Contents
- Kaspersky Container Security 1.0 Help
- About the Kaspersky Container Security platform
- Solution architecture
- Preparing to install the solution
- Solution installation
- Removing the solution
- Updating the solution
- Solution interface
- Licensing the solution
- Data provisioning
- Working with clusters
- Checking images from registries
- Integration with CI/CD
- Risk handling
- Compliance check
- Security policies configuration
- Setting up integration with external image registries
- Setting up integration with notification outputs
- Configuring LDAP server integration
- Users and roles
- Security event log
- Exporting events to SIEM systems
- Contacting Technical Support
- Sources of information about the application
- Limitations and warnings
- Glossary
- Third party code information
- Trademark notices
Kaspersky Container Security 1.0 Help
|
Hardware and software requirements Check the supported orchestration platforms, CI systems, available image registries, and user workstation requirements. |
|
Installing Kaspersky Container Security Prepare for installation and install Kaspersky Container Security in a private or public corporate network. |
|
Licensing Kaspersky Container Security Learn more about license types provided for Kaspersky Container Security. |
|
Scan objects and receive information about detected vulnerabilities, malware, misconfigurations, and sensitive data. |
|
Accepting risks identified by Kaspersky Container Security (vulnerabilities, malware, sensitive data, and misconfigurations) to change the security status of images. |
|
Security policies configuration Configure a scanner policy, assurance policies, response policies and runtime control policies to conduct tests in accordance with your requirements. |
|
Image scanning from registries and integration with CI/CD During the project build in the CI system, run the Kaspersky Container Security scanner to check the objects in the repository for compliance with the enabled security policies. |
|
Configure integrations with Telegram and email addresses to receive notifications about security events. |
|
Integration with Active Directory Configure user roles using data on groups from Active Directory |
|
Learn more about registration of user activity and storage of scan results. |
About the Kaspersky Container Security platform
The Kaspersky Container Security platform (hereinafter also referred to as "the solution") provides comprehensive protection for container environments and for applications and services implemented in containers. Kaspersky Container Security allows you to discover security problems and ensures protection throughout the container application lifecycle, from development and deployment control to runtime.
Solution functionalities:
- Integration with image registries (Docker Hub, JFrog Artifactory, Sonatype Nexus Repository OSS, GitLab Registry, Harbor) to scan images in the registry for known vulnerabilities published by the NVD and VDB (DSTD), secrets (passwords, access keys, tokens), misconfigurations, and malware.
- Integration into the continuous integration / continuous delivery (CI/CD) process as a pipeline stage, as well as scanning IaC for misconfigurations and container images for vulnerabilities, malware, and sensitive data (secrets).
- Checking of cluster nodes for compliance with industry information security benchmarks.
- Monitoring compliance with the configured security policies while building and operating the applications, including monitoring container runs in the runtime.
- Monitoring of resources used by the controlled clusters.
You can configure and access the functionalities of Kaspersky Container Security through the Management Console. The console is implemented as a web interface which can be accessed through the Chromium (Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari) or Mozilla Firefox browsers.
Distribution kit
For information about purchasing the application, please visit https://www.kaspersky.com or contact our partners.
The distribution kit includes a Helm Chart package with the containerized resources necessary for deploying and installing Kaspersky Container Security components, including the following:
- kcs-db-server — update server image that is used when deploying the solution in private corporate networks. An update server is a remote server hosting the data that is used to update Kaspersky Container Security.
- kcs-ih— image of the image handler that forwards jobs to the scanner and receives the scan results. The image handler can be scaled to fit your needs.
- kcs-scanner — image of the scan server that is used to handle object scan requests.
- kcs-middleware — image of the server part of the solution that implements business logic for data processing and provides a REST API for the graphical interface.
- nats and nats-box—images of the service that determines the ordered sequence of requests, thereby enabling the exchange of data that is segmented as messages.
- kcs-postgres — image of the database management system containing tools for analysis and optimization of request parsing and mechanisms for processing requests (rules).
- kcs-panel— image for deploying the graphical user interface of Kaspersky Container Security.
- kcs-updates—image that contains updates and is run to deliver updates when the solution is deployed in private corporate networks.
- kcs-licenses — image of the licensing service containing the text of the End User License Agreement. The End User License Agreement specifies the terms of use of the application.
- values.yaml — configuration file containing the values of settings for configuring the Helm Chart package and installing the solution.
After the Helm Chart package is downloaded, its resources are stored in the directory that you chose.
During the deployment process, the solution interface can be used to generate the following installation files in YAML format to install system agents:
- kube-agent;
- node-agent.
The information required to activate the application is sent to you by email.
Page top
Hardware and software requirements
To install and operate Kaspersky Container Security, the following hardware and software requirements must be met:
- One of the following orchestration platforms:
- Kubernetes 1.22 or later
- OpenShift 4.11 or later
- DeckHouse, versions 1.52, 1.53.
- CI system – GitLab CI.
- Pre-installed Helm package manager.
Kaspersky Container Security supports integration with the following image registries:
- GitLab 14.2 or later.
- Docker Hub V2 API or later.
- JFrog Artifactory 7.55 or later.
- Sonatype Nexus Repository OSS 3.43 or later.
- Harbor 2.х.
Image requirements (OS, version, scanned packages):
- Alpine Linux, versions 2.2—2.7, 3.0—3.18, Edge. Packages installed via apk are scanned.
- Red Hat Universal Base Image, versions 7, 8, 9. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux, versions 6, 7, 8. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- CentOS, versions 6, 7, 8. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- AlmaLinux, versions 8, 9. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- Rocky Linux, versions 8, 9. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- Oracle Linux, versions 5, 6, 7, 8. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- CBL-Mariner, versions 1.0, 2.0. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- Amazon Linux, versions 1, 2, 2023. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- openSUSE Leap, versions 42, 15. Packages installed via zypper/rpm are scanned.
- SUSE Enterprise Linux, versions 11, 12, 15. Packages installed via zypper/rpm are scanned.
- Photon OS, versions 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0. Packages installed via tdnf/yum/rpm are scanned.
- Debian GNU/Linux, versions 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12. Packages installed via apt/apt-get/dpkg are scanned.
- Ubuntu, all versions supported by Canonical. Packages installed via apt/apt-get/dpkg are scanned.
- Distroless, all versions. Packages installed via apt/apt-get/dpkg are scanned.
- RedOS, versions 7.1, 7.2, 7.3.x. Packages installed via yum/rpm are scanned.
- Astra, versions ce 2.12.x., se 1.7.x. Packages installed via apt/apt-get/dpkg are scanned.
When configuring Kaspersky Container Security with three scanner pods (kcs-ih service) and the maximum size of images to be scanned up to 10 GB, the cluster must meet the following requirements:
- At least 7 node processors
- 15 GB of RAM node capacity
- 40 GB of free disk space on a node hard drive
- At least 1 Gbps of communication channel bandwidth between cluster components
The above requirements apply to Kaspersky Container Security deployment only; they do not take into account other loads on the client's resources.
Kaspersky Container Security user workstation requirements:
- Permanent Internet connection when deployed in a public corporate network.
- Access to the Kaspersky Container Security Management Console page (address within customer's corporate network, specified during Kaspersky Container Security Server installation).
- Communication channels with at least 10 Mbit/s bandwidth.
- One of the following browsers:
- Google Chrome version 73 or later.
- Microsoft Edge version 79 or later
- Mozilla Firefox version 63 or later
- Apple Safari version 12.1 or later
- Opera version 60 or later.
Scaling
Kaspersky Container Security supports scaling for the number of scanning pods to ensure that the incoming image volume can be scanned. You can scale the number of scanning pods up or down at any time while the solution is operating.
When a scanning pod is added, the system resources increase as follows:
- The number of node processors—by 2.
- The amount of RAM on the nodes—by 4 GB.
- The amount of free disk space on a node hard drive—by 15 GB.
To scan images larger than 10 GB, the kcs-ih service resources must be increased as follows per scanning pod and for each additional GB.
- The amount of RAM on the nodes—by 300 MB.
- The amount of free disk space on a node hard drive—by 1 GB.
If the images are not scanned for configuration file errors during standard operation mode, it is not necessary to increase the RAM of the scanning pods.
Solution architecture
The Kaspersky Container Security platform consists of three main components:
- The Kaspersky Container Security Server has the following functions:
- Provides an interface for interactive management of the solution (Management Console).
- Ensures integration with external software components (SIEM, CI, image registries, LDAP, Telegram, email) and the receipt of information from them.
- Coordinates the operation of other solution components.
- Ensures the creation and management of security policies.
- Displays the results of solution operations.
- Kaspersky Container Security Agent (hereinafter also referred to as the Agent). This component runs as a containerized application and ensures the appropriate level of node security in accordance with the configured security policies, including control of the following:
- Runtime security of containers running on the nodes.
- Network interaction between pods and applications inside containers.
- Integration with the orchestration platform and flow of data necessary for analysis of the orchestrator configuration and its components.
- Startup of containers from trusted images to prevent unverified images from running.
Agents are installed to all nodes of clusters and all clusters requiring protection. Kaspersky Container Security works with two types of agents: cluster protection agents (csp-kube-agent) and node protection agents (csp-node-agent). Together they form groups of Agents. A separate group of Agents is created for each cluster. Many groups of Agents can be created for one installation of the solution.
If the cluster contains no agents, some of the solution functionality is unavailable (for example, runtime policies, resource monitoring).
- Kaspersky Container Security Scanner. This component scans configuration files and images in the connected registries, searches for and analyzes detected malware, and conducts checks when the solution is integrated into CI/CD.

Overall architecture scheme of Kaspersky Container Security
Kaspersky Container Security can be deployed in a public or private corporate network.
Scanner
Scanner is a Kaspersky Container Security software component that scans objects in real time to assess their security and detect known vulnerabilities, malware, signs of sensitive data, and misconfigurations. The scanner lets you conduct security checks based on active security policies.
Kaspersky Container Security employs the following types of scanners:
- Vulnerability scanner based on the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database
- File threat scanner within the File Threat Protection component
- Configuration file scanner
- Sensitive data (secrets) scanner
About object scans
Kaspersky Container Security checks objects deployed in the solution during the scanning process.
The scanning process searches for and analyzes threats and security risks associated with objects in the solution. Object scans must be performed regularly to keep track of emerging security threats.
When scanning, Kaspersky Container Security identifies the following security threats:
- Vulnerabilities
- Malware
- Misconfigurations
- Sensitive data
- Non-compliance with security policy requirements
Scanning process
The scanner receives scan jobs through the image handler. The image handler is an application deployed in the Kaspersky Container Security infrastructure that forwards scan jobs to the scanner and receives the scan results from the scanner.
When scan jobs are forwarded, the current status of the scanner is determined as one of the following:
- Free — the scanner is not processing objects and can accept a job from the image handler application if requested.
- Busy — the scanner is currently processing a scan job. A new job from the image handler application is put in the queue.
The scan job queue includes all forwarded scan jobs and is generated in the following cases:
- An image registry scan is manually started.
- An image registry scan is automatically started.
- A bulk scan of cluster objects is started.
Jobs in the scan queue receive the following statuses:
- Pending — status assigned by default when a job is created.
- In progress — the job is being processed by the image handler.
- Parsing results — the solution processes the job scanning results to display them in the interface.
- Error— scan job failed.
- Finished — the results of the scan job are available.
Scan tasks from the queue are submitted to the image handler in the order of their receipt. A job then goes to a scanner with Free status and is scanned for security issues. The scan results are sent back to the image handler. The job is considered completed and finished if scanning results are received. If a scan job was performed three or more times but received no results, the job is given the Error status.
Actions after scanning
After scanning, the solution displays the scan results. If security threats are detected in an object, Kaspersky Container Security prompts you to perform one of the following actions:
- Delete the security threat.
- Accept the security risk
File Threat Protection
When scanning registries and objects in CI/CD, Kaspersky Container Security uses the File Threat Protection component to search for and analyze potential file threats. The results of this malware scan are displayed together with the overall scan results.
The databases of the File Threat Protection component are updated from the Kaspersky Container Security update server.
After starting the utility, the File Threat Protection databases are downloaded and saved in the dedicated folder in the solution vendor's cloud object storage.
When the solution is deployed in a public corporate network, an update is performed directly from the update server. When installing the solution in a private corporate network, the updated File Threat Protection databases are added to the kcs-db-server container for subsequent running and updating.
Standard deployment schemes
Kaspersky Container Security supports the following deployment scenarios:
- Deployment in a public corporate network (Internet access from the Kubernetes cluster is allowed):
- Images from which the Kaspersky Container Security components are deployed are located in a public repository.
- After installation, the solution components refer to the vulnerability databases on the Internet.
- Databases are updated using the Update server on the Internet.
A private corporate network with access to servers in the allowed servers list may be considered a public corporate network.
- Deployment in a private corporate network (Internet access from the Kubernetes cluster is prohibited):
- An internal repository is used to host the images from which the Kaspersky Container Security components are deployed.
- Components are installed from a dedicated image with the vulnerability databases and security standards required to operate the solution.
- After installation, the solution components refer to vulnerability databases and security standards located in the corporate network.
- The Update server providing threat database updates is deployed as a separate component in the corporate network.
A private corporate network also allows for a deployment with a proxy server.
Deployment in a private corporate network
When deployed in a private corporate network, Kaspersky Container Security is prohibited from accessing the Internet from a cluster. The solution databases are updated by updating the images of the scanner that is run from the CI / CD and the image scanner.
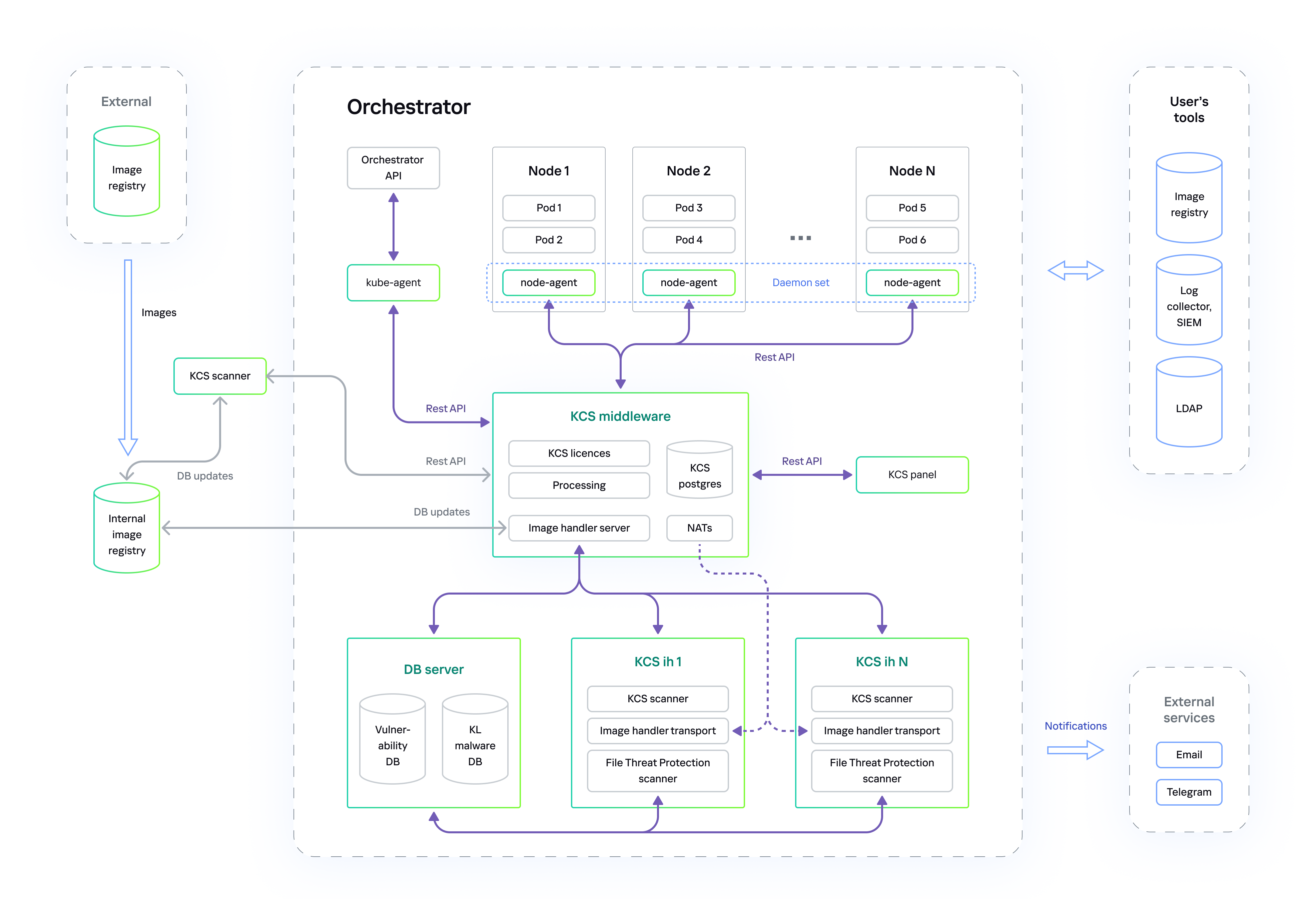
Solution architecture when deployed in a private corporate network
Page top
Deployment in a public corporate network
When deployed in a public corporate network, Kaspersky Container Security is allowed to access the Internet from a cluster. The solution databases are updated from external databases containing updates for the vulnerabilities and malware databases.
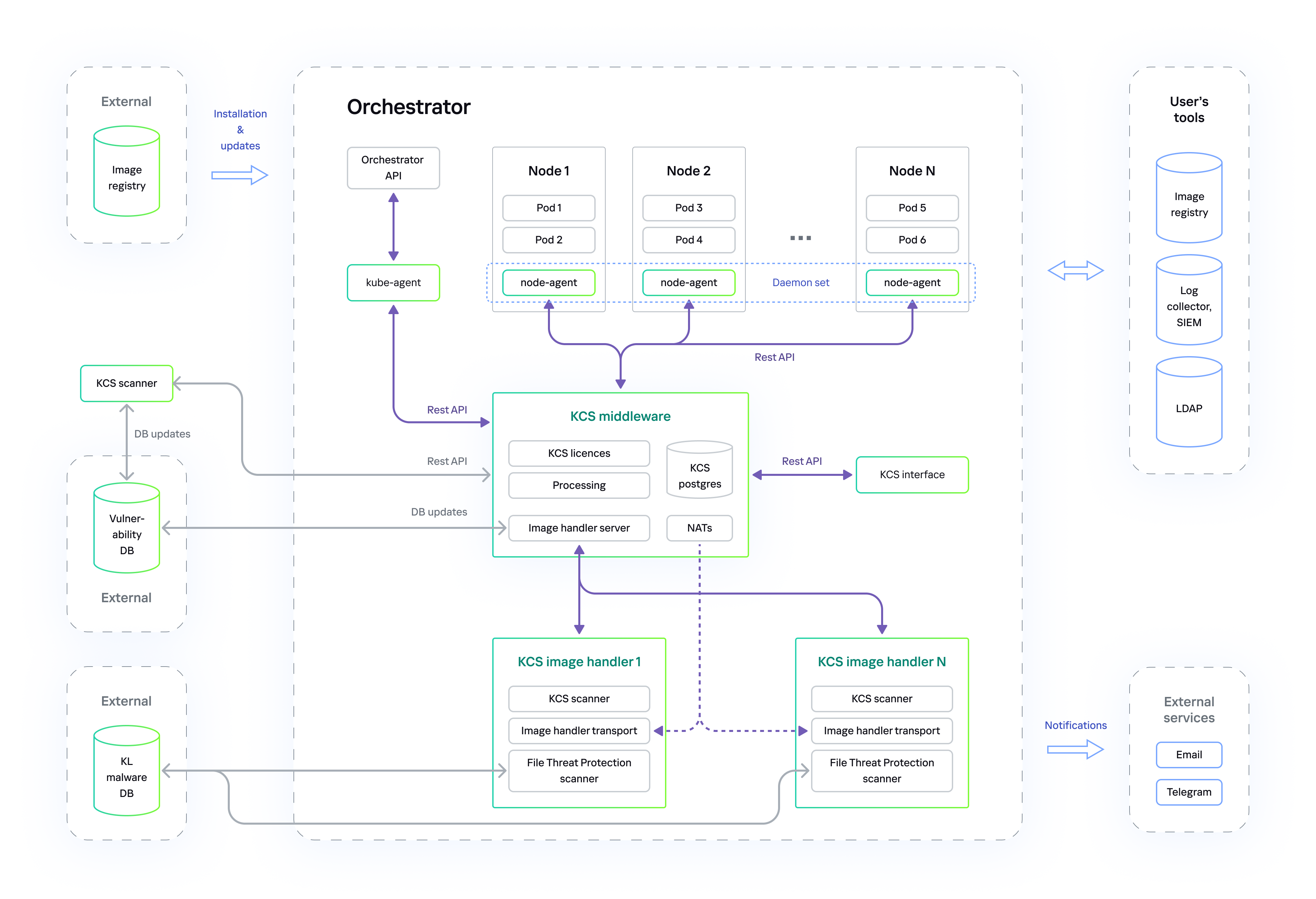
Solution architecture when deployed in a public corporate network
Page top
Preparing to install the solution
Prior to installing Kaspersky Container Security, you must install all certificates required for the corporate network and configure the proxy servers.
The solution can be deployed in a private or public corporate network.
Before installing Kaspersky Container Security, make sure that you have the following components and accesses:
- Virtual or physical machine with access to the Internet and the cluster.
- Helm package manager for packaging, configuring, and deploying applications and services in clusters.
- Internet access to download Helm Chart packages.
- Orchestrator management tool. For example, kubectl for Kubernetes or oc for Openshift.
- Access to a cluster using the kubeconfig file.
To install the solution in a private corporate network, configure a repository for container images. This repository accesses the Kaspersky Container Security vendor repository with the credentials provided by the solution vendor.
To prepare to install the solution in a private corporate network:
- Connect the vendor's Helm repository containing the Helm Chart package.
export CHART_URL="xxxxxx"export CHART_USERNAME="xxxxxx"export CHART_PASSWORD="xxxxxx"export VERSION="xxxxxx"The
CHART_URL, CHART_USERNAME, CHART_PASSWORD, and VERSIONvalues are provided by the vendor. - Fill in the file with the installation settings (values.yaml) included in the solution distribution kit according to the comments in the file.
- Save the file with the installation settings and proceed to install the solution.
Solution installation
Kaspersky Container Security components are supplied as images in the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer registry and deployed as containers.
Installation of the Kaspersky Container Security platform consists of the following steps:
- Installing the Server and Scanner components.
- First launch of the Management Console.
- Configuration of the Agent groups and Agent deployment on the controlled cluster nodes.
After installation, you should prepare the solution for operation:
- Configure integration with image registries.
- Configure integration with outputs.
- Configure security policies.
- Configure integration with CI/CD.
- Configure users and roles.
- Configure integration with LDAP server.
Installing the Server and Scanner
To install Kaspersky Container Security Server and Scanner:
After preparing the configuration file, run the solution installation:
cd kcs/
helm upgrade --install kcs . \
--create-namespace \
--namespace kcs \
--values values.yaml
Following the installation, the solution components are deployed.
The control panel will be available at the address specified in the envs subsection of the environment variables section. This allows you to create the ConfigMap object for the API_URL parameter:
http://${DOMAIN}
Viewing and accepting the End User License Agreement
When you launch the Management Console in a browser for the first time, Kaspersky Container Security prompts you to read the End User License Agreement between you and Kaspersky. To continue working with the solution, confirm that you have fully read and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement for Kaspersky Container Security.
To confirm acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement,
at the bottom of the End User License Agreement window, click the Accept button.
The authorization page opens for launching the Management Console.
After installing a new version of the solution, accept the End User License Agreement again.
Page top
First launch of the Management console
To start the Kaspersky Container Security Management Console:
- In your browser, navigate to the address specified for the Management Console during the Server installation.
The authorization page opens.
- Enter your user name and password and click the Login button.
During the installation of the solution, the user name and password have the same value assigned—admin. You can change the user name and password after launching the Management Console.
After 3 unsuccessful password entry attempts, the user is temporarily blocked. The default block duration is 1 minute.
- Following the request, change the current password for the user account: enter a new password, confirm it, and click the Change button.
Passwords have the following requirements:
- The password must contain numerals, special characters, and uppercase and lowercase letters.
- The minimum password length is 6 characters, and the maximum password length is 72 characters.
The main page of the Management Console opens.
By default, the logged-in user session in the Management Console is 9 hours. In the Settings → Authentication section, you can set your own session duration from the minimum of 1 hour to the maximum of 168 hours. After this time expires, the session ends.
You can change the connection settings in the Settings → Authentication section.
Page top
Agent deployment
You should install Agents on all nodes of the cluster that you want to protect.
To deploy Agents in a cluster:
- In the Management Console, add a group of Agents:
- In the main menu, go to the Components → Agents section.
- In the work pane, click the Add Agent group button.
- Fill in the fields in the form.
- Enter the group name and description. We recommend that you specify the name of the cluster, on the nodes of which Agents are deployed, as the group name for convenient Agent management.
- Select the type of Agent.
- Select the type of target node operating system.
- Select the orchestrator to use.
- If required, enter the deployment token, which is the identifier that the Agent uses to connect to the Server. You can enter the token or leave the field blank for the token to generate automatically.
- Click the Add button.
The right part of the work pane displays the data required to continue Agents deployment in the cluster.
- Use the instruction from the Configuration field (in the .YAML format) to deploy Agents in the cluster. For example:
kubectl apply -f
<file>-n<namespace>Following the application of the guidelines from the instruction on the cluster, the Agent is deployed on all worker nodes of the cluster.
The table in the Agents subsection displays the created group and deployed Agents. Agents server connection status is available for viewing.
Page top
Removing the solution
To uninstall the Kaspersky Container Security Server, do one of the following:
- On a workstation with the Helm package manager installed, access the Target cluster and the namespace with Kaspersky Container Security installed, and run the following command:
helm uninstall kcs-releaseThe Helm package manager does not delete PVC objects, PV objects or secrets. You should delete these manually using the following commands:
kubectl delete pvc<PVC name>kubectl delete secret<secret name>kubectl delete pv<PV name> - If Kaspersky Container Security is installed in a separate namespace, run the following command:
kubectl delete ns<namespace>
To delete the Kaspersky Container Security agent:
Run the following command on the cluster node with the agent deployed:
kubectl delete -f <file> -n kcs
where <file> is the name of the YAML configuration file used to deploy the agent.
If you delete all agents on the nodes of a cluster, we recommend that you remove the group that included these agents.
To delete a group of agents:
- In the main menu, go to the Components → Agents section of Kaspersky Container Security.
- Select the required group from the list. The Status column displays the Disconnected status for the deleted agents.
- Open the action menu from the last column of the row for the group and select Delete group.
- In the window that opens, confirm the action.
Updating the solution
You can find information about the latest versions of the application on the Kaspersky website at https://www.kaspersky.com or contact our partners.
The upgrade process is identical to the installation process. As part of the update process, the current version of the application is indicated.
Page top
Solution interface
The Management Console is implemented through the web interface and consists of the following elements:
- Main menu — sections and subsections of the main menu give access to the key functionalities of the solution.
- Work pane — information and controls in the work pane depend on the section or subsection that you select in the main menu.
Main menu
In the web interface, the main menu of Kaspersky Container Security is on the left pane and lists the main functional capabilities of the solution.
Resources
This section contains the monitoring results of all available Kaspersky Container Security resources: clusters, registries integrated with the solution, and CI/CD processes.
Components
This section contains information about the state of solution components. The Agents subsection also lets you create and delete Agent groups and view the information necessary to deploy Agents.
Compliance
This section contains the results of checks on cluster nodes for compliance with the Kubernetes benchmarks.
Policies
This section allows you to configure security policies when operating Kaspersky Container Security.
The Risk acceptance subsection contains a list of all detected threats and vulnerabilities, the risk of which is accepted by the user. In this subsection, you can cancel a risk acceptance or set the period during which a risk is considered accepted.
Administration
This section allows you to perform the following tasks:
- Manage users and user group access rights
- Set up integration with public image registries
- Set up integration with outputs
- Set up integration with LDAP server
- Manage parameters for scanning launch
Settings
This section allows you to configure the launch settings of the Kaspersky Container Security Management console and manage licensing terms.
The About subsection contains information about the version of the solution and the web address of the technical support service.
Block with the name of the current user
This block displays information about the user who logged in to the Kaspersky Container Security Management console. You can change the current user's password and exit the console using the appearing pop-up menu commands.
Page top
Dashboard
On the main Kaspersky Container Security page, you can configure the dashboard to receive up-to-date analytical data on objects that are processed by the solution. This configuration is performed using filters that let you sort information by object and period.
Analytical data is displayed using widgets or specialized tools that show analytic information.
The Kaspersky Container Security dashboard opens when logging in to an account or when clicking the area containing the logo and name of the solution above the main menu.
Applying filters
Kaspersky Container Security provides the capability to configure the dashboard using the following filters:
- Filter by period:
- For the entire period
- For the year
- For the quarter
- For the month
- For the week
- For the past 24 hours
- For a customized period
For any period you select, the time count begins from the current day. By default, information is displayed for the week.
- Filter by resource:
- All images
- All images outside of clusters
- All images in clusters
- Images of a specific cluster
- CI/CD images
By default, information is displayed for all images.
Widgets on the dashboard
Kaspersky Container Security provides analytical data on the dashboard by using widgets that are organized into groups based on data type. The following widget groups and widgets are available in Kaspersky Container Security:
- Image compliance with security policy requirements. The solution displays the following information:
- Total number of images.
- Number of images with Compliant status.
- Number of images with Non-compliant status.
- Image risk assessment. The widget provides the following information on the statuses of objects:
- Total number of images.
- Number of images with the Critical status.
- Number of images with the High status.
- Number of images with the Medium status.
- Number of images with the Low status.
- Number of images with the Negligible status.
- Number of images with the Ok status.
- Top 10 object benchmarks that most frequently result in failure of cluster nodes to comply with the Kubernetes benchmarks:
- 10 cluster node benchmarks that most frequently result in non-compliance.
- Number of cluster nodes that failed the compliance check due to the specified benchmark.
- Top 10 registries based on the number of images with maximum risk status.
- Vulnerabilities
- Top 10 detected vulnerabilities with Critical, High or Medium severity status, and the number of images containing the specified vulnerability.
- Top 10 images containing the maximum number of identified vulnerabilities with Critical and High severity status.
- Malware
- Top 10 most frequently detected types of malware and number of images containing this malware.
- Top 10 images with the maximum number of detected types of malware.
- Sensitive data
- Top 10 detected types of sensitive data with Critical, High or Medium severity status and the number of images containing this sensitive data.
- Top 10 images containing the maximum amount of detected sensitive data with Critical and High severity status.
- Misconfigurations
- Top 10 detected misconfigurations with Critical, High or Medium severity status, and the number of images containing such sensitive data.
- Top 10 images with the maximum number of detected misconfigurations with Critical and High severity status.
Object lists that specify the severity level are sorted in descending order of severity (first items on the list are objects with the highest severity status).
Specific ways to set up data display
Kaspersky Container Security interface provides the following ways to set up data displaying:
- Filtering: The filter fields are located above the data tables. Filter fields and ways to manage the filter depend on the specifics of the data to be displayed.
In some sections, you must click the filter icon to open the filter fields (
 ).
). - Sorting in ascending or descending order. In some sections, you can sort the list of data by the selected column by using the sort icon (
 ) in the column header.
) in the column header. - Search: You can search the displayed data by using the Search field that is located above the table and designated by the search icon (
 ).
). - Menu. In some tables, you can perform actions on the objects using the menu commands in the table rows. To open the menu for the selected object, click the
 icon in the row of the object.
icon in the row of the object. - Delete. You can delete objects in the solution by using the delete icon (
 ) or the Delete link that appears when selecting objects.
) or the Delete link that appears when selecting objects.
Licensing the solution
This section provides information about the general terms related to the licensing of Kaspersky Container Security.
About the End User License Agreement
The End User License Agreement is a binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab stipulating the terms on which you may use the application.
Please carefully read the terms of the End User License Agreement before you start using the application.
You can read the terms of the End User License Agreement during the Kaspersky Container Security installation.
By confirming that you agree with the text of the End User License Agreement during installation of the application, you signify your acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. If you do not accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, you must cancel installation of the application and must not use the application.
UPDATES FUNCTIONALITY (INCLUDING PROVIDING ANTI-VIRUS SIGNATURE UPDATES AND CODEBASE UPDATES), AS WELL AS KSN FUNCTIONALITY WILL NOT BE AVAILABLE IN THE SOFTWARE IN THE U.S. TERRITORY FROM 12:00AM EASTERN DAYLIGHT TIME (EDT) ON SEPTEMBER 10, 2024 IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE RESTRICTIVE MEASURES.
Page top
About the license
A license is a time-limited right to use Kaspersky Container Security as granted under the End User License Agreement.
A license includes the right to use the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement, and to receive technical support. The available functionality and application usage period depend on the type of license that was used to activate the application.
Kaspersky Container Security supports the following types of licenses:
- NFR (not for resale) is a free license for a specific period intended to familiarize the user with the application and to conduct test deployments.
- A Commercial license is a paid license that is provided when you purchase the solution.
Solution functionality depends on the type of license held. Kaspersky Container Security supports the following licenses:
- Standard license — allows for integration with image registries and platforms, security threat detection scans, risk assessment, and monitoring of object status.
- Enterprise license — in addition to the functionality of the standard license, this license also provides access to components used for the monitoring, control, and analysis of objects, misconfiguration detection and security threat protection.
When the license expires, the application continues to work but with limited functionality. For full Kaspersky Container Security functionality, you must purchase a commercial license or renew your commercial license.
Page top
About the license certificate
A license certificate is a document that you receive together with a key file or activation code.
The license certificate contains the following license information:
- License number or order number
- Information about the user who is granted the license
- Information about the application that can be activated under the provided license
- Restrictions on the number of licensing units (for example, devices on which the application can be used under the provided license)
- Start date of the license term
- License expiration date or license term
- License type
About the license key
A license key is a sequence of bits that you can use to activate and then use the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement. The license key is generated by Kaspersky experts.
You can add a license key to the application by either applying a key file or entering an activation code.
Kaspersky can block a license key over violations of the End User License Agreement. If the license key has been blocked, you have to add a different license key to continue using the application.
Page top
About the key file
A key file is a file with the KEY extension that you receive from Kaspersky. The purpose of a key file is to add a license key that activates the application.
You receive a key file at the email address that you provided when you purchased Kaspersky Container Security.
You do not need to connect to Kaspersky activation servers to activate the solution with a key file.
You can restore a key file if it has been accidentally deleted.
To restore a key file, do one of the following:
- Contact the license vendor.
- Get a key file from the Kaspersky website based on an available activation code.
About the activation code
An activation code is a unique sequence of 20 English letters and numbers. You must enter an activation code to add a license key that activates Kaspersky Container Security. Your activation code will be sent to the email address that you provided when you purchased Kaspersky Container Security.
To activate the application with an activation code, Internet access is required to connect to Kaspersky activation servers.
If you lose your activation code after activating the application, please contact the Kaspersky partner that you purchased the license from.
Page top
Application activation procedure
Application activation is the process of activating a license that grants the right to use Kaspersky Container Security until expiry.
You can activate the application by using the activation code or key file provided to you when you purchased the solution.
An activation code is used for activation when you install the solution in a public corporate network with Internet access. A key file is used for activation when you install Kaspersky Container Security in a public corporate network or private corporate network without Internet connectivity.
To activate the application with an activation code:
- In the Settings → Licensing section, click the Add license key button.
- In the window prompting you to select how you want to add the license key, select Enter activation code.
- In the Activation code field, enter the activation code and click Add.
The application is activated, and the license info page opens.
To activate the application with a key file:
- In the Settings → Licensing section, click the Add license key button.
- In the window prompting you to select how to add the license key, select Upload key file and click the Upload and add button.
- In the window that opens, select a file with the KEY extension and click Open.
The application is activated, and the license info page opens.
When activating the application, the new activation code or key file will replace the previously entered activation code or key file.
Page top
Viewing license information
You can view information about the active license in the Kaspersky Container Security web interface, in the Settings → Licensing section.
The license details page displays the following parameters:
- Licensing information. Kaspersky Container Security displays the following:
- Name of the Kaspersky partner that you purchased the license from.
- License term.
The term begins from the moment you purchase the license, not from the moment you activate the application.
- Customer information. This subsection provides data on the company that purchased the license:
- Company name
- Country where the company is located
- Email address of the customer representative
- Time period remaining until license expiration The solution displays the exact date and time of license expiration.
- Node count—maximum number of nodes and number of active nodes allowed by the license.
- Image scans per month—maximum number of image scans and completed scans allowed by the license. A month is considered to be the last 30 days (30 days from the current day).
- Functionality provided by the license. The solution displays a list of the available functionality under the license you purchased.
Renewing the license
When the license is approaching its expiration date, Kaspersky Container Security displays the following notifications:
- Notification that the license is expiring soon, indicating the time remaining until expiration. You receive this notification 30, 14, and 7 days before the license expires.
- Notification that the license is expiring and the solution will switch to limited functionality mode. This notification is sent on the day of license expiration.
In limited functionality mode, the functionality of Kaspersky Container Security is limited as follows:
- No new object scans are performed.
- The web interface does not display the new nodes added to the previously created clusters after the license expired.
- New clusters cannot be added for monitoring purposes.
- Vulnerabilities databases are not updated.
You can renew a license by applying a new activation code or by adding a new key file. To renew a license, contact the Kaspersky partner you purchased the license from.
Page top
Removing the license key
To remove the license key:
- In the Settings → Licensing section, click the Delete license key button.
- Confirm the removal by clicking the Delete button.
Data provisioning
This section contains information about the data that Kaspersky Container Security can save on the device and forward to Kaspersky during its operation.
If you use an activation code to activate Kaspersky Container Security, you agree to automatically provide information to Kaspersky as part of the regular license key status confirmation process. To confirm the license key status, Kaspersky Container Security periodically contacts Kaspersky activation servers and forwards the following information to Kaspersky:
- regional activation center identifier;
- title of the license to use the solution;
- checksum type and checksum of the license key;
- date and time when the license key was created;
- date and time when the solution license expires;
- solution license identifier;
- identifier of the information model applied when providing a license to use the solution;
- current license key status;
- license type used to activate the solution;
- unique device identifier;
- family name of the device operating system;
- solution installation identifier (PCID);
- identifier, localization, and full version of the solution;
- solution identifier obtained from the license;
- set of compatible software identifiers;
- solution rebrand identifier;
- list of legal agreements shown to the solution user;
- type and version of the legal agreement accepted by the user while using the solution.
In addition, by using the activation code, you agree to forward the following information to Kaspersky:
- activation code entered by the user to activate the solution;
- date and time on the user device;
- version, build number, update number, and revision of the device operating system;
- flag indicating that the user accepted the terms of the legal agreement while using the solution.
By using the activation code, you agree to automatically forward the data listed above to Kaspersky. If you do not agree to provide this information, use a key file to activate Kaspersky Container Security.
If you use Kaspersky update servers to download updates, you agree to automatically provide the following information:
- Identifier of the Kaspersky Container Security solution obtained from the license;
- full version of the solution;
- solution license identifier;
- type of valid license;
- solution installation identifier (PCID);
- Identifier of the solution update launch;
- processed web address.
Kaspersky can use all the obtained data to generate statistical information about the distribution and use of Kaspersky software.
Any received information is protected in accordance with legally established requirements and applicable Kaspersky regulations. Data is transmitted over encrypted communication channels.
More detailed information about the processing, storage, and destruction of information obtained during the use of the solution and transferred to Kaspersky is provided in the End User License Agreement and the Privacy Policy on the Kaspersky website.
Page top
Working with clusters
Kaspersky Container Security provides a tool for displaying and analyzing the connections between various resources within namespaces in clusters.
A cluster is a set of nodes that run applications placed in containers.
By using clusters, you can perform bulk scans of images within those clusters. When doing so, the registries found in a cluster during a scan are automatically created. Kaspersky Container Security automatically reads and records the identification data used for accessing registries in a cluster (user name, password, token), and generates a link to this object. Registries are also assigned a name in the following format: <cluster name>_<registry name>. When working with cluster objects, the received identification data is used to access the registries.
The Inventory → Assets → Clusters section displays a table of clusters where Kaspersky Container Security Agents are installed. This table indicates the number of namespaces and orchestrators included in each cluster.
Cluster resources can be scanned and visually represented only if deployed Agents are available.
Cluster resources
Kaspersky Container Security scans and displays objects included in the cluster and the links between them for all clusters with active Agents. The possible types of objects are presented in the table below.
Components of a cluster infrastructure
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
Node |
Base unit of a cluster where pods with applications are run under the management of services. In most cases, a node is a physical or virtual machine used for data processing. A cluster normally includes multiple nodes. The following types of nodes are distinguished as follows:
An Agent is added for each node. This Agent manages the node and interacts with the master node of Kubernetes. |
Pod |
Object consisting of one or more containers of an application (for example, Docker or rkt) that is deployed and run in a runtime environment with shared namespaces and resources. Resources include the following:
|
Service |
Object determining the set of pods and the access policy for them. Interaction between services and pods occurs via intermediate objects known as entry points. Services provide applications with the capability to exchange data with objects outside of the cluster. |
Endpoints |
Resource which contains the IP addresses and ports of one or more pods. A service contacts this object for communication with pods. The following types of entry points are distinguished:
|
Persistent volume |
Allocated resource for storing cluster data. Permanent storage helps prevent data loss issues in case there are problems with a pod, and allows data to be used by another pod. |
Persistent volume claim |
Mechanism for managing cluster data storage by dynamically allocating block drives with the necessary specifications and connecting them to pods. The request parameters must include the storage volume and the type of access to this storage. |
Ingress rules |
Set of rules enabling external traffic to reach services within the cluster. Ingress rules are set in the same namespace in which the services are deployed. An active Ingress controller is required to route Ingress traffic. |
Ingress controller |
Resource for balancing traffic to applications in the cluster. |
Viewing cluster resources
Kaspersky Container Security allows you to view available clusters and quickly receive consolidated information on specific groups of cluster objects. You can use a filter to define the settings for displaying objects. You can search for objects by, for example, the namespace name or the image name.
To view the resources of a cluster and their interaction schematic:
- In the Inventory → Assets → Clusters section, click the cluster name link in the table.
In the cluster viewing window that opens, resources are displayed on the following tabs:
- Namespaces
- Pods
- Visual representation
- On the Namespaces tab, in the Namespaces drop-down list, select the group of namespaces that you want to view.
The table that opens shows all namespaces of the selected group within the cluster. The following information is indicated for each namespace:
- Number of containers in the namespace.
- Number of scanned images.
- Number of processed scan tasks.
- Number of incomplete scan tasks.
- Risk assessment.
- Detected security issues.
You can click the namespace link to view the image registry for the selected namespace.
- On the Pods tab, in the Namespaces drop-down list, select the group of namespaces that you want to view:
- All namespaces.
- Agent. Kaspersky Container Security displays objects in the cluster based on the Agent that is active within them.
An object search can be performed by using a filter that allows you to define the following search parameters:
- Image name
- Pod name
- Compliance with security policy requirements
An image is assigned the Compliant status if no security issue (such as a vulnerability) is detected in that image.
- Date of last scan
- Detected risks. In this case, the search is performed on objects for which security issues were found. For example, vulnerabilities, malware, traces of sensitive data or misconfigurations were found in these objects.
For each namespace, the table that opens indicates the pod, container running agent, image, status of compliance with security policy requirements, risk assessment, and identified security issues.
You can click the link on the image name to view it in the image registry.
- On the Visualization tab, click the object icon on the cluster resource interaction schematic to open its details window.
A visual representation of cluster resources is generated if active Agents exist for this cluster.
Checking images from registries
The Resources → Assets → Registries section contains a list of images scanned by Kaspersky Container Security and the image scan results. The list includes images from registries integrated with Kaspersky Container Security. You can add images to the list automatically or manually.
The list of images is empty until you configure integration with registries and settings for pulling and scanning images for the registry in the Administration section.
The list of images is displayed as a table, the images are grouped by repositories.
You can perform the following actions in the Resources → Assets → Registries section:
- Search for images by name or checksum.
A search is conducted only in the selected active image registry. If the sought image is absent from the selected registry but is part of a different registry, the search gives no results.
- Filter the list to display images that match the specified criteria:
- Images only from the specified registries;
- Images that comply with or fail to comply with benchmarks;
- Images scanned during a specified period of time;
- Images for which the specified risks are identified.
- Start rescanning of the specified images (the Rescan button is displayed above the table after you select one or more images).
- Add images to the list and remove images from the list.
- View detailed information about the image scanning results.
Adding and removing images
Images from the registries integrated with Kaspersky Container Security can be added to the list of images automatically, in line with the configured settings for pulling and scanning images for each registry. You can also add images to the list of images from registries manually. New images are queued for scanning.
To manually add images to the list:
- In the Resources → Assets → Registries section, do one of the following:
- Select a repository from the list, open the action menu located to the right of the repository name, and select Add images.
- Click the Add images button above the table.
- Do one of the following:
- If you add images from the selected repository, select the required image tags in the window that opens and click the Add images button.
- If you add images using the Add images button above the table, in the window that opens, select a registry, a repository, one or more images and click the Add images button.
To optimize the load on image registries, a list of images in the connected registries is generated every 10 minutes. After a new image appears in the registry, its appearance in the Kaspersky Container Security interface may be delayed by the specified period.
To remove images from the list:
- In the Resources → Assets → Registries section, do one of the following:
- Select one or more images that you want to remove from the list and start removal using the Delete link located above the table.
- In the list, select the repository of images you want to delete, open the action menu on the row with the repository name, and select Delete repository.
- In the window that opens, confirm the action.
Viewing image scanning results from registries
Summary information about the scanning results for all images in the repository and each specific image is displayed in the list of images in the Resources → Assets → Registries section.
Click the image name link to open a page with detailed information on image scanning results.
The tabs at the top of the window contain the following information:
- The Risk tab provides a summary of the scanning results. If threats are detected during scanning, recommended actions to protect the image are available at the bottom of the page. Click the Rescan image button to repeat scanning of the image.
- The Vulnerabilities tab shows the vulnerabilities detected in the image. Clicking the link in the name of the vulnerability can open a detailed description of the vulnerability and find out if it has an .
Kaspersky Container Security receives a description of vulnerabilities from the connected vulnerabilities database. The description is provided in the language of the vulnerabilities database. For example, a description of vulnerabilities from the NVD is displayed in English.
The classification of vulnerabilities in the solution matches the classification used in the connected vulnerabilities database. - The Layers tab displays layers used in the image with the specification of identified vulnerabilities. Click the layer name link to open a detailed description of the identified vulnerabilities.
- The Resources tab demonstrates resources (components) with the specification of identified vulnerabilities. Click the resource name link to open a detailed description of the identified vulnerabilities.
- The Malware tab lists malware detected in the image. Click the malware name link to open a detailed description.
- The Sensitive data tab shows sensitive data (secrets) found in the image such as passwords, access keys, or tokens.
- The Misconfigurations tab displays detected image misconfigurations that constitute a threat. Click the misconfiguration name link to open a detailed description.
- The Information tab provides the basic information about the image and image history.
- The Scan history presents the latest scan results for each version of the image. The results are updated if the same version of an image is scanned, or they are added in a separate row of the table if a different version of the image is scanned.
You can accept each identified risk.
Page top
Detailed information about detected vulnerabilities
You can view detailed information about a vulnerability detected in an image. To do this, in the window with the image scan results, select the Vulnerabilities tab and click the link with the vulnerability entry identifier. The identifier is given in CVE-YYYY-X... format, where:
- CVE is a prefix that indicates that the vulnerability is included in the database of known vulnerabilities and security defects.
- YYYY is the year when the vulnerability was reported.
- X... is the number assigned to the vulnerability by authorized bodies.
A separate window displays the following information about the detected vulnerability:
- Vulnerability entry identifier
- Vulnerability severity level
- Description of the vulnerability and a link to additional information
- Installed resource
- Vulnerability severity score based on the open standard in the , , and vulnerability databases, as well as the final consolidated vulnerability severity score.
- You can accept the risk of the vulnerability by clicking the Accept button.
- Information about the scan:
- Image in which the vulnerability was detected
- Operating system that was scanned
- Date when the vulnerability was first detected
- Date when the image was last scanned
- Performed workloads
Detailed information about detected malware
If image scanning detects malware, the solution displays this on the page with information about the image scan results. To view detailed information about a detected malicious object, in the window with image scan results, select the Malware tab.
For each object, the solution generates the MD5 or SHA256 hash and indicates the path to the location where it was detected.
You can view detailed information about detected malicious objects in the cyberthreat databases created in
and . To do this, click the link to Kaspersky OpenTIP and Kaspersky TIP resources.A page with a threat description on the Kaspersky OpenTIP portal is publicly available. Users must enter their account credentials to access Kaspersky TIP.
Scan statuses
A scan conducted by Kaspersky Container Security results in the assignment of a status to the scanned object. The solution assigns one of the following statuses:
- Ok. This status is assigned if no vulnerabilities, malware, sensitive data or misconfigurations are detected in the object.
- Negligible. This vulnerability status is displayed if Kaspersky Container Security assigns it maximum severity status.
- Low.
- Medium.
- High.
- Critical. This status is assigned to an image if malware is detected during the scan.
The image is assigned the highest severity level of all detected.
If vulnerabilities, sensitive data or misconfigurations are detected, they are assigned statuses that match those indicated in the security threat databases used for the scan (for example, NVD or VDB (DSTD)). These vulnerability and threat databases use special scoring scales to assess the severity of security threats. For example, the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is applied in the NVD.
Integration with CI/CD
Kaspersky Container Security lets you scan images of containers and IaC residing in code repository management systems in the
to detect vulnerabilities, malware, misconfigurations, and exposed sensitive data.At the project build stage in the repository management system, you can run the Kaspersky Container Security scanner to check the objects in the repository for compliance with the enabled security policies. The scanner is started from a registry using an Agent, such as GitLab Runner in GitLab. Data on the scan job and sending scan results are forwarded through the application programming interface (API).
When running an object scan during the project build stage, you must make sure that the Fail CI/CD step is not selected in the settings of the applied assurance policy. If this setting is activated, the solution will notify you of an error during the scan.
The scan results are displayed in the list of images in the Inventory → CI/CD → Scanning in CI/CD section.
Image scanning in CI/CD processes
Kaspersky Container Security allows you to scan images that are used in CI/CD. The solution is incorporated into CI/CD as a pipeline stage, where the Kaspersky Container Security Scanner is run.
To scan images from CI/CD, you should configure the integration of Kaspersky Container Security with CI/CD processes.
Kaspersky Container Security performs the following types of scans in CI/CD:
- Scanning of images in TAR archives A TAR archive is stored as a build artifact that the solution scans in the next build pipeline.
- Scanning a Git repository, which can be performed in one of the following ways:
- for a project branch (individual development path) in the Git repository
- for a commit (state snapshot or checkpoint in the project's timeline)
The scanning results are forwarded to the server and displayed in the Management Console in the Resources → CI/CD section. The provided table lists the images that were scanned, shows the results of the risk assessment, and indicates the detected vulnerabilities.
You can click the image name link to open a page with detailed information about image scanning results. This page is similar to the page showing the results of registry images scanning.
Kaspersky Container Security also displays the type of artifact for each object. Two main artifacts are used:
- File system is repository containing configuration files.
- Container image is a template used for runtime implementation of the container.
The table indicates the build number and build pipeline for each scan object. These parameters can be used to determine the specific stage where the image failed.
For CI/CD images, rescanning is not provided.
Page top
Configuring image and configuration file scan settings
To scan images or repositories (in order to scan configuration files) used in the CI/CD process, add a stage to the CI/CD pipeline that runs the Kaspersky Container Security scanner. The scanning results are forwarded to the Kaspersky Container Security Server and are displayed in the Management console in the Resources → CI/CD section.
Data from listening to and intercepting network traffic must be securely transferred between the CI/CD environment and the product.
Example of configuring integration with GitLab CI/CD
This example uses a specific scanner image with the built-in vulnerability databases located in the image registry of the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer.
To use the image scanning feature in the GitLab CI/CD process, you should enable the use of the GitLab Container Registry.
Integration configuration includes the following steps:
- Authorization of GitLab CI/CD in the image registry of the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer.
- On the cluster operator's workstation, prepare a Base64 hash of the authorization data by running the following command:
printf "login:password" | openssl base64 -Awhere login and password are the user name and password of an account in the image registry of the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer.
- In the GitLab CI/CD environment variables, create the DOCKER_AUTH_CONFIG variable (in the GitLab repository select Settings → CI/CD, click the Expand button to expand Variables, and then click the Add variable button).
- Specify the variable in the following form:
{"auths": {"repo.cloud.tronsec.ru": {"auth": "base64hash"}}}where base64hash is the string obtained in step 1a.
- On the cluster operator's workstation, prepare a Base64 hash of the authorization data by running the following command:
- Authorization of requests from GitLab CI/CD when sending data to Kaspersky Container Security.
- On the cluster operator's workstation, prepare a Base64 hash of the authorization data by running the following command:
printf "login:password" | openssl base64 -Awhere login and password are the user name and password of an account in the image registry of the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer.
- Specify the resulting hash in the API_TOKEN variable in the .gitlab-ci.yml configuration file.
- On the cluster operator's workstation, prepare a Base64 hash of the authorization data by running the following command:
- Adding the image scanning stage to the CI/CD process.
To add scanning to the CI/CD pipeline, you should add the following lines to the .gitlab-ci.yml file:
- Add the information about the image for scanning after the build preparation as follows:
scan_image:stage: scannerimage:name: repo.cloud.tronsec.ru/repository/tron-customer/scanner:v1.0.1-with-dbentrypoint: [""] - Specify the tag and token for authorization of the CI/CD scanner requests to Kaspersky Container Security as follows:
variables:
SCAN_TARGET: ${CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE}:master
API_TOKEN: base64hash
The example below contains the
mastertag, you can also specify another tag. - If you configure scanning for a private repository, specify the authorization data to ensure the scanner access to an image. The authorization data can be set as variables.
TRON_EXT_REGISTRY_USERNAME: ${TRON_EXT_REGISTRY_USERNAME}
TRON_EXT_REGISTRY_PASSWORD: ${TRON_EXT_REGISTRY_PASSWORD}
- Specify the domain name of the Kaspersky Container Security Management console in your corporate network:
API_BASE_URL:
<domain name>script:
- /bin/sh /entrypoint.sh $SCAN_TARGET --stdout > artifact-result.json
artifacts:
paths:
- artifact-result.json
- Add the information about the image for scanning after the build preparation as follows:
Scanning images from CI/CD
To scan images from CI/CD, in the configuration file used to integrate the repository, specify the API_BASE_URL (web-address of the Kaspersky Container Security API server) and API_TOKEN (token to access API of the Kaspersky Container Security) environment variables for the scanner.
To scan an image from a TAR archive:
- Build an image and save it as a TAR archive using any application for creating containerized images.
- Start the scan by running a command in the following format:
/scanner image.tar --file --stdoutwhere:
<--file> is thefile with the image to be scanned<--stdout> isoutput to the security event log
Example of a configuration file with settings for scanning a TAR archive
To scan an image from a Git repository:
- In the configuration file of the Git repository, specify the token for accessing the repository (for example, GitLab requires you to indicate a value for GITLAB_TOKEN).
- Start scanning by running a command in the following format:
/scanner [TARGET] [--repo REPO_URL] [--branch BRANCH] [--commit COMMIT] --stdoutwhere:
<TARGET>is the path to the file with the image to be scanned<--repo>is the web address (URL) of the Git repository<--branch>is the branch of the repository to be scanned<--commit>isthe hash of the commit to be scanned<--stdout>is the output to the security event log.
Risk handling
Threats identified by Kaspersky Container Security (vulnerabilities, malware, sensitive data, and misconfigurations) are subject to the Risk acceptance procedure. If you accept the risk of a threat, it will not be considered by assurance policies when determining image security status (Compliant/Non-compliant with security policies) during the specified acceptance period. Image scanning continues to detect the threat, but does not label the image as Non-compliant.
If you accept the risk of a vulnerability detected in an image, this risk is accepted for the specific image registry. If the risk is accepted for all vulnerabilities in an image, the image is deemed compliant with security policy requirements and is given Compliant status.
If you change the settings of the assurance policy applied to images, the image security status also changes.
The risk from a threat is accepted for a period of 30 days by default. You can extend the period during which the risk is considered accepted. You can also cancel risk acceptance at any time. If you cancel risk acceptance, the associated threat will again affect the security status of the image.
You can view the list of all accepted risks in the Policies → Risk acceptance section.
Risk acceptance
You can accept the risks detected by the solution if they have Medium, Low or Negligible severity level. It is impossible to accept risks with High or Critical severity level.
To accept the risk:
- In the image scanning results window, open the tab with information about the required type of detected threats.
- In the table, select a threat and click Accept or Accept risk in the action menu (depending on selected tab) to start risk acceptance.
- In the window that opens, specify the risk acceptance parameters:
- Select the extent of risk acceptance:
- For the selected image with the detected risk;
- For all images in the repository containing the image with the detected security threat;
- For all images in which this security threat has been or will be detected.
- If required, specify the period after which this security threat must be considered again when determining image security status.
- Specify the reason for risk acceptance.
- Select the extent of risk acceptance:
- Click the Accept button.
The selected threat does not affect the security status of this specific image, images in the repository, or all images for the defined number of days (or for an unlimited term).
An accepted risk can be viewed in the Policies → Risk acceptance section.
Page top
Viewing information about accepted risks
The list of all accepted risks is displayed in the Policies → Risk acceptances section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Search by risk name, repository name, image, or resource where the risk is detected.
- Filter the list by risk type and manufacturer fix availability.
- Sort the list by date of acceptance, risk name, scope (applied to all images or just one image), and acceptance period. Sorting is performed using the (
 ) sort icon.
) sort icon. - View detailed information about risk acceptance and the associated threat. Click the risk name link to open the window with the related detailed information.
Use the buttons in the detailed information window to do the following:
- Specify or extend the time period after which this security threat must be considered again when determining image security status.
- Cancel risk acceptance.
You can also view information about the accepted risk in the list of detected threats in the image scanning results. In the row with the threat with accepted risk, you can find the time of risk acceptance. You can click the link to open a window with detailed information about the risk acceptance and the associated threat.
Page top
Cancelling risk acceptance
To cancel risk acceptance:
- Open the window that shows detailed information about the risk acceptance and the associated threat. You can open the window by clicking the risk name link in the list of accepted risks. Or you can click the link in the row with the security risk with accepted risk, in the list of detected security risks in the image scanning results.
- Click the Cancel risk acceptance button and confirm the action in the window that opens.
Canceling risk acceptance means that the associated threat will again affect the security status of the image(s) for which the risk was accepted.
Page top
Compliance check
Kaspersky Container Security agents can check Kubernetes cluster nodes for compliance with the Kubernetes information security benchmarks.
Kaspersky Container Security checks for compliance with the Kubernetes benchmarks on Kubernetes versions 1.15–1.25.
The agent checks the state of the node where it is installed and sends the results to the Server. Check results are displayed in the Compliance section.
You can view the results of checks on cluster nodes for compliance with the Kubernetes benchmarks in the Compliance → Kubernetes benchmarks section. Kaspersky Container Security displays a summary of the number of checks performed and their status. The solution assigns the following statuses to the checks:
- Passed—check completed successfully.
- Warning—check shows that problems may occur during the execution of operations or tasks.
- Failed—check revealed non-compliance with the benchmark.
The solution displays the node check results in the form of a table, grouping the nodes by clusters.
Click the node name link to open a page with detailed information about the results of the node check.
The solution displays summary information at the top of the window. In the table, each benchmark is correlated with node compliance status.
Click on the benchmark row to open and close a pane to the right of the table; this pane contains detailed information about the benchmark.
You can check a node against the standard benchmarks by clicking the Scan button.
Security policies configuration
Kaspersky Container Security components use the following security policies:
- Scanner policy determines the settings for scanning different types of resources. The scanner policy uses sensitive data detection rules.
- Assurance policies define Kaspersky Container Security actions to provide security if threats detected during image scanning meet the criteria specified in the policy.
- Response policies define the actions of the solution in case events specified in the policy occur. For example, Kaspersky Container Security can notify the user or delete an image with detected threats.
- Runtime policies allow you to control and, where appropriate, restrict the deployment and operation of containers on the cluster in line with your corporate security requirements.
Kaspersky Container Security applies only enabled policies during its operation. Disabled policies cannot be used during checks.
Scanner policy
Scanner policy determines the settings for scanning different types of resources.
The configured scanner policies are displayed as a table in the Policies → Scanner policy section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Change policy settings. You can open the editing window by clicking the policy name link.
You can also enable and disable policies in the edit window. Kaspersky Container Security does not use disabled policies when operating.
- Delete policies.
The release 1.0 distribution kit includes the default scanner policy. You can change the settings of this policy, but you cannot delete it. Scanner policy customization is not available.
Editing scanner policy settings
To change scanner policy settings:
- In the Policies → Scanner policies section, click the policy name link.
The policy settings editing window opens.
- If required, use the Disable / Enable toggle switch to change the policy status (enabled / disabled).
- Make changes to the policy settings. The following settings are open for editing:
- The policy's name, description, and scope.
- Vulnerability control settings. Select the check boxes for the vulnerabilities database(s) to check images against.
- Malware control settings. Select the check box if you need to scan images for malware and other file threats. This control is conducted by using the File Threat Protection component.
- Misconfiguration control settings. Select the check box if you need to check images for misconfigurations. The control is conducted with the default settings configured by the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer.
- Click Save.
Configuration of sensitive data detection rules
The list of configured rules for detecting sensitive data (hereinafter referred to as Secrets) during image scanning is displayed in the Policies → Scanner policies → Sensitive data section.
The rules are grouped into categories depending on the purpose and scope of secrets to be detected. The list of categories is determined by the Kaspersky Container Security manufacturer. Categories contain predefined rules.
You can use the list to do the following:
- View and change the settings for secrets detection rules. You can open the editing window by clicking the rule ID link.
- Add new rules to the selected category. Click the Add rule button located above the table to open the integration settings window. To add rules that do not belong to any of the preset categories, use the Other category.
- Delete rules. Check the box next to one or more rules in the list. The delete icon is then displayed.
To change the settings of sensitive data detection rules:
- In the table, in the Policies → Scanner policies → Policies section, select the scanner policy.
- In the Sensitive data section, select the necessary rules by selecting the check boxes in the rule lines.
- Use the Disable / Enable toggle switch in the Status column in the table with the list of policy rules to enable or disable this policy component.
Do not click the Save button.
Kaspersky Container Security immediately applies the changes to the sensitive data settings and displays the corresponding notification. You can also refresh the page to see the settings change.
Assurance policies
Assurance policy defines Kaspersky Container Security actions to provide security if threats detected during image scanning meet the criteria specified in the policy.
The configured assurance policies are displayed as a table in the Policies → Assurance policies section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new policies. Click the Add policy button located above the table to open the policy settings window.
- Change policy settings. You can open the editing window by clicking the policy name link.
- Enable and disable policies. Policies are disabled and enabled by using the Disable/Enable toggle button in the Status column of the table containing the list of created policies.
- Delete policies.
If you add an assurance policy, modify its settings, or delete a policy, the compliance status is reviewed (Compliant / Non-compliant) for the images to which the policy is applied.
Page top
Creating an assurance policy
To add an assurance policy:
- In the Policies → Assurance policy section, click the Add policy button.
The policy settings window opens.
- Enter a policy name and, if required, policy description.
- In the Scope field, select the scope for the image security policy from the available options.
- Specify the actions that Kaspersky Container Security should perform in accordance with the policy:
- Fail CI/CD step—if Kaspersky Container Security scanner detects threats while scanning the image in the CI/CD pipeline matching the severity level specified in the policy, the scanning ends with an error (Failed). This result is transferred to the CI system.
- Label images as non-compliant—Kaspersky Container Security labels images containing detected threats that meet the criteria specified in the policy.
- In the Vulnerability level section, configure the following settings:
- Use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to configure the scan based on the vulnerability severity level.
- Set the assigned severity level based on the vulnerability databases. You can select this from the Severity level drop-down list or specify a severity score from 0 to 10.
- Use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to configure blocking in case of specific vulnerabilities and specify these vulnerabilities in the Vulnerabilities field.
- In the Malware section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to configure scanning for malware in the image.
- In the Misconfigurations section, configure the following settings:
- Use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to configure the scan based on the misconfiguration severity level.
- Select the misconfiguration severity level from the Severity level drop-down list.
The severity level is assigned based on the vulnerability databases.
- In the Sensitive data section, configure the following settings:
- Use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to configure the scan based on the sensitive data severity level.
- Select the sensitive data severity level from the Severity level drop-down list.
The severity level is assigned based on the vulnerability databases.
- Click Save.
By default, the added policy is Enabled.
Page top
Editing assurance policy settings
To change assurance policy settings:
- In the Policies → Assurance policies section, click the policy name in the list of existing assurance policies.
The policy settings editing window opens.
- Make changes to the relevant policy settings:
- The policy's name, description, and scope.
- Actions of the solution in accordance with this policy.
- Required scans.
- Severity level of vulnerabilities detected during scans.
- Identify number of vulnerabilities for blocking purposes.
- Click Save.
Response policies
Response policy defines the actions of the solution in the case that events specified in the policy occur. For example, Kaspersky Container Security can notify the user about the detected threats.
If you want to configure response policies to notify the user, you should first set up integration with notification outputs.
The configured response policies are displayed as a table in the Policies → Response policies section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new policies. Click the Add policy button located above the table to open the policy settings window.
- Change policy settings. You can open the editing window by clicking the policy name link.
- Enable and disable policies. Policies are disabled and enabled by using the Disable/Enable toggle button in the Status column of the table containing the list of created policies.
If you disable a policy, Kaspersky Container Security will not perform the actions specified in that policy.
- Search for policies. To find a policy, use the search field above the list of response policies to specify the policy name or part of it.
- Delete policies.
In this version of the solution, response policies define only the actions that Kaspersky Container Security takes to notify the user when a specific event detailed in the policy occurs. For example, if an object with a critical vulnerability is detected, the solution can send an email notification to the user.
Page top
Creating a response policy
To add a response policy:
- In the Policies → Response policies section, click the Add policy button.
The policy settings window opens.
- Enter a policy name and, if required, policy description.
- In the Scope field, select the scope for the response policy from the available options.
- In the Trigger field, use the drop-down list to select an event that will trigger Kaspersky Container Security to notify the user if this event occurs during a scan. One of the following events can be selected as a trigger event:
- Sensitive data. A notification is sent if the solution detects signs of exposed sensitive data in an object during a scan.
- Non-compliant. Kaspersky Container Security notifies you if a scanned object contains images that do not comply with the requirements of security policies.
- Critical vulnerabilities. A notification is sent if a scanned object contains vulnerabilities with the Critical status.
- Malware. A notification is sent if a scan finds malware.
- Risk acceptance expiration. Kaspersky Container Security notifies you if a scanned object contains risks that you had previously accepted but the risk acceptance period has expired.
- Configure the required notification methods:
- Select an Output: Email or Telegram.
- From the drop-down list in the Integration name field, select the name of the pre-configured integration with the selected notification output.
- To add another notification method, click the Add button and fill in the fields as described in paragraphs a and b above.
- If required, you can remove the added notification methods by clicking the icon located to the right of the Integration name field.
- Click Save.
By default, the added policy is Enabled.
Page top
Editing response policy settings
To change response policy settings:
- In the Policies → Response policies section, click the policy name in the list of existing response policies.
The policy settings editing window opens.
- If necessary, make changes to the relevant policy settings:
- Change the policy name.
- Add or edit the policy description.
- Add or edit the policy scope.
- Change the trigger event by selecting it from the drop-down list.
- Add an output by clicking the Add button.
- Delete the output by clicking the delete icon (
 ) located next to the line of the selected output.
) located next to the line of the selected output.
- Click Save.
Runtime control policies
A runtime policy determines the actions that are taken by the solution when monitoring and controlling runtime operations of containers in accordance with the security policies. Kaspersky Container Security maintains control based on security threats detected in an image, the severity level of these threats, and the availability of
.Containers in the runtime may run from verified images or from images that are still unknown to the solution.
The configured runtime policies are displayed as a table in the Policies → Runtime policies section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new policies. Click the Add policy button located above the table to open the policy settings window.
- Change policy settings. You can open the editing window by clicking the policy name link.
- Enable and disable policies. Policies are disabled and enabled by using the Disable/Enable toggle button in the Status column of the table containing the list of created policies.
Kaspersky Container Security does not use disabled policies when operating.
- Search for policies. To find a policy, use the search field above the list of response policies to specify the policy name or part of it.
- Delete policies.
Creating a runtime policy
To add a runtime policy:
- In the Policies → Runtime policies section, click the Add policy button.
The policy settings window opens.
- Enter a policy name and, if required, policy description.
- In the Mode section, select one of the following policy enforcement modes:
- Audit. In this mode, a scan takes into account the contents of containers.
- Enforce. In this mode, the solution blocks all objects that do not comply with the rules and criteria defined in the policy.
- In the Scope section, define the policy enforcement scope. In the Clusters field, select the applicable group of clusters from the drop-down list.
If necessary, define exclusions for which the runtime policy will not be applied. To do so, select the relevant objects from the drop-down list, specify their names, then click Add.
Existing exclusions in the policy are checked when deploying a container.
- In the Best practice check section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to activate the scan for compliance with best security practices. From the list of settings, select the scan settings that guarantee that the correct image is run and that the CPU and RAM usage settings are correctly configured.
- In the Block non-compliant images section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to prevent containers running from images that do not comply with the requirements. This check will be performed only for scanned images that are registered in the solution and have the Compliant status.
- In the Block unregistered images section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to block an image check if the image is unknown and has not been fully scanned by Kaspersky Container Security. To deploy the image, you must register it in the solution and wait for it to appear in the registry.
- In the Capabilities block section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to activate a usage lock of defined system functions of Unix. To do so, select specific system functions from the drop-down list. You can also lock the use of all system functions of Unix by selecting ALL from the drop-down list.
- In the Limit container privileges section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to activate blocked startup of containers with a specific set of rights and permissions. From the list of settings, select the settings of rights and permissions to lock the settings of pods.
- In the Registries allowed section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to set the permission to deploy containers in a cluster only from specific registries. To do so, select the relevant registries from the Registries drop-down list.
- In the Volumes blocked section, use the Disabled / Enabled toggle switch to prevent the selected volumes from being mounted in containers. To do so, specify the names of the relevant volumes in the Volumes field.
- Click Save.
By default, the added policy is Enabled.
Page top
Editing runtime policy settings
To change runtime control policy settings:
- In the Policies → Runtime policies section, click the policy name in the list of existing runtime policies.
The policy settings editing window opens.
- Change the policy name.
- Add or edit the policy description.
- Make changes to the relevant sections of the policy:
- Mode.
- Scope.
- Bypass criteria.
- Best practice check.
- Block non-compliant images.
- Block unregistered images.
- Capabilities block.
- Limit container privileges.
- Registries allowed.
- Volumes blocked.
- Click Save.
Deleting policies
To delete a policy:
- Open the list of configured scanner policies, assurance policies, response policies or runtime policies.
- In the line containing the name of the policy that you want to delete, click the delete icon (
 ).
). - In the window that opens, confirm the action.
Setting up integration with external image registries
Kaspersky Container Security can scan images from the following external image registries:
- Docker Hub
- JFrog Artifactory
- Sonatype Nexus Repository OSS
- GitLab Registry
- Harbor
You should integrate Kaspersky Container Security with external registries containing images to be scanned. Images from registries integrated with Kaspersky Container Security can be scanned automatically or manually, depending on the configured image pulling and scanning settings for each registry.
Viewing information about integrations with registries
You can view a list of all registries integrated with Kaspersky Container Security in the Administration → Integrations → Image registries section.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new registry integrations. Click the Add registry button located above the list to open the registry settings window.
- View and modify registry integration settings, including image pull and scan settings. You can open the editing window by clicking the registry name link.
- Delete integrations with registries.
Adding integrations with external image registries
To add an integration with an external registry:
- In the Administration → Integrations → Image registries section, click the Add registry button.
The integration settings window opens.
- On the Registry details tab, specify the settings for connection to the registry:
- Enter the name of the registry.
- If required, enter a description of the registry.
- Select the registry type from the drop-down list.
- If you set up JFrog Artifactory registry integration, to access Docker, in the Repository Path method drop-down list, select one of the following methods:
- Repository path.
- Subdomain.
- Port.
- If you set up a JFrog Artifactory, Harbor, or Sonatype Nexus Repository OSS registry integration, enter the full web address of the registry. We recommend that you use HTTPS connection (HTTP connection is also supported).
If you use HTTP or HTTPS with a self-signed or invalid certificate, you should check the insecure-registry box for the Docker engine on the nodes where the server and scanner are installed.
- If you set up a Gitlab Registry registry integration, provide the full web addresses (URLs) of the registry and registry API.
- If you set up a registry integration for Docker Hub or JFrog Artifactory, choose an authentication method: with an account or API key. For Sonatype Nexus Repository OSS registries, you can only use authentication with an account.
- Specify the data required for authentication.
- Go to the Image scan details tab and specify the scan timeout for scanning images from this registry (in minutes).
If image scanning lasts longer than the specified time, the scanning stops and the image is returned to the scanning queue. The solution will requeue the image up to 3 times. This means that the time required to scan an image from the registry may be tripled.
- Configure the image pull and scan settings for the registry. By default, the Manual option is selected in Pull and scan images: images are not automatically pulled from the registry, but the user can manually add images to the list of images for scanning. New images are automatically queued for scanning.
If you want images to be pulled from the registry and queued for scanning automatically, select Automatic in Pull and scan images and configure the settings for image pulling and scanning. The following options are available:
- Scan timeout—a block of settings that determine the frequency at which images are pulled from the registry for scanning. The time is specified in accordance with the time of the node on which the Kaspersky Container Security Server is deployed.
- Rescan images—if you check this box, images that were previously pulled from the registry are rescanned each time new images are scanned.
- Name/tag criteria—you can use name criterion and/or image tag pattern to specify which images to pull and scan. If you check the box, Kaspersky Container Security will only pull those images that match the specified patterns for scanning.
You can use criteria in the following patterns:
- by image name and tag – <name><:tag>
- by image name only – <name>
- by image tag only – <:tag>
For example:
- for the
alpinepattern, all images with the name "alpine" are pulled, regardless of the tag; - for the
4pattern, all images with tag 4 are pulled, regardless of the image name; - for the
alpine:4pattern, all images with the name "alpine" and tag 4 are pulled.
When generating criteria, you can use the * character, which replaces any number of characters.
To add a criterion, enter it in the field and click the Add button. You can add one or more criteria.
- Additional conditions for image pulling.
- If no additional conditions are required, select No additional conditions.
- Images created within – select this option if you want to only pull images created within a specific period (for a specified number of days, months, or years). Specify the duration of the period and the unit of measurement in the fields on the right. By default, the period is 60 days long.
- Latest - select this option if you want to only pull images with the latest tags (from the date of the image creation). In the field on the right, specify the number of latest tags to consider.
- Never pull images with the name/tag pattern - using image name/tag patterns you can specify, which images are excluded from pulling and scanning.
- Always pull images with the name/tag pattern—using image name/tag patterns you can specify, which images are always pulled and scanned, regardless of other conditions set above.
- Click the Save button in the top of the window to save the registry integration settings.
Deleting integration with external registry
To delete an integration with an external registry:
- In the Administration → Integrations → Image registries section, select the integration you want to delete by selecting the check box in the row with the registry name. You can select one or more integrations.
- In the line containing the name of the integration with the image registry that you want to delete, click the delete icon (
 ).
). - In the window that opens, confirm the action.
Kaspersky Container Security does not scan images from a registry it is no longer integrated with.
Page top
Setting up integration with notification outputs
Kaspersky Container Security can notify users about events while operating in accordance with the response policy settings. To use the notification feature, you should set up an integration of Kaspersky Container Security with one or more notification outputs.
Kaspersky Container Security can use the following outputs:
- Telegram instant messaging system
Viewing the list of email integrations
To open a list of configured email integrations,
go to the Administration → Integrations → Notifications section and select Email integrations.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new email integrations. Click the Add button located above the list to open the integration settings window.
- View and change email integration settings — you can open the editing window by clicking the integration name link.
- Search for an email integration — to perform this search, enter the integration name in the Search field.
- Delete email integration.
Adding email integrations
To add an email integration:
- Do one of the following:
- Under Administration → Integrations → Notification, in the Email integration section, click the Add new button.
- In the Administration → Integrations → Notifications section, select Email integrations. In the window that opens, click the Add button located above the table.
The integration settings window opens.
- Specify the following information in the form:
- Name of the integration — displayed in the response policy settings.
- User name and password of the account used to send messages.
- SMTP server name.
- E-mail encryption method.
- Port that the SMTP server uses.
- Email address of message sender.
- Email addresses of message recipients. You can enter one or more addresses in this field.
- Click the Save button in the top of the window to save the email integration settings.
Example email integration settings
You can use the configured integration in response policies.
Page top
Viewing information about email integration
To view and change an email integration:
- In the Email integrations section under Administration → Integrations → Notifications, click the integration name link in the list of integrations.
- In the editing window that opens, change the following integration settings if necessary:
- Name.
- User name.
- Password of the user account that is used to send messages.
- SMTP server name.
- E-mail encryption method.
- Port that the SMTP server uses.
- Email address of the message sender.
- Email addresses of message recipients.
- Click Save.
Viewing list of Telegram integrations
Integration with Telegram allows you to configure messaging in the chat with the Telegram bot.
To open the list of the configured Telegram integrations, go to the Administration → Integrations → Notifications section, and select Telegram integrations.
You can use the list to do the following:
- Add new Telegram integrations. Click the Add button located above the list to open the integration settings window.
- View and change Telegram integration settings — you can open the editing window by clicking the integration name link.
- Delete integration with Telegram.
Adding Telegram integrations
To add a Telegram integration:
- Do one of the following:
- Under Administration → Integrations → Notifications, in the Telegram integration section, click the Add new button.
- In the Administration → Integrations → Notifications section, select Telegram integrations. In the window that opens, click the Add button located above the table.
The integration settings window opens.
- Specify the following information in the form:
- Name of the integration — it is displayed in the response policy settings.
- ID of the chat to post the messages — you can get the ID in the following way:
- Write the first message to the message bot. The chat ID is generated the first time a message is sent.
- In the address bar of your browser, type:
https://api.telegram.org/bot<token>/getUpdateswhere <token> is the token of the message bot.
- In the received .json response file, find the "ID" value in the "chat" object. This is the chat ID.
After changing the message history visibility settings for new participants in a Telegram chat, the chat ID is also changed. In this case, you must change the Telegram integration settings and specify the new value for the chat ID.
- Token of the message bot — you receive this token as a result of executing the
/newbotcommand in the BotFather bot to create a bot. You can also get the token of a previously created bot by running the/tokencommand.
- Click the Save button in the top of the window to save the Telegram integration settings.
Example Telegram integration settings
You can use the configured integration in response policies.
Page top
Viewing and editing information about Telegram integration
To view and change a Telegram integration:
- In the Telegram integrations section under Administration → Integrations → Notifications, click the integration name link in the list of integrations.
- In the opened editing window, change the following integration settings if necessary:
- Name.
- Chat ID.
- Bot token.
- Click Save.
Deleting integrations with notification outputs
To delete email integration or Telegram integration:
- Open the list of the configured email integrations or Telegram integrations.
- In the line containing the name of the integration that you want to delete, click the delete icon (
 ).
). - In the window that opens, confirm the deletion.
You cannot delete an integration that is used in one or more response policies.
Page top
Configuring LDAP server integration
Kaspersky Container Security lets you connect to servers of external
that are used in your organization . This is an integration with a specific group in .Connection to an external directory service over the LDAP protocol enables you to perform the following tasks:
- Configure user accounts to take into account data from an external directory service for working with Kaspersky Container Security.
- Correlate user roles in Kaspersky Container Security to groups of users from Active Directory. Users in these groups will be able to use their domain account credentials to log in to the solution web interface and access application functionality based on their assigned role.
We recommended that you create these user groups in Active Directory in advance to allow them to complete authorization using their domain accounts in the Kaspersky Container Security web interface.
An email address must be indicated for user accounts in Active Directory.
Creating LDAP server integration
To create an integration with an LDAP server:
- In the Administration → Integrations → LDAP section, click the Connect server button.
The LDAP server settings window opens.
- Specify the following mandatory settings in the form fields:
- Web address (URL) of your company's LDAP server.
The web address of the LDAP server is specified as follows:
ldap://<host>:<port>. For example:ldap://ldap.example.com:389. - Base distinguished name is a name that uniquely identifies and describes a record of the LDAP directory server.
For example, the distinguished name for example.com is
dc=example, dc=com. - Distinguished name of the local user that is associated with the selected Active Directory record and required to access Active Directory.
- Group filter for defining the group search settings in Active Directory.
- User filter for defining the user search settings in Active Directory.
- Web address (URL) of your company's LDAP server.
- Under Base schema, specify the values of the following attributes and classes of objects:
- Object class is the type of object to search for.
- Organizational unit class is the LDAP object class that identifies the object as a container object within the domain.
- User class is the LDAP object class that identifies the object as a user.
- Organization unit name is the attribute of a group that identifies its name.
- Group class is the class that identifies the LDAP object as a group.
- Distinguished name is the distinguished name of the record.
- Under User settings, specify the values of the following object attributes:
- User first name.
- Last name of the user.
- Group name.
- User username.
- User password.
- Group member.
- User email address.
- User member of.
- Click the Save button above the form for LDAP server integration data.
- To verify that the values were filled in correctly, click the Test connection button above the form for LDAP server integration data.
Kaspersky Container Security will display a notification informing you of the successful connection to the LDAP server or a failure to establish the connection.
Example of completed fields when configuring LDAP server integration
If the LDAP server certificate changes, reconfigure the integration.
You can use the configured integration when creating and assigning user roles.
Page top
Viewing and editing information about LDAP server integration
To view the LDAP server connection:
Go to the Administration → Integrations → LDAP section.
Kaspersky Container Security displays the web address of the connected LDAP server above the Test connection, Change settings, and Delete integration buttons.
To change the settings for the connection to the LDAP server:
In the Administration → Integrations → LDAP section, click the Edit settings button.
Kaspersky Container Security opens the page containing the form for LDAP server integration data.
Page top
Testing connection with LDAP server
To test connection with the LDAP server:
- Go to the Administration → Integrations → LDAP section.
- Do one of the following:
- If the integration with the LDAP server is created, click the Test connection button.
- If you are creating an integration with an LDAP server, click the Test connection button above the form for LDAP server integration data.
Kaspersky Container Security will display a notification informing you of the connection to the LDAP server or a failure to establish the connection.
Gaining access to Active Directory group
After the integration with the LDAP server is configured, you can specify an Active Directory group for each Kaspersky Container Security role. After authorizing their account credentials, the users from this group gain access to solution functionality based on their defined roles.
Page top
Users and roles
This section describes how to manage users and user roles, and provides instructions on creating, editing, and deleting them.
Managing users
Multiple users can have access to Kaspersky Container Security. A user account is created for each user, and one or more user roles are assigned to them.
The list of Kaspersky Container Security users is displayed in the table in the Administration → Access management → Users section.
You can do the following:
- Add users.
- View and edit user account settings.
- Reset password for the selected accounts.
- Delete users.
- Sort values in the list of users by clicking the
 icon in the corresponding column (displayed user name, user name, assigned role). Sorting can be done in alphabetic order and reverse alphabetical order.
icon in the corresponding column (displayed user name, user name, assigned role). Sorting can be done in alphabetic order and reverse alphabetical order. - Search by user name by using the Search by user name field above the table.
About user roles
A user role in Kaspersky Container Security is a set of permissions to perform certain actions in the solution web interface. Depending on their role, users have access to different sections and functional capabilities.
Kaspersky Container Security provides user roles as well as system roles, which have predefined sets of access permissions to perform common tasks for protecting container environments.
The following system roles are provided during initial installation of the solution:
- The Administrator of Kaspersky Container Security role is intended for users who are tasked with deploying and supporting the infrastructure and system software required for the solution to work (for example, operating systems, application servers, and databases). These users manage user accounts, roles and access permissions in Kaspersky Container Security.
In the web interface, this role is indicated by the KCSADM abbreviation.
- The Information Security Administrator (IS Administrator) role is intended for users who are tasked with creating and managing user accounts, roles and access permissions of users, changing settings, connecting public image registries, Agents and outputs, and configuring security policies.
In the web interface, this role is indicated by the ISADM abbreviation.
- The IS auditor role is intended for users who view the resources and user list of a solution, and who monitor the results of scans and compliance checks.
In the web interface, this role is indicated by the ISAUD abbreviation.
- The IS officer role is intended for users who view and manage security policies, connect public image registries, and view the results of runtime container analyses for projects in which these users are directly involved.
In the web interface, this role is indicated by the ISOFF abbreviation.
- The Developer role is intended for users who perform compliance checks and view the results of scanning images from registries and CI/CD, cluster resources and accepted risks.
In the web interface, this role is indicated by the DEV abbreviation.
You can assign system roles to user accounts when creating or viewing these user accounts.
Multiple user roles can be assigned to a user.
If a specific system role is not needed, you can delete it.
However, you cannot delete the last active system role that has permissions to manage other roles.
If the available system roles do not offer the required access permissions, you can create your own unique sets of permissions as custom roles.
When creating custom roles, consider the necessary set of permissions for accessing related functionalities. For example:
- To view and configure the settings of the response policies, you need permission to view integrations with notification services. If this permission is not granted, Kaspersky Container Security will display an error when you try to configure a response policy.
- Permissions to manage response policies must be granted with permissions to manage notifications, otherwise, you will not be able to select the outputs in the policy settings.
- To create a user, you need permission to view and manage roles. If such permission is not granted, only the dashboard is displayed to the created user.
- The permission to manage users must be granted together with the permission to manage roles, otherwise you will not be able to assign a role when creating a user.
You can assign user roles to user accounts just like with system roles. In addition, you can also change the settings of user roles and delete user roles.
When assigning the scopes to roles, you must take into account that a security policy can be implemented within a specific scope only if this scope is assigned to one of your roles.
If you integrated the solution with an LDAP server, Kaspersky Container Security also receives and displays the roles and user groups from the Active Directory service.
Page top
Working with system roles
The table below lists the main actions that are available to users with system roles in the Kaspersky Container Security web interface.
User roles and their available actions
Action |
Administrator of Kaspersky Container Security |
IS Administrator |
IS auditor |
IS officer |
Developer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
View image scan results |
|
|
|
|
|
Manually start scanning images |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage risks (accept a risk, edit a risk and cancel risk acceptance) |
|
|
|
|
|
View risks |
|
|
|
|
|
View clusters |
|
|
|
|
|
View registries |
|
|
|
|
|
Add an image to a registry |
|
|
|
|
|
Delete a repository/image from a registry |
|
|
|
|
|
View CI/CD |
|
|
|
|
|
View Agents |
|
|
|
|
|
View standards |
|
|
|
|
|
Start benchmark compliance check |
|
|
|
|
|
View policies |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage policies |
|
|
|
|
|
View the list of users |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage users, roles and permission sets |
|
|
|
|
|
View image registry integrations |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage image registries |
|
|
|
|
|
View integrations with notification services |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage integrations with notification services |
|
|
|
|
|
View connection settings |
|
|
|
|
|
Manage LDAP server integration |
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying the list of roles
Kaspersky Container Security displays the list of active roles in the Administration → Access management → Roles section.
The table presents all active system roles and user roles while indicating their ID, name, and user assigned the specific role.
Page top
Adding users and roles
To add a user account:
- In the Administration → Access management → Users section, click the Add user button above the list of users.
- In the window that opens, specify the following settings:
- User name is a unique value that must be assigned to a user for identification within Kaspersky Container Security.
A user name can include only letters of the English alphabet and numerals. The minimum user name length is 4 characters, and the maximum user name length is 254 characters.
- Display name (optional) is the value that is displayed in the solution web interface. If this parameter is not specified, the user name is displayed in the web interface.
- Email (optional).
- User name is a unique value that must be assigned to a user for identification within Kaspersky Container Security.
- Enter the password in the Password field.
Passwords have the following requirements:
- The password must contain numerals, special characters, and uppercase and lowercase letters.
- The minimum password length is 6 characters, and the maximum password length is 72 characters. The default password length is 8 characters.
- Confirm the entered password in the Confirm password field.
- Select the check box if the user should change the password the next time the solution starts.
- Assign a role to the user by selecting from the list of available roles.
While you are not required to assign a role when creating a user, a new user without an assigned role will not be able to interact with Kaspersky Container Security.
- Click Add.
To add a user, permission to view and configure settings is required. If you do not have this permission, any user you add will only be able to view the main page of the solution.
To add a user role:
- In the Administration → Access management → Roles section, click the Add role button above the list of roles.
- In the window that opens, specify the following values:
- Role ID is a unique value that must be assigned to a role for identification within Kaspersky Container Security.
The role ID can include uppercase Latin letters and numbers. A role ID cannot contain special characters or spaces.
- Role name is the value displayed in the solution web interface.
- Description (optional).
- Role ID is a unique value that must be assigned to a role for identification within Kaspersky Container Security.
- In the Active Directory mapping field, specify the Active Directory groups that the user belongs to.
- Select the check boxes next to the permissions that will be available for the role being added.
- Click Add.
Editing the settings of users and roles
To edit a user account:
- In the Administration → Access management → Users section, click the user name in the list of users.
- In the window that opens, make the necessary changes.
If you make changes to a user account with the administrator privileges, do not delete all roles, since doing so results in the loss of administrator access to the solution.
- Click Save.
To edit a user role:
- In the Administration → Access management → Roles section, click the role identifier in the Role ID column in the list of roles.
- In the opened window, make the necessary changes.
- Click Save.
After a role is modified, all users having the role assigned, must be reauthorized.
Resetting the password for user accounts
To reset the password for a user account,
- Go to the Administration → Access management → Users section.
- Do one of the following:
- In the user list, select the row of the specific user account, then click the Reset password link above the table.
- In the user account row, open the menu (
 ) and select Reset password.
) and select Reset password.
Deleting users and roles
To delete a user account:
- In the Administration → Access management → Users section, do one of the following:
- Select the user from the row of the specific user account, then click the Delete link above the table containing the list of users.
You can select one or more user accounts.
- In the row with the user account, open the menu (
 ) and select Delete user.
) and select Delete user.
- Select the user from the row of the specific user account, then click the Delete link above the table containing the list of users.
- In the window that opens, confirm deletion by clicking Delete.
The user account used for authorization in Kaspersky Container Security cannot be deleted.
To delete a user role:
- In the Administration → Access management → Roles section, in the role row in the list of roles, click the deletion icon (
 ).
). - In the window that opens, confirm deletion by clicking Delete.
The last active system role that has permissions to manage other user roles cannot be deleted.
It is also impossible to delete a role that is assigned to a specific user.
Security event log
In the Administration → Events section, Kaspersky Container Security displays the occurred events that can be used for informational purposes, to track ongoing processes, to analyze security threats, and to determine what caused the solution failures.
Kaspersky Container Security displays the following types of events:
- Audit events. This group of events includes user activity audit data, such as information about configured settings of the solution, user authentications, changes in groups, and modifications or deletion of information within the solution.
- Solution operating results. These events include alerts about a triggered response policy.
- Records of the internal operations of solution applications.
Kaspersky Container Security shows the following security event categories:
- Administration—all events related to solution administration are logged.
- Policies (scanner policies, assurance policies, response policies, runtime policies) — events related to compliance or non-compliance of an image with applicable policies.
- Malware — events that occur when malware is detected during a scan of images and nodes.
- Sensitive data — events related to the detection of exposed sensitive data during a scan (for example, scanned images, functions, and nodes).
- Non-compliance — the following events are recorded:
- Detection of non-compliant images.
- Functions that do not comply with requirements, and runtime implementation of these functions.
- Nodes that do not comply with requirements, and runtime actions of these nodes.
A list of security events is displayed for a specific period. You can select one of the provided options or define your own time period. For any period you select, the time count begins from the current day. Events for the last week are displayed by default.
Kaspersky Container Security displays the events that occurred during scans. The events are displayed as a table for the following components:
- Administration.
- Alerts.
- CI/CD.
- Policies.
- Resources.
- Runtime.
- Scanners.
For each event, the table indicates the date and time of the event, IP address of the user, description, and status. The user name is listed for some events, such as those involving Administration, Malware, and Sensitive data categories. The security threat level is also indicated for Alerts. For events related to the Scanners component, the identifiers generated by the solution and the status of the scan jobs are also logged. For Runtime, indicate the mode (Audit or Block), cluster, and deployed pod.
The security event log of Kaspersky Container Security is maintained and stored in PostgreSQL and does not have data protection mechanisms.
Exporting events to SIEM systems
Kaspersky Container Security allows you to send event messages to
for collection, analysis, and subsequent response to potential threats. The messages contain data for the same types and categories of events that are logged in the security event log.The data about the system events is transmitted as the integration with the SIEM system is configured during the installation of the solution. Event messages are forwarded to the SIEM registration server in the CEF format over TCP or UDP using the provided port (typically port 514). When the solution is deployed, these parameters are specified in the values.yaml configuration file:
CEF_PROTOCOL=tcp
CEF_HOST=<ip address>
CEF_PORT=<port>
The transmitted message consists of the following components:
- The header, which specifies the date, time, and host name.
- Prefix and CEF version number.
- Device vendor.
- Solution name.
- Solution version.
- Solution-generated unique event type code.
- Event description.
- Event severity assessment.
- Additional information, such as device IP address, event reason, event result, and event status.
Example of a message forwarded to a SIEM system
Page top
Contacting Technical Support
If you cannot find a solution to your problem in the application documentation or in other sources of information about the application, you should contact Technical Support. Technical Support experts will answer your questions about installing and using the application.
Kaspersky provides technical support for this application throughout its lifecycle (please refer to the product support lifecycle page). Before contacting Technical Support, please read the technical support rules.
You can contact Technical Support experts in one of the following ways:
- Visit the Technical Support website.
- Submit a request to Kaspersky Technical Support through the Kaspersky CompanyAccount portal.
Sources of information about the application
Kaspersky Container Security page on the Kaspersky website
On the Kaspersky Container Security page, you can view general information about the application, its functions and features.
Discussing Kaspersky applications on the Forum
If your question does not require an immediate answer, you can discuss it with Kaspersky experts and other users on our Forum.
On this Forum, you can view existing threads, leave your own comments, and create new discussion threads.
Page top
Limitations and warnings
Kaspersky Container Security 1.0 has a number of limitations that are not critical to the operation of the solution:
- If you need to run many image vulnerability scans, we advise you to disable the misconfiguration scan option in the scanner policy because this operation may consume a substantially greater number of resources, especially when working with large-sized images.
- If the misconfiguration control is enabled in the scanner policy for the scanner operation, scanning time significantly increases. Images containing up to 1000 configuration files in the YAML, YML and JSON formats were successfully tested, but the correct operation of the scanner on images containing over 1000 configuration files may not be guaranteed.
- You are not recommended to scan images for sensitive data, if the image size is over 10 GB.
Glossary
CI/CD
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery is the combination of continuous software integration and continuous delivery in the development process.
CVE
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures is the database for generally known information security vulnerabilities. Each vulnerability is given an identifier in the CVE-year-number format, description and several open links with descriptions.
CVSS
Common Vulnerability Scoring System is an open standard for scoring vulnerabilities. CVSS specifies a set of metrics and formulas for scoring vulnerability severity, with values from 0 (minimum) to 10 (maximum). CVSS allows you to allocate vulnerability response efforts based on vulnerability severity.
Exploit
Program code that takes advantage of some vulnerability in the system or in application software. Exploits are frequently used to install malware on a computer without the user's knowledge.
FSTEC
The Russian Federal Service for Technical and Export Control.
IaC
Infrastructure as a Code is an approach to managing and describing infrastructure through configuration files instead of manually editing server configurations.
Kaspersky OpenTIP
The publicly available Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal information system. Contains information about cyberthreats, safe objects, and the relationships between them.
Kaspersky TIP
The Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal information system that is available with premium access. Provides additional tools for analyzing cyberthreats, including threat lookup and Kaspersky Cloud Sandbox, as well as analytical reports about APTs, financial crime software, industrial cybersecurity threats, and the digital activity of a specific organization.
LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is a lightweight client-server protocol for accessing directory services.
Namespace
A virtual cluster inside a Kubernetes cluster which isolates cluster resources. Each namespace has its resources: services, pods, and deployments. The Resource names must be unique to operate in one namespace, although you can use the same names in other namespaces.
Node
A physical or virtual machine on which containers with applications are deployed and run. A Kubernetes cluster consists of several nodes. The cluster has a master node which manages the cluster and worker nodes where containers operate.
NVD
National Vulnerability Database is the United States Government repository of standards-based vulnerability management data represented using the Security Content Automation Protocol.
PCI SSC
PCI Security Standards Council is a global forum dedicated to the ongoing development, enhancement, storage, dissemination, and implementation of security standards for payment card data protection.
Pipeline
Continuous software integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) is performed in sequence one by one.
Pod
An abstract Kubernetes object, a group of one or more application containers, including shared storage (volumes), network settings, and information about application launch. Pod is the Kubernetes management unit.
RED OS
Russian general-purpose operating system RED OS supports scanning for vulnerabilities that can threaten the functioning of services and workstations.
SIEM
Security information and event management is a class of software solution that obtains and analyzes data about security events.
Syslog
A standard for sending and logging system event messages used for the UNIX and GNU/Linux platforms.
VDB (DSTD)
The Data Security Threats Database (DSTD or VDB) is a national vulnerability database maintained by the Russian Federal Service for Technical and Export Control (FSTEC).
Page top
Third party code information
Information about third-party code is contained in the file legal_notices.txt, which you can download in the management Console using the Kaspersky Container Security End User License Agreement link in the Settings → About section.
Page top
Trademark notices
Registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Adobe is either a registered trademark or a trademark of Adobe in the United States and/or other countries.
Amazon and AWS are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates.
Apple and Safari are trademarks of Apple Inc.
Ubuntu is a registered trademark of Canonical Ltd.
ClamAV is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
The Grafana Word Mark and Grafana Logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of Coding Instinct AB, in the United States and other countries and are used with Coding Instinct’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by Coding Instinct, or the Grafana community.
Docker and the Docker logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Docker, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Docker, Inc. and other parties may also have trademark rights in other terms used herein.
Dropbox is a trademark of Dropbox, Inc.
Google, Google Chrome, Chromium, and Nexus are trademarks of Google LLC.
S3 is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation registered in many jurisdictions around the world.
LinkedIn is a registered trademark or trademark of LinkedIn Corporation and its affiliates in the United States and/or other countries.
Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
CVE is a registered trademark of The MITRE Corporation.
OpenAPI is a trademark of the Linux Foundation.
Helm, Kubernetes is a registered trademark of The Linux Foundation in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, Active Directory, Excel, Microsoft Edge, Windows, and Windows Server are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
CVE is a registered trademark of The MITRE Corporation.
Mozilla and Firefox are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation in the U.S. and other countries.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and CentOS are trademarks or registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
OpenShift is a registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Debian is a registered trademark of Software in the Public Interest, Inc.
Sonatype Nexus is a trademark of Sonatype, Inc.
SUSE is a registered trademark of SUSE LLC in the United States and other countries.
TWITCH is a trademark of Twitch Interactive, Inc. or its affiliates.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
ClickHouse is a trademark of YANDEX LLC.
Page top