frequently seen in alerts.
- Email recipients. 10 email recipients most frequently seen in alerts.
- TAA hosts. 10 hosts that occur most frequently in events and alerts generated by the Targeted Attack Analyzer (TAA) technology.
- TAA rules. 10 TAA (IOA) rules that occur most frequently in events and alerts generated by the Targeted Attack Analyzer (TAA) technology.
- Sent to Sandbox by TAA rules. 10 TAA (IOA) rules that most frequently cause Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to send files for scanning by the Sandbox component.
The left part of each widget lists the domains, email addresses of recipients, IP addresses and email addresses of message senders, host names, and TAA (IOA) rule names. The right part of each widget displays the number of times the alerts were triggered during the selected period for data display in widgets.
By clicking the link with the name of each domain, recipient address, IP address, and message sender address, you can go to the Alerts section of the application web interface and view related alerts.
Click the link with the host name and the name of the TAA (IOA) rule to go to the Events section of the application web interface and view related events.
Alerts and events are filtered based on the selected element.
Adding a widget to the current layout
To add a widget to the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Click Widgets.
- This opens the Manage widgets window; in that window, turn on the toggle switch next to the widget that you want to add.
The widget is added to the current layout.
Moving a widget in the current layout
To move a widget in the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Select the widget that you want to move within the layout.
- Left-click and hold the upper part of the widget to drag and drop the widget to a different place in the layout.
- Click Save.
The current layout is saved.
Removing a widget from the current layout
To remove a widget from the current layout:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Click the
 icon in the upper right corner of the widget that you want to remove from the layout.
icon in the upper right corner of the widget that you want to remove from the layout.The widget is removed from the workspace of the application web interface window.
- Click Save.
The widget is removed from the current layout.
Saving a layout to PDF
To save a layout to PDF:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Save as PDF.
This opens the Saving as PDF window.
- In the lower part of the window, in the Layout drop-down list, select the page orientation.
- Click Download.
The layout in PDF format is saved to the hard drive of your computer in the downloads folder of the browser.
- Click Close.
Configuring the data display period in widgets
You can configure the display of data in widgets for the following periods:
- Day
- Week
- Month
To configure the display of data in widgets for a day (from 00:00 a.m. to 11:59 p.m.):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Day.
- In the calendar to the right of the Day period name, select the date for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
To configure the display of data on widgets for a week (Monday through Sunday):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Week.
- In the calendar to the right of the Week period name, select the week for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
To display data display in widgets for a month (calendar month):
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, in the drop-down list of data display periods, select Month.
- In the calendar to the right of the Month period name, select the month for which you want to display data in the widget.
All widgets on the Dashboard page display data for the period you selected.
Configuring the widget display scale
You can configure the display scale for "Alerts" type widgets. The ![]() icon in the upper right corner of a widget means you can configure the scale for that widget.
icon in the upper right corner of a widget means you can configure the scale for that widget.
To configure the display scale for widgets:
- Select the Dashboard section in the application web interface window.
- In the upper part of the window, click the
 button.
button. - In the drop-down list, select Customize.
- Click
 in the upper right corner of the widget.
in the upper right corner of the widget. - In the drop-down list, select one of the following widget display sizes:
- 1x1.
- 2x1.
- 3x1.
The display scale of the selected widget is modified.
- Repeat the steps for all widgets for which you want to set the display scale.
- Click Save.
The display scale of widgets is configured.
Basics of managing "Alerts" type widgets
You can configure the display scale for all "Alerts" type widgets.
The left part of each widget displays the legend for colors used in widgets.
Example: The Alerts by importance widget displays the number of alerts of various importance. Importance—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience. In the Alerts by importance widget, the following colors correspond to importance levels:
|
To the right of the legend, the number of alerts of each type for the selected period for displaying data in widgets is displayed.
By clicking the link with the type of each alert, you can go to the Alerts section of the application web interface and view all alerts of this type. Alerts are filtered based on the specific type.
Example: The Alerts by attack vector widget displays Files from email alerts, which indicate the number of files that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform detected in mail traffic for the selected period. Clicking the Files from email link opens the Alerts section and displays all alerts associated with the detection of files in mail traffic for the selected period. Data will be filtered based on the following parameters: Object type=FILE and Object source=MAIL. |
The right part of each widget displays data columns. The vertical axis shows the number of events, and the horizontal axis shows the date and time of the alert. You can edit the period of data display in widgets and select the tenant for which information is displayed in the widget.
Position your mouse cursor on each data column to display the number of alerts counted for the period represented by the specific column. The number of unprocessed alerts is displayed by default. You can enable the display of processed alerts by selecting the Processed check box in the upper-right corner of the window. In this case, the total number of all alerts will be displayed.
Viewing the working condition of modules and components of the application
If modules or components of the application encounter errors that the administrator is advised to look at, a yellow warning box is displayed in the upper part of the Dashboard section of the application web interface.
Users with the Local administrator, Administrator, or Security auditor roles can gain access to information about the working condition of the Central Node, PCN, or SCN server that the user is currently managing.
Users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, or Security auditor roles can gain access to the following information about the working condition:
- If you are using a standalone Central Node server, the user can access information about the working condition of the Central Node server which the user is currently managing.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, and the user is managing an SCN server, the user can gain access to information about the working condition of that SCN server for tenants to whose data the user has access.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, and the user is managing the PCN server, the user can gain access to information about the working condition of the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that server, for tenants to whose data the user has access.
For details about the working condition of application modules and components,
click View details to open the System health window.
In the System health window, one of the following icons is displayed depending on the working condition of the application modules and components:
 if the modules and components of the application are working normally.
if the modules and components of the application are working normally.- An icon with the number of problems (for example,
 ) if problems are found that the administrator is recommended to pay attention to. In this case, detailed problem information is displayed in the right part of the System health window.
) if problems are found that the administrator is recommended to pay attention to. In this case, detailed problem information is displayed in the right part of the System health window.
The System health window contains the following sections:
- Component health contains information on the operational status of application modules and components, quarantine, and database update on all servers where the application is running.
Example:
If the databases of one or more application components have not been updated in 24 hours, the
 icon is displayed next to the name of the server on which the application modules and components are installed.
icon is displayed next to the name of the server on which the application modules and components are installed.To resolve the problem, make sure that update servers are accessible. If you are using a proxy server to connect to update servers, make sure the proxy server has no errors pertaining to the connection to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform servers.
- Processed—Status of receiving and processing incoming data. The status is generated based on the following criteria:
- State of receiving data from servers with the Sensor component, from the server or virtual machine with the mail sensor, from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Information about exceeding the maximum allowed time that objects wait in the queue to be scanned by application modules and components.
- Connection with servers—Status of the connection between the PCN server and connected SCN servers (displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode).
If problems are detected with the performance of application modules or components and you cannot resolve those problems on your own, please contact Kaspersky Technical Support.
Viewing the alert table
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses a table of alerts to display the detected signs of targeted attacks and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
The table of alerts does not display information on objects which satisfy at least one of the following conditions:
- The object has reputation Trusted in the KSN database.
- The object is digitally signed by a trusted vendor:
- Kaspersky.
- Google.
- Apple.
- Microsoft.
Information about these alerts is saved to the application log. You can view this information.
Information about alerts in the application log is rotated every night when the maximum allowed number of alerts is reached:
- Alerts generated by the (IDS) Intrusion Detection System and (URL) URL Reputation components have a maximum of 100,000 alerts for each component.
- All other alerts have a maximum of 20,000 alerts for each module or component.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, rotation is performed on all SCNs and then synchronization with the PCN is performed. After synchronization, all deleted alerts are automatically deleted from the PCN.
The alerts table is in the Alerts section.
By default, this section displays information only on alerts that were not processed by users. To also display information on processed alerts, turn on the Processed switch in the upper-right corner of the window.
You can sort alerts in the table by Created or Updated, Importance, Source, and State columns.
The table of alerts contains the following information:
- VIP specifies if the alert has a status with special access rights. For example, alerts with the VIP status cannot be viewed by program users with the Security officer role.
- Created is the time when the program generated the alert, and Updated is the time when the alert was updated.
 —Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.Alerts can have one of the following importance levels:
- High, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a high level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a high level of importance. - Medium, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a medium level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a medium level of importance. - Low, marked with the
 symbol—the alert has a low level of importance.
symbol—the alert has a low level of importance.
- High, marked with the
- Detected—One or multiple categories of detected objects. For example, when the application detects a file infected with the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad virus, the Detected field shows the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad category for this alert.
- Details—Brief summary of the alert. For example: the name of a detected file or URL address of a malicious link.
- Source—Address of the source of the detected object. For example, this can be the email address from which a malicious file was sent, or the URL from which a malicious file was downloaded.
- Destination—Destination address of a detected object. For example, this can be the email address of your organization's mail domain to which a malicious file was sent, or the IP address of a computer on your corporate LAN to which a malicious file was downloaded.
- Technologies are names of application modules or components that generated the alert.
The Technologies column may indicate the following application modules and components:
- (YARA) YARA.
- (SB) Sandbox.
- (URL) URL Reputation.
- (IDS) Intrusion Detection System.
- (AM) Anti-Malware Engine.
- (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer.
- (IOC) IOC.
- State—Alert status depending on whether or not this alert has been processed by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
Alerts can have one of the following states:
- New for new alerts.
- In process for alerts that are already being processed by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
- Rescan for alerts resulting from a rescan of an object.
- Assigned to is the name of the user to which the alert is assigned.
- Servers is the list of names of servers which created the alert. Servers belong to the tenant that you are managing in the application web interface. This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
If information in table columns is displayed as a link, you can click the link to open a list in which you can select the action to perform on the object. Depending on the type of value of the cell, you can perform one of the following actions:
- Any type of cell value:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- MD5 hash:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256 hash:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Destination IP address:
- Find events.
- Alert state:
- Assign to me.
- Close alert.
The Intrusion Detection System module consolidates information about processed network events in one alert when the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- The name of the triggered rule, version of application databases, and source all match for network events.
- No more than 24 hours elapsed between the events.
One alert is displayed for all network events that meet these conditions. The alert notification contains information only about the first network event.
Page top
Configuring the alert table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the alert table.
To configure the alert table display:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The alert table display is configured.
Page top
Filtering, sorting, and searching alerts
You can filter alerts to be displayed in the table of alerts for one or several columns of the table, or search for alerts in certain table columns according to the search criteria you specify.
You can create, save, and remove filters, and start filtering and searching alerts based on the conditions specified in saved filters.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you cannot save filters on the PCN.
Filters are saved for each user on the server on which they were created.
You can also sort alerts in the table by Created or Updated, Importance, Source, and State columns.
By default, this section displays information only on alerts that were not processed by users. To also display information on processed alerts, turn on the Processed switch in the upper-right corner of the window.
Filtering alerts by VIP status
You can filter alerts and search for alerts in the alerts table based on the ![]() criterion, which indicates whether the alert has a status with special access rights. For example, alerts with the VIP status cannot be viewed by program users with the Security officer role.
criterion, which indicates whether the alert has a status with special access rights. For example, alerts with the VIP status cannot be viewed by program users with the Security officer role.
To filter alerts by VIP status:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the heading of the VIP column to expand the list of filter settings.
- Configure alert filtering settings:
- If you want the table of alerts to display only alerts that have the VIP status, select VIP.
- If you want the table of alerts to display all alerts, select All.
If neither is selected, the table shows all alerts.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by time
You can filter alerts and search the alert table by Created attribute, which is the time when the alert was created, as sell as by Updated attribute, which is the time when the alert was updated.
To filter or search alerts by time:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Created link to open the list of alert display periods.
- Select one of the following alert display periods from the Time list:
- All if you want the application to display all alerts in the table.
- Last hour if you want the application to display alerts that occurred during the last hour in the table.
- Last day if you want the application to display alerts that occurred during the last day in the table.
- Custom range if you want the application to display alerts that occurred during the period you specify in the table.
- If you have selected the Custom range event display range, do the following:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the alert display period.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering alerts by level of importance
You can filter alerts based on the ![]() Importance criterion, which indicated the alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
Importance criterion, which indicated the alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
To filter alerts by importance:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click
 to expand the filter settings list.
to expand the filter settings list. - Select one or several of the following alert importance levels:
- Low—Alert has a low level of importance.
- Medium—Alert has a medium level of importance.
- High—Alert has a high level of importance.
If no value is selected, the table shows alerts of all importance levels.
- Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by categories of objects detected
You can filter alerts and search the alerts table for specific alerts based on the Detected criterion, which indicates one or multiple categories of the object detected in the event. For example, if you want the table to display alerts about files infected by a specific virus, you can set a filter based on the name of this virus.
To filter or search alerts by category of the detected object:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Detected link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following alert filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, type the name of a category (for example, Trojan) or several characters from the name of a category.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by obtained information
You can filter alerts and search the alerts table for specific alerts based on the Details criterion, which refers to brief information about the alert. For example: the name of a detected file or URL address of a malicious link.
To filter or search alerts by obtained information:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Details link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select one of the following search criteria:
- Details. The search will encompass all data on the detected object
- ID.
- File name.
- File type.
- MD5.
- SHA256.
- URL.
- Domain.
- User Agent.
- Subject.
- HTTP status.
- Object source.
- Object type.
- Autosend to Sandbox.
- TAA (IOA) rule.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select one of the following alert filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Equal to.
- Not equal to.
- In the text box, enter one or several characters of alert information.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by source address
You can filter alerts and search the alerts table for specific alerts based on the Source criterion, which indicates the alert source address. For example, this can be the email address from which a malicious file was sent, or the IP address of the computer on your corporate LAN to which a malicious file was downloaded.
To filter or search alerts by source address:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Source link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following alert filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Matches
- Not matches
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the alert source address.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by destination address
You can filter alerts and search the alerts table for specific alerts based on the Destination criterion, which indicates the alert destination address. For example, this can be the email address of your organization's mail domain to which a malicious file was sent, or the IP address of a computer on your corporate LAN to which a malicious file was downloaded.
To filter or search alerts by destination address:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Destination link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following alert filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Matches
- Not matches.
- In the text box, type one or more characters of the destination address of the detected objects.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by server name
You can filter alerts and search for alerts in the alerts table based on the Servers criterion, which indicates the names of servers that created the alert.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, servers belong to the tenant that you are managing in the application web interface. Filtering is available only on the PCN.
To filter or search alerts by server name:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click Servers to expand the list of servers which created alerts.
- Select check boxes next to one or multiple server names.
- Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by technology name
You can filter alerts and search the alerts table for specific alerts based on the Technologies criterion, which indicates the names of program modules or components that generated the alert.
To filter alerts by technology name:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the Technologies link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following alert filtering operators:
- Contain if you want the application to display alerts generated by an application module or component that you specify.
- Not contain if you want the application to hide alerts generated by an application module or component that you specify.
- Equal to if you want the application to display alerts generated by an application module or component that you specify.
- Not equal to if you want the application to hide alerts generated by an application module or component that you specify.
- In the drop-down list to the right of the alert filtering operator that you have selected, select the name of the technology which you want to filter alerts:
- (YARA) YARA.
- (SB) Sandbox.
- (URL) URL Reputation.
- (IDS) Intrusion Detection System.
- (AM) Anti-Malware Engine.
- (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer.
- (IOC) IOC.
For example, if you want the application to display alerts generated by the Sandbox component, select the Contain filtering operator and the name of the (SB) Sandbox component.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering and searching alerts by the status of their processing by the user
You can filter alerts and search for them in the table of alerts based on the State criterion—alert status depending on whether or not this alert has been processed by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
To filter or search alerts by the status of their processing by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- To include processed alerts in the filter, turn on the Processed switch in the upper right corner of the window.
- Click the State link to open a list of possible alert options depending on the status of their processing by the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user.
- Select one of the following values:
- New if you want the application to display new alerts that are not being processed by any user yet.
- In process if you want the application to display alerts that a user of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is already processing.
- Rescan if you want the application to display alerts that resulted from a rescan.
- In the User name field, specify a user name if you want to find alerts that have been assigned to a specific user with the Senior security officer or Security officer role.
- Click Apply.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Sorting alerts in the table
You can sort alerts in the table by Created or Updated, Importance, Source, and State columns.
To sort alerts in the alert table:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- If you want to sort the alerts by date, click one of the icons to the right of the Created (if the table is displaying alert creation dates) or Updated (if the table is displaying alert update dates) column header:
 to display newer alerts at the top of the table.
to display newer alerts at the top of the table. to display older alerts at the top of the table.
to display older alerts at the top of the table.
- If you want to sort the alerts by the level of importance, to the right of the
 icon, click one of the following icons:
icon, click one of the following icons: to display high importance alerts at the top of the table.
to display high importance alerts at the top of the table. to display low importance alerts at the top of the table.
to display low importance alerts at the top of the table.
- If you want to sort alerts by the address of the source of the detected object, click one of the icons to the right of the Source column header:
 to sort alphabetically, A–Z.
to sort alphabetically, A–Z. to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
- If you want to sort alerts by the state of processing by the user, click one of the icons to the right of the State column header:
 to sort alerts in order of processing New - Rescan - In process - Closed.
to sort alerts in order of processing New - Rescan - In process - Closed. to sort alerts in order of processing Closed - In process - Rescan - New.
to sort alerts in order of processing Closed - In process - Rescan - New.
Quickly creating an alert filter
To quickly create an alert filter:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Do the following to quickly add filter conditions to the filter being created:
- Position the mouse cursor on the link containing the table column value that you want to add as a filter condition.
- Left-click it.
This opens a list of actions to perform on the value.
- In the list that opens, select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value, if you want to include this value in the filter condition.
- Exclude from filter, if you want to exclude the value from the filter condition.
- If you want to add several filter conditions to the filter being created, perform the actions to quickly add each filter condition to the filter being created.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Clearing an alert filter
To clear the alert filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the alerts table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the alerts table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table of alerts displays only alerts matching the filter criteria you have set.
Recommendations for processing alerts
Information about alerts made by AM (Anti-Malware Engine), SB (Sandbox), YARA, IOC, and IDS (intrusion Detection System) technologies that is displayed in the right part of the window includes recommendations on processing these alerts.
To view information about an alert:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the line containing the alert whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
Recommendations for processing AM alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts or events that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, expand the Find similar alerts list.
A list of attributes is displayed that can be used to find similar alerts, and the number of similar alerts for each attribute.
Select one of the following attributes:
- By MD5. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the MD5 hash. The MD5 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By SHA256. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the SHA256 hash. The SHA256 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By host name. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The host name from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By sender address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The sender address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By recipient address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Destination column. The recipient address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By URL. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the URL from the alert you are working on.
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, the Scan: detection processing result event type is selected and a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
Recommendations for processing TAA alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts or events that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, expand the Find similar alerts list.
A list of attributes is displayed that can be used to find similar alerts, and the number of similar alerts for each attribute.
Select one of the following attributes:
- By rule name (TAA alerts). Clicking the link opens the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab; the alerts are filtered by Detected and Technologies columns, that is, the name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert, and the name of the (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer technology.
- By rule name (SB alerts). Clicking the link opens the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab; the alerts are filtered by Detected and Technologies columns, that is, the name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert, and the name of the (SB) Sandbox technology.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
Recommendations for processing SB alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts or events that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, expand the Find similar alerts list.
A list of attributes is displayed that can be used to find similar alerts, and the number of similar alerts for each attribute.
Select one of the following attributes:
- By MD5. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the MD5 hash. The MD5 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By SHA256. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the SHA256 hash. The SHA256 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By host name. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The host name from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By sender address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The sender address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By recipient address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Destination column. The recipient address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By URL. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the URL from the alert you are working on.
- By URL from Sandbox. Click the link to display the Alerts table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, that is, the URL address from the alert you are working on, as well as all URLs that were found to be relevant by the Sandbox component as the alert was processed.
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar EPP events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, the Scan: detection processing result event type is selected and a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
Recommendations for processing IOC alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar alerts by host name. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The host name from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar alerts by IOC. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Detected column, the name of the IOC file from the alert you are working on.
- In the Quick response section, select Isolate <host name>. This opens the network isolation rule creation window.
To create a host isolation rule, enter the following settings:
- In the Disable isolation after field, enter the time in hours (1 to 9999) during which network isolation of the host will be active.
- In the Exclusions for the host isolation rule settings group, in the Traffic direction list, select the direction of network traffic that must not be blocked:
- Incoming/Outgoing.
- Incoming.
- Outgoing.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address whose network traffic must not be blocked.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can use a proxy server for the connection of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When you add this proxy server to exclusions, network resources that can be accessed through the proxy server are also added to exclusions. If network resources that are accessed through the proxy server are added to exclusions, but the proxy server itself is not, such exclusions do not work.
- If you selected Incoming or Outgoing, in the Ports field enter the connection ports.
- If you want to add more than one exclusion, click Add and repeat the steps to fill in the Traffic direction, IP and Ports fields.
- Click Save.
Recommendations for processing YARA alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts or events that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, expand the Find similar alerts list.
A list of attributes is displayed that can be used to find similar alerts, and the number of similar alerts for each attribute.
Select one of the following attributes:
- By MD5. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the MD5 hash. The MD5 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By SHA256. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the SHA256 hash. The SHA256 hash of the file from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By host name. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The host name from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By sender address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The sender address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By recipient address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Destination column. The recipient address of the email message from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- By URL. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the URL from the alert you are working on.
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar alerts by host name. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, the Scan: detection processing result event type is selected and a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, a search filter is configured, for example, by RemoteIP, MD5, SHA256, URI. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
The action is only available if you are using KEDR functionality and a KEDR license key has been added.
- In the Quick response section, select Isolate <host name>. This opens the network isolation rule creation window.
Recommendations for processing IDS alerts
In the right part of the window, the Recommendations section displays recommendations that you can follow, as well as the number of alerts or events that have attributes in common with the alert you are working on.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar alerts by IP address. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Source column. The host name or IP address from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- Under Qualifying, select Find similar alerts by URL. Click the link to display the Alerts alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Details column, the URL. The URL from the alert you are working on is highlighted in yellow.
- Under Qualifying, select Add to exclusions.
This opens the Add IDS rule to exclusions window. If you want to add an IDS rule that was used to create the alert to exclusions, enter a comment in the Description field and click Add.
The IDS rule is added to exclusions and is displayed in the exclusion list in the Settings section, Exclusions subsection on the IDS tab in the application web interface.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events by URL. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, the search filter is configured to use the URI from the alert you are working on.
- Under Investigation, select Find similar events by IP address. Click the link to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. In the search criteria, the search filter is configured to use the RemoteIP from the alert you are working on.
- In the Investigation section, click Download IDS artifact to download the file with alert data.
- In the Investigation section, click Download PCAP file to download the file with intercepted traffic data.
Viewing alerts
The web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform displays the following types of alerts that the user should keep track of:
- A file has been downloaded or an attempt was made to download a file to a corporate LAN computer. The application detected this file in mirrored traffic on the organization's local network or in ICAP data of HTTP and FTP traffic, as well as HTTPS traffic if the administrator has configured SSL certificate replacement on the proxy server.
- A file has been sent to the email address of a user on the corporate LAN. The application detected this file in copies of email messages received via the POP3 or SMTP protocol, or received from the virtual machine or server with Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway if it is being used in your organization.
- A website link was opened on a corporate LAN computer. The application detected this website link in mirrored traffic on the organization's local network or in ICAP data of HTTP and FTP traffic, as well as HTTPS traffic if the administrator has configured SSL certificate replacement on the proxy server.
- Network activity has occurred in which the IP address or domain name of a corporate LAN computer was detected. The application detected this network activity in mirrored traffic on the organization's local network.
- Processes have been started on a corporate LAN computer. The application detected the processes using the Endpoint Agent component installed on computers belonging to the corporate IT infrastructure.
If a file was detected, the following information may be displayed in the application web interface depending on which application modules or components generated the alert:
- General information about the alert and the detected file (for example, the IP address of the computer on which the file was detected, and the name of the detected file).
- Results of the virus scan of the file performed by AM Engine.
- Results of scanning the file for signs of intrusion into the corporate IT infrastructure, performed by the YARA module.
- Results of the file behavior analysis performed by the Sandbox component.
- Results of analysis of APK executable files in the cloud infrastructure using machine learning technology.
If a website link was detected, the following information may be displayed in the application web interface depending on which application modules or components generated the alert:
- General information about the alert and the detected website link (for example, the IP address of the computer on which the website link was detected, and the address of the website link).
- Results of the link scan performed by the URL Reputation module for detecting of signs of malware, phishing URL addresses and URL addresses previously used by hackers for targeted attacks on the corporate IT infrastructure.
If the application detects network activity of the IP address or domain name of a computer on a corporate LAN, the application web interface may display the following information:
- General information about the alert and the detected network activity.
- Results of web traffic scanning for signs of intrusion into the corporate IT infrastructure according to preset rules, performed by the Intrusion Detection System module (IDS).
- Results of network activity scanning performed using Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules.
- Results of network activity scanning performed using TAA (IOA), IDS, IOC user rules.
If the application detects processes running on a corporate LAN computer where the Endpoint Agent component is installed, the application web interface can display the following information:
- General information about the alert and processes running on the computer.
- Results of network activity scanning performed for the computer using Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules.
- Results of network activity scanning performed for the computer using TAA (IOA), IOC user rules.
Viewing alert details
To view alert details:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the line containing the alert whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
General information about an alert of any type
Regardless of the technology that was used to create the alert, the header of the window containing the alert information displays the alert ID. The ![]() or
or ![]() icon will be displayed next to the status depending on whether the alert has VIP status.
icon will be displayed next to the status depending on whether the alert has VIP status.
The upper part of the window containing alert information may display the following general information about the alert:
- State—Alert status depending on whether or not this alert has been processed by the user of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Importance—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
- Server is the name of the server where the alert was generated. Servers belong to the organization you are managing in the application web interface.
- Host—Domain name of the computer where the alert occurred.
- Data source—Source of the data. For example, SMTP Sensor or SPAN Sensor.
- Time created—Time when the alert was generated.
- Time updated—Time when information about the alert was updated.
Information in the Object information section
The Object information section can display the following event information about the detected object:
- File name.
To expand the Copy value to clipboard action, click the link with the file name.
- File type. For example: ExecutableWin32.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the
.Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
Click Download to download the file to your computer's hard drive.
The file is downloaded in the form of a ZIP archive encrypted with the password "infected". The name of the file inside the archive is replaced by the file's MD5 hash. The file extension of file inside the archive is not displayed.
- File size in kilobytes.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
Clicking the link with MD5 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of a file.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Email sender—Email address from which the message containing the file was sent.
- Email recipient—One or more email addresses to which the message containing the file was sent.
- Original sender email—Source email address from which the message containing the file was sent.
This field is populated with data from the 'Received' header.
- Original recipient email—Source email address(es) to which the message containing the file was sent.
This field is populated with data from the 'Received' header.
- Subject—Message subject.
- Sender server IP —IP address of the first mail server in the message delivery chain.
Clicking the Sender server IP link with opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Headers—Extended set of email message headers. For example, it can contain information about email addresses of the message sender and recipients, about mail servers that relayed the message, and the type of content in the email message.
Information in the Alert information section
The Alert details section can display the following information about an alert:
 ,
,  or
or  —Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.- Time—Time when the program generated the alert.
- Detected—One or multiple categories of detected objects. For example, when the application detects a file infected with the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad virus, the Detected field shows the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad category for this alert.
- Method—HTTP request method. For example, Get, Post, or Connect.
- URL—Detected URL. It may also contain a response code.
Clicking the link with URL opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by URL.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by domain name.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Referrer—URL from which the user was redirected to the website link requiring attention. In the HTTP protocol, it is one of the headers in the client's request containing the request source URL.
- Destination IP—IP address of the resource requested by the user or the application.
Clicking the link with Destination IP opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- User name—Name of the user account whose actions led to the event.
- Request/Response—Length of the request and response.
Information in the Scan results section
The Scan results section can display the following results of alert scanning:
- The names of the application modules or components that generated the alert.
- One or multiple categories of the detected object. For example, the name of the virus can be shown: Virus.Win32.Chiton.i.
- Versions of databases of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform modules and components that generated the alert.
- Results of alert scanning by application modules and components:
- YARA—Results of streaming scans of files and objects received at the Central Node, or results of scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. Possible values:
- Category of the detected file in YARA rules (for example, category name susp_fake_Microsoft_signer can be displayed).
Displayed for streaming scans.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
- Path to the file and/or name of the memory dump.
Displayed when scanning hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component.
Clicking the link with the file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
You can click Create task to create the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
You can click View in quarantine to display quarantined object details.
- Category of the detected file in YARA rules (for example, category name susp_fake_Microsoft_signer can be displayed).
- SB (Sandbox)—Results of the file behavior analysis performed by the Sandbox component.
You can click Sandbox detection to open a window with detailed information about the results of file behavior analysis.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
You can download a detailed log of file behavior analysis in all operating systems by clicking Download debug info.
The file is downloaded in the form of a ZIP archive encrypted with the password "infected". The name of the scanned file inside the archive is replaced by the file's MD5 hash. The file extension of file inside the archive is not displayed.
By default, the maximum hard drive space for storing file behavior scan logs is 300 GB in all operating systems. Upon reaching this limit, the application deletes the oldest file behavior scan logs and replaces them with new logs.
- URL (URL Reputation) is the category of a malicious, phishing URL or an URL that has been previously used by attackers for targeted attacks on corporate IT infrastructures.
- IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is the category of the detected object based on the Intrusion Detection System database or the name of the IDS user rule that was used to create the alert. For example, the displayed category can be Trojan-Clicker.Win32.Cycler.a.
Click the link to display the category of the object in the Kaspersky Threats database.
- AM (Anti-Malware Engine)—Category of the detected object based on the anti-virus database. For example, the name of the virus can be shown: Virus.Win32.Chiton.i.
Click the link to display the category of the object in the Kaspersky Threats database.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
Click Download to download the file to your computer's hard drive.
- TAA (Targeted Attack Analyzer)—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered
as well as recommendations for reacting to the event. - IOC—Name of the IOC file used to create the alert.
Select an IOC file to open a window with the results of the IOC scan.
Click All alert-related events to display the Threat Hunting event table in a new browser tab. A search filter is configured in the search criteria, for example, by MD5, FileFullName. The filtering values are populated with the properties of the alert you are working on. For example, the MD5 hash of the file in the alert.
- YARA—Results of streaming scans of files and objects received at the Central Node, or results of scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. Possible values:
Information in the IDS rule section
The IDS rule section displays information about the alert made by the IDS (Intrusion Detection System) technology as a hex-editor matrix.
The hex-editor or hexadecimal editor is an application for editing data where data is represented as a sequence of bytes.
The upper part of the matrix displays the length of the IDS rule.
The left part of the matrix displays the data of the rule in text format.
The Rule details subsection of the IDS rule section displays the header of the IDS rule and data of the IDS alert in the Suricata format. For example, it can display information about the direction of the traffic (flow), the HTTP request method (http_method), the HTTP header (http_header), the security ID (sid).
Information in the Network event section
The Network event section can show the following information about the link to the website opened on the computer:
- Date and Time—Date and time of the network event.
- Method—Type of HTTP request, for example, GET or POST.
- Source IP—IP address of the computer on which the website link was opened.
- Destination IP—IP address of the computer on which the website link was opened.
- URL—Type of the HTTP request, for example, GET or POST, and the URL of the website.
Clicking the link with the URL opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by URL.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by domain name.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- User Agent—Information about the browser that was used to download the file or to attempt to download the file, or to open the website link. It is the text string included in the HTTP request, which normally contains the name and version of the browser as well as the name and version of the operating system installed on the user's computer.
Scan results in Sandbox
The object scan results window in Sandbox can display the following alert details:
- File—Full name and path of the scanned file.
- File size—Size of the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
Clicking the link with MD5 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Detected—One or multiple categories of detected objects. For example, when the application detects a file infected with the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad virus, the Detected field shows the Trojan-Downloader.JS.Cryptoload.ad category for this alert.
- Time processed—Time when the file was scanned.
- Database versions—Versions of the databases of modules and components of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform that generated the alert.
You can click New prevention rule in the upper right corner of the window to prevent the file from running.
Information about the file behavior analysis results is provided for each operating system in which the Sandbox component performed a scan. For the Windows 7 operating system (64-bit), you can view file activity logs for two Sandbox component scan modes: Quick scan mode and Full logging mode.
The following activity logs may be available for each scan mode:
- Activity list—Actions of the file within the operating system.
- Activity tree—Graphical representation of the file analysis process.
- HTTP activity log—Log of the file's HTTP activity. It contains the following information:
- Destination IP—IP address to which the file is attempting to go from the operating system.
- Method—HTTP request method, for example, GET or POST.
- URL—URL of the website link that the file is attempting to open from the operating system.
Clicking links in the Destination IP column opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking a link in the URL column opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by URL.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by domain name.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- IDS activity log—Log of the file's network activity. It contains the following information:
- Source IP—IP address of the host on which the file is saved.
- Destination IP—IP address to which the file is attempting to go from the operating system.
- Method—HTTP request method, for example, GET or POST.
- URL—URL of the website link that the file is attempting to open from the operating system.
Clicking links in the Destination IP column opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking a link in the URL column opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by URL.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP by domain name.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- DNS activity log —Log of the file's DNS activity. It contains the following information:
- Request type (Request or Response).
- DNS name —Domain name of the server.
- Type —Type of DNS request, for example A or CNAME.
- Host—Host name or IP address that was interacted with.
Clicking a link in the DNS name or Host columns opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
You can click Download full log in the lower part of each scanning mode (Quick scan mode and Full logging mode) to download the log of file behavior analysis in each operating system to your computer
Page top
IOC scan results
Depending on the type of processed object, the indicator of compromise search result window can display the following information:
- ARP protocol:
- IP address from the ARP table.
- Physical address from the ARP table.
- DNS record:
- Type and name of the DNS record.
- IP address of the protected computer.
- Windows Log event:
- Entry ID in the event log.
- Data source name in the log.
- Log name.
- User account.
- Event time.
- File:
- MD5 hash of the file.
- SHA256 hash of the file.
- Full name of the file (including path).
- File size.
- Port:
- Remote IP address with which a connection was established at the time of the scan.
- Remote port with which a connection was established at the time of the scan.
- IP address of the local adapter.
- Port open on the local adapter.
- Protocol as a number (in accordance with the IANA standard).
- Process:
- Process name.
- Process arguments.
- Path to process file.
- Windows ID (PID) of the process.
- Windows ID (PID) of the parent process.
- Name of the user account that started the process.
- Date and time when the process started.
- Service:
- Service name.
- Service description.
- Path and name of the DLL service (for svchost).
- Path and name of the executable file of the service.
- Windows ID (PID) of the service.
- Service type (for example, kernel driver or adapter).
- Service status.
- Service run mode.
- User:
- User account name.
- Volume:
- Volume name.
- Volume letter.
- Volume type.
- Registry:
- Windows registry value.
- Registry hive value.
- Path to registry key (without hive or value name).
- Registry parameter.
- Environment variables:
- Physical (MAC) address of the protected computer.
- System (environment).
- OS name with version.
- Network name of the protected device.
- Domain and group to which the protected computer belongs.
The IOC section displays the structure of the IOC file. If the processed object matches a condition of the IOC rule, that condition is highlighted. If the processed object matches multiple conditions, the text of the whole branch is highlighted.
Information in the Hosts section
The Hosts section displays the following information about hosts on which the TAA (IOA) rule was triggered:
- Host name—IP address or domain name of the computer where the event occurred. Clicking the link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition containing the ID of the selected rule and the selected host.
- IP—IP address of the computer where the event occurred.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the computer at the moment when the alert was created or updated.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the computer is not displayed.
- Number of events—Number of events that occurred on the host.
- Find events. Clicking the link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition containing the ID of the selected rule.
Information in the Change log section
The Change log section can display the following alert information:
- Date and time of alert modification.
- Author of modifications.
For example, System or the application user name.
- Modification that occurred with the alert.
For example, an alert may be assigned to a VIP group, or it may be marked as processed.
Sending alert data
You can provide Kaspersky with data about an alert (except the URL Reputation and IOC technologies) for further analysis.
To do so, you must copy the alert data to the clipboard and then email it to Kaspersky.
Alert data may contain information about your organization that you consider to be confidential. You must consult with the security department of your organization for approval to send this data to Kaspersky for further analysis.
To copy alert details to the clipboard:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the line containing the alert whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- Click the Provide the alert details to Kaspersky link in the lower part of the window containing alert information.
This opens the Show more window.
- View the alert data to be sent to Kaspersky.
- If you want to copy this data, click the Copy to clipboard button.
The alert data will be copied to the clipboard. You will be able to send it to Kaspersky for further analysis.
User actions performed on alerts
When managing the application web interface using a Senior security officer or Security officer account, you can take the following actions on alerts:
- Assign an alert to yourself or to another user of the application web interface.
You can view all alerts assigned to a specific user by filtering alerts based on the status of their processing by the user.
- Mark an alert as processed.
You can view all alerts that have been processed by a specific user by filtering alerts based on the status of their processing by the user.
- Add a comment to an alert.
You can find commented alerts based on keywords within comments by filtering alerts based on received information.
- Mark the alert as .
This action is available only to users with the Senior security officer role. Users with this role can view all alerts with the VIP status by filtering alerts by VIP status.
Users with the Security auditor role can view information about alerts but cannot edit this information.
Assigning alerts to a specific user
Users with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles can assign an alert or multiple alerts to themselves or to another user of the application web interface with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles.
To assign an alert to yourself or to another user of the application web interface:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Select the check boxes next to the alert or alerts that you want to assign to yourself or to another user.
You can select all alerts by selecting the check box in the table header.
- In the panel that appears in the lower part of the window, click the arrow to the right of the Assign to button to expand the user list.
- Select the user to whom you want to assign the alerts.
This opens the action confirmation window. You can also leave a comment that will be displayed in the alert change history.
- Click Proceed.
The alerts will be assigned to the selected user.
You can view all alerts assigned to a specific user by filtering alerts based on the status of their processing by the user.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot assign alerts to themselves or to other users of the application web interface. Users with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles also cannot assign alerts to users with the Security auditor role.
Page top
Marking the completion of single alert processing
To mark one alert assigned to you as processed in the alerts table:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- In the State column of the alert that you want to mark as processed, click on your user name.
- In the action list, select Close alert.
The alert will be marked as processed.
To mark an alert as processed in the course of managing that alert:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Open the alert that you want to mark as processed.
Expand the list of actions. In the upper right corner of the window, click the arrow to the right of the button showing the alert status.
This opens the list of actions.
- In the action list, select Close alert.
The alert will be marked as processed. If the alert was assigned to a different user, it will be marked as processed by you.
You can view all alerts that have been processed by a specific user by filtering alerts based on the status of their processing by the user.
If an alert based on TAA (IOA), IDS, or URL technology that is similar to a processed alert is received within the day (from 00:00 a.m. to 11:59 p.m.), the application will either create a new alert or update the information about an identical alert with the New or In process status.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot assign and process alerts.
Page top
Marking the completion of alerts processing
To mark one or multiple alerts as processed:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Select the check boxes opposite those alerts that you want to mark as processed.
You can select all alerts by selecting the check box in the table header.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click the Close alert button.
This opens the action confirmation window.
You can also leave a comment that will be displayed in the alert change history.
- Click Proceed.
The selected alerts will be marked as processed. If the alerts were assigned to other users, they will be marked as processed by you.
You can view all processed alerts by filtering alerts based on the status of their processing by the user.
If an alert based on TAA (IOA), IDS, or URL technology that is similar to a processed alert is received within the day (from 00:00 a.m. to 11:59 p.m.), the application will either create a new alert or update the information about an identical alert with the New or In process status.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot assign and process alerts.
Page top
Modifying the status of VIP alerts
Users with the Senior security officer role can assign the VIP status to alerts or clear the VIP status of alerts.
To toggle the VIP status for alerts:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Select the check boxes for alerts for which you want to change the VIP status.
You can select all alerts by selecting the check box in the table header.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to mark alerts as VIP, click the Mark as VIP button in the pane that appears in the lower part of the window.
- If you want to remove the VIP status from alerts, in the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, in the Mark as VIP drop-down list, select Mark as non-VIP.
This opens the action confirmation window.
You can also leave a comment that will be displayed in the alert change history.
- Click Proceed.
The VIP status of alerts is changed.
Users with the Senior security officer and Security auditor roles can view all events with the VIP status by filtering alerts by VIP status.
Page top
Adding a comment to an alert
Users with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles can add a comment to an alert.
To add a comment to an alert:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Select an alert for which you want to add a comment.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- In the comment field under the Change log section, enter a comment for the alert.
- Click Add.
The comment will be added to the alert and will be displayed in the Change log section of this alert.
You can find commented alerts based on keywords within comments by filtering alerts based on received information.
Users with the Security auditor role can view comments for alerts but cannot edit the comments.
Page top
Events database threat hunting
When managing the application web interface, you can generate search queries and use IOC files to search the events database for threats, for tenants to whose data you have access.
To form search queries through the events database, you can use design mode or source code mode.
In design mode, you can create and modify search queries using drop-down lists with options for the type of field value and operators.
In source code mode, you can create and modify search queries using text commands.
You can upload an IOC file and search for events based on conditions defined in this IOC file.
Users with the Senior security officer, Security officer roles can also create TAA (IOA) rules based on event search conditions.
Searching events in design mode
To define event search conditions in design mode:
- Select the Threat Hunting section, Builder tab in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- In the drop-down list, select an event search criterion.
You can view a description of the event search criteria in the Event search criteria section.
- In the drop-down list, select an operator.
For a list of available operators, see the Operators section.
Each type of value of the field has its own relevant set of operators. For example, when the EventType field value type is selected, the = and != operators will be available.
- Depending on the selected type of field value, perform one of the following actions:
- In the field, specify one or several characters by which you want to perform an event search.
- In the drop-down list, select the field value option by which you want to perform an event search.
For example, to search for a full match based on a user name, enter the user name.
- If you want to add a new condition, use the AND or OR logical operator and repeat the necessary actions for adding a condition.
- If you want to add a group of conditions, click the Group button and repeat the actions necessary for adding conditions.
- If you want to delete a group of conditions, click the Remove group button.
- If you want to search events that occurred during a specific period, in the Any time drop-down list select one of the following event search periods:
- Any time if you want the table to display events found as far back as the records go.
- Last hour if you want the table to display events that were found during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display events found during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display events found during the period you specify.
- If you selected Custom range:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the event display range.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
- Click Search.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, found events are grouped in tiers: Server – Tenant names – Server names.
- Click the name of the server for which you want to view events.
The host table of the selected server is displayed. Event grouping levels are displayed above the table.
Event search criteria
The following criteria can be used to search for events:
- General information:
- Host is the host name.
- HostIP is the IP address of the host.
- EventType is the type of the event.
- UserName is the name of the user.
- OsFamily is the family of the operating system.
- OsVersion is the version of the operating system being used on the host.
- TAA properties:
- IOAId is the TAA (IOA) rule ID.
- IOATag is the information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- IOATechnique is the MITRE technique.
- IOATactics is the MITRE tactic.
- IOAImportance is the importance level that is assigned to an event generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.
- IOAConfidence is the level of confidence depending on the likelihood of false alarms caused by the rule.
- File properties:
- CreationTime is the event creation time.
- FileName is the name of the file.
- FilePath is the path to the directory where the file is located.
- FileFullName is the full path to the file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name.
- ModificationTime is the file modification time.
- FileSize is the size of the file.
- MD5 is the MD5 hash of the file.
- SHA256 is the SHA256 hash of the file.
- SimilarDLLPath is the malicious DLL placed in a directory on the standard search path to make the operating system load it before the original DLL.
- Linux processes:
- LogonRemoteHost is the IP address of the host that initiated remote access.
- RealUserName is the name of the user assigned when the user was registered in the system.
- EffectiveUserName is the user name that was used to log in to the system.
- Environment is system environment variables.
- ProcessType is the type of the process.
- OperationResult is the result of the operation.
- FileOwnerUserName is the name of the file owner.
- RealGroupName is the name of the user group.
- EffectiveGroupName is the name of the user group that is used for operation.
- Process started:
- PID is the process ID.
- ParentFileFullName is the path to the parent process file.
- ParentMD5 is the MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- ParentSHA256 is the SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- StartupParameters is the options that the process was started with.
- ParentPID is the parent process ID.
- ParentStartupParameters is the parent process startup settings.
- Remote connection:
- HTTPMethod is the HTTP request method. For example, Get, Post, or Connect.
- ConnectionDirection is the direction of the connection (inbound or outbound).
- LocalIP is the IP address of the local computer from which the remote connection attempt was made.
- LocalPort is the IP address of the local computer from which the remote connection attempt was made.
- RemoteHostName is the name of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt.
- RemoteIP is the IP address of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt.
- RemotePort is the port of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt.
- URl is the address of the resource to which the HTTP request was made.
- Registry modified:
- RegistryKey is the registry key.
- RegistryValueName is the name of the registry value.
- RegistryValue is the data of the registry value.
- RegistryOperationType is the type of the operation with the registry.
- RegistryPreviousKey is the previous registry key.
- RegistryPreviousValue is the previous name of the registry value.
- System event log:
- WinLogEventID is the type ID of the security event in the Windows log.
- LinuxEventType is the type of the event. This criterion is used for Linux and macOS operating systems.
- WinLogName is the name of the log.
- WinLogEventRecordID is the log entry ID.
- WinLogProviderName is the ID of the system that logged the event.
- WinLogTargetDomainName is the domain name of the remote computer.
- WinLogObjectName is the name of the object that initiated the event.
- WinlogPackageName is the name of the package that initiated the event.
- WinLogProcessName is the name of the process that initiated the event.
- Detect and processing result:
- DetectName is the name of the detected object.
- RecordID is the ID of the triggered rule.
- ProcessingMode is the scanning mode.
- ObjectName is the name of the object.
- ObjectType is the type of the object.
- ThreatStatus is the detection mode.
- UntreatedReason is the event processing status.
- ObjectContent (for AMSI events too) is the content of the script sent for scanning.
- ObjectContentType (for AMSI events too) is the type of script content.
- Console interactive input:
- InteractiveInputText is the text entered on the command line.
- InteractiveInputType is the input type (console or pipe).
- File modified:
- FileOperationType is the type of the file operation.
- FilePreviousPath is the path to the directory where the file was previously located.
- FilePreviousName is the previous name of the file.
- FilePreviousFullName is the full name of the file including the path to the directory where the file was previously located and/or the previous file name.
- DroppedFileType is the type of the modified file.
Operators
The following operators are available:
- =
- !=
- CONTAINS
- !CONTAINS
- STARTS
- !STARTS
- ENDS
- !ENDS
- >
- <
Searching events in source code mode
To define event search conditions in source code mode:
- In the application web interface window, select the Threat Hunting section, Source code tab.
This opens a form containing the field for entering event search conditions in source code mode.
- Enter the event search conditions using criteria, operators, logical operators
ORandAND, and parentheses to group conditions.A search condition must conform to the following syntax:
<criterion> <operator> <criterion value>.Example:
EventType = "filechange"AND (FileName CONTAINS "example"OR UserName = "example") - If you want to hide newline special characters in the editor window, click Convert special characters to line breaks
 . If you want to display newline characters, click Convert line breaks to special characters
. If you want to display newline characters, click Convert line breaks to special characters .
.When using a complex search condition consisting of multiple criterion values, in the source code editing window, each criterion value must start on a new line. To display line breaks, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses line separator special characters (^r ^n). To perform an event search correctly, you must make sure the line separator special characters are correctly arranged.
- If you want to search events that occurred during a specific period, click the Any time button and select one of the following event search periods:
- Any time if you want the table to display events found as far back as the records go.
- Last hour if you want the table to display events that were found during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display events found during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display events found during the period you specify.
- If you selected Custom range:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the event display range.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
- Click Search.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, found events are grouped in tiers: Server – Tenant names – Server names.
- Click the name of the server for which you want to view events.
The host table of the selected server is displayed. Event grouping levels are displayed above the table.
Sorting events in the table
You can sort events in the table by the Event time, Event type, Host, and User name columns.
To sort events in the event table:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
This opens the Threat Hunting window.
- Define the criteria for searching events in design mode or source code mode.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
- If you want to sort events by time, click one of the icons to the right of the Event time column name:
 to display newer events at the top of the table.
to display newer events at the top of the table. to display older events at the top of the table.
to display older events at the top of the table.
- If you want to sort events by the event type name, click one of the icons to the right of the Event type column heading:
 to sort alphabetically, A–Z.
to sort alphabetically, A–Z. to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
- If you want to sort events based on the names of host on which the alerts were generated, click one of the icons to the right of the Host column name:
 to sort alphabetically, A–Z.
to sort alphabetically, A–Z. to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
- If you want to sort events based on the user names of hosts, click one of the icons on the right of the User name column name:
 to sort alphabetically, A–Z.
to sort alphabetically, A–Z. to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
to sort alphabetically, Z–A.
- If you want to group events based on the names of hosts or by the event type name, click one of the values in the Group by drop-down list:
- Group by host name if you want to group events by the names of hosts.
- Group by event type if you want to group events by the names of event types.
If events were sorted by the Host or Event type field, the sorting result is cleared when events are grouped by a similar attribute. To return to the sorting results, select the Group by value from the Group by drop-down list.
By default, events in the table are sorted by time, with the newest events at the top of the table.
You can sort events based on one attribute only.
When sorting by event type in a foreign language, events are sorted based on the internal name of the event type in English.
Page top
Changing the event search conditions
To change the event search conditions, perform the following actions in the Threat Hunting section of the application web interface window:
- Click the form containing the event search conditions in the upper part of the window.
- Select one of the following tabs:
- Builder, if you want to change the event search conditions in builder mode.
- Source code, if you want to change the event search conditions in source code mode.
- Make the relevant changes.
- Click one of the following buttons:
- Refresh, if you want to refresh the current event search with the new conditions.
- New search, if you want to perform a new event search.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
Searching events by processing results in EPP applications
To search events by processing results in
in builder mode:- Select the Threat Hunting section, Builder tab in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- To search events by processing status:
- In the search criteria drop-down lost in the Detect and processing result group, select ThreatStatus.
- In the drop-down list of comparison operators, select one of the following options:
- = (equals)
- != (does not equal)
- In the drop-down list of event processing status, select one of the following options:
- Object clean.
- Object disinfected.
- False positive.
- Object added by user.
- Object added to exclusions.
- Object deleted.
- Object quarantined.
- Object not found.
- Object rolled back.
- Object cannot be processed.
- Object not processed.
- Processing terminated.
- Unknown.
- To search events by reasons why they were not processed:
- In the search criteria drop-down lost in the Detect and processing result group, select UntreatedReason.
- In the drop-down list of comparison operators, select one of the following options:
- = (equals)
- != (does not equal)
- In the drop-down list of reasons why the events were not processed, select one of the following options:
- Object already processed.
- Application is running in Report only mode.
- Failed to back up object.
- Failed to copy object.
- Device not ready.
- Object blocked.
- No rights to perform action.
- Object not curable.
- Object not overwritable.
- Object not found.
- No free space on disk.
- Processing canceled.
- Processing postponed.
- Processing task stopped.
- Error reading data.
- Reason unknown.
- This is a critical system object.
- Data write error.
- Data write not supported.
- Object write-protected.
- If you want to add a new condition, use the AND or OR logical operator and repeat the necessary actions for adding a condition.
- If you want to add a group of conditions, click the Group button and repeat the actions necessary for adding conditions.
- If you want to delete a group of conditions, click the Remove group button.
- If you want to search events that occurred during a specific period, in the Any time drop-down list select one of the following event search periods:
- Any time if you want the table to display events found as far back as the records go.
- Last hour if you want the table to display events that were found during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display events found during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display events found during the period you specify.
- If you have selected the Custom range display period for found events:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the event display range.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
- Click Search.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
Uploading an IOC file and searching for events based on conditions defined in the IOC file
To upload an IOC file and search for events based on conditions defined in that IOC file:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- Click Import.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the IOC file that you want to upload and click the Open button.
The IOC file is uploaded.
On the Source code tab, the form containing event search conditions will display the conditions defined in the uploaded IOC file.
You can search for events that match these conditions. You can also change the conditions defined in an uploaded IOC file, or add event search conditions in source code mode.
- If you want to search events that occurred during a specific period, click the Any time button and select one of the following event search periods:
- Any time if you want the table to display events found as far back as the records go.
- Last hour if you want the table to display events that were found during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display events found during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display events found during the period you specify.
- If you have selected the Custom range display period for found events:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the event display range.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
- Click Search.
An event table is displayed that corresponds to criteria specified in the IOC file.
Creating a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions
To create a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
- Click Save as TAA (IOA) rule.
This opens the New TAA (IOA) rule window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the rule.
- Click Save.
The event search condition will be saved. In the TAA (IOA) rule table in the Custom rules section, TAA subsection of the web interface, the new rule is displayed with the specified name.
If you want to save event search conditions as a user-defined TAA (IOA) rule, avoid using the following fields:
- IOAId.
- IOATag.
- IOATechnique.
- IOATactics.
- IOAImportance.
- IOAConfidence.
At the time of saving the user-defined TAA (IOA) rule, the application may not have any events containing data for these fields. When events with this data turn up, the user-defined field that you have created earlier will be unable to mark events by these fields.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create TAA (IOA) rules based on event search conditions.
Event information
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, when managing the application using the web interface, you can view event information for those tenants to whose data you have access.
Event information displays local timestamps of the Endpoint Agent computer that detected the event. The application administrator must make sure the time on computers with the Endpoint Agent component is current.
To enable the display of events for all tenants:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
- Turn on the Search in all tenants toggle switch.
The table of events displays events for all tenants.
Recommendations for processing events
The event window displays recommendations for processing the event in the box between the event tree and the information text for users with the Senior security officer role.
You can follow the following recommendations:
- Isolate <host name> – isolate the host with the Endpoint Agent component where the event was detected from the network. Applies to all event types.
- Create prevention rule – prohibit the execution of the file that was detected in the event. Applies to all event types except System event log.
- Create task — create a task. Applies to all event types except System event log.
Additionally, you can process the event by clicking the link with the name, path, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file and the host name while viewing text information about the event in the lower part of the window.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles are not shown recommendations for processing events.
Following a recommendation to isolate a host
To follow a recommendation to isolate a host from the network:
- In the recommendation box, select Isolate <host name>.
This opens the host isolation settings window for the host from the event you are working on.
- In the Disable isolation after field, enter the time in hours (1 to 9999) during which network isolation of the host will be active.
- In the Exclusions for the host isolation rule settings group, in the Traffic direction list, select the direction of network traffic that must not be blocked:
- Incoming/Outgoing.
- Incoming.
- Outgoing.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address whose network traffic must not be blocked.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can use a proxy server for the connection of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When you add this proxy server to exclusions, network resources that can be accessed through the proxy server are also added to exclusions. If network resources that are accessed through the proxy server are added to exclusions, but the proxy server itself is not, such exclusions do not work.
- If you selected Incoming or Outgoing, in the Ports field enter the connection ports.
- If you want to add more than one exclusion, click Add and repeat the steps to fill in the Traffic direction, IP and Ports fields.
- Click Save.
Information about host isolation is displayed in the Endpoint Agents section of the web interface.
You can also create a network isolation rule by clicking the Isolate <host name> link in the alert information and in the Endpoint Agents section of the web interface.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot isolate a host from the network.
Following a recommendation to prevent a file from running
To follow a recommendation to prevent a file from running:
- In the recommendations box, select Create prevention rule.
This opens the prevention rule creation window with the MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file from the event you are working on.
- Configure the following settings:
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- If you want to enable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to On.
- If you want to disable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to Off.
- Name is the name of the prevention rule.
- If you want the application to display a notification about prevention rule triggering to the user of the computer on which the prevention is applied, select the Notify user about blocking file execution check box.
- If you want to change the scope of the prevention rule, configure the Prevent on setting:
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on all hosts of all servers, select All hosts.
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to apply the prevention rule.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- Click Add.
The file run prevention is created.
Information about the created prevention is displayed in the Prevention section of the web interface.
If you selected the Notify user about blocking file execution check box and an attempt is made to execute a file prevented from running, the user is notified that an execution prevention rule was triggered by this file.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot prevent file execution.
Following a recommendation to create a task
To follow a recommendation to create a task:
- Click Create task, and in the recommendation box, expand the list of task types.
- Select a task type:
- Kill process.
- Get forensics.
- Start YARA scan.
- Service management.
- Get process memory dump.
- Get NTFS metafiles.
- Run application.
- Get file.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Restore file from quarantine.
This opens the task creation window with preset values (for example, host name, file path, MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file) from the event you are working on.
- If you want to modify preset values from the event, edit the corresponding fields.
- If you want to add a comment for the task, enter it in the Description box.
- If you are creating a Kill process, Delete file, Start YARA scan, or Service management task and you want to modify the scope of the task, change the value of the Task for setting:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
- Click Add.
The task is created.
Information about the created task is displayed in the Tasks section of the web interface.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create tasks.
Information about events in the tree of events
The tree of events is displayed in the upper part of the event information window.
The tree of events contains the following information:
- The event for which you are viewing information.
The event you are viewing is displayed on the right side.
- The parent process.
The parent process is displayed to the left of the event you are viewing. If the event you are viewing does not have a parent process, the host name where the event was registered is displayed instead.
Clicking the name of the parent process on the left side displays the process that has initiated the process in question and is a parent process with regard to that process. If there is no parent process, the host name is displayed instead.
To the right of each parent process name, the total number of events generated by this process is displayed. You can view the list of events and information about the selected event.
Viewing parent process information in the tree of events
To display parent process information for the event being viewed:
- Perform an event search in builder mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- Select the event whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the event. The upper part of the window displays the tree of events.
- Click the .
In the bottom part of the window, the Details tab displays information about the process that is the parent process with regard to the event being viewed.
Viewing information about events initiated by the parent process in the tree of events
To view the table of all events initiated by the parent process:
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- Select the event whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the event. The upper part of the event information window displays the tree of events.
- Click the name of the parent process in the event tree.
In the bottom part of the window, the Details tab displays information about the event that is the parent event with regard to the event being viewed.
- Go to the Events tab.
A table of all events initiated by the parent process is displayed. By default, events in the table are sorted by time, with the newest events at the top of the table.
You can view event information by clicking the row of the relevant event. The event node is displayed in the tree of events.
To display the event table grouped by type:
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- Select the event whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the event. The upper part of the event information window displays the tree of events.
- Click the drop-down list to the right of the parent process name in the tree of events.
A list of all events initiated by the parent process is displayed. By default, the events in the list are grouped by type.
- In the tree of events, in the drop-down list to the right of the parent process name, select one of the following options:
- If you want to display all events initiated by the parent process, click All events.
A table of all events initiated by the parent process is displayed. By default, events in the table are sorted by time, with the newest events at the top of the table.
- If you want to view all events of a particular type initiated by the parent process, select the name of the relevant event type.
A table of all events initiated by the parent process is displayed, grouped by type.
You can view event information by clicking the row of the relevant event. The event is displayed in the tree of events.
- If you want to display all events initiated by the parent process, click All events.
Viewing host information in the tree of events
If the event that you are viewing or the parent process do not have a process that initiated it, the process node in the tree of events is replaced with the node of the host where the event was registered or the parent process was running.
To view information for the host where the event was registered or the parent process was started:
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- Select the event whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the event. The upper part of the window displays the tree of events.
- Click the host name in the tree of events.
The bottom part of the window displays information about the host where the event was registered or the parent process was running.
Viewing the table of events
The events table is displayed in the Threat Hunting section of the application web interface window after completion of Threat Hunting in the events database. You can sort events in the table by the Event time, Event type, Host, and User name columns.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, events in the table are grouped by hosts of the selected servers and tenants.
The table of events contains the following information:
- Event time—Date and time when the event was detected.
- Event type, for example, Process started.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
- Details—Information about the event.
- User name—Name of the user on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component whose user account was used to detect the event.
In the events table, the Details column displays the set of data for each type of event in the Event type column (see the table below).
Set of data in the Details column for each event type in the Event type column
Event type |
Details |
|---|---|
Process started |
Name of the process file that was started. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
Module loaded |
Name of the dynamic library that was loaded. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
Connection to remote host |
URL to which a remote connection attempt was made. Name of the file that attempted to establish a remote connection. |
Blocked application (prevention rule) |
Name of the file of the application that was blocked from starting. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
Document blocked |
Name of the document that was blocked from starting. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
File changed |
Name of the created file. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
System event log |
Channel for recording events in the system log. Event type ID. |
Registry modified |
Name of key in registry. |
Port listened |
Server address and port. Name of the file of the process that listens to the port. |
Driver loaded |
File name of the driver that has been loaded. SHA256- and MD5 hash. |
Scan: detection |
Alert |
Scan: detection processing result |
Alert processing result |
AMSI scan |
AMSI scan result |
Process: interpreted file run |
Interpreted run of a file |
Process: console interactive input |
Interactive input of commands in the console |
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, information about the AMSI scan event is available when Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows 3.10 or later and when Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows 11.5 or later. If Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not installed on the computer and is not integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, information about the AMSI scan event is not logged in the event database and is not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the Central Node server generates Scan: detection and Scan: detection processing result events based on data received from EPP applications. If EPP applications are not installed on the computer and are not integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, information about these events is not logged in the event database and is not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
Clicking the link with the name of the event type, data, additional information and user name opens a list in which you can select the action to perform on the object. Depending on the value in the cell, you can do one of the following:
- For all values in the cell:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Host name:
- File name:
- MD5 hash:
- SHA256 hash:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Create prevention rule.
- Find in Storage.
Configuring the event table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the event table.
To configure the event table display:
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The display of the event table is configured.
Page top
Viewing information about an event
To view event details:
- In the application web interface window, select the Threat Hunting section, Builder or Source code tab.
This opens the event search form.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and want to enable the display of events for all tenants, turn on the Search in all tenants toggle switch.
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
The event table is displayed.
- Select the event whose information you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the event.
Information about the "Process started" event
The window showing information about Process started events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Process started section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Process file name.
- Process ID—Process identifier.
- Launch parameters—Process startup settings.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, instead of the Launch parameters field, the Command field is displayed, that is, the command that was used to run the process.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the process file.
- Size—Size of the process file.
- Event time—Process start time.
- Time created—Process file creation time.
- Time modified—Time of last modification of the process file.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Details section:
- Application name—For example, the name of the operating system.
- Vendor—For example, vendor of the operating system.
- File description—For example, Example File.
- Original file name—For example, ExampleFile.exe.
- Signature subject—Organization that issued the digital certificate of the file.
- Signature validation result—For example, "Invalid" or "OK".
- Attributes—File attribute in accordance with the Windows classification. For example, A (archive), D (directory), or S (system file).
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the Details section also includes the following fields:
- Attributes—Attributes of the process file.
- Process type—For example, exec.
- Environment variables—Environment variables of the process.
- Real user name—Name of the user assigned when registering in the system.
- Real group name—Group to which the user belongs.
- Effective user name—User name that was used to log in to the system.
- Effective group name—Group of the user whose name was used to log in to the system.
- Owner user name—Name of the user that created the process file.
- Owner group name—Name of the group whose users can modify or delete the file of the process.
- File permitted capabilities—Permissions that can be used to gain access to the process file. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- File inheritable capabilities—Permissions that an user group has to perform operations on the parent directory of the process file. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- File effective capabilities—Permissions that are relevant to the process file at the current moment. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- Launch parameters—Parent process startup settings.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, instead of the Launch parameters field, the Command field is displayed, that is, the command that was used to run the parent process.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the process was started.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the process was started.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User account type—Type of the account that ran the process. For example, administrator.
- Logon type—For example, using a running service.
- User name—Name of the user that started the process.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the System info section also displays the Logon from remote host field for the name of host from which the remote logon was performed.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the links with the file name or file path to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the Get file task.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the link with the host name to expand a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Process terminated" event
The window displaying information about Process terminated events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Process terminated section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Process file name.
- Process ID—Process identifier.
- Launch parameters—Process startup settings.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, instead of the Launch parameters field, the Command field is displayed, that is, the command that was used to run the process.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the process file.
- Size—Size of the process file.
- Event time— Process termination time.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- Launch parameters—Parent process startup settings.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, instead of the Launch parameters field, the Command field is displayed, that is, the command that was used to run the parent process.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the process was started.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the process was started.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User account type—Type of the account that terminated the process. For example, administrator.
- User name—Name of the user that started the process.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the System info section also displays the Logon from remote host field for the name of host from which the remote logon was performed.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the links with the file name or file path to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the Get file task.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux recorded in the event database, you can click the link with the host name to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get file.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the links with the file name or file path to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the Get file task.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Module loaded" event
The window showing information about Module loaded events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Module loaded section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the loaded module file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the loaded module file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the loaded module file.
- Size—Size of the loaded module.
- Event time—Time when the module was loaded.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Details section:
- Application name—For example, name of the operating system.
- Vendor—For example, vendor of the operating system.
- File description—For example, Example File.
- Original file name—For example, Example File.
- Signature subject—Organization that issued the digital certificate of the file.
- Signature validation result—For example, "Signature invalid" or "Signature OK".
- Time created—Creation time of the loaded module.
- Time modified—Date of last modification of the loaded module.
- Next DLL in bypass path—The field contains the path to the DLL library that could have been loaded instead of the existing library.
The field is displayed if the following conditions are satisfied:
- The source of the loaded DLL is not trusted.
- A folder in the standard search path contains a library with the same name but a different hash.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives the data required to populate the Next DLL in bypass path field only when Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10 for Windows. When integrating the application with older versions of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application the field is not displayed in the event information.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the module was loaded.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the module was loaded.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that loaded the module.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Module loaded section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Event initiator section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Remote connection" event
The window showing information about Connection to remote host events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Connection to remote host section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Connection direction is the direction of the connection (inbound or outbound).
- Remote IP—IP address of the host to which a remote connection attempt was made.
- Local IP – IP address of the local computer from which a remote connection attempt was made.
- Event time—Time of the remote connection attempt.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Name of the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Host name from which a remote connection attempt was made.
- Host IP—IP address of the host from which a remote connection attempt was made.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that attempted to establish a remote connection.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Connection to remote host section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Event initiator section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Prevention rule" event
The window with information about events in which prevention rules were triggered, i. e. events of the Blocked application (prevention rule) type, displays the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Blocked application (prevention rule) section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the file that was prevented from running.
- Launch parameters—Parameters that were used for the attempt to run the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the file that was prevented from running.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the file that was prevented from running.
- Size—Size of the file that was prevented from running.
- Event time—Time when the file startup prevention was triggered.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Details section:
- Application name—For example, the name of the operating system.
- Vendor—For example, vendor of the operating system.
- File description—For example, Example File.
- Original file name—For example, ExampleFile.exe.
- Signature subject—Organization that issued the digital certificate of the file.
- Signature validation result—For example, "Signature invalid" or "Signature OK".
- Time created—Creation time of the file that was prevented from running.
- Time modified—Date of last modification of the file that was prevented from running.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Name of the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the file startup prevention was triggered.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the file startup prevention was triggered.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user whose account was used to run the file.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Document blocked" event
The window showing information about Document blocked events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Document blocked section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the blocked document.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the blocked document.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the blocked document.
- Event time—Time when the document was blocked.
- Process file – name of the file of the process that attempted to open the document.
- Process MD5 – MD5 hash of the process that attempted to open the document.
- Process SHA256 – SHA256 hash of the process that attempted to open the document.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Name of the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the document was blocked.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the document was blocked.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that attempted to open the document.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Document blocked section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Event initiator section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "File modified" event
The window displaying information about File changed events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Depending on the type of operation that was performed with the file, one of the following section names is displayed in the event information:
- File created.
- File modified.
- File renamed.
- File deleted.
- File attributes modified.
- File read.
The section displays the following information:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the created, deleted, or modified file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the created, deleted, or modified file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the created, deleted, or modified file.
- Size—Size of the created, deleted, or modified file.
- Event time—Time when the event was detected.
- Time created—Time when the file was created.
- Time modified—Time of last modification of the file.
- Previous version—Name of the previous version of the file.
The Previous version field is displayed in event details only for operations of the File renamed type.
- Remove file after reboot—Status of the file to be deleted.
If the file to which the "delete" operation was applied is opened in any application or is used by other processes, it is deleted when these processes terminate after a restart of the host. In this case, Remove file after reboot displays Yes.
If the file to which the "delete" operation was applied was deleted immediately, the Remove file after reboot field displays No.
The Remove file after reboot field is displayed in event details only for operations of the File deleted type.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the section also includes the following fields:
- File type—Extension of the created, deleted, or modified file.
- File open flags—Value of the open flags for the created, deleted, or modified file.
- Owner user name—Name of the user that created the file.
- Owner group name—Name of the group whose users can modify or delete the file.
- File permitted capabilities—Permissions that can be used to gain access to a created, deleted, or modified file. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- File inheritable capabilities—Permissions that a user group has to perform operations on the parent directory of the created, deleted, or modified file. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- File effective capabilities—Permissions that are relevant to the created, deleted, or modified file at the current moment. This field is not displayed if the event was recorded by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the Event initiator section also includes the following fields:
- Environment variables—Environment variables of the process.
- Real user name—Name of the user assigned when registering in the system.
- Real group name—Group to which the user belongs.
- Effective user name—User name that was used to log in to the system.
- Effective group name—Group of the user whose name was used to log in to the system.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the file was created.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the file was created.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that created the file.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, the System info section also displays the Logon from remote host field for the name of host from which the remote logon was performed.
Clicking the link with the file name or path to the file in the section with information about the file with which the operation was performed opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Event initiator section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the links with the file name or file path to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the Get file task.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac recorded in the event database, you can click the link with the host name to expand a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- File.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "System event log" event
The window displaying information about System event log events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- System event log section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Event time—Time when the event was detected.
- Security event ID—Identifier of the type of security event in the Windows log.
If the event was logged in the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, the System event log section also includes the following fields:
- Event type—Type of the event.
- Operation result—For example, Success or Failed.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- The Event data section containing information from the system log. The scope of data depends on the type of Windows event.
The Event data section is not displayed in information about events logged to the event database by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Linux.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Process file name.
- Process ID—Process identifier.
- Command—Command used to run the parent process.
- Environment variables—Environment variables of the process.
- Real user name—Name of the user assigned when registering in the system.
- Real group name—Group to which the user belongs.
The Event initiator section is not displayed in information about events logged to events database by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the event occurred.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the event took place.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user who started the process that initiated the system log record.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
Event information logged to events database by Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux also includes the Logon from remote host field, that is, the name of the host from which remote logon was performed.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux recorded in the event database, you can click the links with the file name or file path to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the Get file task.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
In the information about the event that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux recorded in the event database, you can click the link with the host name to open a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Changes in the registry" event
The window showing information about Registry modified events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Registry modified section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Key path is the path to the registry key that was modified
- Value name: for example, RegistrySizeLimit
- Value data is the value of the registry entry
- Value type: for example, REG_DWORD
- Event time is the time of registry modification
When changing the name or value of a registry key, you may see additional fields containing information about the state of the registry key prior to its modification:
- The Previous key path field is displayed when the name of the registry key is modified.
- The Previous value data field is displayed when the registry value is modified.
- The Previous value type field is displayed when the type of the registry value is modified.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives the data required to populate the Previous key path, Previous value data, Previous value type fields only when Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is integrated with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows application version 3.10 and higher. When integrating the application with older versions of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, the fields are not displayed in the event information.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the registry modification was made.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the registry modification was made.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that made the change in the registry.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the registry modification was made.
You can view information about the modification of the selected register key by editing or replacing the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform configuration file. To edit or replace the configuration file of the application, you must contact Technical Support.
You are strongly advised not to perform any operations with the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform configuration file in Technical Support Mode without advice or instructions from Technical Support staff.
Information about the "Port listened" event
The window showing information about Port listened events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Port listened section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Local port—Port that was listened to.
- Local IP—IP address of the network interface whose port was listened to.
- Event time—Port listening time.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host whose port was listened to.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Host IP—IP address of the host whose port was listened.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user whose account was used to listen to the port.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host whose port was listened to.
Information about the "Driver loaded" event
The window showing information about Driver loaded events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Driver loaded section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the loaded driver file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the loaded driver file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the loaded driver file.
- Size—Size of the loaded driver.
- Event time—Time when the driver was loaded.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Details section:
- Application name—For example, the name of the operating system.
- Vendor—For example, vendor of the operating system.
- File description—For example, Example File.
- Original file name—For example, ExampleFile.exe.
- Signature subject—Organization that issued the digital certificate of the file.
- Signature validation result—For example, "Signature invalid" or "Signature OK".
- Time created—Creation time of the loaded driver.
- Time modified—Time of last modification of the loaded driver.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the driver was loaded.
- Host IP—IP address of the host to which the driver was loaded.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user that loaded the driver.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Alert" event
The window showing information about a Scan: detection type event contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- On the Details tab, in the Scan: detection section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Detect—Name of the detected object.
Clicking the link with the object name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- View on Kaspersky Threats.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Last action—Last action taken on the detected object.
- Object name—Full name of the file in which the object was detected.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the file in which the object was detected.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the file in which the object was detected.
- Object type—Type of object (for example, a file).
- Detection mode—Scan mode in which the alert was generated.
- Event time—Date and time of the event.
- Record ID—ID of the record of the alert in the database.
- Database version—Version of the database used to generate the alert.
- Content—Contents of the script sent to be scanned.
You can download this data by clicking Save to file.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- On the Details tab, in the Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- Launch parameters—Parent process startup settings.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- On the Details tab, in the System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the alert was created.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—User account used to complete the action taken on the detected object.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
- On the History tab, in the table:
- Type—Type of event: Scan: detection or Scan: detection processing result.
- Description—Description of the event.
- Time—Date and time of detection and alert processing result.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Alert processing result" event
The window showing information about a Scan: detection processing result type event contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- On the Details tab, under Scan: detection processing result:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Detect—Name of the detected object.
Clicking the link with the object name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- View on Kaspersky Threats.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Last action—Last action taken on the detected object.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the file in which the object was detected.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the file in which the object was detected.
- Object type—Type of object (for example, a file).
- Object name—Full name of the file in which the object was detected.
- Detection mode—Scan mode in which the alert was generated.
- Event time—Date and time of the event.
- Record ID—ID of the record of the alert in the database.
- Database version—Version of the database used to generate the alert.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- On the Details tab, under Event initiator:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- Launch parameters—Parent process startup settings.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- On the Details tab, under System info:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the alert was created.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—User account used to complete the action taken on the detected object.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
- On the History tab, in the table:
- Type is the type of the Scan: detection processing result event.
- Description—Description of the event.
- Time is the date and time of the alert processing result.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "Interpreted file run" event
The window displaying information about Process: interpreted file run events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Process: interpreted file run section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- File—Name of the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of a file.
- Size—Size of the file.
- Time created—Time when the file was created.
- Time modified—Time of last modification of the file.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
- Process ID—Identifier of the parent process.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the file was run.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the file was run.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—Name of the user whose account was used to run the file.
- OS version—Version of the operating system being used on the host.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Process: interpreted file run section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path in the Event initiator section opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Information about the "AMSI scan" event
The window showing information about an AMSI scan event contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- In the AMSI scan section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Event time—Date and time of the event.
- Content type—Type of script.
The application provides two types of scripts:
- If the script is presented as text, the Content type field shows the Text script type.
- If the script is presented in another format, the Content type field displays the Binary script type.
- Content—Contents of the script sent to be scanned.
You can copy this data by clicking Copy to clipboard if the data is presented as text or download a file containing the data by clicking Save to file if the data has a different format.
The Content field is displayed in the event information if the application registers signs of targeted attacks.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- In the Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- In the System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the alert was created.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—User account that was used to make the change in the registry.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the alert was generated.
Information about the "Interactive command input at the console" event
The window displaying information about Process: console interactive input events contains the following details:
- Tree of events.
- Recommendations for processing an event.
- Process: console interactive input section:
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
Click the link to display information about the TAA (IOA) rule. If the rule was provided by Kaspersky experts, it contains information about the triggered MITRE technique as well as recommendations for reacting to the event.
The field is displayed if a TAA (IOA) rule was triggered when the event was created.
- Input type—Type of input of commands that were passed to the console application.
The application provides two ways to enter commands:
- If commands were entered by the user in the console application, the Input type field displays the Console command input type.
- If commands were passed to the console application from another application through a pipe, the Input type field displays the Pipe command input type.
If you are using the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application as the Endpoint Agent component, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives the data required to populate the Input field only when Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.10 for Windows. When integrating the application with older versions of the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows application, the field is not displayed in the event information.
- Input text—Text entered at the command line (for example, CMD) on the host with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows application.
You can copy this text by clicking the Copy to clipboard button located in the Input text field.
- Event time—Time when the event was detected.
- IOA tags—Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert.
- Event initiator section:
- File—Path to the parent process file.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- MD5—MD5 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the MD5 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the parent process file.
Clicking the SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find in Storage.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- File—Path to the parent process file.
- System info section:
- Host name—Name of the host on which the command was entered.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Run the following tasks:
- Get data → File, Forensics, Disk image, Memory dump.
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- Host IP—IP address of the host on which the command was entered.
If you are using dynamic IP addresses, the field displays the IP address assigned to the host at the moment when the event was created.
The application does not support IPv6. If you are using IPv6, the IP address of the host is not displayed.
- User name—User account that was used to enter the command.
- OS version—Version of the operating system that is being used on the host.
- Host name—Name of the host on which the command was entered.
Managing Endpoint Agent host information
The application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component is installed on individual computers (hereinafter also referred to as "hosts") in the IT infrastructure of the organization. The application continuously monitors processes running on those hosts, active network connections, and files that are being modified.
Users with the Senior security officer, Security officer, Security auditor, Local administrator, or Administrator role can assess how regularly data is received from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component on the Endpoint Agents tab of the web interface window of the Central Node server for tenants to whose data the user has access. If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the web interface of the PCN server displays the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for the PCN and all connected SCNs.
Users with the Local administrator and Administrator roles can configure the display of how regularly data is received from hosts with Endpoint Agent for tenants to whose data they have access.
If suspicious network activity is detected, users with the Senior security officer role can isolate from the network any host with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, for tenants to whose data the user has access. In this case, the connection between the server with the Central Node component and a host with the Endpoint Agent component will not be interrupted.
In order to provide support in case of problems with the Endpoint Agent component, Technical Support staff may ask you to perform the following actions for debugging purposes (including in Technical Support Mode):
- Activate collection of extended diagnostic information.
- Modify the settings of individual application components.
- Modify the settings for storing and sending the obtained diagnostic information.
- Configure network traffic to be intercepted and saved to a file.
Technical Support staff will provide all the information needed to perform these operations (description of the sequence of steps, settings to be modified, configuration files, scripts, additional command line functionality, debugging modules, special-purpose utilities, and other resources) and inform you about the scope of data obtained for debugging purposes. The retrieved diagnostic information is saved on the user's computer. The retrieved data is not automatically sent to Kaspersky.
The operations listed above should be performed only when instructed by and under the supervision of Technical Support experts. Unsupervised changes to application settings performed in ways other than those described in this manual or according to the instructions of Technical Support experts can slow down or crash the operating system, reduce computer security, or compromise the availability and integrity of data being processed.
Viewing the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
The table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is located in the Endpoint Agents section of the application web interface window.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the table contains information about hosts with the Endpoint Agent component connected to the PCN and all SCN servers.
The table can display the following data:
- Number of hosts and activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component:
- Critical inactivity is the number of hosts from which latest data was received a very long time ago.
- Warning is the number hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Normal activity is the number of hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Host—Name of the host with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Servers is the name of the server to which the host with the Endpoint Agent component is connected.
This field is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- IP is the IP address of the host where the Endpoint Agent component is installed.
- OS is the version of the operating system that is installed on the host with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Version—Version of the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- Activity—Activity indicator of the Endpoint Agent component.
- Normal activity for hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Warning for hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity for hosts from which latest data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Last connection for the date and time of the last connection of the Endpoint Agent component to the Central Node server.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Run the following tasks:
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Kill by unique PID.
- Get file.
- Get forensics.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- New prevention rule.
- Isolate from network.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
The list of available actions depends on the Endpoint Agent component type (for Windows or Linux), version, and activity indicator.
Clicking the link with the IP opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking a link in any other column of the table opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Configuring the display of the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
To configure the display of the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
. - This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The display of the table of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is configured.
Page top
Viewing information about a host
To view information about a host with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Select the host for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the host.
The window contains the following information:
- Recommendations group:
- Clicking the Alerts link opens the Alerts section with the search condition containing the selected host.
- Clicking the Events link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition containing the selected host.
- Clicking the Events affected by prevention rules link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition containing the selected host and the Blocked application (prevention rule) event type.
The Events affected by prevention rules link is not displayed in the information about hosts that use Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux as the Endpoint Agent component.
- On the Details tab, the Host section displays the following information:
- Name is the name of the host with the Endpoint Agent component.
- IP is the IP address of the host where the Endpoint Agent component is installed.
- OS—Version of the operating system on the host with the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- On the Details tab, the Endpoint Agent section displays the following information:
- Version—Version of the Endpoint Agent component installed.
- Activity is the activity indicator of the Endpoint Agent component. Possible values:
- Normal activity for hosts from which latest data was recently received.
- Warning for hosts from which latest data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity for hosts from which latest data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Server—Name of the SCN or PCN server. Only displayed in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Connected to server—Name of the Central Node server.
- Last connection—time of the last connection to the Central Node, SCN, or PCN server.
- License key status—For example, "OK".
- On the Prevention rules tab, you can see MD5 or SHA256 hashes for files that were prevented from running or opening on the host. The following information is displayed:
- Name—Name of the file.
- State—State of the prevention rule.
- Hash—Hashing algorithm.
The Prevention rules tab is not displayed in the information for hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
- On the Tasks tab, you can see which tasks were run on the host. The following information is displayed:
- Time created—Task creation date and time.
- Name—Task name.
- Details—Full path to the file or data stream for which the task was created.
- State—Task completion status.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Run the following tasks:
- Kill process.
- Delete file.
- Get file.
- Get forensics.
- Quarantine file.
- Run application.
- New prevention rule.
- Isolate from network.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
For hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, the list displayed by clicking the link with the host name includes only Get file, Run application, Find events, and Find alerts.
Clicking the link with the IP opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by host name:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Host link to open the filter configuration window.
- If you want to display only isolated hosts, select the Show isolated Endpoint Agents only check box.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the host name.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that have been isolated from the network
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that are isolated from the network:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Host link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select the Show isolated Endpoint Agents only check box.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by PCN and SCN server names
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter or find hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component based on the names of PCN and SCN servers to which those hosts are connected.
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by the names of PCN and SCN servers:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Servers link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select check boxes next to names of servers by which you want to filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by computer IP address
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by IP address of the computer on which the application is installed:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the IP link to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the computer IP address. You can enter the IP address or subnet mask in IPv4 format (for example,
192.0.0.1or192.0.0.0/16). - To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by operating system version on the computer
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by version of the operating system installed on the computer:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the OS link to open the filter settings window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the operating system version.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version
You can filter hosts by version of the application that is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by component version:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Version link to open the filter settings window.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or more characters of the version of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - If you want to delete the filter condition, click the
 button to the right of the field.
button to the right of the field. - Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity
To filter or search for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component by their activity:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the Activity link to open the filter configuration window.
Select check boxes next to one or multiple activity indicators:
- Normal activity, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was recently received.
- Warning, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was received a long time ago.
- Critical inactivity, if you want to find hosts from which the last data was received an extremely long time ago.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Quickly creating a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To quickly create a filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Do the following to quickly add filter conditions to the filter being created:
- Position the mouse cursor on the link containing the table column value that you want to add as a filter condition.
- Left-click it.
This opens a list of actions to perform on the value.
- In the list that opens, select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value, if you want to include this value in the filter condition.
- Exclude from filter, if you want to exclude the value from the filter condition.
- If you want to add several filter conditions to the filter being created, perform the actions to quickly add each filter condition to the filter being created.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
Resetting the filter for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To clear the Endpoint Agent host filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only those hosts that match the filter criteria you have set.
Removing hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To remove one or more hosts from the Endpoint Agents table:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
- Select check boxes next to one or more hosts that you want to remove. You can select all hosts by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Delete.
- This opens the action confirmation window; in that window, click Yes.
The selected hosts are removed from the Endpoint Agents table.
When hosts are removed the following changes are made in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- You cannot create a task, prevention rule, or network isolation rule for a removed host.
- If a prevention rule was previously created for a host, its name in the rule window (the Prevent on field) is hidden when the host is removed. The rule continues to apply.
If this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the host name is restored in the Prevent on field and the prevention rule is applied to it again.
- If a network isolation rule was previously created for a host, it continues to apply until the time specified in the rule expires.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node, the rule is reapplied to this host.
- The metadata of objects quarantined on the remote host are deleted from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Quarantine.
When this host reconnects to the Central Node server, the metadata of objects in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform Quarantine are not restored. You can avoid Quarantine filling up on a host by clearing it on command line or in Kaspersky Security Center. For details, see the Help of the application that you are using in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
- If an object was quarantined by the Quarantine file task on one host only and that host was removed, the Restore all button in task window is inactive because the file cannot be restored on a removed host.
Event search by the name of the removed host remains available.
Configuring activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component
Users with the Local administrator and Administrator roles can define what durations of inactivity of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component are to be considered normal, low, or very low activity, and can configure the activity indicators for the application. Users with the Security auditor role can only view the settings of application activity indicators. Users with the Senior security officer or Security officer role can see activity indicators that you configured for the Endpoint Agent component in the Activity field of the Endpoint Agent host table in the Endpoint Agents section of the application web interface.
To configure activity indicators for the Endpoint Agent component:
- Sign in to the application web interface under the Local administrator, Administrator or Senior security officer account.
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agents subsection.
- In the fields under the section name, enter the number of days of inactivity of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that you want to display as Warning and Critical inactivity.
- Click Apply.
Activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component are configured.
Supported interpreters and processes
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application monitors the execution of scripts by the following interpreters:
- cmd.exe
- reg.exe
- regedit.exe
- regedt32.exe
- cscript.exe
- wscript.exe
- mmc.exe
- msiexec.exe
- mshta.exe
- rundll32.exe
- runlegacycplelevated.exe
- control.exe
- explorer.exe
- regsvr32.exe
- wwahost.exe
- powershell.exe
- java.exe and javaw.exe (only if started with the –jar option)
- InstallUtil.exe
- msdt.exe
- python.exe
- ruby.exe
- rubyw.exe
Information about the processes monitored by Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application is presented in the table below.
Processes and the file extensions that they open
Process |
File extensions |
|---|---|
winword.exe |
rtf doc dot docm docx dotx dotm docb |
excel.exe |
xls xlt xlm xlsx xlsm xltx xltm xlsb xla xlam xll xlw |
powerpnt.exe |
ppt pot pps pptx pptm potx potm ppam ppsx ppsm sldx sldm |
acrord32.exe |
|
wordpad.exe |
docx |
chrome.exe |
|
MicrosoftEdge.exe |
Network isolation of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
When responding to threats, users with the Senior security officer role can isolate hosts with detected objects that require your attention during the incident investigation.
Network isolation is not a Threat Response action by itself. The security officer should take steps to investigate the incident on his own while the network isolation is active for the host. You can configure the duration of host network isolation when you create the network isolation rule.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows as the Endpoint Agent component, network isolation is available for hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent application version 3.8 and later.
To ensure correct operation of an isolated host, it is recommended to meet the following conditions:
- Create a local administrator account on the host or save the domain account data to the cache before enabling the network isolation rule.
- Do not change the certificate and IP address of the server with the Central Node component while the network isolation rule is enabled.
Isolated hosts can access the following resources over the network:
- Server with the Central Node component.
- Source of application database updates (Kaspersky update server or custom source).
- Servers of the KSN service.
- Hosts added to network isolation rule exclusions.
In cases when the Endpoint Agent component is turned off on the host, and also for a certain period of time after turning on th component or restarting the computer with the component, network isolation of the host may be inactive.
Consider some limitations when applying network isolation.
Creating a network isolation rule
To create a network isolation rule:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Select the host for which you want to enable or disable the network isolation rule.
This opens a window containing information about the host.
- Click Isolate.
- In the Disable isolation after field, enter the time in hours (1 to 9999) during which network isolation of the host will be active.
- In the Exclusions for the host isolation rule settings group, in the Traffic direction list, select the direction of network traffic that must not be blocked:
- Incoming/Outgoing.
- Incoming.
- Outgoing.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address whose network traffic must not be blocked.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can use a proxy server for the connection of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When you add this proxy server to exclusions, network resources that can be accessed through the proxy server are also added to exclusions. If network resources that are accessed through the proxy server are added to exclusions, but the proxy server itself is not, such exclusions do not work.
- If you selected Incoming or Outgoing, in the Ports field enter the connection ports.
- If you want to add more than one exclusion, click Add and repeat the steps to fill in the Traffic direction, IP and Ports fields.
- Click Save.
The host will be isolated from the network.
You can also create a network isolation rule by clicking the Isolate <host name> link in the event information and in the alert information.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create network isolation rules.
The network isolation feature is not available for hosts where Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux is used as the Endpoint Agent component.
Adding an exclusion from a network isolation rule
To add an exclusion to a previously created network isolation rule:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Select the isolated host for which you want to create an exclusion from the network isolation rule.
This opens a window containing information about the host.
- Click the Add to exclusions link to expand the Exclusions for the host isolation rule settings group.
- Select the direction of network traffic that must not be blocked:
- Incoming/Outgoing.
- Incoming.
- Outgoing.
- In the IP field, enter the IP address whose network traffic must not be blocked.
- If you selected Incoming or Outgoing, in the Ports field enter the connection ports.
- If you want to add more than one exclusion, click Add and repeat the steps to fill in the Traffic direction, IP and Ports fields. Click Save.
The network isolation rule exclusion will be added.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can use a proxy server for the connection of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. When you add this proxy server to exclusions, network resources that can be accessed through the proxy server are also added to exclusions. If network resources that are accessed through the proxy server are added to exclusions, but the proxy server itself is not, such exclusions do not work.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create exclusions from a network isolation rule.
Page top
Deleting a network isolation rule
To delete a network isolation rule:
- Select the Endpoint Agents section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of hosts.
- Click the name of the host for which you want to delete a network isolation rule to open the action menu for the host.
- Select the Delete host isolation rule action.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The network isolation rule for the host is deleted.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot remove network isolation rules.
Limitations that are relevant to network isolation
Some limitations apply when network isolation is used:
- When a network isolation rule is enabled on a host, all current connections are disconnected and a VPN connection becomes unavailable.
- If the application administrator replaces the certificate of the server with the Central Node component while a network isolation rule is enabled, you cannot disable the rule.
- The application blocks the connection of isolated hosts with an Active Directory server. If the operating system settings require a connection to Active Directory services for authorization, the user of an isolated host will not be able to log in to the system.
Automatically sending files from Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts to be scanned by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules
If this functionality is enabled, the application can automatically send files from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component for scanning with the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules. Files are sent in accordance with the following principle:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform checks the event database and marks events that match TAA (IOA) rules.
- If relevant conditions are found in TAA (IOA) rules, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends files for scanning by the Sandbox component.
Requests for scanning files by the Sandbox component are not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
- Based on the results of the scan, the application can add alerts to the alert database.
You can view alerts created in this way by filtering alerts by the Details – Autosend to Sandbox attribute.
If automatic sending of files to be scanned by the Sandbox component is enabled, the volume of traffic processed by the component can become very large. If the Sandbox component server cannot support the increased load, some of the objects from the processing request queue are replaced with requests for processing files that are automatically sent for scanning.
To avoid dropping objects from the processing request queue, you can:
- Deploy additional Sandbox servers.
- Disable automatically sending files to be scanned by the Sandbox component.
- Add to exclusions those TAA (IOA) rules that most frequently cause Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to send files for scanning by the Sandbox component.
Information about rules that are most frequently used by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to send files for scanning by the Sandbox component is displayed in the Sent to Sandbox by TAA rules widget. You can add this widget to your current layout.
When you add a file to exclusions, event marking and creation of alerts in accordance with this rule is also stopped.
Files that can be automatically sent for scanning by the Sandbox component are listed in the following table.
List of files that can be automatically sent for scanning by the Sandbox component
Event type |
File type |
|---|---|
Process started |
File of the started process and file of its parent process. |
Module loaded |
File of the loaded module and file of its parent process. |
Connection to remote host |
File of the parent process. |
Blocked application (prevention rule) |
File of the application that was blocked from running, and file of its parent process. |
Document blocked |
File of the document that was blocked from running, and file of its parent process. |
File changed |
Created, deleted, or modified file and file of the parent process. |
System event log |
File of the process (only for Linux). |
Registry modified |
File of the parent process. |
Port listened |
File of the parent process. |
Driver loaded |
File of the loaded driver. |
Scan: detection |
Detected file and file of its parent process (if any). |
Scan: detection processing result |
Detected file and file of its parent process (if any). |
AMSI scan |
File of the process. |
Process: interpreted file run |
File that was started and file of its parent process. |
Process: console interactive input |
File of the parent process. |
Information about files sent for scanning by the Sandbox component is not displayed in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
Enabling and disabling the automatic sending of files from hosts with the Endpoint Agent component to be scanned by the Sandbox component
To enable or disable automatically sending files to be scanned by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agents subsection.
- Under Send files to Sandbox automatically:
- Select the Send files check box if you want files to be sent automatically.
This function is enabled by default.
- Clear the Send files check box if you do not want files to be sent automatically.
Disabling this functionality does not affect the functioning of TAA (IOA) rules; only automatic sending of files is disabled.
- Select the Send files check box if you want files to be sent automatically.
- Click Apply.
Automatically sending files to be scanned by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules is enabled or disabled.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, settings for automatically sending files for scanning by the Sandbox component in accordance with Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules configured on the PCN server are also applied on SCN servers connected to that PCN server. If necessary, you can enable or disable the automatic sending of files on each selected SCN server individually.
Page top
Selecting operating systems to use when scanning objects in Sandbox
Users with the Senior security officer role can select a set of operating systems used as the basis for creating tasks for scanning objects by the Sandbox component. The Sandbox server must have virtual machines installed that match the selected set.
You can view a list of Sandbox servers and virtual machines deployed on a server.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of Sandbox servers and settings for a set of operating systems. Users with the Security officer role cannot view this section.
Page top
Viewing the table of servers with the Sandbox component
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
Users with the Senior security officer role can view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
To view the table of servers with the Sandbox component:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Sandbox servers subsection.
- Select the Servers tab.
A table is displayed with a list of Sandbox servers.
The table contains the following information:
- IP and name—IP address or fully qualified domain name of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Authorization—Status of the request to connect to the Sandbox component.
- Status—Status of the connection to the Sandbox component.
- Certificate fingerprint—Certificate fingerprint of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Virtual machines—List of virtual machines created on the server.
Selecting operating systems to use when scanning objects in Sandbox
To select the set of operating systems:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Sandbox servers subsection.
- Go to the Settings tab.
- Under OS set, select one of the following options:
- Windows 7, Windows 10.
- CentOS 7.8, Windows 7, Windows 10.
- Astra Linux 1.7, Windows 7, Windows 10.
- Custom.
- If you selected Custom, under Set composition, select the check boxes next to the operating systems that you want to include in the set.
Custom operating systems are displayed in the list if virtual machines with these operating systems are installed on the Sandbox server. Preset operating systems are always displayed in the list, but if virtual machines running these operating systems are not deployed, the Unknown status is displayed next to the name of the operating system.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will create tasks for scanning objects in Sandbox in accordance with the selected set.
If the set of operating systems installed on the Sandbox server does not match the set selected on the Central Node server, objects are not sent to be scanned by that Sandbox server. If multiple Sandbox servers are connected to the Central Node server, the application sends objects to those Sandbox servers whose installed operating systems match the set selected on Central Node.
You can change the set of operating systems in the course of using the application. In this case, you need to make sure that the configuration of the Sandbox server satisfies hardware requirements.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the settings of the operating system set configured on the PCN server are not applied to SCN servers connected to that PCN server. You can select the set of operating systems for each PCN and SCN server individually.
Page top
Managing tasks
Users with the Senior security officer role creating tasks on a server have unlimited (root) access rights for all hosts with the Endpoint Agent component that are connected to that server.
In the web interface of the application, users with the Senior security officer role can manage files and applications on hosts by creating and removing tasks.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, Kill process, Get forensics, Get registry key, Start YARA scan, Service management, Run application, Delete file, Restore file from quarantine, Quarantine file tasks can have one of the following types:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These tasks apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These tasks apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
Get file, Get process memory dump, Get NTFS metafiles, Get disk image, Get memory dump tasks run only on the specified host, regardless of the application operating mode.
The maximum task execution time is 24 hours. If the task did not complete in this time, execution is paused.
Users with the Senior security officer role can manage all tasks for tenants to whose data they have access.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the task table and information about the selected task.
Viewing the task table
The tasks table contains a list of created tasks and is in the Tasks section of the application web interface window. You can view all tasks or only tasks created by you (current user).
You can show or hide tasks created by you using the Only mine toggle switch in the upper right corner of the window. The display of tasks created by the current user is enabled by default.
The tasks table contains the following information:
- Time—Task creation date and time.
- Type is the type of the task depending on the operating mode of the application and the server on which the task was created.
Tasks may be one of the following types:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These tasks apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These tasks apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
- Name—Task name.
Clicking the link with the name of the task type opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Details—full path to the file or data stream for which the task was created, or the path to a shared network resource.
Clicking the link containing information about the path to the file or data stream opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Servers—Name of the server with the PCN or SCN role on which the task is being run.
This field is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Hosts—Name of the host on which the task is run.
This field is displayed only if you are using a standalone Central Node server.
- Created by—Name of the user who created the task.
If only tasks created by the current user are displayed, this column is not displayed.
- State—Task completion status.
A task can have one of the following statuses:
- Pending.
- In process.
- Completed.
Viewing information about a task
To view task details:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Select the task for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the task.
The window can contain the following information depending on the task type:
- State—Task completion status.
- Description is the task description.
- File path—Path to the file or data stream.
- Information type—Type of the collected data.
- Registry key—Path to the registry key that you want to get.
- Process ID—Process identifier.
- Mask—Mask of files that are included in the data list.
- Metafiles—NTFS metafiles that you want to get.
- Volume—name of the drive from which you want to receive metafiles, disk image, or memory dump.
- Share path—path to a shared network resource.
- Stored file—link to the file received as a result of the task execution.
- Maximum nesting level—Maximum nesting level of folders which the application searches for files.
- Exclusions—Folders in which searching and scanning files is prohibited.
- Scan scope—Folders which are scanned by YARA rules.
- Action—Action that was performed for the service.
The application supports the following operations with services:
- Start.
- Stop.
- Pause.
- Resume.
- Delete.
- Modify startup type.
- Maximum scan duration—Maximum task execution time, after which the scan is stopped.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of the file that you want to receive.
- Run as—Option to run the application using the name of the local system.
- Created by—Name of the user who created the task.
- Tenant—Name of the tenant. Displayed only when you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Time created—Time when the task was created.
- Time completed—Task completion time.
- Report—Task result on selected hosts.
Creating a get file task
You can retrieve a file from selected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create a get file task.
The file to be downloaded must not exceed 100 MB. If the file exceeds 100 MB, the task finishes with an error.
To create a get file task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select File in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- File path—Path to the file that you want to receive.
If the requested file is linked to other NTFS data streams, running the task yields all files of NTFS data streams that the requested file is linked to.
You can also specify the path to an alternate data stream of this file. In this case, you receive only the files of the specified stream.
When creating a task, the application does not check if the specified path to the file that you want to receive is valid.
- MD5/SHA256—MD5- or SHA256 hash of the file that you want to receive. This field is optional.
- If you do not want to scan the file, clear the Send for scanning check box.
The check box is selected by default.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Host is the name or IP address of the host.
You can specify only one host.
- File path—Path to the file that you want to receive.
- Click Add.
The get file task will be created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
A file received through this task will be placed in Storage. If the get file task completed successfully, you can download the received file to your local computer.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the archive is placed in Storage of the Central Node server to which the host specified in the Host field is connected.
You can also download the file from the task report window.
To download the file from the task report window:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Open the get file task that you want to download.
- In the Report section, click the name or IP address of the host.
This opens a window containing information about the file.
- Click Download.
The file will be saved to your local computer in the browser's downloads folder.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create get file tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a forensic collection task
You can get lists of files, processes, and autorun points from selected Endpoint Agent hosts. To do so, you must create a forensic collection task.
To create a forensic collection task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select Forensics in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Information type is the type of collected data. Select the check box next to one, multiple, or all settings:
- Processes list if you want to get a list of processes running on the host at the time of the task execution.
- Autorun points list if you want to get a list of autorun points.
The autorun points list includes information about applications added to the startup folder or registered in the Run keys of the registry, as well as applications that are automatically run at startup of a host with the Endpoint Agent component and when a user logs in to the operating system on the specified hosts.
- File list if you want to get a list of files stored in the selected folder or in all host folders at the time of the task execution.
- If you have selected the File list check box, in the Source type group of settings, select one of the following options:
- All local disks if you want the list of files to include files stored in all folders on local disks at the time of the task execution.
- Directory if you want the file list to include files stored in the specified folder and its subfolders at the time when the task is run.
- If you selected Directory, in the Start directory field, specify the path to the folder from which the file search should start.
You can use the following prefixes:
- System environment variables.
- User-defined environment variables.
When using user-defined environment variables, the list of files includes information about files in folders of all users who have set the specified environment variables. If user-defined environment variables override system environment variables, the list of files includes information about files in folders based on the values of system environment variables.
- In the Hosts field, enter the IP address or name of the host to which you want to assign the task.
You can specify multiple hosts.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the forensics collection task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.10 and later. Getting a list of autorun points is only supported on hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows 3.12 and higher.
If necessary, you can specify the following search criteria for files in folders:
- Mask is the mask of files to be included in the list of files.
- Alternative data streams is the check box that enables recording information about alternate data streams in the file list.
If the requested file is linked to other NTFS data streams, running the task yields all files of NTFS data streams that the requested file is linked to.
The check box is selected by default.
- Maximum nesting level is the maximum nesting level of folders in which the application searches for files.
- Exclusions is the path to the folders in which you want to prohibit the search for information about files.
- Description is the task description.
- Information type is the type of collected data. Select the check box next to one, multiple, or all settings:
- Click Add.
The forensic collection task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
As a result of the task, the application places a ZIP archive in Storage; the archive contains a file with the selected data. If the task completed successfully, you can download the archive to your local computer.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create forensic collection tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a registry key retrieval task
You can retrieve a registry key from selected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create a registry key retrieval task.
To create a registry key retrieval task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select Registry key in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Registry key is the registry key that you want to get.
You can enter the registry key in one of the following formats:
- Relative to the root key.
For example, \REGISTRY\MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsUpdate\Orchestrator.
- Relative with full name of the root key.
For example, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsUpdate\Orchestrator.
- Relative with an abbreviation instead of the full name of the root key.
For example, HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsUpdate\Orchestrator.
If you want to get data from HKEY_CURRENT_USER, you must specify HKEY_USERS and the SID of the user: HKEY_USERS\<SID of the user>.
- Relative to the root key.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- In the Hosts field, enter the name or IP address of the host to which you want to assign the task.
You can specify multiple hosts.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the registry key retrieval task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.13 and later.
- Registry key is the registry key that you want to get.
- Click Add.
The registry key retrieval task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
As a result of the task, the application places a ZIP archive in Storage; the archive contains a .reg file, which contains a list of all registry keys and values under the key that was specified when creating the task. You can download the archive to your local computer.
If the task results in an error, the archive file contains the description of the error.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create this task.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating an NTFS metafile retrieval task
You can retrieve NTFS metafiles from selected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create an NTFS metafile retrieval task.
To create an NTFS metafile retrieval task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select NTFS metafiles in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Metafiles is the list of metafiles that you can get using the task. Select the relevant metafile by selecting the corresponding check box.
You can select multiple metafiles.
- Volume is the name of the disk from which you want to get metafiles.
By default, the system disk is specified. You can enter the path to a different disk in the
<drive letter>:format. - Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Hostis the name or IP address of the host to which you want to assign the task.
You can specify only one host.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the NTFS metafile retrieval task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.13 and later.
- Metafiles is the list of metafiles that you can get using the task. Select the relevant metafile by selecting the corresponding check box.
- Click Add.
The NTFS metafile creation task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
When the task finishes, the application places a ZIP archive containing the selected metafiles in Storage. You can download the archive to your local computer.
If the task results in an error, the archive file contains the description of the error.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the archive is placed in Storage of the Central Node server to which the host specified in the Host field is connected.
If downloading selected metafiles exhausts Storage capacity, objects in Storage will be rotated. If a metafile is larger than total Storage capacity, it is not downloaded
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create this task. Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a process memory dump retrieval task
You can retrieve a process memory dump from selected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create a process memory dump retrieval task.
To create a process memory dump retrieval task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select Process memory dump in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Process ID is the ID of the process for which you want to get a memory dump.
- MD5/SHA256 is the MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file of the process of which you want to get a memory dump. This field is optional.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Hostis the name or IP address of the host to which you want to assign the task.
You can specify only one host.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the process memory dump retrieval task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.13 and later.
- Click Add.
The process memory dump retrieval task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
The task creates a ZIP archive in Storage, which contains a file with information about the process and a process memory dump file. You can download the archive to your local computer.
If the task results in an error, the archive file contains the description of the error.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, the archive is placed in Storage of the Central Node server to which the host specified in the Host field is connected.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create this task.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a disk image retrieval task
You can retrieve a disk image from selected Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows host. To do so, you must create an NTFS disk image retrieval task.
The resulting file can be saved only to a shared network resource.
To create a disk image retrieval task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select Disk image in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Share path—path to a shared network resource.
You need to specify the path in the Universal Naming Convention (UNC) format:
\\server\share\path.If the last folder with the specified name is absent, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will create one. If creation is unsuccessful, an error will be displayed in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- User name—user name of the account used to access the shared network resource.
- Password—password of the account used to access the shared network resource.
- Under Disk type, select one of the following options:
- Logical.
- Physical.
- If you selected Logical, enter a
% SystemDrive%variable or a drive letter without the colon and slash in the Volume field. - If you selected Physical, enter the disk number in the Physical drive field.
- Select the Split file into parts check box if you want the file to be divided into multiple parts when saved.
- If you selected the check box, in the Part size, GB field, specify the minimum size of one part of the saved file.
The minimum part size must be more than one gigabyte.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Host—the IP address or name of the host to which you want to assign the task.
- Share path—path to a shared network resource.
- Click Add.
The disk image retrieval task will be created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
The application places an archive containing a file or files in the EWF or RAW format in a network share. You can convert files from the RAW format to the EWF format.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.14 and later.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Converting a file from RAW to EWF format
Kaspersky Endpoint Security saves the disk image in the RAW format. Files can also be compressed into an archive. A special Python script allows converting files from the RAW format to the EWF format. The script constantly looks for RAW files in the specified folder. If such files are detected, the script automatically converts the files to the EWF format.
convert_to_ewf_monitor.py script
For the script to work, the following software must be installed on the computer:
- The libewf library for accessing Expert Witness Compression Format (EWF) files.
The libewf library is open source software.
It is recommended to place the library files and the script file in the same folder.
- The Python interpreter.
To enable the conversion of disk image files:
- Start the command line interpreter.
- Change to the folder where the script is located.
- Run the following command:
py convert_to_ewf_monitor.py --source <full path to the source files folder> [additional settings]EWF conversion script parameters
Parameter
Description
--source <full path to folder>The full path to the folder in which the script looks for source files. The script also looks for files in subfolders at the specified path. This is a mandatory parameter.
--destination <full path to folder>The full path to the folder where the script saves converted files. The folder structure is preserved. By default, the script saves converted files in the folder specified in the
sourceparameter.--deleteDelete source files after successful conversion. If the conversion fails, the script skips deleting the source files and you can try again.
--ewftool <full path to folder>The full path to the ewfacquirestream.exe file. The path must include the file name. By default, the script attempts to locate the ewfacquirestream.exe file in the folder where the script is located.
--name_mask <regular expressions>Regular expressions to find source files to convert. You can use this option if you need to convert individual files. By default, the script looks for files using the
^diskdump_regular expression.--convert_single_dumpFind a single file to convert. After successful conversion of the single file, the script exits.
--workers_num <number of files>The maximum number of source files that the script can convert at the same time. You can use this setting to optimize the performance of the script. By default, the script can convert up to four files at a time.
--log_level <log level>Logging level. By default, the script uses the DEBUG logging level.
--log_path <full path to folder>The full path for saving log files. The path must include the file name of the log file. By default, the script displays events on the interpreter console.
Example:
|
Creating a RAM dump retrieval task
You can retrieve a RAM dump from a selected host with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create a memory dump retrieval task.
The resulting file can be saved only to a shared network resource.
To create a memory dump retrieval task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Add button and select Memory dump in the Get data drop-down list.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Share path—path to a shared network resource.
You need to specify the path in the Universal Naming Convention (UNC) format:
\\server\share\path.If the last folder with the specified name is absent, Kaspersky Endpoint Agent will create one. If creation is unsuccessful, an error will be displayed in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- User name—user name of the account used to access the shared network resource.
- Password—password of the account used to access the shared network resource.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Host—the IP address or name of the host to which you want to assign the task.
- Share path—path to a shared network resource.
- Click Add.
The RAM dump retrieval task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
As a result, the application places a RAW file or an archive that contains a RAW file on the shared network resource.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.14 and later.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a process termination task
If you believe that a process running on the computer could threaten the security of the computer or the corporate LAN, you can terminate the process.
To create a process termination task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Kill process.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- File path —Path to the file of the process that you want to terminate.
You can also specify the path to an alternate data stream of this file. In this case, only processes of the specified data stream will be terminated. The processes of the other streams of this file will be executed.
- MD5/SHA256—MD5- or SHA256 hash of the file of the process that you want to terminate. This field is optional.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Task for—Task scope:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
- File path —Path to the file of the process that you want to terminate.
- Click Add.
The process termination task will be created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create process termination tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a task to scan hosts using YARA rules
You can scan hosts with the Endpoint Agent component using YARA rules. To do so, you must create a Start YARA scan task. You can create the task:
- In the Tasks section.
In this case, when creating the task, you must select YARA rules that you want to use to scan hosts.
- In the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
In this case, a task is created to scan hosts using selected YARA rules.
To create a task for scanning hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component using YARA rules in the Tasks section:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Start YARA scan.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Select rules is the name of the rule. You can enter the name of the rule or a sequence of characters from the name of the rule, then select the rule in the list.
You can add multiple rules.
- Scan is the scan scope. Select one of the following options:
- RAM if you want to scan processes that are running at the time of the task execution.
The application does not scan processes with a low priority.
- Autorun points if you want to scan autorun points obtained from the Get forensics task.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, this function is available only when integrated with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.13 or later.
To have autorun points scanned, you must specify hosts for which the Get forensics was previously run.
- Specified directories if you want to scan files that are located in a specified folder and all its nested folders at the time of the task execution.
- All local disks if you want to scan files stored in all folders on local disks at the time of the task execution.
Scanning all local disks can cause high load on the host.
- RAM if you want to scan processes that are running at the time of the task execution.
- If you selected RAM, if necessary, do the following:
- In the Processes field, enter short names of processes or a mask of files that you want to scan.
The application scans all processes with identical names that are running on the host.
If the Processes field is left blank, the application scans all processes that were running at the time of the task execution, except processes with PID under 10 and processes listed in the Exclusions field.
- In the Exclusions field, enter short names of processes or a mask of files that you want to exclude from scanning.
If multiple processes with identical names are running on the host, the application excludes all such processes from scanning.
- In the Processes field, enter short names of processes or a mask of files that you want to scan.
- If you selected Autorun points, in the Scan type field, select the scan type:
- Quick.
In this case, all autorun points are scanned, except COM objects.
- Full.
In this case, all autorun points are scanned, as well as files involved with them.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows as the Endpoint Agent component, a full scan is performed regardless of the selected setting.
- Quick.
- If you selected Specified directories:
- In the Specified directories field, specify the path to the directory in the format C:\<directory name>\*.
- In the Exclusions field, specify the path to the directory in the format C:\<directory name>\*.
- Maximum scan duration is the maximum scan duration.
When this time elapses, the scan is stopped even if some rules were not applied to scan the hosts. The task report contains results that are up-to-date at the moment when the scan was stopped.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Task for—Task scope:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the task for scanning Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts using YARA rules can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.12 and later. If you simultaneously assign a task to hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.12 and earlier versions of the application, the task is executed only on hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent 3.12.
- Select rules is the name of the rule. You can enter the name of the rule or a sequence of characters from the name of the rule, then select the rule in the list.
To create a task for scanning Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows hosts using YARA rules in the Custom rules section, YARA subsection:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
- Select check boxes to the left of rules that you want to use when scanning the hosts.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Start YARA scan.
- Carry out step 3 of the instruction above.
Task creation is complete. The task runs automatically after it is created.
If the scan detects any threats, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform creates corresponding alerts.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create a task for scanning hosts using YARA rules.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a service management task
You can remotely start, stop, pause, or resume a service, as well as remove a service or change its start type on selected hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. To do so, you must create a service management task.
To create a service management task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Service management.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- In the Service name field, enter the name of the service.
- In the MD5/SHA256 field, enter the MD5 or SHA256 hash of the service. This field is optional.
If you enter the hash of a service that is loaded from a DLL, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform simultaneously compares the specified hash with the hash of the service DLL and the hash of the svchost process.
- In the Action field, select the operation that you want to perform on the service.
The application supports the following operations with services:
- Start.
- Stop.
- Pause.
- Resume.
- Delete.
- Modify startup type.
When you remove a service, processes that the service has started keep running until the system is restarted or the process is terminated.
- If you selected Modify startup type, in the Startup type, select the start type for the service.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Task for—Task scope:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Agent as the Endpoint Agent component, the task can be assigned only to hosts running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows version 3.12 and later. Hosts running earlier versions of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows are displayed in the list of hosts, but cannot be selected.
- Click Add.
The service management task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
Stopping, pausing, deleting services or changing the start type of services that affect the functioning on the host is strongly discouraged. |
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create service management tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating an application execution task
You can create an application running task or command execution task.
If the standard output file or error output file reaches a size of 100 KB when the task is running, some of the data is deleted from the file. The file will not contain all the data.
To create a task for running an application or executing a command:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Run application.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- In the File path and Working directory fields, enter values in one of the following ways:
- In the File path field, enter the full path to the executable file (for example,
C:\Windows\System32\ipconfig.exe).Leave the Working directory field empty.When creating a task, the application does not check if the specified path to the executable file is valid.
- In the File path field, enter the name and extension of the executable file (for example,
ipconfig.exe). In the Working directory field, enter the working directory (for example,C:\Windows\System32\).
- In the File path field, enter the full path to the executable file (for example,
- In the Arguments field, enter additional options for running the file or task (for example, the
/allargument). - In the Description field, enter the task description. This field is optional.
- Configure the Task for setting, that is, the task scope:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
- In the File path and Working directory fields, enter values in one of the following ways:
- Click Add.
The application running task or command execution task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
Example: To run the
|
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create application running tasks or command execution tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a file deletion task
To create a file deletion task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Delete file.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- File path—Path to the file that you want to delete.
You can also specify the path to an alternate data stream of this file. In this case, only the specified data stream will be deleted. The other data streams of this file will be left unchanged.
- MD5/SHA256—MD5- or SHA256 hash of the file that you want to delete. This field is optional.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- Task for—Task scope:
- If you want to run the task on all hosts of all servers, select the All hosts option.
- If you want to run the task on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to run the task.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to run the task on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
- File path—Path to the file that you want to delete.
- Click Add.
The file deletion task will be created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
If the file has been blocked by another process, the task will be displayed with the Completed status but the file will be deleted only after the host is restarted. It is recommended to check whether the file is successfully deleted after the host is restarted.
Deleting the file from a mapped network drive id not supported.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create file deletion tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a file quarantine task
If you believe that an infected or probably infected file is on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component, you can isolate it by putting it into quarantine.
To create a file quarantine task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Quarantine file.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- In the File path field, enter the path to the file that you want to quarantine.
- In the MD5/SHA256 field, enter the MD5 or SHA256 hash of the file that you want to quarantine. This field is optional.
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- In the Hosts field, enter the name or IP address of the host to which you want to assign the task.
You can specify multiple hosts.
- Click Add.
The file quarantine task is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
As a result of the task:
- The file is deleted from the folder of the computer where it is located and moved to the Quarantine directory on the same computer, which was specified during configuration of the application that is used as the Endpoint Agent component.
- In the task list of the Tasks section of the application web interface, execution information about the task is displayed.
- In the file list in the Storage section, Quarantine subsection, information about the quarantined file is displayed.
If the file has been blocked by another process, the task is displayed with the Completed status but the file is placed in Quarantine only after the host is restarted. It is recommended to check whether the task was successfully completed after the host is restarted.
The file quarantine task can finish with the Access denied error if you are trying to quarantine an executable file and it is currently running.
To solve this problem, create a process termination task for this file, and then try creating the file quarantine task again.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create file quarantine tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a quarantined file recovery task
If you believe that a previously isolated file is safe, you can restore it from Quarantine to the host.
To create a task for restoring a file from Quarantine:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click Add and select Restore file from quarantine.
This opens the task creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Description is the task description. This field is optional.
- File search—Name of the file in Quarantine.
- Click Add.
The task for restoring a file from Quarantine is created. The task runs automatically after it is created.
After restoring a file from Quarantine to a host, metadata about the file remains in the table of objects placed in Storage.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, a file that is quarantined on an SCN server cannot be restored on the PCN server. You can restore the file on the SCN server on which the quarantine file task was created.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create tasks to restore files from Quarantine.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Creating a copy of a task
To copy the task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Open the task that you want to copy.
- Click Duplicate.
This opens the task creation window. All task settings will be copied.
- If you want to modify task settings, edit one or more settings depending on the type of the task being copied.
- Click Add.
A copy of the selected task will be created.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot copy tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Deleting tasks
If you delete a task while it is running, the task results might not be saved.
If you delete a successfully completed file download task, the file is also deleted.
To delete a task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Open the task that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The task will be deleted.
To delete all or multiple tasks:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Select check boxes next to the tasks that you want to delete.
You can select all tasks by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected tasks are deleted.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete tasks.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to tasks.
Filtering tasks by creation time
To filter tasks by creation time:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Time link to open the task filtering menu.
- Select one of the following task display periods:
- All if you want the application to display all created tasks in the table.
- Last hour if you want the application to display tasks that were created during the last hour in the table.
- Last day if you want the application to display tasks that were created during the last day in the table.
- Custom range if you want the application to display tasks that were created during a specified period in the table.
- If you have selected the Custom range task display period:
- This opens the calendar; in the calendar, specify the start and end dates of the task display period.
- Click Apply.
The calendar closes.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks by type
If you are using distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter tasks by their type.
To filter tasks by type:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Type link to open the task filtering menu.
- Select one of the following task display options:
- All, if you want to display all tasks regardless of their type.
- Global, if you want to display only tasks that were created on the PCN server. These tasks apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
- Local, if you want to display only tasks that were created on a SCN server. These tasks apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Tasks belong to the tenant for which the user is managing the program using the web interface.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks by name
To filter tasks by name:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Name link to open the task filtering menu.
- Select one or more check boxes:
- Kill process
- Run application
- Get forensics
- Start YARA scan
- Service management
- Get file
- Delete file
- Quarantine file
- Restore file
- Click Apply.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks by file name and path
You can filter tasks based on the Details criterion—Name and path to the file or data stream.
To filter tasks by name and path to the file or data stream:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Details link to open the task filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select Details.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select one of the following task filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- Equal to.
- Not equal to.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the file name or path.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks by description
You can filter tasks by the Description criterion, which is the task description that was added when the task was created.
To filter tasks by description:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Details link to open the task filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select Description.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select one of the following task filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- Equal to.
- Not equal to.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the file name or path.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Page top
Filtering tasks by server name
If you are using distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter tasks based on the servers to which the tasks are applied.
To filter tasks by servers to which the tasks are applied:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Servers link to open the task filtering menu.
- Select the check boxes next to the names of the servers whose tasks you want to display.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks based on the name of the user that created the task
To filter tasks based on the user name that created the task, all tasks must be displayed. If only tasks created by the current user are displayed, tasks cannot be filtered by user name.
To filter tasks by the name of the user that created the task:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the Created by link to open the task filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following task filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the user name.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering tasks by processing status
To filter tasks based on the status of their processing by the user:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click the State link to open the task filtering menu.
- Select one or more check boxes:
- Pending.
- In process.
- Completed.
- Click Apply.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a task filter
To clear the task filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- Select the Tasks section in the application web interface window.
This opens the task table.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The tasks table displays only tasks matching the filter criteria you have set.
Managing policies (prevention rules)
When working in the application web interface, users with the Senior security officer role can manage prevention rules for files and processes on selected hosts. For example, you can prevent the running of applications that you consider unsafe to use on the selected host with the Endpoint Agent component. The application identifies files based on their hash by using the MD5 and SHA256 hashing algorithms. You can create, enable, disable, delete, and modify prevention rules. Additionally, you can click the link with the name of the hashing algorithm in the prevention rule table to find objects, events, or alerts that have triggered prevention rules, such as Find events, Find alerts, Find on Kaspersky TIP, or Find on virustotal.com.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, prevention rules can have the following types:
- Global—Created on the PCN. These prevention rules apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These prevention rules apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
Users with the Senior security officer role can create, edit, delete, enable, disable, and import prevention rules for tenants to whose data they have access.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to policies.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the table of file run prevention rules and process run prevention rules, as well as information about the selected prevention rule, but they cannot edit the rules.
All changes to prevention rules are applied on hosts after an authorized connection is established with the selected hosts. If there is no connection with the hosts, the old prevention rules continue to be applied on the hosts. Changes to prevention rules do not affect processes that are already running.
Prevention rules can be created automatically based on preset politics (hereinafter also "presets") added by default. With presets turned on, a prevention rule is created based on a medium or high severity alert of the Sandbox component. The prevention rule thus created prevents running the file based on its MD5 hash. Users with the Senior security officer role can enable and disable presets.
Presets are not supported in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
The same operations can be applied to automatically created or imported prevention rules as for manually created rules.
You can create only one prevention rule for each file hash.
The maximum supported number of prevention rules in the system is 50,000.
Prevention rules are enforced only if the Endpoint Agent component is running on the host. If an attempt to run a file is made before the component is started or after the component is shut down on a host, the file will not be blocked from running.
You can manage file and process running prevention rules on selected hosts using policies only if the Endpoint Agent component is integrated with the Central Node server; to do so, you must use the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows as the Endpoint Agent component, you must take into account that the application supports preventing from running office format files with certain extensions and certain script interpreters.
Viewing the prevention rule table
The table of prevention rules is in the Prevention section of the application web interface window.
The table contains the following information:
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the operating mode of the application and the role of the server which generated the rule:
- Global—Created on the PCN. These prevention rules apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These prevention rules apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Name is the name of the prevention rule.
- Created by—Name of the user whose account was used to create the rule.
- File hash—Hashing algorithm applied to identify a file.
A file can be identified based on one of the following hashing algorithms:
- MD5.
- SHA256.
Clicking the link with the name of the hashing algorithm opens a list in which you can view the file hash and select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com (for SHA256).
- Find events.
When this action is performed, the Threat Hunting section opens with events that are already filtered based on the hash you selected.
- Find alerts.
When this action is performed, the Alerts section opens with alerts that are already filtered based on the hash you selected.
- Enable prevention rule.
- Disable prevention rule.
- Delete prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Servers are names of servers with the PCN or SCN role to which the prevention rule applies.
This field is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Hosts is the name of the server with the Central Node component to whose hosts the prevention rule is applied.
This field is displayed only when you are using a standalone Central Node server.
- State is the current state of the prevention rule.
A prevention rule can have one of the following states:
- Enabled.
- Disabled.
Configuring prevention rule table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the prevention rule table.
To configure prevention rule table display:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The prevention rule table display is configured.
Page top
Viewing a prevention rule
To view a prevention rule:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Select the prevention rule that you want to view.
A prevention rule contains the following information:
- The Events link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition containing your selected prevention rule.
- State is the current state of the prevention rule.
A prevention rule can have one of the following states:
- Enabled.
- Disabled.
- The Details tab contains the following information:
- MD5/SHA256 is the hash of the file prevented from running.
Clicking the MD5/SHA256 link opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
- Name is the name of the prevention rule or file prevented from running.
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the operating mode of the application and the role of the server which generated the rule:
- Global—Created on the PCN. These prevention rules apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These prevention rules apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Notification is the state of the Notify user about blocking file execution setting.
- Prevent on is the list of hosts on which the prevention rule is applied.
If the prevention is in effect on all hosts, the All hosts section is displayed.
- MD5/SHA256 is the hash of the file prevented from running.
- The Change log tab contains a list of changes made to the prevention: time of the change, name of the user that changed the prevention, and actions taken on the prevention.
Creating a prevention rule
To create a prevention rule:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click Add.
- Select Create rule.
This opens the prevention rule creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- If you want to enable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to On.
- If you want to disable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to Off.
- MD5/SHA256—MD5- or SHA256 hash of the file or data stream that you want to prevent from starting.
- Name is the name of the prevention rule.
- If you want the application to display a notification about prevention rule triggering to the user of the computer on which the prevention is applied, select the Notify user about blocking file execution check box.
If you selected the Notify user about blocking file execution check box and an attempt is made to execute a file prevented from running, the user is notified that an execution prevention rule was triggered by this file.
- Prevent on is the prevention rule scope:
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on all hosts of all servers, select All hosts.
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on selected servers, select the Specified servers option and on the right of the Servers parameter name select the check boxes next to the names of the servers on which you want to apply the prevention rule.
This option is available only when distributed solution and multitenancy mode is enabled.
- If you want to apply the prevention rule on selected hosts, select the Specified hosts option and list these hosts in the Hosts field.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, the prevention rule creation functionality is not available. When creating a prevention rule, if you select a host with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux or all hosts as the scope of the rule, the rule is not applied or is only applied to hosts with Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- Click Add.
The file startup prevention will be created.
You can also import prevention rules.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create file launch prevention rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot access prevention rules.
Importing prevention rules
You can import a file with MD5 and SHA256 hashes for files that you want to prevent from running. For each hash, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform creates a separate prevention rule.
The maximum size of the imported file is 10 MB. Only one hash per line is allowed.
To import prevention rules:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click Add.
- Select Import rules.
This opens the prevention rule import window.
- Configure the following settings:
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- If you want to enable all imported prevention rules, set the toggle switch to On.
- If you want to disable all imported prevention rules, set the toggle switch to Off.
- If you want the application to display a notification about prevention rules triggering to the user of the computer on which the prevention is applied, select the Notify user about blocking file execution check box.
The Prevent on field cannot be edited. By default, prevention rules created on a PCN server are applied on all hosts connected to that PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that PCN server (if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode).
- State is the state of the prevention rule:
- Click Browse to upload the file containing hashes of files for which you want to create prevention rules.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the file that you want to upload and click Open.
This closes the file selection window.
- Click Add.
The rules are imported.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot import file launch prevention rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot access prevention rules.
Page top
Enabling and disabling a prevention rule
To enable or disable a prevention rule:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- In the row containing the prevention rule that you want to enable or disable, in the State column, perform one of the following actions:
- If you want to enable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
The prevention rule you selected will be enabled.
- If you want to disable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to Disabled.
The prevention rule you selected will be disabled.
- If you want to enable the prevention rule, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot enable or disable prevention rules.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to the prevention rules for launching files and processes on selected hosts using policies.
Enabling and disabling presets
To enable or disable presets:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Select the Presets tab.
- In the row of the preset that you want to enable or disable, in the State column, set the toggle switch to Enabled or Disabled.
The preset is enabled or disabled. When a preset is disabled, all prevention rules that were previously automatically created are not removed.
Page top
Deleting prevention rules
You can delete a single prevention rule or multiple prevention rules, or all prevention rules at the same time.
To delete a single prevention rule:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click the prevention rule that you want to delete.
This opens the prevention rule details window.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The prevention rule is deleted.
To delete all or multiple prevention rules:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Select check boxes next to prevention rules that you want to delete.
You can select all prevention rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected prevention rules are deleted.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete prevention rules.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to the prevention rules for launching files and processes on selected hosts using policies.
Filtering prevention rules by name
To filter prevention rules by name:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click the Name link to open the prevention filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following prevention filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the text box, enter one or more characters of the prevention rule name.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The prevention rules table displays only the prevention rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering prevention rules by type
If you are using distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter prevention rules by their type.
To filter prevention rules by type:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click the Type link to open the prevention rule filtering menu.
- Select one of the following options for displaying prevention rules:
- All, if you want to display all prevention rules regardless of their type.
- Global, if you want to display only the prevention rules that were created on the PCN. These prevention rules apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Local, if you want to display only prevention rules that were created on a SCN server. These prevention rules apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Prevention rules belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
The prevention rules table displays only the prevention rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering prevention rules by file hash
To filter prevention rules by file hash:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click the File hash link to open the prevention rule filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following prevention filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the text box, enter one or several characters of the file hash.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The prevention rules table displays only the prevention rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering prevention rules by server name
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can filter prevention rules based on the servers to which the prevention rules apply.
To filter prevention rules by server name:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click the Servers link to open the prevention rule filtering menu.
- Select the check boxes next to those servers by which you want to filter the prevention rules.
- Click Apply.
The prevention rules table displays only the prevention rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Page top
Clearing a prevention rule filter
To clear the prevention rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- Select the Prevention section in the application web interface window.
This opens the prevention rule table
- Click
 to the right of the header of the column of the prevention rule table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column of the prevention rule table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The prevention rules table displays only the prevention rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
Managing user-defined rules
You can configure additional security for the IT infrastructure of the company using TAA, IDS, IOC, and YARA rules.
Users with the Senior security officer role can work with custom TAA, IDS, IOC, and YARA rules: load and delete rule files, view lists of rules, and edit the selected rules.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the lists of custom TAA, IDS, IOC, and YARA rules and properties of selected rules without the possibility of editing.
Users with the Security officer role can view the lists of custom TAA, IOC, and YARA rules and properties of selected rules without the possibility of editing.
Using indicators of compromise (IOC) and attack (IOA) for Threat Hunting
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses two types of indicators for threat hunting: IOC (Indicator of Compromise) and IOA (Indicator of Attack).
An IOC is a set of data about a malicious object or malicious activity. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform uses IOC files conforming to the
standard, which is an open standard for describing indicators of compromise. IOC files contain a set of indicators that are compared to the indicators of an event. If the compared indicators match, the application considers the event to be an alert. The likelihood of an alert may increase if a scan detects exact matches between the data of an object and several IOC files.An IOA (also referred to as a "TAA (IOA) rule") is a rule containing the description of a suspicious activity in the system that could be a sign of a targeted attack. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform scans the Events database of the application and marks events that match behaviors described by TAA (IOA) rules. The streaming scan technology is used, which involves continuous real-time scanning of events being received from protected devices.
TAA (IOA) rules created by Kaspersky experts are used by the TAA (Targeted Attack Analyzer) technology and are updated alongside the application databases. They are not displayed in the interface of the application and cannot be edited.
You can add user-defined IOC and TAA (IOA) rules using IOC files in the OpenIOC format as well as create TAA (IOA) rules based on event database search conditions.
The following table contains a comparative analysis of indicators of compromise (IOC) and attack (IOA).
Comparison of IOC and IOA indicators
Characteristic |
IOC in user-defined IOC rules |
IOA in user-defined TAA (IOA) rules |
IOA in TAA (IOA) rules created by Kaspersky experts |
|---|---|---|---|
Scan scope |
Computers with the Endpoint Agent component |
Application events database |
Application events database |
Scanning mechanism |
Periodical scan |
Streaming scan |
Streaming scan |
Can be added to exclusions from scan |
None. |
Not needed. Users with the Senior security officer role can edit the text of the indicator in custom TAA (IOA) rules as necessary. |
Yes. |
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, this section displays information for the selected tenant.
Page top
Managing user-defined TAA (IOA) rules
Custom TAA (IOA) rules are created based on event databased search criteria. For example, if you want Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to generate alerts for events when an application that you consider unsafe is started on computers with the Endpoint Agent component, you can:
- Generate a search query for the event database.
- Create a custom TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions.
When Central Node server receives events matching the created TAA (IOA) rule, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform generates alerts.
You can also create a TAA (IOA) rule based on one or multiple event search criteria from the selected IOC file. To do so:
- Upload an IOC file containing indicators of compromise corresponding to the malware to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Find events corresponding to the criteria of the selected IOC file.
- Create a TAA (IOA) rule based on one or more event search criteria from the selected IOC file.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, TAA (IOA) rules can have one of the following types:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this PCN server and all SCN servers connected to this PCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this SCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
The differences between user rules and Kaspersky rules are summarized in the following table.
Comparison of TAA (IOA) rules
Characteristic |
User-defined TAA (IOA) rules |
Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules |
|---|---|---|
Recommendations on responding to the event |
No |
Yes You can view recommendations in |
Correspondence to technique in MITRE ATT&CK database |
No |
Yes You can view the description of the |
Display in the TAA (IOA) rule table |
Yes |
No |
Ability to disable database lookup for this rule |
||
Ability to delete or add the rule |
You can delete or add a rule in the web interface of the application |
Rules are updated together with application databases |
Searching for alerts and events in which TAA (IOA) rules were triggered |
Using Alerts and Events links in the TAA (IOA) rule information window |
Using Alerts and Events links in the alert information window |
Users with the Senior security officer role can create, import, delete, enable or disable TAA (IOA) rules, and exclude Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rules from scanning. Users with the Security officer or Security auditor roles can use TAA (IOA) rules to search for signs of targeted attacks, infected and possibly infected objects in the database of events and alerts, and to view the TAA (IOA) rule table and TAA (IOA) rule information.
Viewing the TAA (IOA) rule table
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
The table of user-defined TAA (IOA) rules contains information about TAA (IOA) rules that are used to scan events and create alerts; the table is in the Custom rules section, TAA subsection of the application web interface window.
The table contains the following information:
 —Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.
—Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.The importance level can have one of the following values:
 – Low.
– Low. – Medium.
– Medium. – High.
– High.
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the operating mode of the application and the role of the server which generated the rule:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this PCN server and all SCN servers connected to this PCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this SCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Confidence – level of confidence depending on the likelihood of false alarms caused by the rule:
- High.
- Medium.
- Low.
The higher the confidence, the lower the likelihood of false alarms.
- Name – name of the rule.
- Servers are names of servers with the PCN or SCN role to which the rule applies.
This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Generate alerts – requirement to store information on alerts based on matching an event from the database with criteria of the rule.
- Enabled – a record is created for the event in the alerts table with Targeted Attack Analyzer (TAA) technology specified.
- Disabled – not displayed in the alert table.
- State – usage status of the rule in event scans:
- Enabled – the rule is being used.
- Disabled – the rule is not being used.
Creating a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions
To create a TAA (IOA) rule based on event search conditions:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- Perform an event search in design mode or source code mode.
- Click Save as TAA (IOA) rule.
This opens the New TAA (IOA) rule window.
- In the Name field, type the name of the rule.
- Click Save.
The event search condition will be saved. In the TAA (IOA) rule table in the Custom rules section, TAA subsection of the web interface, the new rule is displayed with the specified name.
If you want to save event search conditions as a user-defined TAA (IOA) rule, avoid using the following fields:
- IOAId.
- IOATag.
- IOATechnique.
- IOATactics.
- IOAImportance.
- IOAConfidence.
At the time of saving the user-defined TAA (IOA) rule, the application may not have any events containing data for these fields. When events with this data turn up, the user-defined field that you have created earlier will be unable to mark events by these fields.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create TAA (IOA) rules based on event search conditions.
Importing a TAA (IOA) rule
You can import an IOC format file and use it to scan events and create Targeted Attack Analyzer alerts.
We strongly recommend testing custom TAA (IOA) rules in a test environment before importing them. Custom TAA (IOA) rules may cause performance problems, in which case the stability of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is not guaranteed
To import a TAA (IOA) rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Click Import.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the file that you want to upload and click Open.
This opens the New TAA (IOA) rule window.
- Set the State toggle switch to Enabled if you want to enable the rule for scanning the event database.
- On the Details tab, in the Name field, enter the name of the rule.
- In the Description field, enter any additional information about the rule.
- In the Importance drop-down list, select the importance level to be assigned to alerts generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.
- Low.
- Medium.
- High.
- In the Confidence drop-down list, select the level of confidence of this rule based on your estimate:
- Low.
- Medium.
- High.
- Under Apply to, select check boxes corresponding to servers on which you want to apply the rule.
- On the Query tab, verify the defined search conditions. Make changes if necessary.
- Click Save.
The user-defined TAA (IOA) rule is imported into the application.
You can also add a TAA (IOA) rule by saving events database search conditions in the Threat Hunting section.
Viewing custom TAA (IOA) rule details
To display information about the TAA (IOA) rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the rule for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
The window contains the following information:
- Click the Alerts link to display the alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology and the name of the TAA (IOA) rule that you are working on.
- Click the Find events link to display the events table in a new browser tab. The table is filtered by rule name.
- Click the Run query link to display the events table in a new browser tab. The table is filtered by rule name. The event search conditions are populated with information from the TAA (IOA) rule that you are working on. For example,
EventType=Process started AND FileName CONTAINS <name of the rule you are working on>. You can edit the event search query. - Click the IOA ID link to display the ID that the application assigns to each rule.
IDs cannot be modified. You can copy the ID by clicking the Copy value to clipboard button.
- State – use of the rule in events database scans.
The Details tab shows the following information:
- Name is the name of the rule that you specified when you added the rule.
- Description is any additional information about the rule that you specified.
- Importance is an estimate of the probable impact of the event on the security of computers or the corporate LAN as specified by the user when the rule was added.
- Confidence is the level of confidence depending on the likelihood of false alarms as defined by the user when the rule was added.
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the role of the server which generated it:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this PCN server and all SCN servers connected to this PCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan events on this SCN server. Scanned events belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the program web interface.
- Apply to – name of servers with the Central Node component on which the rule is applied.
The Query tab displays the source code of the query being checked. Click the Run query link in the upper part of the window to go to the Threat Hunting section and run an event search query.
Searching for alerts and events in which TAA (IOA) rules were triggered
To search and display alerts and events that were created by a user-defined TAA (IOA) rule triggering:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the rule for which you want to view the triggering result.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to view alerts generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Alerts to go to the alerts database.
The alert table is opened in a new browser tab.
- If you want to view events generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Events to go to the events database.
The event table is opened in a new browser tab.
- If you want to view alerts generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Alerts to go to the alerts database.
To search and display alerts and events that were created by a Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rule triggering:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the link in the Technologies column to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select Contain.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select the (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer technology.
- Click Apply.
The table displays alerts generated by the TAA technology based on TAA (IOA) rules.
- Select an alert for which the Detected column displays the name of the relevant rule.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- Under Scan results, click the link with the name of the rule to open the rule information window.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to view alerts generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Alerts to go to the alerts database.
The alert table is opened in a new browser tab.
- If you want to view events generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Events to go to the events database.
The event table is opened in a new browser tab.
- If you want to view alerts generated by the TAA (IOA) rule triggering, click Alerts to go to the alerts database.
Filtering and searching TAA (IOA) rules
To filter or search for TAA (IOA) rules by required criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Depending on the filtering criterion, do the following:
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Resetting the TAA (IOA) rule filter
To clear a TAA (IOA) rule filter based on one or multiple filter conditions:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Click
 to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.
to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
Enabling and disabling TAA (IOA) rules
Users with the Senior security officer role can enable or disable one or several rules, as well as all rules at once.
To enable or disable the use of a TAA (IOA) rule when scanning events:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- In the row with the relevant rule, select or clear the check box in the State column.
The use of the rule when scanning events is enabled or disabled.
To enable or disable the use of all or multiple TAA (IOA) rules when scanning events:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules whose use you want to enable or disable.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Enable or Disable to enable or disable all rules.
The use of the selected rules when scanning events is enabled or disabled.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can manage only global TAA (IOA) rules on the PCN server. You can manage local TAA (IOA) rules on SCN servers of tenants to which you have access.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot enable or disable TAA (IOA) rules.
Modifying a TAA (IOA) rule
Users with the Senior security officer role can modify custom TAA (IOA) rules. Rules created by Kaspersky cannot be edited.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can edit only those TAA (IOA) rules that were created on the current server. Consequently, in the web interface of the PCN, you can edit only the rules that were created on the PCN. In the web interface of an SCN, you can edit only the rules that were created on the SCN.
To edit a TAA (IOA) rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the rule that you want to modify.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Make the relevant changes.
- Click Save.
The rule settings are modified.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot modify TAA (IOA) rules based on event search conditions.
Deleting TAA (IOA) rules
Users with the Senior security officer role can delete one or more TAA (IOA) rules, or all rules at the same time.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can delete only those TAA (IOA) rules that were created on the current server. Consequently, in the web interface of the PCN, you can delete only the rules that were created on the PCN. In the web interface of an SCN, you can delete only the rules that were created on the SCN.
To delete a custom TAA (IOA) rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the rule that you want to delete.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The rule is deleted.
To delete all or multiple custom TAA (IOA) rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, TAA subsection.
This opens the TAA (IOA) rule table.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules that you want to delete.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules will be deleted.
You cannot delete TAA (IOA) rules defined by Kaspersky. If you do not want to use a Kaspersky TAA (IOA) rule for scanning, add it to exclusions.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot modify TAA (IOA) rules based on event search conditions.
Managing user-defined IOC rules
You can use IOC files to search indicators of compromise in the event database and on computers with the Endpoint Agent component. For example, if you have received third-party information about a piece of malware currently spreading, you can:
- Create an IOC file with indicators of compromise for the malware and upload it to the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Find events corresponding to the criteria of the selected IOC file.
You can view such events, and if you want Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to generate alerts for selected events, you can create a TAA (IOA) rule.
- Enable automatic use of the selected IOC file to search indicators of compromise on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- If while scanning the computers, the Endpoint Agent component detects indicators of compromise, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform generates an alert.
You can find these alerts in the table of alerts by filtering by technology name.
- Configure the schedule for searching for indicators of compromise using IOC files on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, IOC files can have the following types:
- Local—IOC files uploaded to an SCN server. These IOC files are used to search for indicators of compromise on Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts connected to the SCN server.
- Global—IOC files uploaded to the PCN server. These IOC files are used to search for indicators of compromise on Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts connected to the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to the PCN server.
An IOC file is a text file saved with the .ioc extension. When creating the IOC file, review the list of IOC terms supported by the application that you are using in the Endpoint Agent role. You can view the list of supported IOC terms by downloading the files from the links below.
![]() Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
![]() Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 12 for Linux
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 11.4 for Linux and Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac do not support IOC files.
Example of an IOC file for finding a file by its hash
Each IOC file can contain only one rule. The rule can be of any complexity.
Users with the Senior security officer role can import, delete, download IOC files to their computer, enable or disable the search of indicators of compromise using IOC files, as well as configure the schedule for searching indicators of compromise on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
Users with the Security officer and Security auditor roles can view the list of IOC files and information about the selected file, and export IOC files to their computer.
Viewing the table of IOC files
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, use the web interface of the PCN or SCN server for which you want to configure parameters.
The table of IOC files contains information about IOC files used for scanning on computers with the Endpoint Agent component installed; you can find the table in the Custom rules section, IOC subsection of the application web interface window.
The table of IOC files contains the following information:
 —Importance level that will be assigned to an alert generated using this IOC file.
—Importance level that will be assigned to an alert generated using this IOC file.The importance level can have one of the following values:
 – Low importance.
– Low importance. – Medium importance.
– Medium importance. – High importance.
– High importance.
- Type—Type of IOC file depending on the application operating mode and the server to which the IOC file was uploaded:
- Local—IOC files uploaded to an SCN server. These IOC files are used to search for indicators of compromise on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component connected to the SCN server.
- Global—IOC files uploaded to the PCN server. These IOC files are used to search for indicators of compromise on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component connected to the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to the PCN server.
- Name—Name of the IOC file.
- Servers are names of servers with the PCN or SCN role to which the rule applies.
This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Autoscan—The IOC file is used when automatically scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
Host scanning using this IOC file can have one of the following statuses:
- Enabled
- Disabled
Viewing information about an IOC file
To view IOC file details:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Select the IOC file for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the IOC file.
The window contains the following information:
- Clicking the Find alerts link opens the Alerts section with the filter condition populated with the name of your selected IOC file.
- Clicking the Find events link opens the Threat Hunting section with the search condition populated with indicators of compromise of your selected IOC file.
- Clicking the Download link opens the IOC file download window.
- Autoscan—The IOC file is used when automatically scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Name—Name of the IOC file.
- Importance—Importance level that must be assigned to an alert generated using this IOC file.
The importance level can have one of the following values:
 – Low importance.
– Low importance. – Medium importance.
– Medium importance. – High importance.
– High importance.
- Apply to—Displays the name of the tenant and the names of servers associated with events scanned based on this IOC file (in distributed solution and multitenancy mode).
- XML—Displays the IOC file contents in XML format.
Uploading an IOC file
IOC files having UserItem properties for domain users are not supported.
To upload an IOC file:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Click Import.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the file that you want to upload and click Open.
- Specify the following parameters:
- Autoscan—The IOC file is used when automatically scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Enabled
- Disabled
- Name—Name of the IOC file.
- Importance—Importance level that must be assigned to an alert generated using this IOC file:
- Low.
- Medium.
- High.
- Apply to—Name of the tenant and names of the servers which you want to scan using this IOC file (in distributed solution and multitenancy mode).
- Autoscan—The IOC file is used when automatically scanning hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- Click Save.
The IOC file will be uploaded in XML format.
Downloading an IOC file to a computer
You can download a previously uploaded IOC file to a computer.
To download an IOC file:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Select the IOC file that you want to download.
This opens a window containing information about the IOC file.
- Depending on your browser settings, click the Download link to save the file to the default folder or specify a folder in which to save the file.
The IOC file is saved to your computer in the browser's downloads folder.
Enabling and disabling the automatic use of an IOC file when scanning hosts
You can enable or disable the automatic use of an IOC file for searching for indicators of compromise on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
To enable or disable the automatic use of an IOC file for searching for indicators of compromise on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- In the row containing the IOC file whose use you want to enable or disable, in the State column, set the toggle switch to one of the following positions:
- Enabled
- Disabled
Automatic use of an IOC file for searching for indicators of compromise on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is enabled or disabled.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot enable or disable automatic application of an IOC file.
Deleting an IOC file
To delete an IOC file:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Select the IOC file that you want to delete.
This opens a window containing information about the IOC file.
- Click Delete.
The IOC file will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot delete IOC files.
Searching for alerts in IOC scan results
To find and view scan results for the selected IOC file:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Select the IOC file for which you want to view scan results.
This opens a window containing information about the IOC file.
- Go to the alert database by clicking Find alerts.
The alert table is opened in a new browser tab.
You can also view scan results for all IOC files by filtering alerts by technology name.
Searching for events using an IOC file
To view events found using an IOC file:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
This opens the table of IOC files.
- Select the IOC file to use for searching for events in the event database.
This opens a window containing information about the IOC file.
- Go to the event database by clicking Find events.
The event table is opened in a new browser tab.
Filtering and searching IOC files
To filter or search for IOC files by required criteria:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
- This opens the table of IOC files. Depending on the filtering criterion, do the following:
The table of IOC files will display only IOC files that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing an IOC file filter
To clear the IOC file filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, IOC subsection.
- This opens the IOC file table. Click
 to the right of the header of the IOC file table column for which you want to clear the filtering conditions.
to the right of the header of the IOC file table column for which you want to clear the filtering conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table of IOC files will display only IOC files that match the filter criteria you have set.
Configuring an IOC scan schedule
You can configure the schedule for searching for indicators of compromise using IOC files on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
Users with Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot configure the schedule for searching for indicators of compromise using IOC files.
To configure the schedule for searching for indicators of compromise using IOC files on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Endpoint Agents subsection, IOC scanning schedule group of settings.
- In the Start time drop-down lists, select the start time of the indicator of compromise search.
- In the Maximum scan duration drop-down list, select a time limit for completing the indicator of compromise search.
- Click Apply.
The new schedule for searching for indicators of compromise using IOC files on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component becomes active immediately after changes are saved. Results of the indicator of compromise search are displayed in the alert table.
Managing the search for indicators of compromise using IOC files is limited to the functionality provided by the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. No alternative ways of managing the search for indicators of compromise are provided.
If you are using Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, make sure that the IOC files comply with the requirements. You must also take into account that when adding the RegistryItem data type to the IOC search scope, the application analyzes only certain registry keys.
For more details on the requirements for IOC files and the scanned registry keys, refer to the Online Help for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows:
Managing user-defined IDS rules
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, custom IDS rules can have one of the following types:
- Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan traffic on the PCN server.
- Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan traffic on the SCN server.
Users with the Senior security officer role can import, replace, and delete user-defined IDS rules, as well as add Kaspersky-defined IDS rules to exclusions from scanning. Users with the Senior security officer or Security auditor roles can use IDS rules to search for signs of targeted attacks, infected and possibly infected objects in the alert database, and to view the IDS rule information.
Users with the Security officer role cannot gain access to user-defined IDS rules.
Importing a user-defined IDS rule
You can import a Snort or Suricata file and use it to scan events and create Intrusion Detection System alerts.
We strongly recommend testing custom rules in a test environment before importing them. Custom IDS rules may cause performance problems, in which case the stability of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is not guaranteed
For example, loading user-defined rules can cause the following errors:
- The application may create too many IDS alerts.
- If the application cannot record all IDS alerts in time, some network traffic objects may remain unscanned.
- Regular expressions in user-defined rules may impact performance or cause faulty operation of the application.
- Even formally correct user-defined rules may impact performance or cause faulty operation of the application.
IDs and attributes of custom rules may be modified when they are uploaded. Reject and Drop actions are changed to Alert. Rules with the Pass action are deleted
To import a user-defined IDS rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
This opens the user-defined IDS rule window.
- Click Import.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the file that you want to upload and click Open.
The user-defined IDS rule is imported into the application.
Viewing the information of a user-defined IDS rule
To view the information of a user-defined IDS rule,
In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
The web interface displays the following information about the IDS rule:
- State—Usage status of the rule in event scans.
- File size—Size of the rule file.
- Last update—Time when the rule was imported.
- Created by—Name of the user whose account was used to import the rule.
- Importance—Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this IDS rule.
Enabling and disabling the use of an IDS rule when scanning events
To enable or disable an IDS rule when scanning events:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
- This opens the user-defined IDS rule window.
- Move the State switch to one of the following positions:
- Enabled
- Disabled
The use of the IDS rule when scanning events is enabled or disabled.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot enable or disable IDS rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot gain access to user-defined IDS rules.
Configuring the importance of alerts generated by the user-defined IDS rule
To configure the importance level that is assigned to alerts generated using the IDS rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
- This opens the user-defined IDS rule window. In the Importance drop-down list, select the importance level to be assigned to alerts generated using this IDS rule.
- Low.
- Medium.
- High.
- If necessary, use the State switch to enable this IDS rule.
The importance of alerts generated using this IDS rule is configured.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot configure IDS rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot gain access to user-defined IDS rules.
Replacing a user-defined IDS rule
You can replace a previously imported Snort or Suricata file and use it to scan events and create Intrusion Detection System alerts.
We strongly recommend testing custom rules in a test environment before importing them. Custom IDS rules may cause performance problems, in which case the stability of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is not guaranteed
IDs and attributes of custom rules may be modified when they are uploaded. Reject and Drop actions are changed to Alert. Rules with the Pass action are deleted
To replace a user-defined IDS rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
- This opens the user-defined IDS rule window. Below the rule information, click Replace.
This opens the file selection window on your local computer.
- Select the file that you want to upload and click Open.
The user-defined IDS rule is imported into the application, replacing the previously imported rule.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot replace user-defined IDS rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot gain access to user-defined IDS rules.
Exporting a user-defined IDS rule file to the computer
You can export a previously imported IDS rule file.
To export a user-defined IDS rule file:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
This opens the user-defined IDS rule window.
- Below the rule information, click Download.
The file will be saved to your local computer in the browser's downloads folder.
Deleting a user-defined IDS rule
When working in distributed solution mode, users with the Senior security officer role can delete only a user-defined IDS rule that was imported into the current server. It means that in the PCN web interface, you can only delete a rule that was created on the PCN. In the SCN web interface, you can only delete a rule that was created on the SCN.
To delete a user-defined IDS rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, IDS subsection.
- This opens the user-defined IDS rule window. Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The rule is deleted.
You cannot delete IDS rules defined by Kaspersky. If you do not want to use a Kaspersky IDS rule for scanning, add it to exclusions.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete user-defined IDS rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot gain access to user-defined IDS rules.
Managing user-defined YARA rules
You can use YARA rules as YARA module databases to scan files and objects received at the Central Node and to scan hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, custom YARA rules can have one of the following types:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that PCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the SCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
When managing the application web interface, users with the Senior security officer role can import a YARA rule file into Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform using the application web interface.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles can only view YARA rules.
Viewing the YARA rule table
The table of user-defined YARA rules contains information about YARA rules that are used to scan files and objects and to create alerts; the table is displayed in the Custom rules section, YARA subsection of the application web interface window.
The table contains the following information:
- Created is the rule creation time.
 —Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.
—Alert importance for the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform user depending on the impact this alert may have on computer or corporate LAN security based on Kaspersky experience.By default, alerts generated by uploaded YARA rules are assigned a high level of importance.
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the operating mode of the application and the role of the server which generated the rule:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that PCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the SCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Name – name of the rule.
- File name is the name of the file from which the rule was imported.
- Created by is the name of the user whose account was used to import the rule.
- Servers is the name of the server with the PCN or SCN role to which the rule applies.
This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Traffic scanning is the usage status of the rule when stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node:
- Enabled – the rule is being used.
- Disabled – the rule is not being used.
Configuring YARA rule table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the table.
To configure the table display:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The table display is configured.
Page top
Importing YARA rules
To import YARA rules:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
- Click Upload.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the YARA rules file that you want to upload and click the Open button.
This closes the file selection window and opens the Import YARA rules window.
The maximum allowed size of an uploaded file is 20 MB.
A report is displayed in the lower part of the window. The report contains the following information:
- The number of rules that can be successfully imported.
- The number of rules that will not be imported (if any).
For each rule that cannot be imported, its name is listed.
- Select the Traffic scanning check box if you want to use imported rules for streaming scans of objects and data received at the Central Node.
- If necessary, enter any additional information in the Description field.
The Importance field cannot be edited. By default, alerts generated by uploaded YARA rules are assigned a high level of importance.
- Under Apply to, select check boxes corresponding to servers on which you want to apply the rules.
This field is displayed only when you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Click Save.
Imported rules are displayed in the table of YARA rules.
Viewing YARA rule details
To view YARA rule details:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Select the rule for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
The window contains the following information:
- Click the Alerts link to display the alert table in a new browser tab. The alerts are filtered by the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology and the name of the TAA (IOA) rule that you are working on.
- The Start YARA scan link opens the task creation window.
- The Download link lets you download a file with YARA rules.
- Rule name is the name of the rule specified in the file.
- Traffic scanning is the usage status of the rule when stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node:
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the role of the server which generated it:
- Global—Created on the PCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the PCN server and all SCN servers connected to that PCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These rules are used to scan files and objects received at the SCN server. Scanned files and objects belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Importance—Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this rule.
By default, alerts generated by uploaded YARA rules are assigned a high level of importance.
- Description is any additional information about the rule that you specified.
- Apply to – name of servers with the Central Node component on which the rule is applied.
Filtering and searching YARA rules
To filter or search for YARA rules by required criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Depending on the filtering criterion, do the following:
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a YARA rule filter
To clear the YARA rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Click
 to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.
to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.If you want to clear multiple filter conditions, take steps to clear each filter condition individually.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
Enabling and disabling YARA rules
Users with the Senior security officer role can enable or disable one or several rules, as well as all rules at once.
When working in distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can enable or disable only those YARA rules that were created on the current server. It means that in the web interface of the PCN, you can enable or disable only the rules that were created on the PCN server. In the web interface of an SCN, you can enable or disable only the rules that were created on the SCN server.
If YARA rules with identical names are enabled on the PCN and SCN servers, the PCN rule takes precedence over the SCN rule when scanning files and objects.
To enable or disable a YARA rule for stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- In the row with the relevant rule, select or clear the check box in the Traffic scanning column.
The rule is enabled or disabled for stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node.
To enable or disable all or multiple YARA rules for stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules whose use you want to enable or disable.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Enable or Disable to enable or disable all rules.
Selected rules are enabled or disabled for stream scanning files and objects arriving at the Central Node.
Deleting YARA rules
To delete a YARA rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Select the rule that you want to delete.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Click Delete.
- This opens the action confirmation window; in that window, click Yes.
The rule is deleted.
To delete all or multiple YARA rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, YARA subsection.
This opens the YARA rule table.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules that you want to delete.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Delete.
- This opens the action confirmation window; in that window, click Yes.
The selected rules will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot delete YARA rules.
Managing objects in Storage and quarantine
Storage is used for storing files that must be sent for scanning as well as files obtained as a result of running tasks: Get file, Restore file from quarantine, Get forensics, Get NTFS metafiles, Get registry key, Get process memory dump.
Storage is located on the Central Node server.
You can manage objects in Storage as follows: delete, download, upload, and send objects to be scanned, and filter lists of objects.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform displays the objects in Storage as a table of objects.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, Storage is located on PCN and SCN servers. The web interface of the PCN server displays information about Storage of all connected SCNs for those tenants to which the user has access.
Users with the Senior security officer role can place copies of objects into Storage using tasks or by uploading the object to Storage using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface on the PCN or SCN server that is used for managing tenants to which the user has access.
Users with the Security officer role can only work with files received as part of tasks that the same user created on the PCN or SCN server which is used to manage tenants to which the user has access.
If you consider a file threatening, you can quarantine it on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component. Metadata of the quarantined file are displayed in the Storage section, Quarantine subsection of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
Quarantine on a Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server is an area of Storage of the server part of the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution, which is used for storing metadata of objects quarantined on Endpoint Agent computer, in the Storage section, Quarantine subsection of the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
You can manage quarantined objects: restore objects from quarantine and upload copies of objects quarantined on Endpoint Agent computers to Storage of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform displays the information about quarantined objects as a table.
The maximum capacity of Storage is determined when configuring the sizing of the application. As soon as this threshold value is exceeded, the application starts to remove the oldest copies of objects from Storage. When the amount of occupied space is again below the threshold value, the application stops removing copies of objects from Storage.
The actual size of the object can be greater than the apparent size of the object due to the metadata required to restore the object from quarantine. When an object is quarantined, its actual size is considered. Encrypted files may be sent in decrypted form (depending on encryption settings), compressed files are sent as-is.
Viewing the table of objects that were placed in Storage
The table of objects placed in Storage is in the Storage section, Files subsection of the application web interface window.
The table of objects placed in Storage contains the following information:
- Type is the method by which the object was placed in Storage.
The following methods are possible:
 – The object was placed in Storage in one of the following ways:
– The object was placed in Storage in one of the following ways:- The Get file task was run.
- A copy was received of an object that was quarantined on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component (in the Storage section, Quarantine subsection, Get file from quarantine action was selected in the menu for the link with the directory of the object).
 – The object was placed in Storage in one of the following ways:
– The object was placed in Storage in one of the following ways:- The Get forensics task was run.
- The Get process memory dump task was run.
- The Get registry key task was run.
- The Get NTFS metafiles task was run.
 – The object was manually downloaded by the user in the Storage section, Files subsection.
– The object was manually downloaded by the user in the Storage section, Files subsection.
- Object—Information about the object. For example, the file name or file path.
- Scan results—Object scan result.
The scan result is displayed as one of the following values:
- Not detected—As a result of a scan, the application did not detect signs of a targeted attack, probably infected objects, or suspicious activity.
- Error—Object scan ended with an error.
- In process—Object scan has not yet completed.
- Not scanned—Object was not sent to be scanned.
- Detected—As a result of a scan, the application detected signs of a targeted attack, a probably infected object, or suspicious activity.
- Servers is the name of the server with the PCN or SCN role. The host from which the object was received is connected to this server.
This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Source—IP address or name of the host from which the object was received, or the name of the user account that uploaded the object.
- Time stored—Date and time when the object was placed in Storage.
- Actions—Actions that can be performed with the object. The following actions are available:
 — delete an object from Storage.
— delete an object from Storage. — send the object in Storage for scanning by the Anti-Malware Engine, YARA, and Sandbox technologies.
— send the object in Storage for scanning by the Anti-Malware Engine, YARA, and Sandbox technologies. — download the object from Storage to your computer.
— download the object from Storage to your computer.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Download.
- Send file for scanning.
- Find events:
- File path
- MD5
- SHA256
- Find alerts:
- File path
- MD5
- SHA256
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Viewing information about an object manually placed in Storage using the web interface
To view information about an object manually placed in Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object with the
 icon for which you want to view information.
icon for which you want to view information.This opens the object details window.
The window contains the following information:
- File name—Name of the file.
- Size—Size of the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of a file.
- Time uploaded—Time of upload for objects that were manually uploaded by a user.
- User name—Name of the user account that manually uploaded the object to Storage.
- Scan results—Result of object scan by the application.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
You can click Download to download the file to your computer's hard drive.
Clicking the link with the file name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with MD5 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with SHA256 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Viewing information about an object placed in Storage by a get file task
To view information about an object placed in Storage by a Get file or Get file from quarantine task:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object with the
 icon for which you want to view information.
icon for which you want to view information.This opens the object details window.
The window contains the following information:
- Recommendations group. The following recommendations can be displayed:
- The Task link opens the Tasks section; this is the task that has placed the object in Storage.
- The Alert link opens the Alerts section; this is the alert containing the object that was placed in Storage.
- The Quarantined object link opens the Storage section, Quarantine subsection; this is the metadata of the quarantined object.
- Object—File name or path.
- Size—Size of the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of a file.
- Time stored—Time when the object was placed in Storage.
- Tenant —Name of the tenant to which the Central Node, PCN, or SCN server belongs.
- Server—Name of the Central Node, PCN, or SCN server. The host from which the object was received is connected to this server.
- Host—Name of the host from which the object was received.
- Scan results—Result of object scan by the application.
You can click Sandbox detection to open a window with detailed information about the results of file behavior analysis.
The Find on Kaspersky TIP button allows to find a file on the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal.
Click Create prevention rule to prevent the file from running.
You can click Download to download the file to your computer's hard drive.
Clicking the link with the file name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with MD5 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with SHA256 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Viewing information about an object placed in Storage by a get data task
To view information about an object placed in Storage by Get forensics, Get process memory dump, Get registry key, Get NTFS metafiles tasks:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object with the
 icon for which you want to view information.
icon for which you want to view information.This opens the object details window.
The window contains the following information:
- Object is the file name or path.
- Size—Size of the file.
- MD5—MD5 hash of a file.
- SHA256—SHA256 hash of a file.
- Time stored—Time when the object was placed in Storage.
- Host—Name of the host from which the object was received.
You can click Download to download the file to your computer's hard drive.
Clicking the link with the file name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with MD5 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with SHA256 opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find on Kaspersky TIP.
- Find on virustotal.com.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Create prevention rule.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Downloading objects from Storage
If you consider an object in Storage to be safe, you can download it to a local computer.
Downloading infected objects could pose a threat to the security of your local computer.
To download an object from Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the right part of the line with the name of the object that you want to download, click
 .
.
The object will be saved to your local computer in the browser's downloads folder. The file is downloaded as a ZIP archive protected with the password "infected".
Uploading objects to Storage
If you need to scan a specific object, you can upload this object to Storage and send it to be scanned.
To upload an object to Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the upper-right corner of the window, click Upload.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select the object that you want to upload to Storage.
- If you want to upload a file with the .Lnk extension to Storage:
- In the File name field, enter *.Lnk and press Enter.
- Select the object.
- Click Open.
The object is uploaded to Storage and displayed in the table of objects.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot upload objects to Storage.
Sending objects in Storage for scanning
You can scan Storage objects with the Central Node component using the Anti-Malware Engine and YARA technologies, and with the Sandbox component.
It is recommended to send objects from Storage to be scanned in the following cases:
- Scanning of objects when placed in Storage had been disabled.
- Application databases have been updated.
- An object was manually uploaded to Storage.
To send an object from Storage for scanning:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the object that you want to scan.
This opens the object details window.
- Click Scan.
The object scan will start.
After the object scan is complete, its status will be displayed in the object table.
You can also send an object in Storage for scanning by clicking ![]() in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects placed in Storage.
in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects placed in Storage.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot scan objects in Storage.
Deleting objects from Storage
To delete an object from Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the object that you want to delete.
This opens the object details window.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The object will be deleted from Storage.
You can also delete an object in Storage by clicking ![]() in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects placed in Storage.
in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects placed in Storage.
To delete all or multiple objects from Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Select check boxes next to objects that you want to delete from Storage.
You can select all objects by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected objects are removed from Storage.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete objects in Storage.
Filtering objects in Storage by object type
To filter objects in Storage by type:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Type link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one or more check boxes:
- Uploaded by a Get file task if you want the table to display objects that were placed in Storage by Get file and Restore file from quarantine tasks.
- Uploaded through the web interface if you want the table to display objects uploaded by the user using the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform web interface.
- Uploaded by a get data task if you want the table to display objects placed in Storage by Get forensics, Get NTFS metafiles, Get registry key, Get process memory dump tasks.
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering objects in Storage by object description
To filter objects in Storage by object description:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Object link to open the object filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following options:
- File path.
- MD5.
- SHA256.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following object filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- Equal to.
- Not equal to.
- Matches.
- Not matches.
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the object description.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering objects in Storage based on scan results
To filter objects in Storage by scan results for these objects:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Scan results link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one or more check boxes:
- Not detected
- Error
- In process
- Not scanned
- Detected
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering objects in Storage based on the name of Central Node, PCN, or SCN server
To filter objects in Storage by the name of Central Node, PCN, or SCN server:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Servers link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one or multiple check boxes opposite those servers by which you want to filter objects in Storage.
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering objects in Storage by object source
To filter objects in Storage by the source from which they were received:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Source link to open the object filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following object filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the IP address, host name or name of the user account that manually uploaded the object.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering objects based on the time they were placed in Storage
To filter objects by the time when they were placed in Storage:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Time stored link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one of the following object display periods:
- All if you want the table to display all objects that were placed in Storage.
- Last hour if you want the table to display objects that were placed in Storage during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display objects that were placed in Storage during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display objects that were placed in Storage during the period you specify.
- If you have selected the Custom range object display period:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the object display period.
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a Storage objects filter
To clear the Storage objects filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Files subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the Storage objects table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the Storage objects table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
Viewing the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
The table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component can be found in the Storage section, Quarantine subsection of the application web interface.
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server stores metadata of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component. The objects themselves are kept in special storage on each computer where the threatening object was detected.
The table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component contains the following information:
- Object—Information about the object. For example, the file name or file path.
- Source—IP address or host name of the computers with the Endpoint Agent component where the object is quarantined.
- Time stored—Date and time when the object was quarantined.
- State—State of the object.
The right part of the object information row contains buttons:
- You can click
 to delete the metadata of the object on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
to delete the metadata of the object on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. - You can click
 to restore the object from Quarantine on a computer the Endpoint Agent component.
to restore the object from Quarantine on a computer the Endpoint Agent component. - You can click
 to copy the object from Quarantine on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
to copy the object from Quarantine on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Download.
- Send file for scanning.
- Find events:
- File path
- MD5
- SHA256
- Find alerts:
- File path
- MD5
- SHA256
- Copy value to clipboard.
Clicking the link with the host name opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Filter by this value.
- Exclude from filter.
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Viewing information about a quarantined object
To view information about an object quarantined on a computer with the Endpoint Agent component:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object whose information you want to view.
This opens the object details window.
The window contains the following information:
- Recommendations group. The Task recommendation can be displayed, which is a link that opens the Tasks section; this is the task that has quarantined the object.
- Type is the type of the quarantined object.
The following types of objects are available:
 — file.
— file. — process memory dump.
— process memory dump.
- Object—File name or path.
- State is the state of the file (whether the file can be restored from Quarantine).
- Source is the name of the computer with the Endpoint Agent component on which the object is quarantined.
- Recording time is the date and time when the object was quarantined.
- Actions is the state of the file (whether the file can be restored from Quarantine).
The following actions are available:
 — delete the file from Quarantine.
— delete the file from Quarantine. — obtain a copy of the file on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
— obtain a copy of the file on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
Clicking the link with the file name or file path opens a list in which you can select one of the following actions:
- Find events.
- Find alerts.
- Copy value to clipboard.
Restoring an object from Quarantine
To restore the object from Quarantine on a computer the Endpoint Agent component:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object that you want to restore from Quarantine on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component.
This opens the object details window.
- Click Restore in the lower part of the window.
This opens the Tasks section and the Restore file from quarantine task.
- In the Description field, enter the task description.
- Click Add.
The file is restored from Quarantine.
You can also run the task to restore the file from Quarantine by clicking ![]() in the right part of the row with object information of the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
in the right part of the row with object information of the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
In distributed solution and multitenancy mode, a file that is quarantined on an SCN server cannot be restored on the PCN server. You can restore the file on the SCN server on which the quarantine file task was created.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot restore objects from Quarantine.
Obtaining a copy of a quarantined object on a Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server
The object that you want to download a copy of must not exceed 100 MB. If the object exceeds 100 MB, the task finishes with an error.
To copy an object quarantined on a computer with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component to a Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- In the table, select the object that you want to restore from Quarantine on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component.
This opens the object details window.
- Click Get file in the lower part of the window.
This creates a task for getting a copy of an object that was quarantined on a computer with the Endpoint Agent component. If the task completes successfully, the copy of the object is uploaded to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. The object is displayed in the Storage section, Files subsection of the application web interface in the table of objects placed in Storage.
Information about the created task is displayed in the Tasks section of the web interface.
You can also copy an object from Quarantine on a computer with the Endpoint Agent component to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server by clicking ![]() in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
in the right part of the object information row in the table of objects quarantined on computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot get copies of objects from Quarantine.
Removing information about the quarantined object from the table
To delete the information of an object quarantined on a computer with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform table:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the object for which you want to delete information from the table.
This opens the object details window.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The information about the object quarantined on the computer with the Endpoint Agent component is deleted from the table.
You can also delete the information of an object quarantined on a computer with the Endpoint Agent component from the table by clicking ![]() in the right part of the object information row in the table of quarantined objects.
in the right part of the object information row in the table of quarantined objects.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete information about a quarantined object from the table.
Filtering information about quarantined objects by object type
To filter quarantined object details by object type:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Type link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one or more check boxes:
- File if you want the table to display metadata of quarantined objects.
- Process memory dump if you want the table to display metadata of quarantined dumps.
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering information about quarantined objects by object description
To filter quarantined object details by object description:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Object link to open the object filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following object filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the object description.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering information about quarantined objects by host name
To filter quarantined object details by the name of the host where they were quarantined:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Source link to open the object filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following object filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- In the entry field, specify one or several characters of the host name.
- To add a filter condition using a different criterion, click
 and specify the filter condition.
and specify the filter condition. - Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering information about quarantined objects by time
To filter quarantined object details by the time when the objects were quarantined:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click the Time stored link to open the object filtering menu.
- Select one of the following object display periods:
- All if you want the table to display all objects.
- Last hour if you want the table to display objects that were quarantined during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the table to display objects that were quarantined during the last day.
- Custom range if you want the table to display objects that were quarantined during the period you specify.
- If you have selected the Custom range object display period:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the object display period.
- Click Apply.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Resetting the filter for information about quarantined objects
To clear the filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the application web interface window, select the Storage section, Quarantine subsection.
This opens the object table.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the column of the quarantined objects table for which you want to reset the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column of the quarantined objects table for which you want to reset the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The objects table will display only objects matching the filter criteria you have set.
Managing reports
When managing the application web interface, users with the Senior security officer role can manage reports about application alerts: create report templates, create reports based on a template, view, and delete reports and report templates.
Users with the Security auditor role can view reports and report templates and create reports from templates.
A report is generated based on a selection of alerts for a specified period. If you are using distributed solution and multitenancy mode, data is also selected based on the tenant and servers of that tenant.
You can manage report templates and reports in all operating modes of the application in accordance with the license.
Perform the report creation steps in the following order:
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to reports.
Viewing the table of templates and reports
Templates and reports are displayed in the Reports section of the application web interface window.
The Generated reports subsection contains a report table. The table contains the following information:
- Time created—Date and time of report creation.
- Report name—Name of the report created based on the template.
- Period—Period for which the report was generated.
- Servers is the name of the server with the PCN or SCN role to which the rule applies.
This column is displayed if you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
- Created by—Name of the user that created report.
- State—Report state (whether the file can be downloaded).
The Templates subsection displays the table of templates. The table contains the following information:
- Time created—Date and time when the template was created.
- Time updated—Date and time of last modification of the template.
- Report name—Name of the template.
- Created by—Name of the user that created the template.
Creating a template
When creating a report template, you need to specify all the information that you want to display in the report: report name, its description, availability of a table, graph or image. You can also select the data that you want to display in the report and define the position of report elements.
When creating a report in the Reports section, Generated reports subsection of the interface, you can only select the template for creating the report and the data display period.
A new report template is created for each data sample.
To create a template:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
This opens the table of templates.
- Click Add.
This opens the template creation window. This window contains the body of the report and the report builder in a floating window. You can move the report builder over the workspace of the web interface window.
- In the Template name field in the upper-right corner of the window, type the name that you want to assign to reports that are created from this template. For example, Alerts by technology.
This name is displayed in the table in the Reports section, Generated reports subsection when creating all reports in this template.
- In place of the Report title text, type the report name that will be displayed in a report after the report is created. If you do not want to add a report name, you can delete the Report title text and leave this report section blank.
You can format text using the buttons in the Text section in the template builder.
- In place of the Report description text, type the report description that will be displayed in a report after the report is created. If you do not want to add a report description, you can delete the Report description text and leave this report section blank.
You can format text using the buttons in the Text section in the template designer.
- Using the report builder, add one or more report elements:
- Table.
- Pie chart.
- Image.
- If you chose to add an image, the Image window opens. Do the following:
- Click Upload.
- Upload the image. For example, you can upload your company logo.
- In the list on the right of the upload button, select the alignment of the image on the report page: Left, Right or Center.
- Click Apply.
- If you chose to add a pie chart, the Pie chart of alert attributes window opens. Do the following:
- In the Name field, type the name of the pie chart. For example, Top 5 alerts by technology. You can also leave the field blank.
- In the Data source list, select the alert property for which you want to create a pie chart. For example, Technologies.
- In the Number of slices field, specify the maximum number of sectors of the pie chart. When a report is created, the application selects the most frequently encountered data. For example, if you specified 5 sectors and want to create a pie chart by technology, the application will show a pie chart for the 5 technologies that generated the highest number of alerts. The technologies that generated the lowest number of alerts are not displayed on the pie chart.
Click Apply.
- If you chose to add a table, the Alerts table window opens. Do the following:
- In the Available columns field, double-click to select the alert properties that you want to add to the report table.
The selected properties are moved to the Selected columns field. You can drag the names of columns between the Available columns and Selected columns fields, and change the order of columns in the report table.
For example, if you moved the Technologies, Detected and Time created properties to the Selected columns field, the table of the created report will show the technologies that generated alerts, a list of detected objects, and the time when the alerts were generated.
- If you want to filter alerts by the State property, select the check boxes next to the processing statuses of alerts whose data you want to display in the report.
- If you want to filter alerts by the Technologies property, select the check boxes next to the names of application modules and components whose data you want to display in the report.
- If you want to filter alerts by the Importance property, select the check boxes next to the importance levels of alerts whose data you want to display in the report.
- If you want to filter alerts by the VIP status, select VIP in the list. Only alerts with the VIP status are displayed in the report.
- Click Apply.
- In the Available columns field, double-click to select the alert properties that you want to add to the report table.
- Click the Save button in the upper-right corner of the window.
A new template will be created.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot create report templates.
Creating a report based on a template
To create a report based on a template:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click Add.
This opens the New report window.
- Do the following:
- In the Template drop-down list, select one of the templates for creating a report.
- Under Period, select one of the following options:
- Last hour if you want the report to contain information about application operation during the last hour.
- Last day if you want the report to contain information about application operation during the last day.
- Last 7 days if you want the report to contain information about application operation during the last week.
- Last 30 days, if you want the report to contain information about system operation during the last month.
- Custom, if you want the report to contain information about system operation during the period you specify.
- If you have selected the Custom display period for information about application operation:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the period for which the report will be generated.
- Click Apply.
- If you are using distributed solution and multitenancy mode, in the Servers settings group, select the check boxes next to the tenants and servers whose data you want to include in the report.
- Click Create.
The created report is displayed in the table of reports. You can download the report for viewing on your computer.
Users with the Security officer role cannot create report templates.
Viewing a report
To view a report:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Select the report that you want to view.
The report opens in a new tab in your browser.
Downloading a report to a local computer
To download a report to your computer:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- In the line containing the report that you want to view, click the
 icon.
icon.The report is saved in HTML format to your local computer in the browser's downloads folder.
To view a report, you can use any application that lets you view HTML files (for example, a browser).
Editing a template
To edit a template:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Select the template that you want to edit.
This opens the template editing window.
- You can edit the following settings:
- Template name is the report name that is displayed in the table in the Reports section, Generated reports subsection when creating all reports based on this template.
- Report title is the report name that is displayed in the report after the report is created.
You can format text using the buttons in the Text section in the template builder.
- Report description is the report description that is displayed in a report after the report is created.
You can format text using the buttons in the Text section in the template builder.
- Image. You can upload or delete an image.
- Pie chart. You can change the following pie chart settings:
- Name.
- Data source.
- Number of slices.
Click Apply.
- Table. You can change the following table settings:
- Selected columns. You can drag the names of columns between the Available columns and Selected columns fields, and change the order of columns in the report table.
- State.
- Technologies.
- Importance.
- VIP status.
- Select one of the following methods to save the template:
- If you want to apply changes to the current template, click the Save button.
The template is modified.
- If you want to create a new template, enter a name for the template and click Save as.
The name of the new template must not be the same as the name of an already existing template.
The new template will be saved.
- If you want to apply changes to the current template, click the Save button.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot edit templates.
Filtering templates by name
To filter templates by name:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Click the Report name link to open the template filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following template filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Enter one or several characters of the template name.
- If you want to add a filtering criterion to the filter, click the
 button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria.
button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria. - Click Apply.
The table of templates will display only templates that match the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering templates based on the name of the user that created the template
To filter templates by the name of the user that created the template:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Click the Created by link to open the menu for filtering templates.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following template filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Enter one or several characters of the user name.
- If you want to add a filtering criterion to the filter, click the
 button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria.
button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria. - Click Apply.
The table of templates will display only templates that match the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering templates by creation time
To filter report templates by creation time:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Click the Time created link to open the menu for filtering templates.
- Select one of the following template display periods:
- All if you want the application to display all created templates in the table.
- Last hour if you want the application to display the templates that were created during the last hour in the table.
- Last day if you want the application to display the templates that were created during the last day in the table.
- Custom range if you want the application to display templates that were created during the period you specify in the table.
- If you have selected the Custom range template display period:
- This opens the calendar; in the calendar, specify the start and end dates of the template display period.
- Click Apply.
The table of templates will display only templates that match the filter criteria you have set.
Clearing a template filter
To clear the template filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Click
 to the right of the header of the column of the template table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column of the template table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table of templates will display only templates that match the filter criteria you have set.
Deleting a template
To delete a template:
- In the application web interface window, select the Reports section, Templates tab.
- This opens the table of templates. Select the check box in the line containing the template that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The template that you selected will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot delete templates.
Filtering reports by creation time
To filter reports by creation time:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click the Time created link to open the report filtering menu.
- Select one of the following report display periods:
- All if you want the application to display all created reports in the table.
- Last hour if you want the application to display the reports that were created during the last hour in the table.
- Last day if you want the application to display the reports that were created during the last day in the table.
- Custom range if you want the application to display reports that were created during the period you specify in the table.
- If you have selected the Custom range report display period:
- In the calendar that opens, specify the start and end dates of the report display period.
- Click Apply.
The table of reports will display only reports that match the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering reports by name
To filter reports by name:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click the Report name link to open the report filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following report filtering operators:
- Contain.
- Not contain.
- In the text box, enter one or more characters of the report name.
- If you want to add a filtering criterion to the filter, click the
 button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria.
button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria. - Click Apply.
The table of reports will display only reports that match the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering reports by the name of the server with the Central Node component
To filter reports by the name of the server with the Central Node component:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click the Servers link to open the report filtering menu.
- Select the check boxes opposite those servers by which you want to filter reports.
- Click Apply.
The table of reports will display only reports that match the filter criteria you have set.
Filtering reports based on the name of the user that created the report
To filter reports by the name of the user that created the report:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click the Created by link to open the report filtering menu.
- In the drop-down list, select one of the following report filtering operators:
- Contain
- Not contain
- Enter one or several characters of the user name.
- If you want to add a filtering criterion to the filter, click the
 button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria.
button under the list of filtering operators and repeat the sequence for specifying filtering criteria.
The table of reports will display only reports that match the filter criteria you have set.
Clearing a report filter
To clear the report filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the column of the reports table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column of the reports table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table of reports will display only reports that match the filter criteria you have set.
Deleting a report
To delete an application operation report:
- In the window of the program web interface, select the Reports section, Generated reports subsection.
This opens the table of reports.
- Select the check box in the line containing the report that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected report will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot delete reports.
Managing rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts
Users with the Senior security officer role can create, delete, modify, import and export a list of rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts.
You can create the following types of rules:
- IP. The VIP status will be assigned to new alerts associated with this IP address of the computer.
- Host name. The VIP status will be assigned to new alerts associated with this host name.
- Email. The VIP status will be assigned to new alerts associated with this email address.
Users with the Security auditor role can view and export a list of rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the list of rules for assigning VIP status to alerts.
Viewing the table of VIP status assignment rules
The table of rules for assigning the VIP status is located in the Settings section, VIP status subsection of the web interface of the application.
The table contains the following information:
- Criteria—Criterion for adding an entry to the list of rules.
- Value—Value of the criterion.
- Description—Additional information specified when creating the rule.
Creating a VIP status assignment rule
To add a rule for assigning the VIP status to alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Add.
This opens the window for adding a rule.
- In the Criteria drop-down list, select one of the following rule types:
- IP, if you want to add a rule for a computer IP address.
- Host, if you want to add a rule for a host name.
- Email, if you want to add a rule for an email address.
- Enter the necessary value in the Value field.
For example, if under Criteria, you selected Email, enter the email address that you want to add in the Value field.
- In the Description field, enter additional information if necessary.
- Click Add.
The rule is added. The VIP status will be assigned to new alerts associated with the added IP address, host name, or email address.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create VIP status assignment rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the list of rules for assigning VIP status to alerts.
Deleting a VIP status assignment rule
To delete a rule for assigning the VIP status to alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Select the check box to the left of each rule that you want to remove from the list.
- If you want to delete all rules, select the check box above the list.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Delete.
The action confirmation window is displayed.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete VIP status assignment rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the list of rules for assigning VIP status to alerts.
Modifying a VIP status assignment rule
To modify a rule for assigning the VIP status to alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Select the rule that you want to modify.
This opens the rule editing window.
- Make the necessary changes to the Criteria, Value and Description fields.
- Click Save.
The rule is modified.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot modify VIP status assignment rules.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the list of rules for assigning VIP status to alerts.
Importing a list of VIP status assignment rules
To import a list of rules for assigning VIP status to alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Click Import.
You will be prompted for confirmation of the list import.
The imported list of rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts will replace the current list of VIP status alert assignment rules.
- Click Yes.
This opens the file selection window.
- Select a JSON file containing the list of rules that you want to import and click Open.
This closes the file selection window.
The list is imported.
Exporting the list of data excluded from the scan
To export the scan exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Export.
The JSON file containing the exported list of scan exclusions is saved in the browser's downloads folder on your computer.
Filtering and searching by type of VIP status assignment rule
To filter or search for VIP status assignment rules by rule type:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Click the Criteria link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select one or several check boxes next to the types of rules:
- IP.
- Host.
- Email.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table will display only the rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching by value of VIP status assignment rule
To filter or search for VIP status assignment rules by rule value:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Click the Value link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter one or several characters of the rule value.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table will display only the rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching by description of VIP status assignment rule
To filter or search for VIP status assignment rules by description:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Click the Description link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter one or several characters of the description.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table will display only the rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a VIP status assignment rule filter
To clear the VIP status assignment rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings tab, VIP status section.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the table column for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table will display only the rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
Managing the list of scan exclusions
Users with the Senior security officer role can create, import and export the list of scan exclusions, that is, the list of data that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform treats as safe and does not display in the alerts table. You can create scan exclusion rules for the following data:
- MD5
- Format
- URL mask
- Email recipient
- Email sender
- Source IP or subnet
- Destination IP or subnet
- User Agent
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles can view the list of scan exclusion rules as well as export it.
Viewing the table of data excluded from the scan
To view the table with data excluded from the scan:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
This opens the table with a list of data that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will treat as safe and will not create alerts for. You can filter the rules by clicking links in column headers.
The table contains the following information:
- Criteria—Criterion for adding an entry to the list of allowed objects.
- Value—Value of the criterion.
Adding a scan exclusion rule
To add to scan exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Add.
This opens the New rule window.
- In the Criteria drop-down list, select one of the following criteria for adding a rule to the list of scan exclusions:
- MD5.
- Format.
- URL mask.
- Email recipient.
- Email sender.
- Source IP or subnet.
- Destination IP or subnet.
- User Agent.
- If you selected Format, select the file format that you want to add from the Value drop-down list.
For example, you can select the MSOfficeDoc format.
- If you selected MD5, URL mask, Email recipient, Email sender, Source IP or subnet, Destination IP or subnet, or User Agent, in the Value field, enter the value of the relevant criterion that you want to add to the list of scan exclusions:
- If you selected MD5, enter the MD5 hash of the file in the Value field.
- If you selected URL mask, enter the URL mask in the Value field.
You can use the following special characters in the mask:
* – any sequence of characters.
Example:
If you enter
*abc*as the mask, the application considers as safe any URL that contains the sequenceabc. For example,www.example.com/download_virusabc? – any single character.
Example:
If you enter
example_123?.comas the mask, the application considers as safe any URL that contains the given character sequence and any character following3. For example,example_1234.comIf the
*or?characters are part of the full URL that you want to add to the list of scan exclusions, use the\character when entering the URL to escape a single*,?, or \ character that follows it.Example:
You need to add the following URL as a trusted address:
www.example.com/download_virus/virus.dll?virus_name=You do not want the application to treat
?as a special mask character so you put a\character before the?character.The URL added to the list of scan exclusions looks as follows:
www.example.com/download_virus/virus.dll\?virus_name= - If you selected Email recipient or Email sender, enter the email address in the Value field.
- If you selected User Agent, enter the User agent header of HTTP requests containing browser information in the Value field.
- If you selected Source IP or subnet or Destination IP or subnet, enter the address or subnet (for example, 255.255.255.0) in the Value field.
In the URL mask, Email recipient, and Email sender field, you can enter domain names containing Cyrillic characters. In this case, the address is converted to Punycode and processed in accordance with application settings.
- Click Add.
The rule is added to the scan exclusion list.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot add a scan exclusion rule.
Deleting a scan exclusion rule
To remove one or multiple rules from scan exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- Select the check box to the left of each rule that you want to remove from the list of scan exclusions.
If you want to delete all rules, select the check box above the list.
- In the lower part of the window, click Delete.
The action confirmation window is displayed.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules are removed from the list of scan exclusions.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot remove entries from the list of scan exclusions.
Editing a rule added to scan exclusions
To edit a rule in the scan exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- Select the rule that you want to modify.
This opens the Edit rule window.
- Make the necessary changes to the Criteria and Value fields.
- Click Save.
The rule is modified.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot edit rules in the list of scan exclusions.
Exporting the list of data excluded from the scan
To export the scan exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Export.
The JSON file containing the exported list of scan exclusions is saved in the browser's downloads folder on your computer.
Filtering rules in the scan exclusion list by criterion
To filter scan exclusion list entries by rule type:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- Click the Criteria link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select one or more check boxes next to criteria by which you want to filter the rules:
- MD5
- Format
- URL mask
- Email recipient
- Email sender
- Source IP or subnet
- Destination IP or subnet
- User Agent
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The list of scan exclusions displays only those rules that match your criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Searching rules in the scan exclusion list by value
To search rules in the scan exclusion list by value:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- Click the Value link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter value characters.
- Click Apply.
The list of scan exclusions displays only those rules that match your criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Resetting the rule filter in the scan exclusion list
To clear an exclusion list record filter by one or more filtering criteria:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the Scan tab.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the column in the table of scan exclusion list entries for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column in the table of scan exclusion list entries for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The list of scan exclusions displays only those rules that match your criteria.
Managing IDS exclusions
Users with the Senior security officer role can add Kaspersky IDS rules to scan exclusions. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not create alerts for excluded IDS rules.
You can add to exclusions only IDS rules defined by Kaspersky. If you do not want to apply a user-defined IDS rule when scanning, you can disable this rule or delete it.
If you want to configure a singular exclusion, for example, for a specific source address, you can:
- Add Kaspersky IDS rules to scan exclusions.
- Add a new rule based on the excluded Kaspersky rule to the list of user-defined IDS rules in one of the following ways:
- If the system already has user-defined IDS rules, export a file with the rules and add a new rule to this file with conditions that narrow down the rule using the Suricata syntax.
- If no user-defined IDS rules exist in the system yet, create a text file and add to it a rule with qualifying conditions using the Suricata syntax.
- Import a file with the added rule.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of IDS rules added to exclusions, and view the properties of a selected rule.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the list of IDS rules added to exclusions.
Viewing the table of IDS rules added to exclusions
To view the table of IDS rules added to exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Go to the IDS tab.
The table of excluded IDS rules is displayed. You can filter the rules by clicking links in column headers.
The table contains the following information:
- Time created—Date and time when the IDS rule was added to exclusions.
- Rule name—Name of the IDS rule.
- Rule ID—ID of the IDS rule. sid (signature ID) in Suricata format.
- Description—Description of the IDS rule.
- Created by—Name of the user whose account was used to add the IDS rule to exclusions.
Adding an IDS rule to exclusions
You can exclude Kaspersky IDS rules with medium or high importance alerts from event scanning.
You can add to exclusions only IDS rules defined by Kaspersky. If you do not want to apply a user-defined IDS rule for event scanning, you can disable that rule or delete it.
To add an IDS rule to exclusions:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the link in the Technologies column to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select Contain.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select the (IDS) Intrusion Detection System technology.
- Click Apply.
- If you want to filter detections, click
 to expand the list of filtering parameters and select the required filter.
to expand the list of filtering parameters and select the required filter. - Select an alert for which the Detected column displays the name of the relevant IDS rule.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- In the right part of the window, in the Recommendations section, Qualifying subsection, click Add to exclusions.
This opens the Add IDS rule to exclusions window.
- In the Description field, enter a description for the IDS rule.
- Click Add.
The IDS rule is added to exclusions and is displayed in the exclusion list in the Settings section, Exclusions subsection on the IDS tab in the application web interface. This rule is no longer used for creating alerts.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot modify entries in the list of allowed objects.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to the list of IDS rules added to exclusions.
Editing the description of an IDS rule added to exclusions
To edit the description of an excluded IDS rule, in the Alerts section:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the link in the Technologies column to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select Contain.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select the (IDS) Intrusion Detection System technology.
- Click Apply.
- If you want to filter detections, click
 to expand the list of filtering parameters and select the required filter.
to expand the list of filtering parameters and select the required filter. - Select an alert for which the Detected column displays the name of the relevant IDS rule.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- In the right part of the window, in the Recommendations section, Qualifying subsection, click Edit IDS exclusion.
This opens the Edit IDS exclusion window.
In the Description field, edit the description of the rule.
Click Save.
The description of the excluded IDS rule is changed. This rule is no longer used for creating alerts.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot edit IDS rule descriptions.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to the list of IDS rules added to exclusions.
Removing an IDS rule from exclusions
You can remove from exclusions a single IDS rule, multiple rules, or all rules at the same time.
To remove an IDS rule from exclusions:
- In the program web interface window, select the Settings → Exclusions section and go to the IDS tab.
- A list of excluded IDS rules is displayed.
- Select the rule that you want to remove from exclusions.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The rule is removed from exclusions. The rule is no longer used for creating alerts.
To remove all or multiple IDS rules from exclusions:
- In the program web interface window, select the Settings → Exclusions section and go to the IDS tab.
- A list of excluded IDS rules is displayed.
- Select check boxes next to rules that you want to remove from exclusions.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules are removed from exclusions. The rules are no longer used for creating alerts.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot remove IDS rules from exclusions.
Users with the Security officer role do not have access to the IDS exclusion list.
Managing TAA exclusions
TAA (IOA) rules created by Kaspersky experts contain indicators of suspicious behavior of an object in the corporate IT infrastructure. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform scans the events database of the application and creates alerts for events that match behaviors described by TAA (IOA) rules. If you do not want the application to create alerts for events generated as part of host activity that is normal for your organization, you can add a TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions.
TAA (IOA) rule modes added to exclusions can work in the following modes:
- The rule is always excluded.
In this case, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events as matching the TAA (IOA) rule and does not create alerts based on that rule.
- The rule is supplemented by a condition.
In this case, the TAA (IOA) rule is supplemented by conditions in the form of a search query. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events that match specified conditions as matching the TAA (IOA) rules. For events that match the TAA (IOA) rule, but do not satisfy the conditions of the applied exclusion, the application marks the events and creates alerts.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, TAA exclusions can have the following types:
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These exclusions apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Exclusions belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Global—Created on the PCN server. Exclusions apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Exclusions belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
Users with the Senior security officer role can create, edit, and delete exclusions for tenants to whose data they have access.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles can only view the list of TAA exclusions and the properties of a selected exclusion.
For each TAA (IOA) rule, you can create only one local or global exclusion.
If one TAA (IOA) rule has exclusions created both on an SCN server and the PCN server, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform processes events in accordance with exclusion settings on the PCN server.
Viewing the table of TAA (IOA) rules added to exclusions
To view the table of TAA (IOA) rules added to exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Click the TAA tab.
The table of excluded TAA (IOA) rules is displayed. You can filter the rules by clicking links in column headers.
The table contains the following information:
 —Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.
—Importance level that is assigned to an alert generated using this TAA (IOA) rule.The importance level can have one of the following values:
 – Low.
– Low. – Medium.
– Medium. – High.
– High.
- Type is the type of the rule depending on the role of the server which generated it:
- Local—Created on the SCN server. These exclusions apply only to hosts that are connected to this SCN server. Exclusions belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Global—Created on the PCN server. Exclusions apply to hosts that are connected to this PCN server and to all SCN servers that are connected to this PCN server. Exclusions belong to the tenant which the user is managing in the application web interface.
- Confidence – level of confidence depending on the likelihood of false alarms caused by the rule:
- High.
- Medium.
- Low.
The higher the confidence level, the lower the likelihood of false alarms.
- Exclude rule is the operating mode of the rule that is added to exclusions.
- Always means the rule is always excluded. In this case, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events as matching the TAA (IOA) rule and does not create alerts based on that rule.
- Based on conditions means the rule is excluded if a condition is added. In this case, the TAA (IOA) rule is supplemented by conditions in the form of a search query. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events that match specified conditions as matching the TAA (IOA) rules. For events that match the TAA (IOA) rule, but do not satisfy the conditions of the applied exclusion, the program marks the events and creates alerts.
- Name is the name of the rule.
Adding a TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions
You can add to exclusions only TAA (IOA) rules made by Kaspersky. If you do not want to apply a user-defined TAA (IOA) rule for scanning events, you can disable that rule or delete it.
To add a TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions from the Alerts section:
- Select the Alerts section in the window of the application web interface.
This opens the table of alerts.
- Click the link in the Technologies column to open the filter configuration window.
- In the drop-down list on the left, select Contain.
- In the drop-down list on the right, select the (TAA) Targeted Attack Analyzer technology.
- Click Apply.
The table displays alerts generated by the TAA technology based on TAA (IOA) rules.
- Select an alert for which the Detected column displays the name of the relevant rule.
This opens a window containing information about the alert.
- Under Scan results, click the link with the name of the rule to open the rule information window.
- To the right of the TAA exclusions setting name, click Add to exclusions.
This opens a window that allows you to add the TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions.
- In the Exclude rule field, select the exclusion operating mode:
- Always if you do not want the application to create alerts for events that match the selected TAA (IOA) rule.
- Based on conditions if you do not want the application to create events only for events that match specified conditions. Alerts are created for events that match the TAA (IOA) rule with the configured exclusion conditions taken into account.
If you selected Based on conditions:
- Click Configure additional conditions to open the event search form.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and want to enable the display of events for all tenants, turn on the Search in all tenants toggle switch.
- Perform an event search in builder mode.
A table is displayed of events that match the TAA (IOA) rule given the specified exclusion criteria.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, found events are grouped in tiers: Server – Tenant names – Server names.
- Click the name of the server for which you want to view events.
The host table of the selected server is displayed. Event grouping levels are displayed above the table.
If necessary, you can change event search conditions.
- Click Add exclusion.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, in the Apply to servers* field, select check boxes for tenants and servers to which the rule must be applied.
- Click Add.
The TAA (IOA) rule is added to exclusions and is displayed in the exclusion list in the Settings section, Exclusions subsection on the TAA tab in the application web interface. This rule is no longer used for creating alerts.
To add a TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions from the Threat Hunting section:
- Select the Threat Hunting section in the application web interface window.
This opens the event search form.
- Define the search conditions and click the Search button. For example, you can select event search criteria in the TAA properties group in builder mode.
The table of events that satisfy the search criteria is displayed.
- Select an event.
- To the right of the IOA tags setting, click the name of the rule.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- To the right of the TAA exclusions setting name, click Add to exclusions.
This opens a window that allows you to add the TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions.
- In the Exclude rule field, select the exclusion operating mode:
- Always if you do not want the application to create alerts for events that match the selected TAA (IOA) rule.
- Based on conditions if you do not want the application to create events only for events that match specified conditions. Alerts are created for events that match the TAA (IOA) rule with the configured exclusion conditions taken into account.
If you selected Based on conditions:
- Click Configure additional conditions to open the event search form.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and want to enable the display of events for all tenants, turn on the Search in all tenants toggle switch.
- Perform an event search in builder mode.
A table is displayed of events that match the TAA (IOA) rule given the specified exclusion criteria.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, found events are grouped in tiers: Server – Tenant names – Server names.
- Click the name of the server for which you want to view events.
The host table of the selected server is displayed. Event grouping levels are displayed above the table.
If necessary, you can change event search conditions.
- Click Add exclusion.
- Click Add.
The TAA (IOA) rule is added to exclusions and is displayed in the exclusion list in the Settings section, Exclusions subsection on the TAA tab in the application web interface. This rule is no longer applied when scanning events.
When creating a search query to be saved as an exclusion criterion, avoid using the following fields:
- IOAId.
- IOATag.
- IOATechnique.
- IOATactics.
- IOAImportance.
- IOAConfidence.
These fields are only displayed after Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform marks events as matching TAA (IOA) rules.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot add TAA (IOA) rules to exclusions.
Viewing a TAA (IOA) rule added to exclusions
To view a TAA (IOA) rule added to exclusions:
- In the application web interface window, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection and go to the TAA tab.
The table of excluded TAA (IOA) rules is displayed.
- Select the rule that you want to view.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
The window contains the following information:
- TAA (IOA) rule: click this link to open a window containing a description of the MITRE technique corresponding to this rule, recommendations on responding to the event, and information about the likelihood of false alarms.
- ID is the ID that the application assigns to each rule.
- Name is the name of the rule that you specified when you added the rule.
- Importance is an estimate of the probable impact of the event on the security of computers or the corporate LAN as assessed by Kaspersky experts.
- Confidence is the level of confidence depending on the probability of false positives as estimated by Kaspersky experts.
- Exclude rule is the operating mode of the rule that is added to exclusions.
- Always means the rule is always excluded. In this case, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events as matching the TAA (IOA) rule and does not create alerts based on that rule.
- Based on conditions means the rule is excluded if a condition is added. In this case, the TAA (IOA) rule is supplemented by conditions in the form of a search query. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not mark events that match specified conditions as matching the TAA (IOA) rules. For events that match the TAA (IOA) rule, but do not satisfy the conditions of the applied exclusion, the program marks the events and creates alerts.
- Configure additional conditions: click this link to open the event search form with search conditions.
The field is displayed if, when adding the TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions, you have selected the Based on conditions mode, and configured some search criteria.
- The search criteria are configured in the
<IOA ID> AND NOT <search criteria>format.Search criteria are displayed if, when adding the TAA (IOA) rule to exclusions, you have selected the Based on conditions mode, and configured some search criteria.
- Apply to servers* are hosts to which the exclusion applies.
This field is displayed in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
Removing a TAA (IOA) rule from exclusions
You can remove from exclusions a single TAA (IOA) rule, multiple rules, or all rules at the same time.
To remove a TAA (IOA) rule from exclusions:
- In the application web interface window, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection and go to the TAA tab.
The table of excluded TAA (IOA) rules is displayed.
- Select the rule that you want to remove from exclusions.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The rule is removed from exclusions. The rule is applied when creating alerts or scanning events.
To remove all or multiple TAA (IOA) rules from exclusions:
- In the application web interface window, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection and go to the TAA tab.
- The table of excluded TAA (IOA) rules is displayed.
- Select check boxes next to rules that you want to remove from exclusions.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
- In the pane that appears in the lower part of the window, click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules are removed from exclusions. The rules are applied when creating alerts or scanning events.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot remove TAA (IOA) rules from exclusions.
Managing ICAP exclusions
Users with the Senior security officer can create an ICAP exclusion list, that is, a list of data that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform must not scan. You can create ICAP exclusion rules for the following data:
- Format.
- User Agent.
- MD5.
- URL mask.
- Source IP or subnet.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles can view the list of ICAP exclusion rules.
In distributed solution mode, ICAP exclusions created on an SCN apply to all Sensor components connected to that SCN. ICAP exclusions created on a PCN apply to the SCN installed on the same device as the PCN and to all Sensor components connected to that SCN.
Viewing the ICAP exclusion table
To view the ICAP exclusion table:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
The table of data that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform must not scan is displayed. You can filter the rules by clicking links in column headers.
The table columns contain the following information:
- Value—Value of the criterion.
- Criteria—Criterion for adding an entry to the list of allowed objects.
- State is the state of the rule.
Adding a rule to ICAP exclusions
ICAP exclusion rules are processed if a rule for the data has not been previously added to the scan exclusion rules.
To add rule to ICAP exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- In the upper-right corner of the application web interface window, click Add.
This opens the New rule window.
- Move the State toggle switch to the position you need.
By default, the toggle switch is in the Enabled position.
- In the Criteria drop-down list, select one of the following criteria for adding a rule to the list of ICAP exclusions:
- Format.
- User Agent.
- MD5.
- URL mask.
- Source IP or subnet.
- Depending on the selected criterion, in the Value field, specify the following information:
- If you selected Format, select the file format that you want to add from the drop-down list.
When you add an ICAP exclusion rule by format, web page content of the corresponding format is loaded without scanning, and the display of web pages is not disrupted.
- If you selected User Agent, enter the
User agent header of HTTP requestscontaining browser information. - If you selected MD5, enter the MD5 hash of the file.
- If you selected URL mask, enter the URL mask.
You can use the following special characters in the mask:
* – any sequence of characters.
? – any single character.
If the
*or?characters are part of the full URL that you want to add to the list of scan exclusions, use the\character when entering the URL to escape a single *,?, or \characterthat follows it.In the URL mask field, you can enter domain names containing Cyrillic characters. In this case, the address is converted to Punycode and processed in accordance with application settings.
- If you selected Source IP or subnet, enter an address or subnet (for example, 255.255.255.0).
- If you selected Format, select the file format that you want to add from the drop-down list.
- Click Add.
The rule is added to the ICAP exclusion list.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot add an ICAP exclusion rule.
Page top
Removing rules from ICAP exclusions
To remove one or more rules from ICAP exclusions:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Select the check box to the left of each rule that you want to remove from the list of ICAP exclusions.
If you want to delete all rules, select the check box above the list.
- In the lower part of the window, click Delete.
- This opens a window; in that window, click Yes to confirm the deletion of rules.
The selected rules are removed from the list of ICAP exclusions. Data that was previously listed in the ICAP exclusion rules are now scanned by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot remove entries from the list of ICAP exclusions.
Editing or disabling a rule in the ICAP exclusion list
To edit a rule in the ICAP exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Select the rule that you want to modify.
This opens the Edit rule window.
- Make the necessary changes to the State, Criteria, and Value fields.
- Click Save.
The rule is modified.
To disable a rule in the ICAP exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- To the right of the rule that you want to disable in the ICAP exclusion list, in the State column, move the toggle switch to the Disabled position.
- This opens a window; in that window, click Yes to confirm the disabling of the rule.
The rule is disabled.
Users with the Security auditor and Security officer roles cannot edit or disable rules in the list of ICAP exclusions.
Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by criterion
To filter rules in the ICAP exclusion list by criterion:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Click the Criteria link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select one or more check boxes next to criteria by which you want to filter the rules:
- Format.
- User Agent.
- MD5.
- URL mask.
- Source IP or subnet.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The list of ICAP exclusions displays only rules that match the specified filtering conditions. You can filter by the Value and State columns at the same time.
Page top
Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by value
To filter rules in the ICAP exclusion list by value:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Click the Value link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter a value.
- Click Apply.
The list of ICAP exclusions displays only rules that match the specified search conditions. You can filter by the Criteria and State columns at the same time.
Filtering rules in the ICAP exclusion list by state
To filter rules in the ICAP exclusion list by state:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Click the State link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select the check box next to one of the values:
- Enabled.
- Disabled.
- Click Apply.
The list of ICAP exclusions displays only rules that match the specified search conditions. You can filter by the Criteria and Value columns at the same time.
Page top
Clearing rule filter conditions in the ICAP exclusion list
To clear the filter conditions for rules in the ICAP exclusion list:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Exclusions subsection.
- Open the ICAP tab.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the Value, Criteria, or State column in the table for which you want to reset the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the Value, Criteria, or State column in the table for which you want to reset the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filter conditions are cleared. The list of ICAP exclusions displays only rules that match the specified conditions.
Page top
Creating a list of passwords for archives
The application does not scan password-protected archives. You can create a list of the most frequently encountered passwords for archives that are used when exchanging files within your organization. If you do so, the application will try passwords from the list when scanning an archive. If one of the passwords match, the archive will be unlocked and scanned.
The list of passwords set in application settings is also transmitted to the server with the Sandbox component.
To create a list of archive passwords:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Passwords for archives subsection.
- In the Passwords for archives field, enter the passwords that the application will use for password-protected archives.
Enter each password on a new line. You can enter up to 50 passwords.
- Click Apply.
The list of passwords for archives will be created. When scanning PDF files and files of Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint that are password protected, the application will use the passwords from the defined list.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of passwords for archives, but cannot edit it.
Page top
Viewing server settings
Users with the Security auditor role can view Central Node server and PCN settings in distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
The server settings are located in the Settings section of the web interface window. In this section, you can view the following information:
- Users—List of user accounts of application web interface users.
- General settings—General settings of the server.
- Database update—Database update.
- Monitoring—Maximum allowed hard disk space usage for Central Node and Sensor servers.
- SNMP—SNMP connection settings.
- Certificates—Status of server certificates and computers with the Endpoint Agent component.
- Date and time—Server date and time settings.
- Endpoint Agents—Program functionality available when integrating with the Endpoint Agent component.
- IOC scanning schedule—Settings for the IOC scan schedule.
- Send files to Sandbox automatically—Automatically send files to be scanned by the Sandbox component.
- Activity indicators—Activity indicators of the Endpoint Agent component.
- Delete inactive hosts automatically—Automatic removal of inactive hosts from the Endpoint Agents table.
- KSN/KPSN and MDR—Settings for participation in Kaspersky Security Network and Kaspersky Private Security Network.
- KPSN reputation database—Settings for using the KPSN reputation database.
- SIEM system—Settings for integration with a SIEM system.
- Notifications—Settings for sending notifications.
- VIP status—List of rules for assigning the VIP status to alerts.
- Exclusions—List of allowed objects and lists of exclusions from TAA and IDS rules.
- Network settings—Settings for the network interface parameters.
- Passwords for archives—List of passwords for archives.
- License—State of the license key.
- Activity log—Settings for the activity log.
Viewing the table of servers with the Sandbox component
Users with the Security auditor role can view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
The table of servers with the Sandbox component is located in the Sandbox servers section, on the Servers tab of the application web interface window.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
The Server list table contains the following information:
- IP and name—IP address or fully qualified domain name of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Certificate fingerprint—Certificate fingerprint of the server with the Sandbox component.
- Authorization—Status of the request to connect to the Sandbox component.
- Status—Status of the connection to the Sandbox component.
Users with the Security officer role cannot view the table of servers with the Sandbox component.
Page top
Viewing the settings of the set of operating systems used for scanning objects in Sandbox
Users with the Security auditor role can view the settings of a set of operating systems used as the basis for creating tasks for scanning objects by the Sandbox component. The Sandbox server must have virtual machines installed that match the selected set.
Information about the settings of the set of operating systems for scanning objects in Sandbox is located in the Sandbox servers section, on the Settings tab of the application web interface window.
Sets of operating systems on which the Sandbox component can scan objects are displayed under OS set.
Operating systems that are part of the selected set are displayed under Set composition.
Page top
Viewing the table of servers with the Sensor component
The table of servers with the Sensor component is located in the Sensor servers section of the application web interface window.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
The Server list table contains the following information:
- IP/name—IP address or domain name of the server with the Sensor component.
- Type—Type of Sensor component. Possible values:
- Central Node—The Sensor component is installed on the same server as the Central Node component.
- Remote—The Sensor component is installed on a different server or a mail sensor is used as the Sensor component.
- Certificate fingerprint—Fingerprint of the TLS certificate used to establish an encrypted connection between servers with the Sensor and Central Node components.
- KSN/KPSN—Status of the connection to the KSN/KPSN reputation databases.
- SPAN—Status of SPAN traffic processing.
- SMTP—Status of integration with a mail server via SMTP.
- ICAP—Status of integration with a proxy server via ICAP.
- POP3—Status of integration with a mail server via POP3.
- State—Status of the connection request.
Managing raw network traffic
When managing the web interface, users with the Senior security officer role can download raw network traffic dumps in PCAP format from servers with the Sensor component and conduct investigations to detect suspicious activity.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, follow the steps on the PCN or SCN server to which the server with the Sensor component is connected.
To download raw network traffic captured from network interfaces:
- Select the Sensor servers section in the window of the application web interface.
The Server list table will be displayed.
- Select the Sensor component from which you want to download raw network traffic.
This opens the Sensor component settings page.
- Select the network interfaces for which you want to download raw network traffic by selecting the check box to the left of the network interface name.
By default, all network interfaces are selected.
If in the SPAN traffic scanning column, the toggle switch to the right of the network interface name is set to Disabled, you cannot download raw network traffic dumps from that network interface.
- Click Download traffic.
This opens the raw network traffic download settings settings window.
In this window, the First saved dump field displays the date and time of the first saved raw network traffic dump, and the Last saved dump field displays the date and time of the last raw network traffic dump. In the Available dump storage space field, the first number indicates the free space in dump storage, and the second number indicates the total size of the dump storage.
- Select the Period field and do the following:
- In the calendar, specify the start date and time and end date and time of the period for which you want to download raw network traffic. By default, the current date and time are selected as the end of the period, and the current day and the previous hour are selected as the start of the period.
- Click Apply.
If recorded traffic does not exist for your selected period, when you click Download, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform suggests selecting the period from the first recorded network traffic dump to the last. If no recorded dumps of raw network traffic exist at all, a warning is displayed indicating the lack of data for the specified period.
- In the Maximum dump size field, specify the maximum size of the downloaded raw network traffic dump.
The default value is 100 MB. The minimum value is 1 MB, and the maximum value is 1,000,000 TB. The downloaded raw network traffic dump of the specified size contain data starting with the last record of the selected period.
- If you want to restrict the download of raw network traffic data, in the BPF traffic filtering field, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
By default, the toggle switch is in the Disabled position.
- If you have set the toggle switch in the BPF traffic filtering field to Enabled, enter the filtering rule in the Filtering rule field. The BPF filtering rule is written in the libpcap format. For more details about the syntax, please refer to the pcap-filter manual page. The downloaded raw network traffic dump contains data that matches the entered filtering rule.
Example of a filtering expression:
tcp port 102 or tcp port 502 - If you want to restrict the download of raw network traffic data, in the Regexp traffic filter field, set the toggle switch to Enabled.
By default, the toggle switch is in the Disabled position.
- If you have set the toggle switch in the Regexp traffic filter field to Enabled, in the Filtering rule field, enter the filtering rule. The downloaded raw network traffic dump contains data that matches the entered filtering rule.
Example of a filtering expression:
^test.+xABxCD - Click Download.
Raw network traffic dumps are downloaded in PCAP format.
Page top
Viewing the table of external systems
Users with the Security auditor role can view the table of external systems.
The table of external systems is in the External systems section of the application web interface window.
The Certificate fingerprint field displays the fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the Central Node server.
The Server list table contains the following information:
- Sensor—IP address or domain name of the external system server.
- Type—Type of external system (mail sensor or other system).
- Name—Name of the integrated external system that is not a mail sensor.
A dash is displayed in this column for a mail sensor.
- ID—ID of the external system.
- Certificate fingerprint—Fingerprint of the TLS certificate of the server with the external system used to establish an encrypted connection with the Central Node server.
The certificate fingerprint of the server with the Central Node component is displayed in the upper part of the window in the Certificate fingerprint field.
- State—State of the integration request.
Users with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles cannot view the table of external systems.
Page top
Managing user-defined Sandbox rules
Users with the Senior security officer and Administrator roles can create rules for scanning files and URLs in their user environments. If no rules are added, objects are not sent for scanning.
You can create, edit, delete, enable, or disable rules. File scanning rules can also be imported and exported.
You do not need to create rules to send objects for scanning in preset images: by default, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends objects for scanning.
In distributed solution mode, you must create rules for scanning files in custom environments on each PCN and SCN server from which you want to send files for scanning.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of rules. Users with the Security officer role cannot view this section.
Page top
Viewing the table of user-defined Sandbox rules
To view the table of user-defined Sandbox rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
The table of user-defined rules for file scanning contains the following information:
- Created is the rule creation time.
- Virtual machine is the name of the virtual machine to which files are sent for scanning.
- Mask is the mask of files sent for scanning.
- Mask exclusion is the mask of files that are excluded from scanning.
- File category are categories of files sent for scanning.
- State is the state of the rule. It can have the values Enabled and Disabled.
The table of user-defined URL scanning rules contains the following information:
- Created is the rule creation time.
- Virtual machine is the name of the virtual machine to which files are sent for scanning.
- State is the state of the rule. It can have the values Enabled and Disabled.
Configuring the Sandbox rule table display
You can show or hide columns and change the order of columns in the table.
To configure the table display:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- In the heading part of the table, click
 .
.This opens the Customize table window.
- If you want to show a column in the table, select the check box next to the name of the parameter that you want displayed in the table.
If you want to hide a parameter in the table, clear the check box.
At least one check box must be selected.
- If you want to change the order of columns in the table, move the mouse cursor to the row with the relevant parameter, click
 and move the row to its new place.
and move the row to its new place. - If you want to restore default table display settings, click Default.
- Click Apply.
The rule table display is configured.
Page top
Filtering and searching Sandbox rules
To filter or search for Sandbox rules by required criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
- Depending on the filtering criterion, do the following:
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a Sandbox rule filter
To clear the Sandbox rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
- Click
 to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.
to the right of that column heading of the rule table for which you want to clear filtering criteria.If you want to clear multiple filter conditions, take steps to clear each filter condition individually.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table displays only rules that match the specified criteria.
Viewing the information of a user-defined Sandbox rule
To view the information of a user-defined Sandbox rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
- Select the rule for which you want to view information.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
The window with information about the user-defined file scanning rule contains the following information:
- State is the state of the prevention rule.
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which files are scanned in accordance with this rule.
- Mask is the mask of files sent for scanning.
- Mask exclusion is the mask of files that are excluded from scanning.
- File category are categories of files that are sent for scanning.
- File size is the size of the files being scanned.
The window with information about the user-defined URL scanning rule contains the following information:
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which URLs are scanned.
- State is the state of the prevention rule.
Creating a user-defined Sandbox rule for scanning files
To add a user-defined Sandbox rule for file scanning:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files tab.
- Click Add.
- Select Create rule.
This opens the rule creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- State is the state of the prevention rule. Select the check box if you want to enable the rule.
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which files will be scanned in accordance with this rule.
Only virtual machines with custom operating system images can be selected. These virtual machines must belong to the set of operating systems selected on the Central Node.
- Specify at least one of the values: mask or file category. If you fill in all the fields, the rule is triggered for files that match the category and size conditions or mask and size conditions, and are not exclusions.
- Mask is the mask of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple values.
To specify a mask, you can use the * and ? wildcard characters. Other wildcard characters are not supported.
- Mask exclusion is the mask of files that must be excluded from scanning. You can specify multiple values.
To specify an exclusion mask, you can use the * and ? wildcard characters. Other wildcard characters are not supported.
- File category are categories of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple categories.
You can view the full list of extensions for each category in the List of extensions for file categories section.
- File size is the size of the files being scanned.
- If you want to set multiple ranges, click Add file size.
- Mask is the mask of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple values.
- Click Add.
The rule is created.
If you want to send an archive for scanning, you must take into account the special considerations involved in scanning archives.
Archives are scanned as follows:
- Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform unpacks the archive.
- Files from the archive that match the rule are sent for scanning.
Files with the MSI extension are scanned in the same way as archives.
Page top
Creating a user-defined Sandbox rule for URL scanning
To add a user-defined Sandbox rule for URL scanning:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the URLs tab.
- Click Add.
- Select Create rule.
This opens the rule creation window.
- Configure the following settings:
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which URLs will be scanned.
Only virtual machines with custom operating system images can be selected. These virtual machines must belong to the set of operating systems selected on the Central Node.
- State is the state of the prevention rule. Select the check box if you want to enable the rule.
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which URLs will be scanned.
- Click Add.
The rule is created.
Page top
Copying a user-defined Sandbox rule
To copy a user-defined Sandbox rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
- Select the relevant rule.
- In the rule window, click Duplicate.
The rule is copied with all settings. You can change the values of settings if necessary.
Page top
Importing user-defined Sandbox rules for file scanning
To import user-defined Sandbox rules for file scanning:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files tab.
- Click Add.
- Select Import rules.
- This opens the file upload window.
- Select the file that you want to import.
- Click Open.
The file is imported.
Page top
Editing a user-defined Sandbox rule
To edit a user-defined Sandbox rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- Select a rule.
This opens the rule editing window.
You can edit the following fields:
- In the user-defined Sandbox rules for scanning files:
- State is the state of the prevention rule. Select the check box if you want to enable the rule.
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which files will be scanned in accordance with this rule.
Only virtual machines with custom operating system images can be selected. These virtual machines must belong to the set of operating systems selected on the Central Node.
- Specify at least one of the values: mask or file category. If you fill in all the fields, the rule is triggered for files that match the category and size conditions or mask and size conditions, and are not exclusions.
- Mask is the mask of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple values.
To specify a mask, you can use the * and ? wildcard characters. Other wildcard characters are not supported.
- Mask exclusion is the mask of files that must be excluded from scanning. You can specify multiple values.
To specify an exclusion mask, you can use the * and ? wildcard characters. Other wildcard characters are not supported.
- File category are categories of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple categories.
You can view the full list of extensions for each category in the List of extensions for file categories section.
- File size is the size of the files being scanned.
If you want to set multiple ranges, click Add file size.
- Mask is the mask of files that you want to send for scanning. You can specify multiple values.
- In the user-defined Sandbox rules for scanning URLs:
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which URLs will be scanned.
Only virtual machines with custom operating system images can be selected. These virtual machines must belong to the set of operating systems selected on the Central Node.
- State is the state of the prevention rule. Select the check box if you want to enable the rule.
- Virtual machine is the virtual machine on which URLs will be scanned.
Enabling or disabling user-disabling Sandbox rules
To enable or disable a Sandbox rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- In the row with the relevant rule, select or clear the check box in the State column.
The rule is enabled or disabled.
To enable or disable the use of all or multiple Sandbox rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules whose use you want to enable or disable.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Enable or Disable to enable or disable selected rules.
Selected rules are enabled or disabled.
Page top
Exporting user-defined Sandbox rules for file scanning
To export user-defined Sandbox rules for object scanning:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files tab.
- Click Export.
The rules file is saved to your local computer. The file is downloaded in the JSON format.
Page top
Deleting user-defined Sandbox rules
Users with the Senior security officer role can delete one or more user-defined Sandbox rules, or all rules at the same time.
To delete a user-defined Sandbox rule:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- Select the rule that you want to delete.
This opens a window containing information about the rule.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The rule is deleted.
To delete all or multiple user-defined Sandbox rules:
- In the window of the application web interface, select the Custom rules section, Sandbox subsection.
- Open the Files or URLs tab.
The table of user-defined Sandbox rules for file or URL scanning is displayed.
- Select the check boxes on the left of the rules that you want to delete.
You can select all rules by selecting the check box in the row containing the headers of columns.
A control panel appears in the lower part of the window.
- Click Delete.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Yes.
The selected rules will be deleted.
Page top
List of extensions for file categories
Extensions for file categories are listed in the table below.
Extensions for file categories
Category |
Extensions |
|---|---|
1C |
.epf, .ert, .erf, .cf, .dt, .deb, .bsl, .os, .ertx, .xls, .xml, .html, .txt, .cfu, .rptdesign, .xdt, .xslt, .wsdl |
Adobe Flash Player |
.swf, .fla, .flv, .f4v, .f4p, .f4a, .f4b, .mxml, .as, .asc, .ascs, .asv, .fxp, .fxpl, .xfl, .swc, .cfx, .spl, .dcr, .dir, .dxr, .aam, .swz |
Java |
.jar, .class, .war, .ear, .jad, .jnlp, .ser, .jsp, .jspx, .properties, .policy |
Html |
.html, .htm, .shtml, .xhtml, .xml, .svg, .mathml, .rss, .atom, .json, .mht, .mhtml, .webarchive |
Network packet |
.pcap, .pcapng, .cap, .netcap, .etl, .erf, .pkts, .pkt, .tcpdump, .snoop, .ngc, .dump, .cat, .smb, .vpcap, .dmp, .shb, .npl, .nfcapd, .wcap, .arpd, .pc, .tr1, .tr2, .trace |
SAP |
.abap, .adt, .bak, .cct, .cdp, .cpf, .dsc, .erd, .glo, .grc, .lis, .log, .lsa, .msg, .olap, .pgm, .prd, .sap, .sd, .se, .so, .spf, .tpz, .trc, .trex, .ttx, .wri, .xlf |
XML |
.xml, .xsl, .xslt, .rdf, .rss, .opf, .svg, .wsdl, .xhtml, .xjb, .xmi, .xpl, .xsl-fo, .xquery, .xsd, .dtd, .xht, .atom, .mathml, .mml, .plist, .xul, .fodt, .fo, .mxf, .xspf, .gpx, .unity, .ac, .ad, .aw, .ccxml, .csd, .dms, .epub, .fxml, .glb, .glTF, .glTF-Binary, .gml, .iif, .imdi, .jelly, .kml, .mrc, .msh, .mshxml, .mtl, .nib, .nws, .nzb, .osdx, .owl, .pbix, .plistxml, .ptx, .qti, .rdfxml, .rl, .rng, .ros, .rpj, .scml, .scxml, .shex, .sketch, .soap, .srdf, .srx |
Archive |
.snb, .apk, .mht, .crx, .dd, .r01, .mpkg, .pup, .tbz, .ace, .arj, .bin, .cab, .cbr, .deb, .exe, .gzip, .one, .pak, .pkg, .ppt, .rpm, .sh, .sib, .sis, .sisx, .sit, .sitx, .spl, .tar-gz, .xar, .zipx, .zip, .rar, .7z, .tar, .gz, .bz2, .xz, .tgz, .tbz2, .txz, .z, .jar, .war, .ear, .iso, .img |
Audio |
.a52, .adt, .dct, .dss, .dvf, .iklax, .ivs, .rm, .rmvb, .8svx, .amb, .avr, .cdda, .cvs, .cvsd, .cvu, .dts, .dvms, .fap, .fssd, .gsrt, .hcom, .htk, .ima, .ircam, .maud, .nist, .paf, .prc, .pvf, .sd2, .smp, .snd, .sndr, .sndt, .sou, .sph, .spx, .tta, .txw, .vms, .voc, .vox, .w64, .wv, .wve, .ac3, .aob, .asf, .aud, .bin, .bwg, .cdr, .gpx, .ics, .m, .m3u, .mod, .mpp, .msc, .msv, .mts, .nkc, .ps, .sdf, .sib, .sln, .spl, .srt, .temp, .vb, .wave, .wm, .wpd, .xsb, .xwb, .mpc, .aac, .flac, .m4a, .mmf, .mp3, .ogg, .wav, .wma, .mid, .amr, .ape, .au, .caf, .gsm, .oma, .qcp, .vqf, .ra, .aif, .mp2, .m4p, .awb, .m4r, .ram, .asx, .mpga, .aiff, .koz, .m4b, .kar, .iff, .midi, .3ga, .opus, .aup, .xspf, .aifc, .rta, .cda, .m3u8, .mpa, .aa, .aax, .oga, .nfa, .adpcm, .cdo, .flp, .aimppl, .4mp, .mui |
Video |
.drc, .f4a, .f4b, .f4p, .gifv, .mng, .mp2, .mpe, .mpv, .nsv, .roq, .svi, .3gp2, .3gpp2, .asx, .bin, .dat, .drv, .gtp, .moov, .spl, .stl, .vcd, .vid, .wm, .yuv, .hevc, .m2v, .mjpeg, .wtv, .avi, .mpeg, .m4v, .mov, .mp4, .wmv, .mpg, .swf, .3gp, .3g2, .mkv, .ogv, .webm, .asf, .ts, .mxf, .rm, .thp, .mts, .rmvb, .f4v, .mod, .vob, .h264, .flv, .3gpp, .divx, .qt, .amv, .dvsd, .m2ts, .ifo, .mswmm, .srt, .cpi, .wlmp, .vpj, .ced, .vep, .veg, .264, .dav, .pds, .dir, .arf, .mepx, .xesc, .bik, .nfv, .tvs, .imoviemobile, .rcproject, .esp3, .vproj, .aep, .camproj, .camrec, .cmproj, .cmrec, .modd, .mproj, .osp, .trec, .g64, .vro, .braw, .mse, .pz |
Document |
.sxi, .odg, .svg, .vsd, .eps, .cwk, .wp, .ott, .asp, .cdd, .cpp, .dotm, .gpx, .indd, .kdc, .kml, .mdb, .mdf, .mso, .one, .pkg, .pl, .pot, .potm, .potx, .ppsm, .ps, .sdf, .sgml, .sldm, .xar, .xlt, .xltm, .xltx, .pdf, .txt, .doc, .odt, .xps, .chm, .rtf, .sxw, .docx, .wpd, .wps, .docm, .hwp, .pub, .xml, .log, .oxps, .vnt, .dot, .pages, .m3u, .dotx, .shs, .msg, .odm, .pmd, .vmg, .eml, .tex, .wp5, .csk, .fdxt, .adoc, .afpub, .tcr, .acsm, .opf, .mbp, .apnx, .cbt, .vbk, .kfx, .lrf, .snb, .odp, .ppt, .pptx, .pps, .ppsx, .pptm, .key, .flipchart, .epub, .mobi, .azw, .azw3, .fb2, .djvu, .cbz, .cbr, .ibooks, .lit, .pdb, .prc, .tr2, .tr3, .ods, .xls, .xlsx, .csv, .wks, .xlsm, .xlsb, .xlr, .wk3, .numbers |
Image |
.dib, .pdf, .mrw, .icns, .wdp, .fig, .epsf, .cur, .erf, .fts, .heif, .jfif, .jpe, .jps, .mng, .pam, .pbm, .pes, .pfm, .picon, .pnm, .ppm, .ras, .rw2, .sgi, .x3f, .xbm, .xpm, .xwd, .art, .arw, .bmp, .cr2, .crw, .dcm, .dds, .djvu, .dng, .exr, .fpx, .gif, .ico, .jpg, .jp2, .jpeg, .nef, .orf, .pcd, .pcx, .pef, .pgm, .pict, .png, .psd, .raf, .sfw, .tga, .tiff, .wbmp, .xcf, .yuv, .kdc, .pct, .sr2, .tif, .hdr, .webp, .nrw, .plist, .ithmb, .thm, .pspimage, .mac, .heic, .rwl, .flif, .avif, .raw, .pictclipping, .jxr, .emf, .eps, .svg, .wpg, .ai, .svgz, .wmf, .odg, .cdr, .vsd, .std, .pd, .emz, .mix, .otg, .cvs, .gvdesign |
Android executable file |
.apk, .aab, .dex, .so, .jar, .aar, .class, .obb, .odex, .vdex, .vmx, .vmem, .img |
Windows executable file |
.cgi, .ds, .air, .cpp, .gadget, .hta, .jar, .msu, .paf.exe, .pwz, .thm, .vbs, .exe, .msi, .bat, .cmd, .com, .pif, .scr, .vb, .vbe, .js, .jse, .ws, .wsf, .wsh, .ps1, .psm1, .psd1, .ps1xml, .psc1, .scf, .lnk |
Executable file |
.rc, .p, .d, .asc, .bas, .cbl, .vbp, .iwb, .pb, .yml, .pika, .s19, .xt, .suo, .fsproj, .pbj, .pbxuser, .pyw, .xq, .cd, .sb, .sb2, .ise, .kv, .cod, .nib, .pwn, .b, .hpp, .apa, .bet, .bluej, .erb, .fxc, .m4, .owl, .sma, .trx, .vc, .def, .xap, .o, .pas, .qpr, .resources, .vbproj, .vbx, .xib, .md, .ccc, .wwp, .ss, .asf, .asm, .asp, .cfm, .dot, .dtd, .fla, .ged, .gv, .icl, .jse, .lua, .m, .mb, .mdf, .mod, .msp, .obj, .pkg, .po, .pot, .pub, .rss, .sln, .so, .vbe, .vbs, .vc4, .vcproj, .vcxproj, .wsc, .xcodeproj, .xsd, .c, .class, .cpp, .cs, .css, .go, .h, .htaccess, .html, .java, .json, .kml, .sql, .swift, .vb, .yaml, .sh, .bat, .cmd, .ps1, .py, .pl, .rb, .js, .ts, .php, .jsp, .aspx, .cgi, .jar |
Disk image |
.img, .cue, .dsk, .vmdk, .vhd, .vhdx, .tc, .crypt, .dmgpart, .sparsebundle, .xva, .cif, .pqi, .udf, .fvd, .arc, .fcd, .gi, .giz, .ima, .udif, .vdi, .vim, .wim, .b5t, .b6t, .bin, .bwi, .bwt, .ccd, .cdi, .cdr, .dmg, .i00, .i01, .i02, .iso, .isz, .md0, .md1, .md2, .mdf, .mds, .nrg, .pdi, .po, .rom, .sub, .tib, .toast, .vc4, .vcd |
Windows event log |
.evt, .evtx, .log, .txt, .xml |
Windows registry file |
.reg, .dat, .pol, .hiv, .srd |
Font |
.bin, .ps, .sfd, .fnt, .afm, .ttf, .otf, .woff, .woff2, .eot, .svg, .dfont, .pfa, .pfb, .pfm, .fon, .suit, .bdf, .pcf, .snf, .ufo, .lib, .cff |
Database file |
.bup, .csv, .json, .xml, .myi, .sqlplan, .abs, .abx, .ac, .accdb, .accdc, .accde, .accdr, .accdt, .accdw, .accft, .adb, .ade, .adf, .adn, .adp, .alf, .anb, .approj, .aq, .ask, .bacpac, .bak, .btr, .caf, .cat, .cdb, .chck, .ckp, .cma, .cpd, .crypt, .dab, .dacpac, .dad, .daschema, .db, .db-journal, .db-shm, .db-wal, .db2, .db3, .dbc, .dbf, .dbs, .dbt, .dbv, .dbx, .dcb, .dct, .dcx, .ddl, .dlis, .dp1, .dqy, .dsk, .dsn, .dtsx, .dxl, .eco, .ecx, .edb, .epim, .erx, .exb, .fcd, .fdb, .fic, .frm, .ftb, .gdb, .grdb, .gwi, .hdb, .his, .ib, .ibd, .icdb, .idb, .ihx, .ipj, .itdb, .itw, .jet, .jtx, .kdb, .lgc, .lwx, .maf, .maq, .mar, .marshal, .mas, .mav, .maw, .mdb, .mdbhtml, .mdf, .mdn, .mdt, .mfd, .mpd, .mrg, .mud, .mwb, .myd, .ndf, .nnt, .ns2, .ns3, .ns4, .nsf, .nv2, .nwdb, .nyf, .odb, .odl, .oqy, .ora, .orx, .owc, .pan, .pdb, .pdm, .pnz, .pqa, .pvoc, .qry, .qvd, .rbf, .rctd, .realm, .rod, .rsd, .sbf, .scx, .sdb, .sdc, .sdf, .sis, .spq, .sql, .sqlite, .sqlite3, .sqlitedb, .te, .temx, .tmd, .tps, .trc, .trm, .tvdb, .udb, .udl, .vis, .vvv, .wdb, .wmdb, .wrk, .xdb, .xld, .xmlff |
Sending notifications
Users with the Administrator, Senior security officer, or Security officer roles can configure forwarding of notifications to one or multiple email addresses.
You can create notifications about alerts and system health.
Notifications contain a link to the application web interface. Make sure that the name assigned to the Central Node server for use by DNS servers is correct and can be resolved by the DNS server. If the name is incorrect or if the DNS server cannot resolve it, the link to the web interface in the notification will not work.
Users with the Security auditor role can view the list of rules for sending notifications, the properties of a selected rule, and the mail server connection settings, but cannot edit them.
For notifications to be sent to an email address correctly, you must first configure the connection to the mail server. The connection must be configured by the Administrator.
Viewing the table of rules for sending notifications
Rules for sending notifications are displayed in the Settings section, Notifications subsection of the application web interface window.
The table of rules for sending notifications contains the following information:
- Type is the type of rule for sending notifications.
The following types of rules are possible:
- Alerts is a rule for sending a notification about alerts.
- Application operation is a rule for sending a notification about the operation of application components.
- Subject—Subject of the message containing the notification.
- To—Email addresses to which the notifications are sent.
- State—Status of the rule for sending a notification.
Creating a rule for sending notifications about alerts
To create a rule for sending notifications about alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click Add.
This opens the New rule window.
- In the To field, enter one or multiple email addresses to which you want to send notifications.
You can enter several email addresses if you separate them with commas.
- In the Subject field, enter the subject of the notification message.
- If you want the application to insert the alert importance into the message subject, add the
%importance%macro to the Subject field. - In the Notification type field, select Alerts.
- In the Alert importance drop-down list, select the minimum alert importance for which you want notifications to be sent.
For example, you can configure forwarding of notifications for only alerts that have high importance, or for only those that have medium or high importance.
- In the Source or destination field, enter an IP address and network mask if you want to send notifications about alerts associated with a specific source or destination IP address or subnet address.
- In the Email field, enter an email address if you want to send notifications about alerts associated with a specific email sender or recipient address.
- Under Components, select check boxes next to the names of one or multiple technologies if you want to send notifications about alerts generated by specific technologies.
- Click Add.
The rule for sending notifications about alerts will be added to the list of rules. To send notifications to the specified email address, you must enable the notification rule. Notifications are sent once to each of the email addresses configured for this rule.
Users with the Administrator and Security auditor roles cannot create rules for sending alert notifications.
In distributed solution mode, you must create notifications separately for each subordinate server (Secondary Central Node, SCN).
Creating a rule for sending notifications about the operation of application components
To create a rule for sending notifications about the operation of application components:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click Add.
This opens the New rule window.
- In the To field, enter one or multiple email addresses to which you want to send notifications.
You can enter several email addresses if you separate them with commas.
- In the Subject field, enter the subject of the notification message.
- If you want the application to insert the alert importance into the message subject, add the
%importance%macro to the Subject field. - In the Notification type field, select Application operation.
- Under Components, select check boxes next to the names of the application's functional areas for which you want to receive notifications.
- Click Add.
The rule for sending notifications about the operation of application components is added to the list of rules. To send notifications to the specified email address, you must enable the notification rule. Notifications are sent once to each of the email addresses configured for this rule.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot create rules for sending notifications about application operation.
In distributed solution mode, notifications are configured separately for each subordinate server (Secondary Central Node, SCN).
Enabling and disabling a rule for sending notifications
To enable or disable a rule for sending notifications about alerts:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- In the State column, enable or disable the rule for sending notifications using the toggle switch next to the rule.
The state of the rule for sending notifications about alerts will be modified.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot enable or disable notification rules.
Modifying a rule for sending notifications
To edit a rule for sending notifications:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- In the list of rules for sending notifications, select the rule that you want to modify.
This opens the Edit rule window.
- Make the relevant changes.
- Click Save.
The rule for sending notifications will be modified.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot edit rules for sending notifications.
Deleting a rule for sending notifications
To delete a rule for sending notifications:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Select the check box to the left of the name of each rule that you want to delete.
If you want to delete all rules, select the check box above the list.
- Click Delete in the lower part of the window.
- In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The selected rules will be deleted.
Users with the Security auditor role cannot delete rules for sending notifications.
Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules by rule type
To filter or search notification rules by rule type:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click the
 icon in the table of rules for sending notifications.
icon in the table of rules for sending notifications.This opens the filter configuration window.
- Select one of the following options:
- All
- Alerts
- Application operation
The table of notification forwarding rules will display only rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules based on the notification subject
To filter or search for notification rules by notification subject:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click the Subject link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter one or several characters of the notification subject.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table of notification forwarding rules will display only rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules by email address
To filter or search for notification rules by destination email address:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click the To link to open the filter configuration window.
- Enter one or several characters of the email address.
- Click Apply.
The table of notification forwarding rules will display only rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Filtering and searching notification forwarding rules based on their status
To filter or search for notification rules by status:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click the State link to open the filter configuration window.
- Select one or several check boxes next to the values of statuses:
- Enabled.
- Disabled.
- Click Apply.
The filter configuration window closes.
The table of notification forwarding rules will display only rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
You can use multiple filters at the same time.
Clearing a notification forwarding rule filter
To clear the notification rule filter for one or more filtering criteria:
- In the main window of the application web interface, select the Settings section, Notifications subsection.
- Go to the Notification rules tab.
- Click
 to the right of the header of the column in the notification forwarding rules table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.
to the right of the header of the column in the notification forwarding rules table for which you want to clear the filter conditions.If you want to clear several filter conditions, perform the necessary actions to clear each filter condition.
The selected filters are cleared.
The table of notification forwarding rules will display only rules that match the filter criteria you have set.
Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent is an application that is installed on individual devices in the corporate IT infrastructure. The application continuously monitors processes running on those devices, active network connections, and files that are being modified.
Kaspersky Endpoint Agent enables the interaction of the protected device with other Kaspersky solutions for detection of complex threats, such as targeted attacks.
When the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is configured, the application runs tasks, applies parameters coming from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and sends telemetry from the protected device to the KATA Central Node server. For more details about what Kaspersky Endpoint Agent can do when integrated with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see the Operating principle of the application section.
For details about managing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent, see the Online Help of the application:
- Application activation
- Installing and removing the application.
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent settings using the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console and the Kaspersky Security Center Web Console:
- Managing policies
- Managing tasks
- Opening the settings window
- Configuring security settings
- Configuring the connection of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent with a proxy server
- Configuring Kaspersky Security Center as a proxy server to activate Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Configuring KSN usage in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Configuring storage settings in Kaspersky Endpoint Agent
- Configuring failure diagnostics
- Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Agent using the command line interface:
- Activation management
- Authentication management
- Configuring tracing
- Configuring the creation of dumps of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent processes
- Viewing information about quarantine settings and quarantined objects
- Actions for quarantined objects
- Running Kaspersky Endpoint Agent database and module updates
- Starting, stopping and viewing the current application status
- Password protection of the application
- Protecting application services with the PPL technology
- Managing self-defense settings
- Managing Standard IOC Scan tasks
- Managing file and process scanning in accordance with YARA rules
- Creating a memory dump
- Creating a disk dump
Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is an application that is installed on individual devices in the corporate IT infrastructure. The application continuously monitors processes running on those devices, active network connections, and files that are being modified. Information about events on the computer (telemetry) is sent to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. Kaspersky Endpoint Security also sends information about threats detected by the application and information about the results of processing these threats to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
When the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is configured, the application runs tasks, applies parameters coming from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and sends telemetry from the protected device to the KATA Central Node server. For more details about what Kaspersky Endpoint Security can do when integrated with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see the Operating principle of the application section.
For details about managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security, see the Online Help of the application:
- Installing and removing the application.
- Application licensing.
To integrate with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, in addition to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation key, you must also add the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on key. For details on application licensing, see Kaspersky Endpoint Security Online Help → Integration with EDR (KATA).
- Integration with EDR (KATA).
- Configuring telemetry.
- Managing the quarantine.
- Commands for managing Detection and Response KATA EDR: Integration with EDR (KATA).
Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is an application that is installed on individual devices running Linux operating systems that are part of the corporate IT infrastructure. The application continuously monitors processes running on those devices, active network connections, and files that are being modified. Information about events on the computer (telemetry) is sent to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux also sends information about threats detected by the application and information about the results of processing these threats to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
When the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is configured, the application runs tasks, applies parameters coming from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and sends telemetry from the protected device to the KATA Central Node server. For more details about what Kaspersky Endpoint Security can do when integrated with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see the Operating principle of the application section.
For details about managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux, see the Online Help of the application:
- Installing, removing, and updating the application.
- Managing the application using the command line:
- License key management: Licensing task (License, ID:9).
- Integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform: Integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) task (KATAEDR, ID:24).
- Managing the application using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console:
- License key management: for more details, see Managing tasks in Web Console → Creating a task and Task settings → Adding a key.
- Integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform: for more details, see Managing policies in Web Console → Creating a policy and Policy settings → Integration with Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
For integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you do not need to add an additional license key in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
Page top
Managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac is an application that is installed on individual devices running macOS operating systems that are part of the corporate IT infrastructure. The application continuously monitors processes running on those devices, active network connections, and files that are being modified. Information about events on the computer (telemetry) is sent to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac also sends information about threats detected by the application and information about the results of processing these threats to the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
When the integration of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is configured, the application runs tasks, applies parameters coming from Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and sends telemetry from the protected device to the KATA Central Node server. For more details about what Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac can do when integrated with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see the Operating principle of the application section.
For details about managing Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, see the Online Help of the application.
- Installing, removing, and updating the application.
- Application licensing.
To integrate with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, in addition to the Kaspersky Endpoint Security activation key, you must also add the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA) Add-on key. For more details about application licensing, see Kaspersky Endpoint Security Help → Advanced configuration of the application → Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
- Managing the application using the command line:
- Remotely managing the application using Kaspersky Security Center Web Console and Cloud Console:
- For details about license key management, see sections: Create tasks → Configure the Add key task settings.
- For details about integration with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, see sections: Create policies → Configure Detection and Response settings → Configure Endpoint Detection and Response (KATA).
Creating a backup copy and restoring the application from backup
You can create a backup copy of the application and then restore it from backup.
Note that you cannot restore data between Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on different operating systems. For example, you cannot restore data of Ubuntu-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based in Astra Linux-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and vice versa.
For a standalone Central Node server, you can create a backup copy of the data from this Central Node server.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you can:
- Create a backup copy of PCN data.
- Create a backup copy of SCN data.
Restoring data from a backup copy of the SCN will change the role of the server from SCN to standalone Central Node server.
Follow the procedure for creating the backup copy of the application on the server for which you want to create a backup copy of the data.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform may contain user data and other confidential information. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator must take steps to ensure the security of this data when creating a backup copy of the application, when replacing equipment on which the application is installed, or in other cases when it may be necessary to permanently delete data. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator bears responsibility for access to data stored on application servers.
You can create a backup copy of the following data:
- The application database.
- Objects in Storage.
- Files from alerts generated during a rescan.
- Sandbox artifacts.
- Configuration files.
- Central Node or PCN settings:
- If you are using a standalone Central Node server, a backup copy of Central Node settings is created.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and are managing the PCN server, a backup copy of PCN settings is created.
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and are managing the SCN server, you can create a backup copy of the SCN, but restoring data from a backup copy will change the role of the server from SCN to standalone Central Node server.
You can clear the directory before creating a backup copy of the application.
Before the application is restored from a backup copy, the following is cleared on the Central Node or PCN server on which the application is being restored:
- The application database.
- Objects in Storage.
- Files from alerts generated during a rescan.
- Sandbox artifacts.
- Configuration files.
- Central Node or PCN settings.
Contents and volume of data exported for the creation of a backup copy of the application
Data type
Exported data
Application operation mode
Deployment method
- Central Node settings.
- The application database on Central Node:
- Alerts and VIP statuses of alerts
- Tasks and task execution results
- Policies
- User-defined TAA (IOA) rules and exclusions
- User-defined IDS rules and exclusions
- IOC files
- Scan exclusion rules
- Information about files in Storage
- Information about quarantined objects
- List of computers with Endpoint Agent
- Reports and report templates
- User account data
- Notifications
Central Node settings, if selected.
Application databases, by default.
Standalone Central Node server.
All deployment methods.
PCN settings.
Custom
Distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
All deployment methods.
SCN settings.
Custom
As for a standalone Central Node server.
Distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
All deployment methods.
Application databases on the PCN:
- Alerts and VIP statuses of alerts
- Task execution results
- Policies
- User-defined TAA (IOA) rules and exclusions
- User-defined IDS rules and exclusions
- IOC files
- List of data excluded from the scan
- Information about files in Storage
- Information about quarantined objects
- List of Kaspersky Endpoint Agent hosts
- Reports and report templates
- User account data
- Notifications
Default
Distributed solution and multitenancy mode.
All deployment methods.
Configuration files.
Yes
All modes.
All deployment methods.
Backup
Custom
All modes.
Non-high-availability version.
Sandbox artifacts.
Custom
All modes.
Non-high-availability version.
Files from alerts generated during a rescan.
Custom
All modes.
Non-high-availability version.
Events database.
None.
All modes.
All deployment methods.
Files that are in the scan queue when the backup copy of the application is created are not exported.
The versions of the application being restored must match the version of the application installed on the server. If the versions do not match, an error message is displayed when the application restoration is initiated, and the restoration process is terminated.
Creating a backup copy of Central Node server settings from the application administrator menu
To create a backup copy of the Central Node (PCN or SCN in distributed solution and multitenancy mode), do the following in the administrator menu of the server:
- In the list of sections of the application administrator menu, select the System administration section.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the action selection window.
- In the list of actions, select Backup/Restore settings.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Backup/Restore settings window.
- In the list of actions, select New.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Backup settings window.
- Click Back up.
A backup copy of server settings is created.
The backup copy of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform contains databases (alerts database, VIP status details, the list of data excluded from the scan, notifications) and Central Node or PCN settings only.
Page top
Downloading a file containing a backup copy of server settings from the Central Node or PCN server to the hard drive of the computer
It is recommended to save files containing a backup copy of the Central Node server settings to the hard drive of your computer.
To download a file containing a backup copy of the Central Node server settings to the hard drive of your computer, run the following command in the command line interface of the Linux operating system on your computer:
scp <name of the account used for working in the administrator menu and in the server management console>@<IP address of the server>:<name of the file containing the backup copy of the application in the form of settings-<date and time of backup copy creation>.tar.gz>
Example: Command for downloading to the hard drive of your computer an archive containing a backup copy of server settings that was created on a Central Node server with the IP address 10.0.0.10 under the "admin" account on April 10, 2020 at 10 hours 00 minutes 00 seconds:
The file containing a backup copy of server settings is saved to the hard drive of your computer in the current directory. |
Uploading a file containing a backup copy of server settings from your computer to the Central Node server
To upload a file containing a backup copy of server settings from the hard drive of your computer to the Central Node server, run the following command in Technical Support Mode:
scp <name of the file containing a backup copy of server settings in the form of settings-<backup copy creation date and time>.tar.gz> <name of the account used for working in the administrator menu and in the server management console>@<IP address of the server>:
Example: Command for uploading an archive containing a backup copy of server settings created on April 10, 2020 at 10 hours 00 minutes 00 seconds to the Central Node server with the IP address 10.0.0.10 under the "admin" account:
The file containing the backup copy of server settings is uploaded to the Central Node server in the current directory. |
Restoring server settings from a backup copy using the application administrator menu
To restore Central Node server settings from a backup copy, you must first create a backup copy of current server settings. In case of an error when restoring server settings you will be able to use a backup copy of server settings.
To restore server settings from a previously created backup copy, perform the following actions in the administrator menu of the server:
- In the list of sections of the application administrator menu, select the System administration section.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the action selection window.
- In the list of actions, select Backup/Restore settings.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the Backup/Restore settings window.
- In the list of files containing backup copies of the application, select the file from which you want to restore the server settings.
If the necessary file is not listed, upload the file containing the backup copy of the settings to the server.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the action selection window.
- In the list of actions, select Restore <name of the file with the backup copy of server settings>.
- Press ENTER.
This opens the action confirmation window.
- Click Restore.
The process of restoring the server settings from the backup copy starts.
- When prompted, enter the administrator password of the server on which the backup copy of server settings was created.
- Press ENTER.
- Enter the administrator password of the server on which you are restoring server settings from backup.
- Press ENTER.
Server settings are restored from the selected file.
The backup copy of the server settings does not include settings for receiving mirrored traffic from SPAN ports. If you have previously configured the receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports and want to keep receiving it, you need to configure the receipt of mirrored traffic before restoring server settings from backup. Then you need to enable the receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports when updating the application, at the Configuring receipt of mirrored traffic from SPAN ports step.
The backup copy of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform settings does not contain ICAP exclusion settings. If you need to save and restore ICAP exclusion settings, contact Technical Support before you restore server settings.
If the hardware configuration of the Central Node server on which the backup copy was created differs from the hardware configuration of the server on which you are planning to restore the server settings, you need to reconfigure the application scaling settings after restoring.
Page top
Creating a backup copy of the application in Technical Support Mode
Note that you cannot restore data between Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on different operating systems. For example, you cannot restore data of Ubuntu-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based in Astra Linux-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and vice versa.
To create a backup copy of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, run the following command in Technical Support Mode of the server:
kata-run.sh kata-backup-restore backup
You can also specify one or multiple parameters for this command (see the table below).
You can use the -h command to receive tips on using parameters.
Parameters of the command for creating a backup copy of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Required parameter |
Parameter |
Description |
Yes |
|
Create a file containing a backup copy of the application at the specified path, where <path> is the absolute path or relative path to the folder in which the file with the backup copy of the application is created. |
No |
|
Clear the directory before saving the application backup file. |
No |
|
Specify the maximum number of files from the backup copy of the application stored in the directory, where <number> is the number of files. |
No |
|
Save files in Storage. |
No |
|
Save files in quarantine. |
No |
|
Save files awaiting rescan. |
No |
|
Save Sandbox artifacts. |
No |
|
Save Central Node or PCN settings. |
No |
|
Save the command execution result to a file, where <filepath> is the name of the event log file, including the absolute path or relative path to the file. |
If additional settings are not defined, the backup copy of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform contains only databases (alerts database, VIP status details, the list of data excluded from the scan, notifications). If you are creating a backup copy of the application installed as a high availability cluster, you cannot use the -q, -a, -s, and -e options.
If you are using the application installed as a high availability cluster, you can back up the settings and restore only servers with the 'manager' role in Docker swarm from the backup copy.
All files containing a backup copy of the application are saved to one TAR archive. Archive file name: data_kata_ddmmyyyyhhMM, where ddmmyyyy is the date and hhMM is the hour and minute when the backup copy of the application was created. The name of the database is KATA6.0.sql for the backup copy of the application version 6.0.
Example: Command for creating a backup copy of the application:
|
Restoring the application from a backup copy in Technical Support Mode
To restore Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from a backup copy, you must first create a backup copy of the current state of the application and download it to the hard drive of your computer. If an error occurs when restoring the application or if it becomes necessary to reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you will be able to use the saved copy of the application.
Note that you cannot restore data between Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on different operating systems. For example, you cannot restore data of Ubuntu-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based in Astra Linux-based Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, and vice versa.
The versions of the application being restored must match the version of the application installed on the server. If the versions do not match, an error message is displayed when the application restoration is initiated, and the restoration process is terminated.
To restore Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from a backup copy, run the following command in Technical Support Mode of the server:
kata-run.sh kata-backup-restore restore
You can also specify one or multiple parameters for this command (see the table below).
You can use the -h command to receive tips on using parameters.
Parameters of the command for restoring Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from a backup copy
Required parameter |
Parameter |
Command description |
Yes |
|
Restore data from a file containing a backup copy of the application, where <path> is the full path to the file containing a backup copy of the application. |
No |
|
Save the command execution result to a file, where <filepath> is the name of the event log file, including the absolute path or relative path to the file. |
Example: Command for restoring the application from a backup copy:
|
Upgrading Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
You can upgrade Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from version 5.1 to version 6.0.
You cannot migrate from the non-high-availability version of the application to the high availability version by upgrading it — if you are using the non-high-availability version of the application, you can only install the non-high-availability version during the upgrade, and vice versa.
Upgrading the application involves the following steps:
- Upgrading the Sandbox component.
The application does not have a standard upgrade procedure. You must install version 6.0 of the component and then install the 6.0.2 and 6.0.4 upgrade packages.
After installing the component you need to set the maximum number of simultaneously running virtual machines. The default value is 48.
When installing the component on a VMware ESXi virtual machine, you must set up a configuration described in Calculations for the Sandbox component section.
- Upgrading the Central Node component.
You can upgrade the component to version 6.0 only from version 5.1. If you are using an older version, you must upgrade it to 6.0 in the following order: 3.7 → 3.7.1, 3.7.1 → 3.7.2, 3.7.2 → 4.0, 4.0 → 4.1, 4.1 → 5.0, 5.0 → 5.1
If you are not using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode and are using a standalone Central Node server, you can upgrade the application on the Central Node server.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode:
- You can update the application on the PCN server. After the application upgrade is complete, the PCN server belongs to the same tenant it belonged to before the upgrade.
- If you want to update the application on an SCN server, change the role of the server from SCN to standalone Central Node server before performing the update.
The application is updated on the standalone Central Node server.
After upgrading the application, you can assign the SCN role to servers and select the tenant to which the SCN server belongs.
- After the application update is complete, by default, all users with the Administrator role are granted access to the web interface of the PCN server and all SCN servers.
If before the application update, each user's access to SCN web interfaces was configured individually, you can configure it again.
After the program update is complete, by default, all users with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles are granted access to the web interface of the PCN server and all SCN servers.
If before the application update, each user's access to SCN web interfaces was configured individually, you can configure it again. To do so, in the web interface of the PCN server:
- Add the relevant tenants.
- Configure the access of user accounts with the Senior security officer and Security officer roles to those tenants and servers.
- Delete all SCNs that are temporarily disconnected from the PCN during the update.
- Re-connect all relevant SCNs to the PCN.
The application prompts you to select a tenant for each SCN server.
User access to SCN web interfaces is configured.
Perform the application update procedure on the server where you want to update the data.
If the Central Node component is deployed as a cluster, you can update the component on any server in the cluster.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform may contain user data and other confidential information. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator must take steps to ensure the security of this data when upgrading the application, or in other cases when it may be necessary to permanently delete data. The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform administrator bears responsibility for access to data stored on application servers.
- Upgrading the Sensor component installed on a standalone server.
The application does not have a standard upgrade procedure. You must install version 6.0 of the component and then install the 6.0.2 and 6.0.4 upgrade packages.
- Upgrading the Endpoint Agent component:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows.
If you use the solution together with Kaspersky Security for Windows Server, you can migrate from Kaspersky Security for Windows Server to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows version 12.1 or later that contains the built-in agent. For more information about migration, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows.
Special considerations for updating Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from version 5.1 to version 6.0
- After upgrading Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to version 6.0, you must add license keys again.
- A short interruption in the operation of the application is considered acceptable, including for the high availability version of the application.
- If the Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway solution is used in the role of the Sensor component, the settings for integration with it are saved.
- Sensor and Sandbox component data are not preserved.
- Central Node 6.0 is not compatible with Sensor and Sandbox components of earlier versions.
Upgrading the Central Node component installed on a server
You can upgrade the component to version 6.0 only from version 5.1. If you are using an older version, you must upgrade it to 6.0 in the following order: 3.7 → 3.7.1, 3.7.1 → 3.7.2, 3.7.2 → 4.0, 4.0 → 4.1, 4.1 → 5.0, 5.0 → 5.1.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you must prepare the PCN and SCN servers as well as standalone servers with the Sensor component for the upgrade. For more details on the preparation procedure, see the Updating Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform section.
The upgrade is delivered as an upgrade package. The package is included in the application distribution kit.
To upgrade the Central Node component installed on a server:
- Place the application upgrade package on the server with the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory. - Sign in to the management console of the Central Node server where you want to upgrade the component via SSH or through the terminal.
- Make sure that the /dev/sda2 file system has more than 100 GB of free space.
- Unpack the update archive:
- If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Ubuntu operating system, run the following command:
tar xvf /data/kata-cn-ubuntu-upgrade-6.0.0-200-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /data/. - If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Astra Linux operating system, run the following command:
tar xvf /data/kata-cn-astra-upgrade-6.0.0-200-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /data/.
- If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Ubuntu operating system, run the following command:
- Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /data/upgrade/chmod +x ./install_kata_upgrade.sh./install_kata_upgrade.sh - Install the upgrade by running the following commands:
source /tmp/upgrade-venv/venv/bin/activatekata-upgrade --data-dir /data/upgrade/ --password <password of the 'admin' user>.If the password contains special characters, the password variable must be specified in the following format: --password '<password>'.
- Mount the iso image of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version 6.0 and restart the server. If you are using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system, follow these instructions to create an iso image.
- Boot from the device that has the mounted iso image.
- In the GRUB menu, select Upgrade KATA 5.1
- Follow the remaining steps of the wizard to complete the upgrade on the server.
- Install the application upgrade package to version 6.0.2
If you are upgrading the application from version 6.0, you do not need to install the version 6.0.1 upgrade package.
- Install the application upgrade package to version 6.0.4
The Central Node component is upgraded.
After updating the component, you must log in again to the Central Node server management console over SSH or through the terminal.
Page top
Upgrading the Central Node component installed as a cluster
You can upgrade the component to version 6.0 only from version 5.1. If you are using an older version, you must upgrade it to 6.0 in the following order: 3.7 → 3.7.1, 3.7.1 → 3.7.2, 3.7.2 → 4.0, 4.0 → 4.1, 4.1 → 5.0, 5.0 → 5.1.
If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you must prepare the PCN and SCN servers as well as standalone servers with the Sensor component for the upgrade. For more details on the preparation procedure, see the Updating Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform section.
The upgrade is delivered as an upgrade package. The package is included in the application distribution kit.
To upgrade the Central Node component installed as a cluster:
- Place the application upgrade package on any server of the cluster with the Central Node component in the
/datadirectory. - Sign in to the management console of the Central Node server where you want to upgrade the component via SSH or through the terminal.
- Make sure that the /dev/sda2 file system on each server of the cluster has more than 100 GB of free space.
- Unpack the update archive:
- If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Ubuntu operating system, run the following command:
tar xvf /data/kata-cn-ubuntu-upgrade-6.0.0-200-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /data/. - If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Astra Linux operating system, run the following command:
tar xvf /data/kata-cn-astra-upgrade-6.0.0-200-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /data/.
- If you are upgrading the application to version 6.0 on an Ubuntu operating system, run the following command:
- Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /data/upgrade/chmod +x ./install_kata_upgrade.sh./install_kata_upgrade.sh - Install the upgrade by running the following commands:
source /tmp/upgrade-venv/venv/bin/activatekata-upgrade --data-dir /data/upgrade/ --password <password of the 'admin' user>.If the password contains special characters, the password variable must be specified in the following format:
--password '<password>'.After some time, the console displays a message telling you to power off one of the servers in the cluster.
- Connect to the server that you want to power off over SSH or through a terminal.
- Run the
poweroffcommand. - Mount the iso image of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform version 6.0. If you are using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform based on the Astra Linux operating system, follow these instructions to create an iso image.
- Boot from the device that has the mounted iso image.
- In the GRUB menu, select Upgrade KATA 5.1.
- Follow the remaining steps of the wizard to complete the upgrade on the server.
- After the upgrade is complete, go to the console of the server you connected to at step 2 and press Enter.
A script is started that completes the upgrade process. After the update is complete, the console displays a message telling you to shut down the next server in the cluster.
- Repeat steps 7 to 13 for each server in the cluster.
The last server to be updated is the server to which you connected at step 2. For that server, step 13 is omitted.
- Install the application upgrade package to version 6.0.2
If you are upgrading the application from version 6.0, you do not need to install the version 6.0.1 upgrade package.
- Install the application upgrade package to version 6.0.4
The Central Node component is upgraded.
After updating the component, you must log in again to the Central Node server management console over SSH or through the terminal.
If you want to add a server to a Central Node cluster that has been upgraded to version 6.0.4, you need to install Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on that server from the kata-cn-distribution-6.0.4-13-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz ISO image. The image is included in the application distribution kit.
Page top
Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.1
If you upgraded the application to version 6.0 or installed version 6.0 of the application, skip this step and install the version 6.0.2 upgrade package.
Before installing the application upgrade package, it is recommended to first create a backup of the current state of each Central Node server to be updated and download it to the hard drive from the application administrator menu. If an error occurs during installation of an application upgrade package or if you need to reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you can use your backup copy of the application.
The upgrade is delivered as an upgrade package. The package is included in the application distribution kit.
To install the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform 6.0.1 upgrade package, Central Node version 6.0 and Sensor version 6.0 must be installed. The upgrade package installation depends on how the application is deployed and used:
- If you are using the application as a high availability cluster, you must install the upgrade package on any server in the cluster with the 'manager' role in Docker swarm. To view the role, use the
$ docker node lscommand. - If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you must install the upgrade package on each Central Node and Sensor server installed on standalone servers. You do not need to disconnect the SCN servers from the PCN to install the upgrade package.
- If you are using the Sensor installed on a standalone server, to install the upgrade package, you need to connect to each Sensor via the SSH protocol or through the terminal and enter the management console. You do not need to disconnect Sensor from Central Node to install the upgrade package.
- In other cases, to install the upgrade package, you need to connect to the server via the SSH protocol or through the terminal and enter the management console of the Central Node.
To install the application upgrade package:
- Place the application upgrade package on the server in the
/datadirectory. If the function of network traffic saving is enabled, make sure that the amount of free disk space is more than 100 GB. - Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to install the upgrade package via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Make sure that the /dev/sda2 file system has more than 100 GB of free space.
- Unpack the upgrade package by running the
tar xvf /data/upgrade.tar.gz -C /data/command. - If you are upgrading the application installed as a high availability cluster based on the Astra Linux operating system, run the following command:
mv /data/upgrade/ubuntu_image_versions.json /data/upgrade/astra_image_versions.json - Increase the privileges of the user by running
sudo -i. - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /data/upgrade/chmod +x ./install_kata_upgrade.sh./install_kata_upgrade.sh - Install the upgrade by running the following commands:
kata-upgrade --data-dir /data/upgrade/ --password <password of the 'admin' user>.If the password contains special characters, the password variable must be specified in the following format: --password '<password>'.
- Log in again to the management console of the updated server via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Set the Maximum storage size parameter value, if you are using Sensor with the Central Node component on the server, or the Traffic storage size parameter value, if you are using Sensor on a standalone server. The default value is set to 100 GB after upgrade.
The upgrade package will be installed.
Page top
Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.2
Before installing the application upgrade package, it is recommended to first create a backup of the current state of each Central Node server to be updated and download it to the hard drive from the application administrator menu. If an error occurs during installation of an application upgrade package or if you need to reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you can use your backup copy of the application.
The upgrade is delivered as an upgrade package. The package is included in the application distribution kit.
The version 6.0.2 upgrade package must be installed on Central Node, Sensor, and Sandbox servers of versions 6.0 or 6.0.1. Installation of the upgrade package on the Central Node and Sensor servers depends on the way the application is deployed and used:
- If you are using the application as a high availability cluster, you must install the upgrade package on any server in the cluster with the 'manager' role in Docker swarm. To view the role, use the
$ docker node lscommand. - If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you must install the upgrade package on each Central Node and Sensor server installed on standalone servers. You do not need to disconnect the SCN servers from the PCN to install the upgrade package.
- In the rest of the cases, to install the upgrade package, you must connect to each Central Node and Sensor server over SSH or using the terminal and log in to the management console. You do not need to disconnect Sandbox and Sensor from the Central Node to install the upgrade package.
To install the version 6.0.2 upgrade package on Sandbox servers, follow the separate instructions below.
To install the upgrade package on Central Node and Sensor servers:
- Place the kata-cn-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz upgrade package for the Central Node and Sensor components on the server, in the
/datadirectory. If the function of network traffic saving is enabled, make sure that the amount of free disk space is more than 100 GB. - Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to install the upgrade package via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Make sure that the /dev/sda2 file system has more than 100 GB of free space.
- Unpack the upgrade archive by running the
tar xvf /data/kata-cn-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /data/command. - Raise the privileges of the user by running
sudo -i. - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /data/upgrade/chmod +x ./install_kata_upgrade.sh./install_kata_upgrade.sh - Install the upgrade by running the following commands:
kata-upgrade --data-dir /data/upgrade/ --password <password of the 'admin' user>.If the password contains special characters, the password variable must be specified in the following format: --password '<password>'.
- Log in again to the management console of the updated server via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Set the Maximum storage size parameter value, if you are using Sensor with the Central Node component on the server, or the Traffic storage size parameter value, if you are using Sensor on a standalone server. The default value is set to 100 GB after upgrade.
The upgrade package is installed on the Central Node and Sensor servers.
To install the upgrade package on Sandbox servers:
- Place the kata-sb-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz upgrade package for the Sandbox component on the server, in the
/tmpdirectory. - Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to install the upgrade package via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Unpack the upgrade archive by running the
tar xzvf /tmp/kata-sb-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ru.tar.gz -C /tmp/command. - Raise the privileges of the user by running
sudo -i. - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmp/kata-sb-upgrade-6.0.2-x86_64_en-ruchmod +x ./patch.sh./patch.sh - Wait for the upgrade package to install successfully.
The upgrade package is installed on the Sandbox servers.
Page top
Installing the application upgrade package to version 6.0.4
Before installing the application upgrade package, it is recommended to first create a backup of the current state of each Central Node server to be updated and download it to the hard drive from the application administrator menu. If an error occurs during installation of an application upgrade package or if you need to reinstall Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, you can use your backup copy of the application.
The upgrade is delivered as an upgrade package. The package is included in the application distribution kit.
The 6.0.4 application upgrade package is installed on the Central Node, Sensor (if the component is not installed on the same server as Central Node) and Sandbox 6.0.2 servers. Installation of the upgrade package on the Central Node and Sensor servers depends on the way the application is deployed and used:
- If you are using the distributed solution and multitenancy mode, you must install the upgrade package on each Central Node and Sensor server installed on standalone servers. You do not need to disconnect the SCN servers from the PCN to install the upgrade package.
- To install the update on Central Node servers that are part of a high availability cluster, you must follow special steps that are described below.
- In other cases, to install the update package, you must connect to each Central Node and Sensor server
over SSH or through the terminal
and log in to the management console. You do not need to disconnect Sandbox and Sensor from the Central Node to install the upgrade package.
To install the update package on Central Node deployed as a cluster:
- Enter the management console of any cluster server over SSH or using a terminal.
- Find out which servers in the cluster have the 'manager' role by running the following commands:
sudo -idocker node lsA list of cluster servers is displayed. Look at the MANAGER STATUS column in the list: if a server has Leader or Reachable in that column, it means it has the 'manager' role.
- Log in to the management console of any of the 'manager' servers over SSH or using a terminal.
- Place the component upgrade package, upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz, in the
/tmpdirectory. If the function of network traffic saving is enabled, make sure that the amount of free disk space is more than 100 GB. - Raise the privileges of the user by running the following command:
sudo -i - Unpack the upgrade archive:
tar xvf /tmp/upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz -C /tmp/ - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmpchmod +x ./install.sh./install.sh server - Copy the upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz package to the
/tmpdirectory on each worker server in the cluster. - Enter the management console of any worker server over SSH or using a terminal.
- Raise the privileges of the user by running the following command:
sudo -i - Unpack the upgrade archive:
tar xvf /tmp/upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz -C /tmp/ - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmpchmod +x ./ks_patch.ks.sh./ks_patch.ks.sh - Repeat steps 9 to 12 for each worker server in the cluster.
- Make sure the application setup log contains a check_klava record in the 'after' section. To view the log, run the following command:
cat /tmp/ks_check_klava_patch.logThe log is updated every minute. If the entry is missing from the log or the log file does not exist, please contact Technical Support.
The upgrade package will be installed.
To install the upgrade package on Central Node installed on a server:
- Place the component upgrade package, upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz, in the
/tmpdirectory on the server. If the function of network traffic saving is enabled, make sure that the amount of free disk space is more than 100 GB. - Log in to the management console of the server on which you want to install the upgrade package
over SSH or through the terminal.
- Unpack the upgrade archive:
tar xvf /tmp/upgrade-6.0.4.tar.gz -C /tmp/ - Raise the privileges of the user by running the following command:
sudo -i - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmpchmod +x ./install.sh./install.sh serverchmod +x ./ks_patch.ks.sh./ks_patch.ks.sh - Make sure the application setup log contains a check_klava record in the 'after' section. To view the log, run the following command:
cat /tmp/ks_check_klava_patch.logThe log is updated every minute. If the entry is missing from the log or the log file does not exist, please contact Technical Support.
The upgrade package will be installed.
To install the upgrade package on the Sensor server:
- Place the component update package, upgrade.tar.gz, in the
/tmpdirectory on the server. If the function of network traffic saving is enabled, make sure that the amount of free disk space is more than 100 GB. - Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to install the upgrade package via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Make sure that the /dev/sda2 file system has more than 100 GB of free space.
- Unpack the upgrade package by running the
tar xvf /tmp/upgrade.tar.gz -C /tmp/command. - Raise the privileges of the user by running
sudo -i. - Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmp/upgrade/chmod +x ./install.sh./install.sh sensor
The upgrade package is installed on the Sensor server.
To install the upgrade package on the Sandbox server:
- Place the Sandbox component update package, upgrade.tar.gz, in the
/tmpdirectory on the server. - Sign in to the management console of the server where you want to install the upgrade package via the SSH protocol or through the terminal.
- Install the upgrade package by running the following commands:
cd /tmpchmod +x ./install.sh./install.sh sandbox - Wait for the upgrade package to install successfully.
The upgrade package is installed on the Sandbox server.
Page top
Contents and amount of information kept when upgrading the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Information about the contents and amount of data kept when upgrading Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform from version 5.1 to version 6.0 is listed in the following table.
Contents and volume of data saved when upgrading the application from version 5.1 to version 6.0
Data type |
Data saved during upgrade |
|---|---|
Central Node or PCN settings. |
All data except:
|
Application database on Central Node or PCN (alert database, application operation monitoring data, custom rule database, tasks, policies, rules added to exclusions). |
All data except:
|
Events database. |
All data. |
Storage and quarantine |
All data. |
Sandbox artifacts. |
All data. |
Interaction with external systems via API
You can configure the integration of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform with external systems to manage Threat Response actions, to scan files that are stored in those systems, and to provide access to information about all application alerts and events to the external systems.
External systems interact with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform via an API. API method calls are available only to authorized external systems. For authorization, the application administrator must create a request to integrate the external system with the application. Then the administrator must process the request in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
If you have deployed the Central Node and Sensor components as a cluster, you can configure high availability integration with an external system using one of the following options:
- Using the Round Robin function.
- Configure the external system so that if a timeout occurs, the external system switches between the IP addresses of the cluster servers.
To configure high availability integration with an external system using the Round Robin function:
- Configure Round Robin on the DNS server for the domain name corresponding to the Central Node cluster.
- Specify this domain name in the mail server settings.
Integration with the mail server will be configured based on the domain name. The mail server will communicate with a random server in the cluster. If this server fails, the mail server will communicate with another healthy server in the cluster.
Integrating an external system with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
To start working with the API, you need to integrate an external system with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. The external system must complete authorization on the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform server.
To integrate an external system with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Generate a unique identifier of the external system for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform –
sensorId. - Generate a certificate for the external system server.
- Create any request containing a
sensorIdfrom the external system in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. For example, you can create a request to scan an object from an external system in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
The web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform will display the request for authorization from the external system. Contact the application administrator to process the request.
If you need to change the external system server certificate, repeat the steps for integrating the external system with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Page top
API for scanning objects of external systems
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides the HTTPS REST interface for scanning objects saved in external systems.
For scanning objects stored in external systems, the following Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform interaction scenario is recommended:
- Creating a request for scanning objects using the
HTTP POSTmethod - Creating a request for scan results using the HTTP
GETmethodThe API interface is asynchronous, which means that Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform scans objects in the background instead of immediately upon request of the external system. For this reason, you must periodically send a request from the external system using the HTTP
GETmethod to receive the scan results. The recommended frequency for sending a request is once per minute.You can also configure forwarding of notifications about detected objects in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
- Creating a request to delete scan results using the HTTP method
DELETEYou can delete the results of scanning a specified object or all objects.
Working with a cluster
If the external system consists of several servers that are combined into a cluster, it is recommended to use one ID (sensorId) for all servers. If this is the case, a single integration request will be displayed for the entire system in the web interface of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. If it is necessary to differentiate the receipt of scan results over individual servers, you can assign a unique instance ID (sensorInstanceId) to each server.
Restrictions
The maximum allowed number of object scan requests from external systems and the maximum allowed size of a scanned object are set in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform configuration file.
If the maximum allowed number of simultaneous object scan requests is exceeded, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not process further requests until the number of object scan requests is less than the maximum allowed number. Until this condition is met, the return code 429 is issued. You must try the scan request again later.
If the maximum allowed object size is exceeded, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform does not scan the object. Return code 413 is generated when the HTTP POST method is created. You can find out the maximum allowed size of an object by using the GET method to view the list of object scan restrictions.
Request to scan objects
To create a request for scanning objects, the HTTP POST method is used. You can create a request by using the cURL command-line utility, for example.
You can set the parameters for executing a cURL command by using additional switches (see the table below).
Please refer to the cURL documentation for more information about cURL command switches.
Command syntax
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X POST "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/scanner/v1/sensors/<sensorId>/scans?sensorInstanceId=<sensorInstanceId>" -F "content=<path to the file that you want to scan>" -F scanId=<scan request ID> -F "objectType=file"
If the request is processed successfully, the OK status will be displayed.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
file |
Contents of the scanned object. |
|
string |
Unique ID of the scan request. It must be generated in the external system. It cannot contain spaces or special characters. Do not use file names as a scan request ID. If this parameter is not defined, viewing scan results is not available. |
|
string |
Type of scanned object. Possible value of the parameter: |
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system instance. Servers combined into a cluster are also considered to be instances of an external system. This parameter is optional. |
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scan completed successfully. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Number of requests exceeded. Repeat the request later. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Request for scan results
To create a request for receiving scan results, the HTTP GET method is used. You can create a request by using the cURL command-line utility, for example.
You can set the parameters for executing a cURL command by using additional switches (see the table below).
Please refer to the cURL documentation for more information about cURL command switches.
Command syntax
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/scanner/v1/sensors/<sensorId>/scans/state?sensorInstanceId=<sensorInstanceId>&state=<one or more scan statuses that you want to display in scan results>"
If the request is sent successfully, a list of requests for scanning objects and the results of scanning these objects will be displayed. The scan results will be filtered by the statuses that you specified in the state parameter. For example, if you specified state=processing,detect in the request for scan results, the application will display only the object scan requests that are being processed or in which the application has detected a threat.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
array (string element type) |
Object scan status. When this parameter is defined, the scan results will be filtered by status. Indicate one or more statuses separated by commas. The following parameter values are available:
|
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system instance. Servers combined into a cluster are also considered to be instances of an external system. This parameter is optional. |
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
No contents. |
|
No scan results found for the specified ID. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Example of entering a command with switches if you want to display all object scan statuses in the scan results
|
Request to delete scan results
To create a request to delete the scan results for one or more objects, use the DELETE method. You can create a request by using the cURL command-line utility, for example.
Command syntax
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X DELETE "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<default port 443>/kata/scanner/v1/sensors/<sensorId>/scans/<scanId>"
If the request is processed successfully, the object scan results will be deleted. The OK status is displayed.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
string |
Unique ID of the object scan request. If this parameter is not defined, the scan results for all objects will be deleted. |
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scan completed successfully. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
No scan results found for the specified ID. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Command input example
|
Request to display object scan restrictions
To create a request to display the application's restrictions on scanning objects (for example, by size), the HTTP GET method is used. You can create a request by using the cURL command-line utility, for example.
Command syntax
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<default port 443>/kata/scanner/v1/sensors/<sensorId>/scans/filters"
If the request is processed successfully, the application's object scan restrictions will be displayed. For example, the maxObjectSize restriction is the maximum allowed size of an object that you can submit for scanning.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Authorization required. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Command input example
|
API that external systems can use to receive information about application alerts
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides an API that lets external systems access information about all alerts of the application and not just to scan results for objects stored in these external systems.
In order to receive information only for alerts that satisfy certain conditions, you can specify filters in the request parameters.
The application does not automatically send information about new alerts based on prior requests. A new request must be sent to receive up-to-date information.
Special considerations for operation in the distributed solution
If the application runs in distributed solution mode, you must separately configure the integration with the external system for each PCN and SCN server from which you want to receive information about alerts. This limitation is due to the fact that the web interface of the PCN server displays information about all alerts, but the alerts database stores only those alerts that have been registered on that specific server.
Request to display alert information
To create a request to display information about Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform alerts, the HTTP GET method is used. You can create a request by using the cURL command-line utility, for example.
Command syntax
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/scanner/v1/sensors/<sensorId>/detects?detect_type=<one or more technologies that were used to generate the alert>&limit=<number of alerts in the response to the request>&token=<request ID>"
If the request is processed successfully, you will see a list of alerts generated by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform on the server of the external system.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
Array |
Technology that was used to generate the alert. You can specify a comma-separated list of technologies. Possible values:
If the parameter is not specified, information about all alerts is provided. |
|
Integer |
Number of objects for which information is provided in response to the request. Allowed values: integers from 1 to 10,000. The default value is |
|
String |
Request ID. If this parameter is specified, a repeated request does not show alert information that was obtained by prior requests. This helps avoid the duplication of information about the same alerts in case of repeated requests. If this parameter is not specified, information about all alerts is provided. |
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Number of requests exceeded. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Scope of transmitted data
Information that is transmitted for each alert is listed in the following table.
Scope of transmitted alert data
Parameter |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Integer value. |
Alert ID. |
|
Date and time. |
Event time. |
|
Date and time. |
Time when alert information was recorded in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform database. |
|
One of the following values:
|
Alert importance. |
|
One of the following values:
|
Source of the detected object. |
|
One of the following values:
|
Technology that was used to detect the object. |
|
One of the following values:
|
Type of detected object. |
|
Depends on the type of detected object. |
|
|
Depends on the technology that was used to detect the object. |
|
|
Depends on the source of detected object. |
Data on detected objects
The scope of transmitted data on detected objects depending on the type of the object is listed in the following table.
Data on detected objects
|
Parameter |
Data type |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
MD5 |
MD5 hash of the file or composite object that was sent for scanning. |
|
|
SHA256 |
SHA256 hash of the file or composite object that was sent for scanning. |
|
|
|
String |
Name of the file or composite object that was sent for scanning. |
|
|
|
String |
Type of the file or composite object that was sent for scanning. |
|
|
|
Integer |
Size of the file or composite object that was sent for scanning, in bytes. |
|
|
|
MD5 |
MD5 hash of the file (simple object or file within a composite object) in which the threat was detected. |
|
|
|
String |
Name of the file (simple object or file within a composite object) in which the threat was detected. |
|
|
|
Integer |
Size of the file (simple object or file within a composite object) in which the threat was detected, in bytes. |
|
|
|
|
String |
URL of the detected object. |
|
|
|
Array |
List of domains to which detected objects belong. For the |
|
Data on detected threats
The scope of transmitted data on detected threats depending on the technology that was used to generate the alert is listed in the table below.
Data on detected threats
Technology |
Parameter |
Description |
Data type |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
One of the following technologies:
|
|
List of detected threats. |
Array |
|
|
Version of databases used to scan the file. |
Integer |
|
|
Sandbox |
|
List of detected threats. |
Array |
|
|
Name of the virtual machine image where the file was scanned. |
String |
|
|
|
Database version in the following format: |
Integer |
|
|
URL Reputation |
|
List of URL Reputation categories for the detected object (for objects of type |
Array |
|
Data on the environment of detected objects
The scope of transmitted data on the environment of detected objects depending on the source of the object is listed in the following table.
Data on the environment of detected objects
Source of the object |
Parameter |
Description |
Data type |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
IP address of the computer that established the connection. |
IP address |
|
|
Name of the computer that established the connection. |
String |
|
|
|
IP address of the computer with which the connection was established. |
IP address |
|
|
|
Port of the computer with which the connection was established. |
Integer |
|
|
|
URL of the web resource that was accessed. IDS technology alerts do not have this parameter. For URL technology alerts, this parameter has the same value as the |
String |
|
|
|
HTTP request method. |
String |
|
|
|
URL from which the redirect was made. |
String |
|
|
|
|
String |
|
|
|
|
Sender's email address. |
String |
|
|
Comma-separated list of recipient email addresses. |
Array |
|
|
|
Subject of the message. |
String |
|
|
|
Email message ID. |
String |
|
|
|
|
Name of the computer on which the alert was generated. |
String |
|
|
IP address of the computer on which the alert was generated. |
IP address |
|
|
|
|
IP address of the computer which initiated the DNS connection. |
IP address |
|
|
IP address of the computer with which the DNS connection was established (typically, a DNS server). |
IP address |
|
|
|
Port of the computer with which the DNS connection was established (typically, a DNS server). |
Integer |
|
|
|
Type of the DNS message:
|
String |
|
|
|
One of the following DNS request types:
|
String |
|
|
|
Domain name from the DNS request. |
String |
|
API that external systems can use to receive information about application events
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides an API for external systems that provides access to information about events registered by the application.
To receive information only for events that satisfy certain conditions, you can specify filters in the request parameters.
The application does not automatically send information about new events based on prior requests. A new request must be sent to receive up-to-date information.
Information about new events can be retrieved for no more than two hours after these events appear in the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform database.
Special considerations for operation in the distributed solution
If the application runs in distributed solution mode, you must separately configure the integration with the external system for each PCN and SCN server from which you want to receive events. This limitation is due to the fact that the web interface of the PCN server displays information about all events, but the events database stores only those events that have been registered on that specific server.
Page top
Request for querying event information
To create a request for getting information about events, the HTTP GET method is used.
You can set the parameters for executing a cURL command by using additional switches (see the table below).
Please refer to the cURL documentation for more information about cURL command switches.
At the first request, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform creates a ContinuationToken (hereinafter also referred to as the "token"). The application sends events available in the system at the time of the token creation. When a new token is created, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform sends events available in the system at the time of creation of this token.
The token contains information about which data were transmitted last. If you want to receive events recorded after the last request, you must save the created token and use it in future requests.
Command syntax
For the first request:
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/events_api/v1/<external_system_id>/events"
If the request is processed successfully, information about requested events and the token value are displayed.
For subsequent requests:
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/events_api/v1/<external_system_id>/events&continuation_token=<token value received by the first request>"
If the request is processed successfully, information about events received since the last request is displayed.
You can create a request to output information about events by specifying the maximum collection time and number of events, as well as event filtering parameters:
curl --cert <path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to the private key file> -X GET "<URL of the server with the Central Node component>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/events_api/v1/<external_system_id>/events?filter=<event filter>&max_timeout=<maximum event collection time>&max_events=<maximum number of events>&continuation_token=<token value received by the first request>"
If you specified the value of the filter parameter for the first request, you do not have to specify it during subsequent requests: the filtering parameters are saved from the previous request and are used if no new parameters are passed in subsequent requests. If you do not want to use filtering, do not specify a value for the parameter.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
string |
Event filtering settings. These are set using the event query language. |
|
int |
Maximum event collection time. Specified in the following format: PT<integer value>S. For example, PT300S. The server sends information about events collected during the specified time. The default value is 5 minutes. This value is used unless otherwise specified in the request. The maximum event collection time may not exceed 5 minutes. If you specify a value greater than 5 minutes, the Central Node server returns an error. The actual total time to wait for events may be increased. |
|
int |
Maximum number of events If no value is specified in the request, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform calculates it based on the number of hosts on which the Endpoint Agent component is installed. Examples of values for typical configurations:
The value specified in the request must not exceed these limits. |
|
string |
Value of the token. |
Example of entering commands with parameters
|
|
If parameter values contain special characters, you must use URL encoding or the
--data-urlencode option in requests.
Example of commands with URL-encoded parameters
|
Example of commands with parameters that use the --data-urlencode option
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Query language for filtering events
The event filtering query language supports the following functions and operators:
- Functions:
in. - Comparison operators for String or Boolean values:
==!=
- Comparison operators for numbers and variables:
ANDORNOT==!=>>=<<=
You can view the list of fields by which you can filter events in the Fields for filtering events section.
If you want to receive information about events of different types, you must create a separate request for each type of event.
|
Numerical and string constants are supported. String constants must be enclosed in single quotation marks: 'example'. Wildcards * and ? are supported for string constants. If you do not want to use these characters as wildcards, you must escape them: \*, \?. Also, in string constants, you must escape special characters.
Fields for filtering events
The fields for filtering events are listed in the table below.
If field values contain special characters, you must use URL encoding or the
--data-urlencode option in requests.
List of fields for filtering events
Field name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
hostName |
string |
Host name. |
HostIp |
string |
IP address of the host. |
EventType |
string |
Event type. Possible values:
|
UserName |
string |
User name. |
OsFamily |
string |
Family of the operating system. |
OsVersion |
string |
Version of the operating system being used on the host. |
Ioa.Rules.Id |
string |
TAA (IOA) rule ID. |
Ioa.Rules.Name |
string |
Information about the results of file analysis using the Targeted Attack Analyzer technology: name of the TAA (IOA) rule that was used to create the alert. |
Ioa.Rules.Techniques |
string |
MITRE technique |
Ioa.Rules.Tactics |
string |
MITRE tactic |
Ioa.Severity |
string |
Importance level that is assigned to an event generated using this TAA (IOA) rule. Possible values:
|
Ioa.Confidence |
string |
Level of confidence depending on the likelihood of false alarms caused by the rule. Possible values:
|
FileCreationTime |
integer |
File creation time. |
DllCreationTime |
integer |
DLL creation time. |
DroppedCreationTime |
integer |
Creation time of the modified file. |
InterpretedFileCreationTime |
integer |
Creation time of the interpreted file. |
FileName |
string |
File name. |
DllName |
string |
DLL name. |
DroppedName |
string |
Name of the modified file. |
BlockedName |
string |
Name of the blocked file. |
InterpretedFileName |
string |
Name of the interpreted file. |
FilePath |
string |
Path to the directory where the file is located. |
DllPath |
string |
Path to the directory where the DLL is located. |
DroppedPath |
string |
Path to the directory where the modified file is located. |
BlockedPath |
string |
Path to the directory where the blocked file is located. |
InterpretedFilePath |
string |
Path to the directory where the interpreted file is located. |
FileFullName |
string |
Full path to the file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
DllFullName |
string |
Full path to the DLL. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
DroppedFullName |
string |
Full path to the modified file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
BlockedFullName |
string |
Full path to the blocked file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
DetectedName |
string |
Full path to the detected file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
OriginalFileName |
string |
Full path to the original file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
InterpretedFileFullName |
string |
Full path to the interpreted file. Includes the path to the directory and the file name. |
FileModificationTime |
integer |
File modification time. |
DllModificationTime |
integer |
DLL modification time. |
DroppedModificationTime |
integer |
Modification time of the modified time. |
InterpretedFileModificationTime |
integer |
Modification time of the interpreted time. |
FileSize |
integer |
File size. |
DllSize |
integer |
DLL size. |
DroppedSize |
integer |
Size of the modified file. |
InterpretedFileSize |
integer |
Size of the interpreted file. |
Md5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the file. |
DllMd5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the DLL |
DroppedMd5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the modified file. |
InterpretedMd5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the interpreted file. |
DetectedMd5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the detected file. |
Sha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the file. |
DllSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the DLL. |
DroppedSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the modified file. |
BlockedSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the blocked file. |
InterpretedSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the interpreted file. |
DetectedSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the detected file. |
HijackingPath |
string |
A malicious DLL placed in a directory on the standard search path to make the operating system load it before the original DLL. |
LogonRemoteHost |
string |
IP address of the host that initiated remote access. |
RealUserName |
string |
Name of the user assigned when the user was registered in the system. |
EffectiveUserName |
string |
User name that was used to log in to the system. |
Environment |
string |
Environment variables. |
ProcessType |
integer |
Process type. Possible values:
|
LinuxOperationResult |
string |
Result of the operation. Possible values:
|
SystemPid. |
integer |
Process ID. |
ParentFileFullName. |
string |
Path to the parent process file. |
ParentMd5 |
string |
MD5 hash of the parent process file. |
ParentSha256 |
string |
SHA256 hash of the parent process file. |
StartupParameters |
string |
Process start options. |
ParentSystemPid |
integer |
Parent process ID. |
ParentStartupParameters |
string |
Parent process startup settings. |
Method. |
string |
HTTP request method. |
Direction. |
string |
Connection direction. Possible values:
|
LocalIp |
string |
IP address of the local computer from which the remote connection attempt was made. |
LocalPort |
integer |
Port of the local computer from which the remote connection attempt was made. |
RemoteHostName |
string |
Name of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt. |
RemoteIp |
string |
IP address of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt. |
RemotePort |
integer |
Port of the computer that was the target of the remote connection attempt. |
URI |
string |
Address of the resource to which the HTTP request was made. |
KeyName |
string |
Path to the registry key. |
ValueName |
string |
Registry value name. |
ValueData |
string |
Registry value data. |
RegistryOperationType |
integer |
Type of the operation with the registry. Possible values:
|
PreviousKeyName |
string |
Previous path to the registry key. |
PreviousValueData |
string |
Previous name of the registry value. |
System.EventID.value |
string |
Type ID of the security event in the Windows log. |
LinuxEventType |
string |
Event type. Possible values:
|
System.Channel.value |
string |
Log name. |
System.EventRecordID.value |
string |
Entry ID in the log. |
System.Provider.Name.value |
string |
ID of the system that logged the event. |
EventData.Data.TargetDomainName.value |
string |
Domain name of the remote computer. |
EventData.Data.ObjectName.value |
string |
Name of the object that initiated the event. |
EventData.Data.PackageName.value |
string |
Name of the package that initiated the event. |
EventData.Data.ProcessName.value |
string |
Name of the process that initiated the event. |
VerdictName |
string |
Name of the detected object. |
RecordId |
integer |
ID of the triggered rule. |
ProcessingMode |
string |
Scanning mode. Possible values:
|
DetectedName |
string |
Name of the object. |
DetectedObjectType |
string |
Type of the object. Possible values:
|
ThreatStatus |
string |
Discovery mode. Possible values:
|
UntreatedReason |
string |
Object processing status. Possible values:
|
InteractiveInputText |
string |
Interpreter command. |
ObjectContent |
string |
Contents of the script sent to be scanned. |
ObjectContentType |
integer |
Content type of the script. Possible values:
|
FileOperationType |
integer |
Type of the file operation. Possible values:
|
PreviousFileName |
string |
Path to the directory where the file was previously located. |
PreviousFileFullName |
string |
Full name of the file including the path to the directory where the file was previously located and/or the previous file name. |
DroppedFileType |
integer |
Type of the modified file. Possible values:
|
API for managing Threat Response actions
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform provides an API for performing Threat Response actions. Commands to carry out operations are received at the Central Node server and then relayed to the Endpoint Agent component.
You can use external systems to perform the following operations on hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
All of the above operations are available on hosts that use Kaspersky Endpoint Agent for Windows or Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows in the role of the Endpoint Agent component.
If Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux is used in the role of the Endpoint Agent component, you can manage network isolation and run applications.
Request for getting the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
To create a request for information about hosts with the Endpoint Agent component, the GET HTTP method is used.
Command syntax
GET "<URL of the Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/sensors"
If the request is processed successfully, a list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is displayed.
You can create a request for information about hosts with filters by IP address, name, or ID of the host. You can specify one, multiple, or all of these filters.
When specifying a host name, you need to keep in mind that the filter is case-sensitive.
GET "<URL of the Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/sensors?ip=<IP address of the host>&host=<host name>&sensor_id=<sensor_id>"
If the request is processed successfully, information about the selected host with the Endpoint Agent component is displayed.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
external_system_id |
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
sensor_id |
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
ip |
string |
IP address of the host with the Endpoint Agent component. |
host |
string |
Name of the host with the Endpoint Agent component. |
Example of entering commands with parameters
GET "https://10.10.0.22:443/kata/response_api/v1/15301050-0490-4A41-81EA-B0391CF21EF3/sensors" |
GET "https://10.10.0.22:443/kata/response_api/v1/15301050-0490-4A41-81EA-B0391CF21EF3/sensors?ip=10.16.40.243&host=host4&sensor_id=DF64838B-B518-414B-B769-2B8BE341A2F0" |
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
400 |
Authorization required. |
401 |
Incorrect parameters. |
500, 502, 503, 504 |
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Request for information about network isolation and the existence of prevention rules for hosts with the Kaspersky Endpoint Agent component
HTTP method GET is used to create a request to display information about network isolation and the existence of prevention rules for hosts with the Endpoint Agent component.
Command syntax
GET "<URL of the Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id>&settings_type=<network_isolation or prevention>"
If the request is processed successfully, the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component is displayed, listing hosts that had prevention rules or network isolation rules applied at the moment when the request was processed.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
enum |
Rule type: network_isolation or prevention. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Authorization required. |
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal error. Repeat the request later. |
Host network isolation management
To isolate a host with the Endpoint Agent component using the API, the following procedure is recommended for interacting with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Creating a request for getting the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Creating a request for getting information about hosts that already have network isolation enabled
- Creating a request for one of the following operations with hosts with the Endpoint Agent component:
You can manage the created network isolation rules in the web interface of the application.
Page top
Request to enable network isolation
To enable network isolation for a selected host, you must add a network isolation rule. To create the request, the HTTP POST method is used.
Command settings are passed in the body of the request in JSON format.
Command syntax
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X POST "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id>&settings_type=network_isolation" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"settings": {
"autoTurnoffTimeoutInSec": <network isolation time period>}
}
'
If the request is processed successfully, the network isolation rule is added. Network isolation for the selected host becomes active at the moment when the rule is added.
After a period of time specified when the request is created, network isolation becomes inactive. The network isolation rule itself is not deleted. If necessary, you can delete the selected rule.
To disable network isolation, you must create a request to disable the selected rule.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
integer |
Period of time during which the network isolation will be active. Allowed range - 1 to 9999 hours. Network isolation time period is specified in seconds. For example, if you want to enable network isolation of a host for two hours, you must specify 7200 seconds. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
If you want to edit the settings of the created network isolation rule, you must create a new request to add the rule with the new settings.
Page top
Request to disable network isolation
To disable network isolation for a selected host, you must create a request to disable the network isolation rule. HTTP method DELETE is used to create the request.
Command syntax
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X DELETE "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id>&settings_type=network_isolation"
If the request is processed successfully, the network isolation rule is disabled.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
Example of entering a command with the DELETE parameter
|
To verify that network isolation is disabled, make a request for information about a task using the HTTP GET method.
Example of entering a command with the GET parameter
|
If network isolation is disabled, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform returns a response to the external system in the following format:
{ "error": "Not Found" } |
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Request to add an exclusion to a network isolation rule
To add an exclusion to a previously created network isolation rule, you must create a request to add an exclusion. To create the request, the HTTP POST method is used.
Command settings are passed in the body of the request in JSON format.
Command syntax
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X POST "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id>&settings_type=network_isolation" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{"settings": {"excludedRules": [{"direction": "<outbound, inbound, or both>","protocol": <number of the IP protocol>,"remoteIpv4Address": "<IP address of the host with the Endpoint Agent component whose traffic must not be blocked>","localPortRange":{"fromPort": <port number>,"toPort": <port number>}},{"direction": "<outbound, inbound, or both>","protocol": <number of the IP protocol>,"remoteIpv4Address": "<IP address of the host with the Endpoint Agent component whose traffic must not be blocked>","remotePortRange":{"fromPort": <port number>,"toPort": <port number>}},{"direction": "<outbound, inbound, or both>","protocol": <number of the IP protocol>,"remoteIpv4Address": "<IP address of the host with the Endpoint Agent component whose traffic must not be blocked>"}],"autoTurnoffTimeoutInSec": <network isolation duration>}}'
If the request is processed successfully, the exclusion from the network isolation rule is added.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|
|
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
|
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
|
Direction of network traffic that must not be blocked. Possible values:
If you do not specify a value for this parameter, the default value is 'both', which means the application transmits traffic in both directions. |
|
|
IP protocol number assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). If you do not specify a value for this parameter, by default, network isolation is applied to all protocols. |
|
|
IP address of the host with the Endpoint Agent component whose traffic must not be blocked |
|
|
Destination port. You can specify a destination port only if you have selected an outbound direction of network traffic. Port ranges cannot be specified for bidirectional traffic. |
|
|
Port from which the connection is initiated. You can specify a destination port only if you have selected an inbound direction of network traffic. Port ranges cannot be specified for bidirectional traffic. |
|
|
Period of time during which the network isolation will be active. Allowed range - 1 to 9999 hours. Network isolation time period is specified in seconds. For example, if you want to enable network isolation of a host for two hours, you must specify 7200 seconds. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
If you want to edit the settings of the created exclusion, you must create a new request to add the exclusion with the new settings.
Page top
Managing prevention rules
You can use prevention rules to prevent files or processes from running on a selected hosts or all hosts with the Endpoint Agent component. For example, you can block certain applications that you consider insecure. The application identifies files based on their hash by using the MD5 and SHA256 hashing algorithms. A prevention rule created through external systems can contain multiple file hashes.
You can use external systems to manage all prevention rules created for a single host or all hosts at the same time. When you create a prevention rule for a selected host through external systems, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform replaces all prevention rules applied to this host with a prevention rules with new parameters. For example, if you had added multiple prevention rules for a selected hosts through the application's web interface, and subsequently added a prevention rule through external systems, all prevention rules added in the web interface are replaced with the rule added through external systems.
When the parameters of a prevention rule created through external systems are modified, the application saves only the new parameters. For example, if you have added a prevention rule that contains hashes for multiple files, and want to add another hash to that rule, you must create a request to add a prevention rule and specify all hashes for which you had a prevention previously, plus the new hash.
The described scenario is also relevant for prevention rules applied to all hosts.
To create a prevention rule using the API, the following procedure is recommended for interacting with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Creating a request for getting the list of hosts with the Endpoint Agent component
- Create a request for getting information about hosts that already have prevention rules.
- Create a request for one of the following operations with prevention rules:
Added prevention rules are displayed in the web interface of the application in the Prevention section, Prevention rules subsection.
If you are creating a prevention rule for all hosts through an external system, you must first make sure that no prevention rule for the same file exists on the server or is applied to one or multiple hosts. This prerequisite is also relevant if you want to create a prevention rule through an external system for a selected host: you must make sure that a prevention rule for the same file does not exist on the server and is not applied to all hosts. Otherwise, the server returns an error to the external system with a list of hosts that already have a prevention rule applied.
If the prevention rule created through an external system contains multiple file hashes, the error information mentions only the first file that caused the error. Information about other duplicated prevention rules is not displayed.
To modify a prevention rule previously created through the web interface or external systems, you must create a request to add a prevention rules with updated parameters.
Page top
Request to create a prevention rule
To create the request, the HTTP POST method is used. Command settings are passed in the body of the request in JSON format.
Command syntax
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X POST "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id or all, if you want to create the prevention rule for all hosts>&settings_type=prevention" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"settings": {
"objects": [
{
"file": {
"<sha256 or md5>": "<SHA256- or MD5-hash of the file that you want to prevent from starting>"
}
},
{
"file": {
"<sha256 or md5>": "<SHA256- or MD5-hash of the file that you want to prevent from starting>"
}
}
]
}
}
'
If the request is processed successfully, the prevention rule is added. The prevention rule becomes active at the moment when it is added.
If necessary, you can delete the prevention rule.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
string |
Type of the object that you want to prevent from running. Possible value of the parameter: file. |
|
string |
SHA256 or MD5 has of the object that you want to prevent from running. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Request to delete a prevention rule
You can delete a prevention rule using a new request with blank values or a request with the DELETE parameter. POST and DELETE HTTP methods are used to create requests.
Command syntax for a new request
Command settings are passed in the body of the request in JSON format.
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X POST "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id or all, if you want to delete the prevention rule for all hosts>&settings_type=prevention" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"settings": {
"objects": []
}
}
'
Command syntax with the DELETE parameter
curl -k --cert <path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X DELETE "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/settings?sensor_id=<sensor_id or all, if you want to delete the prevention rule for all hosts>&settings_type=prevention"
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
Example of command for a new request
|
Example of entering a command with the DELETE parameter
|
If the request is processed successfully, the prevention rule is deleted.
To verify that the prevention rule is deleted, make a request for information about the prevention rule using the HTTP GET method.
Example of entering a command with the GET parameter
|
If the prevention rule was deleted, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform returns a response to the external system in the following format:
{ "error": "Not Found" } |
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
Specified hosts with the Endpoint Agent component not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Managing the application run task
To manage the application run task using the API, the following procedure is recommended for interacting with Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform:
- Creating a request for information about settings, creation time, and completion status of the task
- Creating a request for one of the following operations with the task:
Added tasks are displayed in the web interface of the application in the Tasks section.
Page top
Request to obtain information about a task
To create a request for getting information about a task, the HTTP GET method is used.
Command syntax
GET "<URL of the Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/tasks/<task_id>?settings=<true or false>"
If the request is processed successfully, information is displayed about settings, creation time, and completion status of the task.
Settings
Settings |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
|
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
|
Unique ID of the task. |
|
|
Possible values:
|
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
} } }
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
The task with the specified ID was already exists. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Request to create a task
The HTTP POST method is used for requests to run the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform application. Command settings are passed in the body of the request in JSON format.
Command syntax
curl -k --<path to the TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X POST "<URL of Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/tasks/<task_id>?sensor_id=<sensor_id>&task_type=run_process" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"task": {
"schedule": {"startNow": <true or false>},
"execCommand": "<name of the application that you want to run>",
"cmdLineParameters": "<additional options for running the file or command>",
"workingDirectory": "<working directory>"
}
}
'
If the request is processed successfully, the run application task is created.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the host with the Endpoint Agent component |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the task. |
Example of entering a command with switches
|
Response
HTTP code: 200
Format: JSON
} } }
|
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
The task with the specified ID was not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
If you want to edit the settings of the created task, you must create a new request to add the task with the new settings.
Page top
Request to delete a task
To create a request to delete a Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform task, the HTTP DELETE method is used.
Command syntax
curl -k --<path to TLS certificate file> --key <path to private key file> -X DELETE "<URL of the Central Node server>:<port, 443 by default>/kata/response_api/v1/<external_system_id>/tasks/<task_id>
If the request is processed successfully, the application run task is deleted.
Settings
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the external system used for authorization in Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform. |
|
UUID |
Unique ID of the task. |
Example of entering a command with the DELETE parameter
|
If the request is processed successfully, the prevention rule is deleted.
To verify that the task is deleted, make a request for information about the task using the HTTP GET method.
Example of entering a command with the GET parameter
|
If the task was deleted, Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform returns a response to the external system in the following format:
{ "error": "Not Found" } |
Returned value
Return code |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incorrect parameters. |
|
Authorization required. |
|
The task with the specified ID was not found. |
|
Internal server error. Repeat the request later. |
Sources of information about the application
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform page on the Kaspersky website
On the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform page, you can find general information about the application, its capabilities and features.
The Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform page contains a link to the online store. In the online store, you can buy the application or renew the license.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform page in the Knowledge Base
Knowledge Base is a section on the Technical Support website.
On the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform page in the Knowledge Base, you can read articles that provide useful information, recommendations, and answers to frequently asked questions about purchasing, installing, and using the application.
Knowledge Base articles can answer questions related not only to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform but also to other Kaspersky applications. Knowledge Base articles may also contain news from Technical Support.
Discussing Kaspersky software on the Forum
If your question does not require an immediate answer, you can discuss it with Kaspersky experts and other users on our Forum.
On the Forum, you can view existing topics, post comments, and create new discussion topics.
Page top
Contacting the Technical Support Service
This section describes the ways to get technical support and the terms on which it is available.
How to obtain Technical Support
If you cannot find a solution to your problem in the program documentation or in one of the sources of information about Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform, we recommend that you contact Technical Support. Technical Support staff will answer your questions about installing and using Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
Kaspersky provides support of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform throughout its life cycle (see the product life cycle page). Before you contact Technical Support, please read the technical support rules.
You can contact Technical Support in one of the following ways:
- Visit the Technical Support website.
- Send a request to Technical Support through the Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal.
Technical Support via Kaspersky CompanyAccount
Kaspersky CompanyAccount is a portal for companies that use Kaspersky software. The Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal is designed to facilitate interaction between users and Kaspersky experts through online requests. The Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal allows monitoring the progress of online request processing by Kaspersky staff and keeping the history of electronic requests.
You can register all of your organization's employees under a single account on Kaspersky CompanyAccount. A single account lets you centrally manage electronic requests from registered employees to Kaspersky and also manage the privileges of these employees via Kaspersky CompanyAccount.
The portal Kaspersky CompanyAccount is available in the following languages:
- English
- Spanish
- Italian
- German
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Russian
- French
- Japanese
To learn more about Kaspersky CompanyAccount, visit the Technical Support website.
Page topGlossary
Advanced persistent threat (APT)
A sophisticated targeted attack against the corporate IT infrastructure that simultaneously uses different methods to infiltrate the network, hide on the network, and gain unobstructed access to confidential data.
Alternate data stream
Data streams of the NTFS file system (alternate data streams) are intended for additional attributes or information on a file.
Each file in the NTFS file system consists of a set of streams. The main stream contains the file contents. The other (alternate) streams are intended for metadata. Streams can be created, deleted, individually saved, renamed, and can even be run as a process.
Alternate streams can be used by hackers for concealed transmission or receipt of data from a computer.
Anti-Malware Engine
Application core. Scans files and objects for viruses and other threats to the corporate IT infrastructure using anti-virus databases.
Backdoor program
A program planted by hackers on a compromised computer in order to be able to access this computer in the future.
Central Node
Application component. Scans data, analyzes the behavior of objects, and publishes analysis results in the web interface of the application.
Communication channel bandwidth
The highest possible speed of information transfer in the specific communication channel.
CSRF attack
Cross-Site Request Forgery (also referred to as an "XSRF attack"). Attack on website users by exploiting vulnerabilities of the HTTP protocol. The attack enables actions to be performed under the guise of an authorized user of a vulnerable website. For example, under the guise of an authorized user of a vulnerable website, a hacker can covertly send a request to the server of an external payment system to transfer money to the hacker's account.
Distributed solution
Two-level hierarchy of servers with Central Node components installed. This hierarchy allocates a primary control server (Primary Central Node (PCN)) and secondary servers (Secondary Central Nodes (SCN)).
Dump
Contents of the working memory of a process or the entire RAM of the system at a specified moment of time.
End User License Agreement
Binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab, stipulating the terms on which you may use the application.
Endpoint Agent component
Application component. Installed on workstations and servers of the corporate IT infrastructure that run Microsoft Windows, Linux and macOS operating systems. Continuously monitors processes running on those computers, active network connections, and files that are modified.
ICAP client
The system through which Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives traffic.
ICAP data
Data received by the ICAP protocol (Internet Content Adaptation Protocol). This protocol allows filtering and modifying data of HTTP requests and HTTP responses. For example, it allows scanning data for viruses, blocking spam, and denying access to personal resources. The ICAP client is normally a proxy server that interacts with the ICAP server by the ICAP protocol. Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform receives data from the proxy server of your organization after this data was processed on the ICAP server.
Intrusion Detection System
Application module. Scans the Internet traffic for signs of intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure.
IOA
Indicator of Attack. Description of suspicious behavior of objects within a corporate IT infrastructure that may indicate a targeted attack on that organization.
IOC
Indicator of Compromise. A set of data about a malicious object or malicious activity.
IOC file
IOC files contain a set of indicators that are compared to the indicators of an event. If the compared indicators match, the application considers the event to be an alert. The likelihood of an alert may increase if a scan detects exact matches between the data of an object and several IOC files.
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform
Solution designed for the protection of a corporate IT infrastructure and timely detection of threats such as zero-day attacks, targeted attacks, and complex targeted attacks known as advanced persistent threats (hereinafter also referred to as "APT").
Kaspersky Private Security Network
A solution that allows users of Kaspersky anti-virus applications to access Kaspersky Security Network databases without sending data from their computers to Kaspersky Security Network servers.
Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway
A solution designed for protection of incoming and outgoing email against malicious objects and spam, and for content filtering of messages. The solution lets you deploy a virtual mail gateway and integrate it into the existing corporate mail infrastructure. An operating system, mail server, and Kaspersky anti-virus application are preinstalled on the virtual mail gateway.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
An infrastructure of cloud services that provides access to the online Knowledge Base of Kaspersky which contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the performance of some protection components, and reduces the likelihood of false alarms.
Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal
Kaspersky information system Contains and displays reputation information for files and URL addresses.
KATA
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack. Functional block of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform which detects threats on the perimeter of the enterprise IT infrastructure.
KEDR
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response. Functional block of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform which provides protection for the local area network of the organization.
Kerberos authentication
A mechanism for mutual authentication of client and server before a connection is established between them, which allows communication over unprotected networks. The mechanism is based on using a ticket, which is issued to the user by a trusted authentication center.
Keytab file
A file containing pairs of unique names (principals) of clients that are allowed to use Kerberos authentication and encrypted keys derived from the user password. Systems that support Kerberos use keytab files to authenticate users without entering a password.
Local reputation database of KPSN
Database of the reputations of objects (files or URLs) that is stored on the Kaspersky Private Security Network server but not on Kaspersky Security Network servers. Local reputation databases are managed by the KPSN administrator.
Malicious web addresses
URLs of resources distributing malicious software.
MIB (Management Information Base)
Virtual database used to manage objects that are transmitted over the SNMP protocol.
Mirrored traffic
A copy of traffic redirected from one switch port to another port of the same switch (local mirroring) or to a remote switch (remote mirroring). The network administrator can configure which part of traffic should be mirrored for transmission to Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
MITM attack
Man in The Middle. An attack on the IT infrastructure of an organization in which a hacker hijacks the communication link between two access points, relays it, and modifies the connection between these access points if necessary.
MITRE technique
The MITRE ATT&CK (Adversarial Tactics, Techniques & Common Knowledge) database contains descriptions of hacker behavior based on the analysis of real attacks. It is a structured list of known hacker techniques represented as a table.
Multitenancy
Operation mode in which Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is used to protect the infrastructure of multiple organizations or branch offices of the same organization simultaneously.
New generation threats
Corporate IT infrastructure threats capable of overwriting, altering, encrypting, or distorting their code to a point where matches against signatures can no longer be detected by a security system.
NTP server
Precision time server using the Network Time Protocol.
OpenIOC
An open, XML-based standard for describing indicators of compromise containing over 500 different indicators of compromise.
Phishing URL addresses
URL addresses of resources designed to obtain unauthorized access to confidential data of users. Phishing is usually aimed at stealing various financial data.
Sandbox
Application component. Starts virtual images of operating systems. Starts files in these operating systems and tracks the behavior of files in each operating system to detect malicious activity and signs of targeted attacks to the corporate IT infrastructure.
Sensor
Application component. Receives data.
Service principal name (SPN)
Unique ID of the service on the network for Kerberos authentication.
SIEM system
Security Information and Event Management System. Solution for managing information and events in an organization's security system.
Signature
Code in information protection databases that contains a description of known threats.
SPAN
Switch Port Analyzer. Technology for mirroring traffic from one port to another.
Syslog
The standard for sending and recording messages about events occurring in the system employed on UNIX and GNU/Linux platforms.
TAA (IOA) rule
One sign of suspicious behavior of an object in the corporate IT infrastructure that causes Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to consider an event to be an alert. A TAA (IOA) rule contains a description of a sign of an attack and recommended countermeasures.
Targeted attack
Attack that targets a specific person or organization. Unlike mass attacks by computer viruses designed to infect as many computers as possible, targeted attacks can be aimed at infecting the network of a specific organization or even a separate server within the corporate IT infrastructure. A dedicated Trojan program can be written to stage each targeted attack.
Targeted Attack Analyzer
Application module. Analyzes and monitors network activity of software installed on computers of the corporate LAN using TAA (IOA) rules. Searches for signs of network activity that the user of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform is advised to direct his/her attention, as well as signs of targeted attacks to the corporate IT infrastructure.
Tenant
An individual organization or branch office of an organization to which the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform solution is being provided.
TLS encryption
Encryption of connection between two servers, which ensures secure transmission of data between servers on the Internet.
Tracing
The application is run in debugging mode; after each command is executed, the application is stopped and the result of this step is displayed.
VIP status
Status of alerts with special access permissions. For example, alerts with the VIP status cannot be viewed by users with the Security officer role.
YARA
Application module. Scans files and objects for signs of targeted attacks on the corporate IT infrastructure using YARA Rules databases created by users of Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform.
YARA rules
A publicly available classification of malware, which contains signatures of signs of targeted attacks and intrusions into the corporate IT infrastructure, which is used by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack Platform to scan files and objects.
Zero-day attack
An attack targeting the corporate IT infrastructure by exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities in software. These are software vulnerabilities that hackers find and exploit before the software vendor has a chance to release a patch.
Zero-day vulnerability
A software vulnerability that hackers find and exploit before the software vendor has a chance to release a patch with fixed program code.
Page top
Information about third-party code
Information about third-party code is contained in the file legal_notices.txt, in the program installation directory.
Page top
Trademark notices
Registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Adobe, Flash are registered trademarks or trademarks of the Adobe company in the United States and/or other countries.
AMD is a trademark or registered trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Apple, Mac, Macintosh, macOS, and Safari are trademarks of Apple Inc.
Ubuntu is a registered trademark of Canonical Ltd.
Snort is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
Citrix is a registered trademark or trademark of the Cloud Software Group, Inc. and / or its subsidiaries in the United States and / or other countries.
Docker and the Docker logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Docker, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Docker, Inc. and other parties may also have rights to trademarks described in other terms used herein.
Google, Google Chrome, Android are trademarks of Google LLC.
Intel, Core, and Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, Active Directory, Excel, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, PowerPoint, PowerShell, Win32, Windows, Windows Server, Windows XP are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
Mozilla and Firefox are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation in the United States and other countries.
NVIDIA is a registered trademark of the NVIDIA Corporation.
Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Python is a trademark or registered trademark of the Python Software Foundation.
CentOS is a trademark or registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Debian is a registered trademark of Software in the Public Interest, Inc.
VMware ESXi is a trademark of VMware, Inc. or a registered trademark in the United States or other jurisdictions of VMware, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
Page top