Contents
Flow security model
The Flow security model associates resources with finite-state machines, receives and modifies the states of finite-state machines, and checks whether the state of the finite-state machine is within the defined set of states. For example, a process can be associated with a finite-state machine to allow or prohibit this process from using storage and/or the network depending on the state of the finite-state machine.
A PSL file containing a description of the Flow security model is located in the KasperskyOS SDK at the following path:
toolchain/include/nk/flow.psl
Flow security model object
To use the Flow security model, you need to create an object or objects of this model.
One Flow security model object associates a set of resources with a set of finite-state machines that have the same configuration. A resource can be associated with only one finite-state machine of each Flow security model object.
A Flow security model object has the following parameters:
type State– type that determines the set of states of the finite-state machine (variant type that combines text literals).config– configuration of the finite-state machine:states– set of states of the finite-state machine (must match the set of states defined by theStatetype).initial– initial state of the finite-state machine.transitions– description of the permissible transitions between states of the finite-state machine.
All parameters of a Flow security model object are required.
Example:
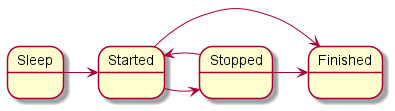
Diagram of finite-state machine states in the example
A Flow security model object can be covered by a security audit. You can also define the audit conditions specific to the Flow security model. To do so, use the following construct in the audit configuration description:
omit : [<"state 1">[, ...]] – the audit is not performed if the finite-state machine is in one of the listed states.
It is necessary to create multiple objects of the Flow security model in the following cases:
- You need to configure a security audit differently for different objects of the Flow security model (for example, you can apply different audit profiles or different audit configurations of the same profile for different objects).
- You need to distinguish between calls of methods provided by different objects of the Flow security model (audit data includes the name of the security model method and the name of the object that provides this method, so you can verify that the method of a specific object was called).
- You need to use finite-state machines with different configurations.
Flow security model init rule
It creates a finite-state machine and associates it with the sid resource. The created finite-state machine has the configuration defined in the settings of the Flow security model object being used.
It returns the "granted" result if an association was created between the finite-state machine and the sid resource.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The
sidresource is already associated with a finite-state machine of the Flow security model object being used. - The
sidvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
Flow security model fini rule
It deletes the association between the finite-state machine and the sid resource. The finite-state machine that is no longer associated with the resource is destroyed.
It returns the "granted" result if the association between the finite-state machine and the sid resource was deleted.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The
sidresource is not associated with a finite-state machine of the Flow security model object being used. - The
sidvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Flow security model enter rule
It switches the finite-state machine associated with the sid resource to the specified state.
It returns the "granted" result if the finite-state machine associated with the sid resource was switched to the specified state.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The transition to the specified
statefrom the current state is not permitted by the configuration of the finite-state machine associated with thesidresource. - The
sidresource is not associated with a finite-state machine of the Flow security model object being used. - The
sidvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
Flow security model allow rule
It verifies that the state of the finite-state machine associated with the sid is in the set of defined states.
It returns the "granted" result if the state of the finite-state machine associated with the sid resource is in the set of defined states.
It returns the "denied" result in the following cases:
- The state of the finite-state machine associated with the
sidresource is not in the set of definedstates. - The
sidresource is not associated with a finite-state machine of the Flow security model object being used. - The
sidvalue is outside of the permissible range.
Example:
Flow security model query expression
It is intended to be used as an expression that verifies fulfillment of the conditions in the choice construct (for details on the choice construct, see "Binding methods of security models to security events"). It checks the state of the finite-state machine associated with the sid resource. Depending on the results of this check, various options for security event handling can be performed.
It runs incorrectly in the following cases:
- The
sidresource is not associated with a finite-state machine of the Flow security model object being used. - The
sidvalue is outside of the permissible range.
When the expression runs incorrectly, the Kaspersky Security Module returns the "denied" decision.
Example: