Contents
echo example
The echo example demonstrates the use of IPC transport.
It shows how to use the main tools that let you implement interaction between entities.
About the echo example
The echo example describes a basic case of interaction between two entities:
- The
Cliententity sends a number (value) to theServerentity. - The
Serverentity modifies this number and sends the new number (result) to theCliententity. - The
Cliententity prints theresultto the screen.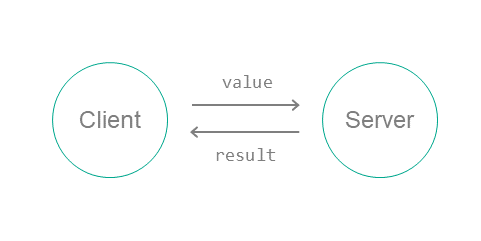
To set up this interaction between entities:
- Connect the
ClientandServerentities by using the init description. - On the server, implement an interface with a single
Pingmethod that has one input argument (the original number (value)) and one output argument (the modified number (result)).Description of the
Pingmethod in the IDL language:Ping(in UInt32 value, out UInt32 result);

- Create static description files in the EDL, CDL and IDL languages. Use the NK compiler to generate files containing transport methods and types (proxy object, dispatchers, etc.).
- In the code of the
Cliententity, initialize all required objects (transport, proxy object, request structure, etc.) and call the interface method. - In the code of the
Serverentity, prepare all the required objects (transport, component dispatcher and entity dispatcher, etc.), accept the request from the client, process it and send a response.
The echo example consists of the following source files:
client/src/client.c– implementation of theCliententity.server/src/server.c– implementation of theServerentity.resources/Server.edl,resources/Client.edl,resources/Ping.cdl,resources/Ping.idl– static descriptions.init.yaml– init description.
Implementation of the Client entity in the echo example
The code of the Client entity uses the transport types and methods that will be generated during the solution build by the NK compiler based on the IDL description of the Ping interface.
However, to obtain the descriptions of types and signatures of methods required for implementing the entity, you can use the NK compiler immediately after creating an EDL description of the entity, CDL descriptions of components and IDL descriptions of the interfaces used for interaction. As a result, the required types and signatures of methods will be declared in the generated *.h files.
In the Client entity implementation, the following is required:
- Get the client IPC handle of the connection (channel) by using the
ServiceLocatorConnect()function.Input the name of the IPC
server_connectionpredefined in the init.yaml file. - Initialize
NkKosTransportby passing the obtained IPC handle to theNkKosTransport_Init()function. - Obtain the ID of the required interface (
RIID) by using theServiceLocatorGetRiid()function. - Input the full name of the
Pinginterface implementation. It consists of the names of the component instance (Echo.ping) and interface (ping) that were previously defined in Server.edl and Ping.cdl. - Initialize the proxy object by passing the transport and interface ID to the
Ping_proxy_init()function. - Prepare the request and response structures.
- Call the
Ping_Ping()interface method by passing the proxy object and the pointers to the request and response.
client.c
/* Files required for transport initialization. */
/* Description of the server interface used by the client entity. */
/* Client entity entry point. */
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
NkKosTransport transport;
struct echo_Ping_proxy proxy;
int i;
fprintf(stderr, "Hello I'm client\n");
/* Get client IPC handle of
* "server_connection". */
Handle handle = ServiceLocatorConnect("server_connection");
assert(handle != INVALID_HANDLE);
/* Initialize IPC transport for interaction with the server entity. */
NkKosTransport_Init(&transport, handle, NK_NULL, 0);
/* Get Runtime Interface ID (RIID) for interface echo.Ping.ping.
* Here ping is the name of the echo.Ping component instance,
* echo.Ping.ping is the name of the Ping interface implementation. */
nk_iid_t riid = ServiceLocatorGetRiid(handle, "echo.Ping.ping");
assert(riid != INVALID_RIID);
/* Initialize proxy object by specifying transport (&transport)
* and ID of the server interface (riid). Each method
* of the proxy object will be implemented by sending a request to the server. */
echo_Ping_proxy_init(&proxy, &transport.base, riid);
/* Request and response structures */
echo_Ping_Ping_req req;
echo_Ping_Ping_res res;
/* Test loop. */
req.value = EXAMPLE_VALUE_TO_SEND;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
/* Call Ping interface method.
* Server will be sent a request for calling Ping interface method
* ping_comp.ping_impl with the value argument. Calling thread is locked
* until a response is received from the server. */
if (echo_Ping_Ping(&proxy.base, &req, NULL, &res, NULL) == rcOk)
{
/* Print "result" value from response
* (result is the output argument of the Ping method). */
fprintf(stderr, "result = %d\n", (int) res.result);
/* Include received "result" value into "value" argument
* to resend to server in next iteration. */
req.value = res.result;
}
else
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to call echo.Ping.Ping()\n");
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Implementation of the Server entity in the echo example
The code of the Server entity uses the transport types and methods that will be generated during the solution build by the NK compiler based on the EDL description of the Server entity.
However, to obtain the types and signatures of methods required for implementing the entity, you can use the NK compiler immediately after creating an EDL description of the entity, CDL descriptions of components and IDL descriptions of the interfaces used for interaction. As a result, the required types and signatures of methods will be declared in the generated *.h files.
In the server entity implementation, the following is required:
- Implement the
Ping()method.The signature of the
Ping()method implementation must exactly match the signature of thePing_Ping()interface method that is declared in the Ping.idl.h file. - Get the server IPC handle of the connection (channel) by using the
ServiceLocatorRegister()function.Input the name of the IPC
server_connectionpredefined in the init.yaml file. - Initialize
NkKosTransportby passing the obtained IPC handle to theNkKosTransport_Init()function. - Prepare the request and response structures.
- Initialize the dispatch method (dispatcher) of the
Pingcomponent by using thePing_component_init()function. - Initialize the dispatch method (dispatcher) of the
Serverentity by using theServer_entity_init()function. - Receive a request by calling
nk_transport_recv(). - Process the received request by calling the
Server_entity_dispatch()dispatcher.The dispatcher calls the required implementation of the method based on the interface ID (
RIID) received from the client. - Send the response to the
Cliententity by callingnk_transport_reply().
server.c
/* Files required for transport initialization. */
/* Server entity descriptions in EDL. */
/* Type of interface implementing object. */
typedef struct IPingImpl {
struct echo_Ping base; // base interface of object
int step; // Additional parameters
} IPingImpl;
/* Implementation of the Ping method. */
static nk_err_t Ping_impl(struct echo_Ping *self,
const echo_Ping_req *req,
const struct nk_arena* req_arena,
echo_Ping_res* res,
struct nk_arena* res_arena)
{
IPingImpl *impl = (IPingImpl *)self;
/* Increment value in the client request by
* one step and include into result argument that will be
* sent to the client in the server response. */
res->Ping.result = req->Ping.value + impl->step;
return NK_EOK;
}
/* IPing object constructor.
* step is the number by which the input value is increased. */
static struct echo_Ping *CreateIPingImpl(int step)
{
/* Table of IPing interface method implementations. */
static const struct echo_Ping_ops ops = {
.Ping = Ping_impl
};
/* Object implementing the interface. */
static struct IPingImpl impl = {
.base = {&ops}
};
impl.step = step;
return &impl.base;
}
/* Server entry point. */
int main(void)
{
NkKosTransport transport;
ServiceId iid;
/* Get server IPC handle of "server_connection". */
Handle handle = ServiceLocatorRegister("server_connection", NULL, 0, &iid);
assert(handle != INVALID_HANDLE);
/* Initialize transport to client. */
NkKosTransport_Init(&transport, handle, NK_NULL, 0);
/* Prepare the structures of the request to the server entity: constant
* part and arena. Because none of the methods of the server entity has
* sequence type arguments, only constant parts are used
* request and response. Arenas are effectively unused. However, the valid
* arenas of the request and response must be passed to
* the server transport methods (nk_transport_recv, nk_transport_reply) and
* the dispatch method server_entity_dispatch. */
echo_Server_entity_req req;
char req_buffer[echo_Server_entity_req_arena_size];
struct nk_arena req_arena = NK_ARENA_INITIALIZER(req_buffer, req_buffer + sizeof(req_buffer));
/* Prepare response structures: constant part and arena. */
echo_Server_entity_res res;
char res_buffer[echo_Server_entity_res_arena_size];
struct nk_arena res_arena = NK_ARENA_INITIALIZER(res_buffer, res_buffer + sizeof(res_buffer));
/* Initialize ping component dispatcher. 3 is the value of the "step",
* which is the number by which the input value is increased. */
echo_Ping_component component;
echo_Ping_component_init(&component, CreateIPingImpl(3));
/* Initialize server entity dispatcher. */
echo_Server_entity entity;
echo_Server_entity_init(&entity, &component);
fprintf(stderr, "Hello I'm server\n");
/* Dispatch loop implementation. */
do
{
/* Reset request/response buffers. */
nk_req_reset(&req);
nk_arena_reset(&req_arena);
nk_arena_reset(&res_arena);
/* Wait for request from client entity. */
if (nk_transport_recv(&transport.base, &req.base_, &req_arena) != NK_EOK) {
fprintf(stderr, "nk_transport_recv error\n");
} else {
/* Process received request by calling Ping_impl implementation
* of the requested Ping interface method. */
echo_Server_entity_dispatch(&entity, &req.base_, &req_arena, &res.base_, &res_arena);
}
/* Send response. */
if (nk_transport_reply(&transport.base, &res.base_, &res_arena) != NK_EOK) {
fprintf(stderr, "nk_transport_reply error\n");
}
}
while (true);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Description files in the echo example
Description of the Client entity
The Client entity does not implement an interface, so all you need to do is declare the entity name in its EDL description:
Client.edl
/* Description of the Client entity. */
entity echo.Client
Server entity description
The description of the Server entity must contain information stating that it implements the Ping interface. Using static descriptions, you need to insert the implementation of the Ping interface into the new component (for example, Ping) and insert the instance of this component into the Server entity.
The Server entity contains an instance of the Ping component:
Server.edl
/* Description of the Server entity. */
entity echo.Server
/* Server is a named instance of the echo.Ping component. */
components {
Server: echo.Ping
}
The Ping component contains the implementation of the Ping interface:
Ping.cdl
/* Description of the Ping component. */
component echo.Ping
/* ping is the Ping interface implementation. */
interfaces {
ping: echo.Ping
}
The Ping package contains a declaration of the Ping interface:
Ping.idl
/* Description of the Ping package. */
package echo.Ping
interface {
Ping(in UInt32 value, out UInt32 result);
}
Init description
To enable the Client entity to call a method of the Server entity, a connection (IPC channel) must be created between them.
To do so, in the init description indicate that the Client and Server entities must be started and connect them:
init.yaml
entities:
- name: echo.Client
connections:
- target: echo.Server
id: server_connection
- name: Server
The Server entity is indicated as - target, so it will perform the server entity role, meaning it will accept requests from the Client entity and respond to them.
The created IPC channel is named server_connection. You can obtain the handle of this channel by using the Service Locator.
Building and running the echo example
See the Building and running examples section.
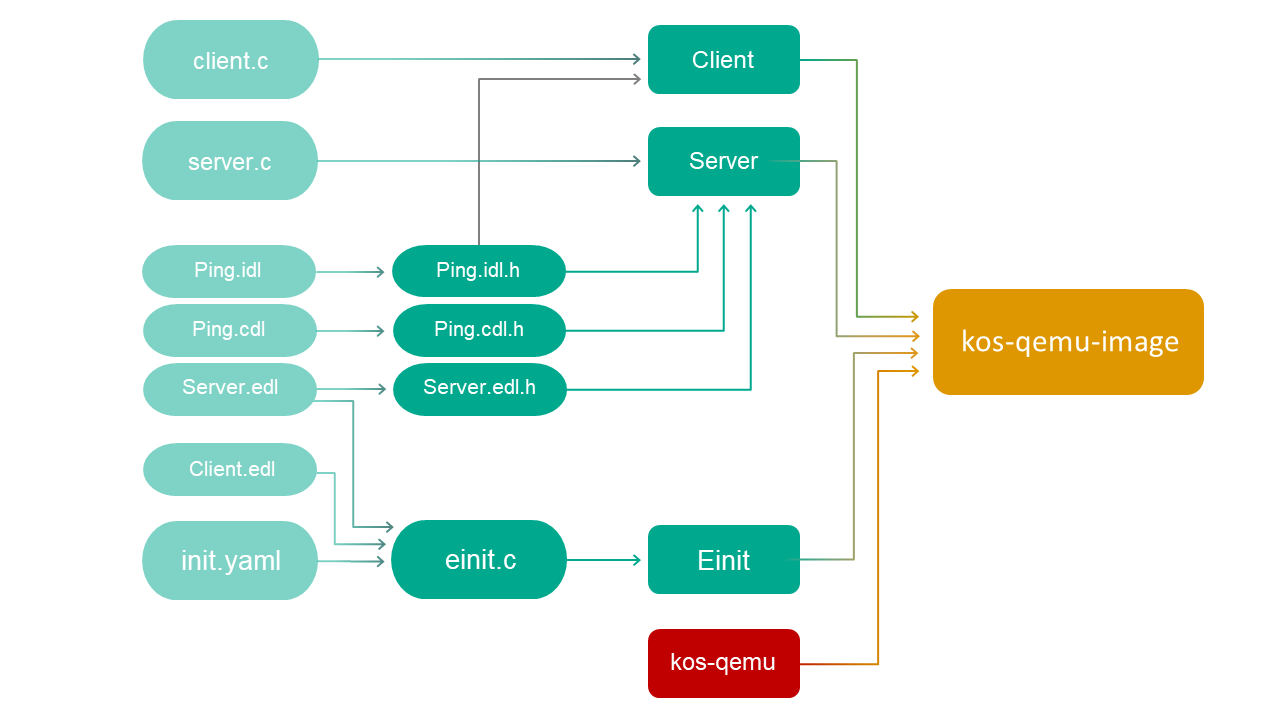
The build scheme for the echo example looks as follows: