Contents
- Configuring network protection
- Scenario: Configuring network protection
- About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
- Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
- Policy setup and propagation: User-centric approach
- Network Agent policy settings
- Comparison of Network Agent policy settings by operating systems
- Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
- Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Tasks
- Managing client devices
- Settings of a managed device
- Device selections
- Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
- About device statuses
- Configuring the switching of device statuses
- Changing the Administration Server for client devices
- Avoiding conflicts between multiple Administration Servers
- Creating Administration Server connection profiles
- About clusters and server arrays
- Properties of a cluster or server array
- Device tags
- Creating a device tag
- Renaming a device tag
- Deleting a device tag
- Viewing devices to which a tag is assigned
- Viewing tags assigned to a device
- Tagging devices manually
- Removing assigned tags from devices
- Viewing rules for tagging devices automatically
- Editing a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Creating a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Running rules for auto-tagging devices
- Deleting a rule for tagging devices automatically
- Quarantine and Backup
- Remote diagnostics of client devices
- Opening the remote diagnostics window
- Enabling and disabling tracing for applications
- Downloading trace files of an application
- Deleting trace files
- Downloading application settings
- Downloading system information from a client device
- Downloading event logs
- Starting, stopping, restarting the application
- Running the remote diagnostics of an application and downloading the results
- Running an application on a client device
- Generating a dump file for an application
- Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
- Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
- Triggering of rules in Smart Training mode
- Managing administration groups
- Policies and policy profiles
- About policies
- About lock and locked settings
- Inheritance of policies and policy profiles
- Managing policies
- Viewing the list of policies
- Creating a policy
- Modifying a policy
- General policy settings
- Enabling and disabling a policy inheritance option
- Copying a policy
- Moving a policy
- Exporting a policy
- Importing a policy
- Viewing the policy distribution status chart
- Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
- Forced synchronization
- Deleting a policy
- Managing policy profiles
- Data encryption and protection
- Users and user roles
- About user accounts
- Adding an account of an internal user
- About user roles
- Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
- Assigning a role to a user or a security group
- Creating a user role
- Editing a user role
- Editing the scope of a user role
- Deleting a user role
- Associating policy profiles with roles
- Creating a security group
- Editing a security group
- Adding user accounts to an internal group
- Deleting a security group
- Configuring ADFS integration
- Configuring integration with Microsoft Entra ID
- Assigning a user as a device owner
- Assigning a user as a Linux device owner after installation of Network Agent
- Managing object revisions
- Kaspersky Security Network (KSN)
- Deletion of objects
Configuring network protection
This section contains information about manual configuration of policies and tasks, about user roles, about building an administration group structure and hierarchy of tasks.
Scenario: Configuring network protection
The quick start wizard creates policies and tasks with the default settings. These settings may turn out to be sub-optimal or even disallowed by the organization. Therefore, we recommend that you fine-tune these policies and tasks and create other policies and tasks, if they are necessary for your network.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have completed the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console initial configuration scenario, including the quick start wizard.
When the quick start wizard is running, the following policies and tasks are created in the Managed devices administration group:
- Policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Group task for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Policy of Network Agent
- Find vulnerabilities and required updates (task of Network Agent)
Stages
Configuring network protection proceeds in stages:
- Setup and propagation of Kaspersky application policies and policy profiles
To configure and propagate settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices, you can use two different security management approaches: device-centric or user-centric. You can also combine these two approaches.
- Configuring tasks for remote management of Kaspersky applications
Check the tasks created with the quick start wizard and fine-tune them, if necessary.
How-to instructions:
- Setting up the group task for updating Kaspersky Endpoint Security
- Creating the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task
If necessary, create additional tasks to manage the Kaspersky applications installed on the client devices.
- Evaluating and limiting the event load on the database
Information about events that occur during the operation of managed applications is transferred from a client device and registered in the Administration Server database. To reduce the load on the Administration Server, evaluate and limit the maximum number of events that can be stored in the database.
How-to instructions: Setting the maximum number of events.
Results
Upon completion of this scenario, your network will be protected by configuration of Kaspersky applications, tasks, and events received by the Administration Server:
- The Kaspersky applications are configured according to the policies and policy profiles.
- The applications are managed through a set of tasks.
- The maximum number of events that can be stored in the database is set.
When the network protection configuration is complete, you can proceed to configuring regular updates to Kaspersky databases and applications.
About device-centric and user-centric security management approaches
You can manage security settings from the standpoint of device features and from the standpoint of user roles. The first approach is called device-centric security management and the second is called user-centric security management. To apply different application settings to different devices you can use either or both types of management in combination.
Device-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to managed devices depending on device-specific features. For example, you can apply different settings to devices allocated in different administration groups. You can also differentiate the devices by usage of those devices in Active Directory, or their hardware specifications.
User-centric security management enables you to apply different security application settings to different user roles. You can create several user roles, assign an appropriate user role to each user, and define different application settings to the devices owned by users with different roles. For example, you may want to apply different application settings to devices of accountants and human resources (HR) specialists. As a result, when user-centric security management is implemented, each department—accounts department and HR department—has its own settings configuration for Kaspersky applications. A settings configuration defines which application settings can be changed by users and which are forcibly set and locked by the administrator.
By using user-centric security management you can apply specific application settings to individual users. This may be required when an employee has a unique role in the company or when you want to monitor security issues related to devices of a specific person. Depending on the role of this employee in the company, you can expand or limit the rights of this person to change application settings. For example, you might want to expand the rights of a system administrator who manages client devices in a local office.
You can also combine the device-centric and user-centric security management approaches. For example, you can configure a specific application policy for each administration group, and then create policy profiles for one or several user roles of your enterprise. In this case the policies and policy profiles are applied in the following order:
- The policies created for device-centric security management are applied.
- They are modified by the policy profiles according to the policy profile priorities.
- The policies are modified by the policy profiles associated with user roles.
Policy setup and propagation: Device-centric approach
This section provides a scenario for a device-centric approach to the centralized configuration of Kaspersky applications installed on managed devices. When you complete this scenario, the applications will be configured on all of the managed devices in accordance with the application policies and policy profiles that you define.
You might also want to consider user-centric security management as an alternative or additional option to the device-centric approach.
Process
The scenario of device-centric management of Kaspersky applications consists of the following steps:
- Configuring application policies
Configure settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices by creating a policy for each application. The set of policies will be propagated to the client devices.
When you configure the protection of your network in quick start wizard, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console creates the default policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows. If you completed the configuration process by using this wizard, you do not have to create a new policy for this application. Proceed to the manual setup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
If you have a hierarchical structure of several administration groups, the child administration groups inherit the policies from the primary Administration Server by default. You can force the inheritance by the child groups to prohibit any modifications of the settings configured in the upstream policy. If you want only part of the settings to be forcibly inherited, you can lock them in the upstream policy. The remaining unlocked settings will be available for modification in the downstream policies. The created hierarchy of policies will allow you to effectively manage devices in the administration groups.
How-to instructions: Creating a policy
- Creating policy profiles (optional)
If you want devices within a single administration group to run under different policy settings, create policy profiles for those devices. A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings. This subset is distributed on target devices together with the policy, supplementing it under a specific condition called the profile activation condition. Profiles only contain settings that differ from the "basic" policy, which is active on the managed device.
By using profile activation conditions, you can apply different policy profiles, for example, to the devices located in a specific unit or security group of Active Directory, having a specific hardware configuration, or marked with specific tags. Use tags to filter devices that meet specific criteria. For example, you can create a tag called Windows, mark all devices running Windows operating system with this tag, and then specify this tag as an activation condition for a policy profile. As a result, Kaspersky applications installed on all devices running Windows will be managed by their own policy profile.
How-to instructions:
- Propagating policies and policy profiles to the managed devices
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console automatically synchronizes the Administration Server with the managed devices several times per hour. During the synchronization, the new or changed policies and policy profiles are propagated to the managed devices. You can circumvent auto-synchronization and run the synchronization manually by using the Force synchronization command. When synchronization is complete, the policies and policy profiles are delivered and applied to the installed Kaspersky applications.
You can check whether the policies and policy profiles were delivered to a device. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console specifies the delivery date and time in the properties of the device.
How-to instructions: Forced synchronization
Results
When the device-centric scenario is complete, the Kaspersky applications are configured according to the settings specified and propagated through the hierarchy of policies.
The configured application policies and policy profiles will be applied automatically to the new devices added to the administration groups.
Policy setup and propagation: User-centric approach
This section describes the scenario of user-centric approach to the centralized configuration of Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices. When you complete this scenario, the applications will be configured on all of the managed devices in accordance with the application policies and policy profiles that you define.
You might also want to consider device-centric security management as an alternative or additional option to the user-centric approach. Learn more about two management approaches.
Process
The scenario of user-centric management of Kaspersky applications consists of the following steps:
- Configuring application policies
Configure settings for Kaspersky applications installed on the managed devices by creating a policy for each application. The set of policies will be propagated to the client devices.
When you configure the protection of your network in quick start wizard, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console creates the default policy for Kaspersky Endpoint Security. If you completed the configuration process by using this wizard, you do not have to create a new policy for this application. Proceed to the manual setup of Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy.
If you have a hierarchical structure of several administration groups, the child administration groups inherit the policies from the primary Administration Server by default. You can force the inheritance by the child groups to prohibit any modifications of the settings configured in the upstream policy. If you want only part of the settings to be forcibly inherited, you can lock them in the upstream policy. The remaining unlocked settings will be available for modification in the downstream policies. The created hierarchy of policies will allow you to effectively manage devices in the administration groups.
How-to instructions: Creating a policy
- Specifying owners of the devices
Assign the managed devices to the corresponding users.
How-to instructions: Assigning a user as a device owner
- Defining user roles typical for your enterprise
Think about different kinds of work that the employees of your enterprise typically perform. You must divide all employees in accordance with their roles. For example, you can divide them by departments, professions, or positions. After that you will need to create a user role for each group. Keep in mind that each user role will have its own policy profile containing application settings specific for this role.
- Creating user roles
Create and configure a user role for each group of employees that you defined at the previous step or use the predefined user roles. The user roles will contain set of rights of access to the application features.
How-to instructions: Creating a user role
- Defining the scope of each user role
For each of the created user roles, define users and/or security groups and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
How-to instructions: Editing the scope of a user role
- Creating policy profiles
Create a policy profile for each user role in your enterprise. The policy profiles define which settings will be applied to the applications installed on users' devices depending on the role of each user.
How-to instructions: Creating a policy profile
- Associating policy profiles with the user roles
Associate the created policy profiles with the user roles. After that: the policy profile becomes active for a user that has the specified role. The settings configured in the policy profile will be applied to the Kaspersky applications installed on the user's devices.
How-to instructions: Associating policy profiles with roles
- Propagating policies and policy profiles to the managed devices
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console automatically synchronizes the Administration Server with the managed devices several times per hour. During the synchronization, the new or changed policies and policy profiles are propagated to the managed devices. You can circumvent auto-synchronization and run the synchronization manually by using the Force synchronization command. When synchronization is complete, the policies and policy profiles are delivered and applied to the installed Kaspersky applications.
You can check whether the policies and policy profiles were delivered to a device. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console specifies the delivery date and time in the properties of the device.
How-to instructions: Forced synchronization
Results
When the user-centric scenario is complete, the Kaspersky applications are configured according to the settings specified and propagated through the hierarchy of policies and policy profiles.
For a new user, you will have to create a new account, assign the user one of the created user roles, and assign the devices to the user. The configured application policies and policy profiles will be automatically applied to the devices of this user.
Network Agent policy settings
To configure the Network Agent policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the name of the Network Agent policy.
The properties window of the Network Agent policy opens.
See the comparison table detailing how the settings below apply depending on the type of operating system used.
General tab
On this tab you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- In the Policy status block, you can select one of the policy modes:
- Active
- Inactive
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration tab
This tab allows you to configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed according to importance level in the following sections on the Event configuration tab:
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
In each section, the event type list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). Clicking the Properties button lets you specify the settings of event logging and notifications about events selected in the list. By default, common notification settings specified for the entire Administration Server are used for all event types. However, you can change specific settings for required event types.
Application settings tab
Settings
In the Settings section, you can configure the Network Agent policy:
- Distribute files through distribution points only
- Maximum size of event queue, in MB
- Application is allowed to retrieve policy's extended data on device
- Protect Network Agent service against unauthorized removal or termination, and prevent changes to the settings
- Use uninstallation password
Repositories
In the Repositories section, you can select the types of objects whose details will be sent from Network Agent to Administration Server. If modification of some settings in this section is prohibited by the Network Agent policy, you cannot modify these settings:
- Details of installed applications
- Include information about patches
- Details of Windows Update updates
- Details of software vulnerabilities and corresponding updates
- Hardware registry details
Software updates and vulnerabilities
In the Software updates and vulnerabilities section, you can configure search of Windows updates, as well as enable scanning of executable files for vulnerabilities. The settings in the Software updates and vulnerabilities section are available only on devices running Windows:
- In the Windows Update search mode settings group, you can select the update search mode:
- Scan executable files for vulnerabilities when running them
Restart management
In the Restart management section, you can specify the action to be performed if the operating system of a managed device has to be restarted for correct use, installation, or uninstallation of an application:
- Do not restart the operating system
- Restart the operating system automatically, if necessary
- Prompt user for action
- Force closure of applications in blocked sessions
Windows Desktop Sharing
In the Windows Desktop Sharing section, you can enable and configure the audit of the administrator's actions performed on a remote device when desktop access is shared. The settings in the Windows Desktop Sharing section are available only on devices running Windows:
Manage patches and updates
In the Manage patches and updates section, you can configure download and distribution of updates, as well as installation of patches, on managed devices: enable or disable the Automatically install applicable updates and patches for components that have the Undefined status option.
Connectivity
The Connectivity section includes three subsections:
- Network
- Connection profiles
- Connection schedule
In the Network subsection, you can configure the connection to Administration Server, enable the use of a UDP port, and specify the UDP port number.
- In the Connection to Administration Server settings group, you can specify the following settings:
- Use UDP port
- UDP port number
- Use the distribution point to force a connection to Administration Server
In the Connection profiles subsection, no new items can be added to the Administration Server connection profiles list so the Add button is inactive. The preset connection profiles cannot be modified, either.
In the Connection schedule subsection, you can specify the time intervals during which Network Agent sends data to the Administration Server:
- Connect when necessary
- Connect at specified time intervals
In the Connection schedule subsection, you can specify the time intervals during which Network Agent sends data to the Administration Server:
Network polling by distribution points
In the Network polling by distribution points section, you can configure automatic polling of the network. The polling settings are available only on devices running Windows. You can use the following options to enable the polling and set its frequency:
Network settings for distribution points
In the Network settings for distribution points section, you can specify the internet access settings:
- Use proxy server
- Address
- Port number
- Bypass proxy server for local addresses
- Proxy server authentication
- User name
- Password
KSN Proxy (distribution points)
In the KSN Proxy (distribution points) section, you can configure the application to use the distribution point to forward KSN requests from the managed devices:
Comparison of Network Agent policy settings by operating systems
The table below shows which Network Agent policy settings you can use to configure Network Agent with a specific operating system.
Network Agent policy settings: comparison by operating systems
Policy section |
Windows |
macOS |
Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
General |
|
|
|
Event configuration |
|
|
|
Settings |
|
Except the Use uninstallation password check box. |
Except the Use uninstallation password check box. |
Repositories |
|
The Hardware registry details option is available. |
The following options are available:
|
Software updates and vulnerabilities |
|
|
|
Restart management |
|
|
|
Windows Desktop Sharing |
|
|
|
Manage patches and updates |
|
|
|
Connectivity → Network |
|
Except the Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall check box. |
Except the Open Network Agent ports in Microsoft Windows Firewall check box. |
Connectivity → Connection schedule |
|
|
|
Network polling by distribution points |
The following options are available:
|
|
The following options are available:
|
Network settings for distribution points |
|
|
|
KSN Proxy (distribution points) |
|
|
|
Manual setup of the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy
This section provides recommendations on how to configure the Kaspersky Endpoint Security policy. You can perform setup in the policy properties window. When you edit a setting, click the lock icon to the right of the relevant group of settings to apply the specified values to a workstation.
Configuring Kaspersky Security Network
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is the infrastructure of cloud services that has information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. Kaspersky Security Network enables Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows to respond faster to different kinds of threats, enhances the performance of the protection components, and decreases the likelihood of false positives. For more information about Kaspersky Security Network, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
You can configure the Kaspersky Security Network work in the policy properties window of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, in the Application settings → Advanced Threat Protection section.
To specify recommended KSN settings:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → Advanced Threat Protection → Kaspersky Security Network.
- Make sure that the Use Administration Server as a KSN proxy server option is enabled. Using this option helps to redistribute and optimize traffic on the network.
If you use Managed Detection and Response, you must enable Kaspersky Security Network option for the distribution point and enable extended KSN mode.
- Enable use of KSN servers if the KSN proxy service is not available. To do this, enable the Use Kaspersky Security Network servers if the KSN proxy server is unavailable option.
KSN servers may be located either on the side of Kaspersky (when KSN is used) or on the side of third parties (when KPSN is used).
- Click OK.
The recommended KSN settings are specified.
Checking the list of the networks protected by Firewall
Make sure that Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Firewall protects all your networks. By default, Firewall protects networks with the following types of connection:
- Public network. Security applications, firewalls, or filters do not protect devices in such a network.
- Local network. Access to files and printers is restricted for devices in this network.
- Trusted network. Devices in such a network are protected from attacks and unauthorized access to files and data.
If you configured a custom network, make sure that Firewall protects it. For this purpose, check the list of the networks in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties. The list may not contain all the networks.
For more information about Firewall, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To check the list of networks:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → Essential Threat Protection → Firewall.
- Under Available networks, click the Network settings link.
The Network connections window opens. This window displays the list of networks.
- If the list has a missing network, add it.
Excluding software details from the Administration Server memory
We recommend that Administration Server does not save information about software modules that are started on the network devices. As a result, the Administration Server memory does not overrun.
You can disable saving this information in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows policy properties.
To disable saving information about installed software modules:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- In the policy properties, go to Application settings → General Settings → Reports and Storage.
- Under Data transfer to Administration Server, disable the About started applications check box if it is still enabled in the top-level policy.
When this check box is selected, the Administration Server database saves information about all versions of all software modules on the networked devices. This information may require a significant amount of disk space in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console database (dozens of gigabytes).
The information about installed software modules is no longer saved to the Administration Server database.
Configuring the registration of important policy events in the Administration Server database
To avoid the Administration Server database overflow, we recommend that you save only important events to the database. For the events that you consider unimportant, you can reduce the storage period or disable the storing.
To configure the event storage settings:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the name of the required policy.
The properties window of the selected policy opens.
- Go to the Event configuration tab, and then click the name of the event type for which you want to configure the registration in the database.
- In the right pane that opens, do one of the following:
- If you want to change the storage period for the event type, make sure that the Store in the Administration Server database for (days) toggle button is turned on, and then enter the required number of days for the event type to be stored.
- If you do not want to store the event type in the in the Administration Server database, turn off the Store in the Administration Server database for (days) toggle button.
- Click OK, and then after the right pane is closed, click the Save button.
The policy properties window is closed, and setting that you configured is applied.
Manual setup of the group update task for Kaspersky Endpoint Security
The optimal and recommended schedule option for Kaspersky Endpoint Security is When new updates are downloaded to the repository when the Use automatically randomized delay for task starts check box is selected.
About tasks
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console manages Kaspersky security applications installed on devices by creating and running tasks. Tasks are required for installing, launching, and stopping applications, scanning files, updating databases and software modules, and performing other actions on applications. Tasks can be performed on the Administration Server and on devices.
The following types of tasks are performed on devices:
- Local tasks—Tasks that are performed on a specific device
Local tasks can be modified either by the administrator, who uses administration tools, or by the user of a remote device (for example, through the security application interface). If a local task has been modified simultaneously by the administrator and the user of a managed device, the changes made by the administrator will take effect because they have a higher priority.
- Group tasks—Tasks that are performed on all devices of a specific group
Unless otherwise specified in the task properties, a group task also affects all subgroups of the selected group.
- Global tasks—Tasks that are performed on a set of devices, regardless of whether they are included in any group
For each application, you can create multiple group tasks, global tasks, or local tasks.
You can make changes to the settings of tasks, view the progress of tasks, and copy, export, import, and delete tasks.
A task is started on a device only if the application for which the task was created is running.
Execution results of tasks are saved in the OS event log on each device and in the Administration Server database.
Do not include private data in task settings. For example, avoid specifying the domain administrator password.
About task scope
The scope of a task is the set of devices on which the task is performed. The types of scope are as follows:
- For a local task, the scope is the device itself.
- For an Administration Server task, the scope is the Administration Server.
- For a group task, the scope is the list of devices included in the group.
When creating a global task, you can use the following methods to specify its scope:
- Specifying certain devices manually.
You can use an IP address (or IP range), NetBIOS name, or DNS name as the device address.
- Importing a list of devices from a TXT file with the device addresses to be added (each address must be placed on an individual line).
If you import a list of devices from a file or create a list manually, and if devices are identified by their names, the list can only contain devices for which information has already been entered into the Administration Server database. Moreover, the information must have been entered when those devices were connected or during device discovery.
- Specifying a device selection.
Over time, the scope of a task changes as the set of devices included in the selection change. A selection of devices can be made on the basis of device attributes, including software installed on a device, and on the basis of tags assigned to devices. Device selection is the most flexible way to specify the scope of a task.
Tasks for device selections are always run on a schedule by the Administration Server. These tasks cannot be run on devices that lack connection to the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run directly on devices and therefore do not depend on the device connection to the Administration Server.
Tasks for device selections are not run on the local time of a device; instead, they are run on the local time of the Administration Server. Tasks whose scope is specified by using other methods are run on the local time of a device.
Creating a task
You can create a task in the task list. Alternatively, you can select devices in the Managed devices list, and then create a new task assigned to the selected devices.
To create a task in the task list:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Follow its instructions.
- If you want to modify the default task settings, enable the Open task details when creation is complete option on the Finish task creation page. If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
To create a new task assigned to the selected devices:
In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, select the check boxes next to the devices to run the task for them. You can use the search and filter functions to find the devices you're looking for.
- Click the Run task button, and then select Create new task.
The New task wizard starts.
On the first step of the wizard, you can remove the devices selected to include in the task scope. Follow the wizard instructions.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created for the selected devices.
Viewing the task list
You can view the list of tasks that are created in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
To view the list of tasks,
In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
The list of tasks is displayed. The tasks are grouped by the names of applications to which they are related. For example, the Uninstall application remotely task is related to the Administration Server, and the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task refers to the Network Agent.
To view properties of a task,
Click the name of the task.
The task properties window is displayed with several named tabs. For example, the Task type is displayed on the General tab, and the task schedule—on the Schedule tab.
Starting a task manually
The application starts tasks according to the schedule settings specified in the properties of each task. You can start a task manually at any time from the task list. Alternatively, you can select devices in the Managed devices list, and then start an existing task for them.
To start a task manually:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- In the task list, select the check box next to the task that you want to start.
- Click the Start button.
The task starts. You can check the task status in the Status column or by clicking the Result button.
Starting a task for selected devices
You can select one or more client devices in the list of devices, and then launch a previously created task for them. This allows you to run tasks created earlier for a specific set of devices.
This changes the devices to which the task was assigned to the list of devices that you select when you run the task.
To start a task for selected devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices. The list of managed devices is displayed.
In the list of managed devices, use the check boxes to select the devices to run the task for them. You can use the search and filter functions to find the devices you're looking for.
- Click the Run task button, and then select Apply existing task.
The list of the existing tasks is displayed. - The selected devices are displayed above the task list. If necessary, you can remove a device from this list. You can delete all but one device.
- Select the desired task in the list. You can use the search box above the list to search for the desired task by name. Only one task can be selected.
- Click Save and start task.
The selected task is immediately started for the selected devices. The scheduled start settings in the task are not changed.
General task settings and properties
This section contains the settings that you can view and configure for most of your tasks. The list of settings available depends on the task you are configuring.
Settings specified during task creation
You can specify the following settings when creating a task. Some of these settings can also be modified in the properties of the created task.
- Devices to which the task will be assigned:
- Account settings:
- Operating system restart settings:
Settings specified after task creation
You can specify the following settings only after a task is created.
- Group task settings:
- Task scheduling settings:
- Start task setting:
- Manually
- Once
- Immediately
- Every N minutes
- Every N hours
- Every N days
- By days of week
- Monthly
- Every month on specified days of selected weeks
- When new updates are downloaded to the repository
- On virus outbreak
- On completing another task
The scheduling settings may depend on the local time zone of the device operating system.
- Run missed tasks
- Use automatically randomized delay for task starts
- Use automatically randomized delay for task starts within an interval of
- Turn on devices by using the Wake-on-LAN function before starting the task
- Shut down the devices after completing the task
- Stop the task if it runs longer than
- Start task setting:
- Notifications:
- Store task history block:
- Save all events
- Save events related to task progress
- Save only task execution results
- Store in the Administration Server database for (days)
- Store in the OS event log on device
- Notify of errors only
- Notify by email
- Store task history block:
- Task scope settings
- Exclusions from scope
- Revision history
Exporting a task
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to save a task and its settings to a KLT file. You can use this KLT file to import the saved task both to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
To export a task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Select the check box next to the task that you want to export.
You cannot export multiple tasks at the same time. If you select more than one task, the Export button will be disabled. Administration Server tasks are also unavailable for export.
- Click the Export button.
- In the opened Save as window, specify the task file name and path. Click the Save button.
The Save as window is displayed only if you use Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Opera. If you use another browser, the task file is automatically saved in the Downloads folder.
Importing a task
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to import a task from a KLT file. The KLT file contains the exported task and its settings.
To import a task:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click the Import button.
- Click the Browse button to choose a task file that you want to import.
- In the opened window, specify the path to the KLT task file, and then click the Open button. Note that you can select only one task file.
The task processing starts.
- After the task is processed successfully, select the devices to which you want to assign the task. To do this, select one of the following options:
- Specify the task scope.
- Click the Complete button to finish the task import.
The notification with the import results appears. If the task is imported successfully, you can click the Details link to view the task properties.
After a successful import, the task is displayed in the task list. The task settings and schedule are also imported. The task will be started according to its schedule.
If the newly imported task has an identical name to an existing task, the name of the imported task is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page topViewing task run results stored on the Administration Server
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to view the results for group tasks, tasks for specific devices, and Administration Server tasks.
To view the task results:
- In the task properties window, select the General section.
- Click the Results link to open the Task results window.
Managing client devices
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to manage client devices:
- View settings and statuses of managed devices, including clusters and server arrays.
- Configure distribution points.
- Manage tasks.
You can use administration groups to combine client devices in a set that can be managed as a single unit. A client device can be included in only one administration group. Devices can be allocated to a group automatically based on Rule conditions:
- Creating device moving rules.
- Copying device moving rules.
- Conditions for a device moving rule.
You can use device selections to filter devices based on a condition. You can also tag devices for creating selections, for finding devices, and for distributing devices among administration groups.
Settings of a managed device
To view the settings of a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
The list of managed devices is displayed.
- In the list of managed devices, click the link with the name of the required device.
The properties window of the selected device is displayed.
The following tabs are displayed in the upper part of the properties window representing the main groups of the settings:
Page topDevice selections
Device selections are a tool for filtering devices according to specific conditions. You can use device selections to manage several devices: for example, to view a report about only these devices or to move all of these devices to another group.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console provides a broad range of predefined selections (for example, Devices with Critical status, Protection is disabled, Active threats are detected). Predefined selections cannot be deleted. You can also create and configure additional user-defined selections.
In user-defined selections, you can set the search scope and select all devices, managed devices, or unassigned devices. Search parameters are specified in the conditions. In the device selection you can create several conditions with different search parameters. For example, you can create two conditions and specify different IP ranges in each of them. If several conditions are specified, a selection displays the devices that meet any of the conditions. By contrast, search parameters within a condition are superimposed. If both an IP range and the name of an installed application are specified in a condition, only those devices will be displayed where both the application is installed and the IP address belongs to the specified range.
Viewing the device list from a device selection
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to view the list of devices from a device selection.
To view the device list from the device selection:
- In the main menu, go to the Assets (Devices) → Device selections or Discovery & deployment → Device selections section.
- In the selection list, click the name of the device selection.
The page displays a table with information about the devices included in the device selection.
- You can group and filter the data of the device table as follows:
- Click the settings icon (
 ), and then select the columns to be displayed in the table.
), and then select the columns to be displayed in the table. - Click the filter icon (
 ), and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu.
), and then specify and apply the filter criterion in the invoked menu. The filtered table of devices is displayed.
- Click the settings icon (
You can select one or several devices in the device selection and click the New task button to create a task that will be applied to these devices.
To move the selected devices of the device selection to another administration group, click the Move to group button, and then select the target administration group.
Page topCreating a device selection
To create a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections.
A page with a list of device selections is displayed.
- Click the Add button.
The Device selection settings window opens.
- Enter the name of the new selection.
- Specify the group that contains the devices to be included in the device selection:
- Find any devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Managed Devices or Unassigned devices group.
- Find managed devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Managed Devices group.
- Find unassigned devices—Searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and included in the Unassigned devices group.
You can enable the Include data from secondary Administration Servers check box to enable searching for devices that meet the selection criteria and managed by secondary Administration Servers.
- Click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, specify conditions that must be met for including devices in this selection, and then click the OK button.
- Click the Save button.
The device selection is created and added to the list of device selections.
Page topConfiguring a device selection
To configure a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections.
A page with a list of device selections is displayed.
- Select the relevant user-defined device selection, and click the Properties button.
The Device selection settings window opens.
- On the General tab, click the New condition link.
- Specify conditions that must be met for including devices in this selection.
- Click the Save button.
The settings are applied and saved.
Below are descriptions of the conditions for assigning devices to a selection. Conditions are combined by using the OR logical operator: the selection will contain devices that comply with at least one of the listed conditions.
General
In the General section, you can change the name of the selection condition and specify whether that condition must be inverted:
Network infrastructure
In the Network subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network data:
- Device name
- Domain
- Administration group
- Description
- IP range
- Managed by a different Administration Server
In the Active Directory subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on their Active Directory data:
- Device is in an Active Directory organizational unit
- Include child organizational units
- This device is a member of an Active Directory group
In the Network activity subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their network activity:
- Acts as a distribution point
- Do not disconnect from the Administration Server
- Connection profile switched
- Last connected to Administration Server
- New devices detected by network poll
- Device is visible
In the Cloud segments subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to their respective cloud segments:
Device statuses
In the Managed device status subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on the description of the devices status from a managed application:
In the Status of components in managed applications subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses of components in managed applications:
- Data Leakage Prevention status
- Collaboration servers protection status
- Anti-virus protection status of mail servers
- Endpoint Sensor status
In the Status-affecting problems in managed applications subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to the list of possible problems detected by a managed application. If at least one problem that you select exists on a device, the device will be included in the selection. When you select a problem listed for several applications, you have the option to select this problem in all of the lists automatically.
You can select check boxes for descriptions of statuses from the managed application; upon receipt of these statuses, the devices will be included in the selection. When you select a status listed for several applications, you have the option to select this status in all of the lists automatically.
System details
In the Operating system section, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their operating system type.
- Platform type
- Operating system service pack version
- Operating system bit size
- Operating system build
- Operating system release number
In the Virtual machines section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to whether these are virtual machines or part of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI):
In the Hardware registry subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on their installed hardware:
Ensure that the lshw utility is installed on Linux devices from which you want to fetch hardware details. Hardware details fetched from virtual machines may be incomplete depending on the hypervisor used.
- Device
- Vendor
- Device name
- Description
- Device vendor
- Serial number
- Inventory number
- User
- Location
- CPU clock rate, in MHz, from
- CPU clock rate, in MHz, to
- Number of virtual CPU cores, from
- Number of virtual CPU cores, to
- Hard drive volume, in GB, from
- Hard drive volume, in GB, to
- RAM size, in MB, from
- RAM size, in MB, to
Third-party software details
In the Applications registry subsection, you can set up the criteria to search for devices according to applications installed on them:
- Application name
- Application version
- Vendor
- Application status
- Find by update
- Name of incompatible security application
- Application tag
- Apply to devices without the specified tags
In the Vulnerabilities and updates subsection, you can specify the criteria that will be used to include devices in the selection according to their Windows Update source:
WUA is switched to Administration Server
Details of Kaspersky applications
In the Kaspersky applications subsection, you can configure criteria for including devices in a selection based on the selected managed application:
- Application name
- Application version
- Critical update name
- Select the period of the last update of modules
- Device is managed through Administration Server
- Security application is installed
In the Anti-virus protection subsection, you can set up the criteria for including devices in a selection based on their protection status:
The Application components subsection contains the list of components of those applications that have corresponding management plug-ins installed in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
In the Application components subsection, you can specify criteria for including devices in a selection according to the statuses and version numbers of the components that refer to the application that you select:
Tags
In the Tags section, you can configure criteria for including devices into a selection based on key words (tags) that were previously added to the descriptions of managed devices:
Apply if at least one specified tag matches
To add tags to the criterion, click the Add button, and select tags by clicking the Tag entry field. Specify whether to include or exclude the devices with the selected tags in the device selection.
Users
In the Users section, you can set up the criteria to include devices in the selection according to the accounts of users who have logged in to the operating system.
Page topExporting the device list from a device selection
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to save information about devices from a device selection and export it as a CSV or a TXT file.
To export the device list from the device selection:
- Open the table with the devices from the device selection.
- Use one of the following ways to select the devices that you want to export:
- To select particular devices, select the check boxes next to them.
- To select all devices from the current table page, select the check box in the device table header, and then select the Select all on current page check box.
- To select all devices from the table, select the check box in the device table header, and then select the Select all check box.
Click the Export to CSV or Export to TXT button. All information about the selected devices included in the table will be exported.
Note that if you applied a filter criterion to the device table, only the filtered data from the displayed columns will be exported.
Page topRemoving devices from administration groups in a selection
When working with a device selection, you can remove devices from administration groups right in this selection, without switching to the administration groups from which these devices must be removed.
To remove devices from administration groups:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Device selections or Discovery & deployment → Device selections.
- In the selection list, click the name of the device selection.
The page displays a table with information about the devices included in the device selection.
- Select the devices that you want to remove, and then click Delete.
The selected devices are removed from their respective administration groups.
Viewing and configuring the actions when devices show inactivity
If client devices within a group are inactive, you can get notifications about it. You can also automatically delete such devices.
To view or configure the actions when the devices in the group show inactivity:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- Click the name of the required administration group.
The administration group properties window opens.
- In the properties window, go to the Settings tab.
- In the Inheritance section, enable or disable the following options:
- In the Device activity section, enable or disable the following options:
- Click Save.
Your changes are saved and applied.
Page topAbout device statuses
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console assigns a status to each managed device. The particular status depends on whether the conditions defined by the user are met. In some cases, when assigning a status to a device, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console takes into consideration the device's visibility flag on the network (see the table below). If Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console does not find a device on the network within two hours, the visibility flag of the device is set to Not Visible.
The statuses are the following:
- Critical or Critical/Visible
- Warning or Warning/Visible
- OK or OK/Visible
The table below lists the default conditions that must be met to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device, with all possible values.
Conditions for assigning a status to a device
Condition |
Condition description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
Security application is not installed |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but a security application is not installed. |
|
Too many viruses detected |
Some viruses have been found on the device by a task for virus detection, for example, the Virus scan task, and the number of viruses found exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0. |
Real-time protection level differs from the level set by the Administrator |
The device is visible on the network, but the real-time protection level differs from the level set (in the condition) by the administrator for the device status. |
|
Malware scan has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but neither the Malware scan task nor a local scan task has been run within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 7 days ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Databases are outdated |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device, but the anti-virus databases have not been updated on this device within the specified time interval. The condition is applicable only to devices that were added to the Administration Server database 1 day ago or earlier. |
More than 1 day. |
Not connected in a long time |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device has not connected to an Administration Server within the specified time interval, because the device was turned off. |
More than 1 day. |
Active threats are detected |
The number of unprocessed objects in the Active threats folder exceeds the specified value. |
More than 0 items. |
Restart is required |
The device is visible on the network, but an application requires the device restart longer than the specified time interval and for one of the selected reasons. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Incompatible applications are installed |
The device is visible on the network, but software inventory performed through Network Agent has detected incompatible applications installed on the device. |
|
Software vulnerabilities have been detected |
The device is visible on the network and Network Agent is installed on the device, but the Find vulnerabilities and required updates task has detected vulnerabilities with the specified severity level in applications installed on the device. |
|
License expired |
The device is visible on the network, but the license has expired. |
|
License expires soon |
The device is visible on the network, but the license will expire on the device in less than the specified number of days. |
More than 0 days. |
Check for Windows Update updates has not been performed in a long time |
The device is visible on the network, but the Perform Windows Update synchronization task has not been run within the specified time interval. |
More than 1 day. |
Invalid encryption status |
Network Agent is installed on the device, but the device encryption result is equal to the specified value. |
|
Mobile device settings do not comply with the policy |
The mobile device settings are other than the settings that were specified in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Android policy during the check of compliance rules. |
|
Unprocessed security issues detected |
Some unprocessed security issues have been found on the device. Security issues can be created either automatically, through managed Kaspersky applications installed on the client device, or manually by the administrator. |
|
Device status defined by application |
The status of the device is defined by the managed application. |
|
Device is out of disk space |
Free disk space on the device is less than the specified value or the device could not be synchronized with the Administration Server. The Critical or Warning status is changed to the OK status when the device is successfully synchronized with the Administration Server and free space on the device is greater than or equal to the specified value. |
More than 0 MB |
Device has become unmanaged |
During device discovery, the device was recognized as visible on the network, but more than three attempts to synchronize with the Administration Server failed. |
|
Protection is disabled |
The device is visible on the network, but the security application on the device has been disabled for longer than the specified time interval. In this case, the state of the security application is stopped or failure, and differs from the following: starting, running, or suspended. |
More than 0 minutes. |
Security application is not running |
The device is visible on the network and a security application is installed on the device but is not running. |
|
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console enables you to set up automatic switching of the status of a device in an administration group when specified conditions are met. When specified conditions are met, the client device is assigned one of the following statuses: Critical or Warning. When specified conditions are not met, the client device is assigned the OK status.
Different statuses may correspond to different values of one condition. For example, by default, if the Databases are outdated condition has the More than 3 days value, the client device is assigned the Warning status; if the value is More than 7 days, the Critical status is assigned.
When Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console assigns a status to a device, for some conditions (see the Condition description column) the visibility flag is taken into consideration. For example, if a managed device was assigned the Critical status because the Databases are outdated condition was met, and later the visibility flag was set for the device, then the device is assigned the OK status.
Configuring the switching of device statuses
You can change conditions to assign the Critical or Warning status to a device.
To enable changing the device status to Critical:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Critical.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Critical if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Critical status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Critical status.
To enable changing the device status to Warning:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the list of groups that opens, click the link with the name of a group for which you want to change switching the device statuses.
- In the properties window that opens, select the Device status tab.
- In the left pane, select Warning.
- In the right pane, in the Set to Warning if these are specified section, enable the condition to switch a device to the Warning status.
You can change only settings that are not locked in the parent policy.
- Select the radio button next to the condition in the list.
- In the upper-left corner of the list, click the Edit button.
- Set the required value for the selected condition.
Values cannot be set for every condition.
- Click OK.
When specified conditions are met, the managed device is assigned the Warning status.
Changing the Administration Server for client devices
You can change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server using the Change Administration Server task. After the task completion, the selected client devices will be put under the management of the Administration Server that you specify. You can switch the device management between the following Administration Servers:
- Primary Administration Server and one of its virtual Administration Servers
- Two virtual Administration Servers of the same primary Administration Server
To change the Administration Server that manages client devices to a different Server:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tasks.
- Click Add.
The New task wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- At the New task settings step, specify the following settings:
- In the Application drop-down list, select Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- In the Task type field, select Change Administration Server.
- In the Task name field, specify the name for the task that you are creating.
A task name cannot be more than 100 characters long and cannot include any special characters ("*<>?\:|).
- Select devices to which the task will be assigned:
- At the Task scope step, specify an administration group, devices with specific addresses, or a device selection.
- At the next step, confirm that you agree to the terms of changing the Administration Server for client devices.
- At the next step, select the virtual Administration Server that you want to use to manage the selected devices.
- At the Selecting an account to run the task step, specify the account settings:
- If on the Finish task creation page you enable the Open task details when creation is complete option, you can modify the default task settings.
If you do not enable this option, the task is created with the default settings. You can modify the default settings later, at any time.
- Click the Finish button.
The task is created and displayed in the list of tasks.
- Click the name of the created task to open the task properties window.
- In the task properties window, specify the general task settings according to your needs.
- Click the Save button.
The task is created and configured.
- Run the created task.
After the task is complete, the client devices for which it was created are put under the management of the Administration Server specified in the task settings.
Avoiding conflicts between multiple Administration Servers
If you have more than one Administration Server on your network, they can see the same client devices. This may result, for example, in remote installation of the same application to one and the same device from more than one Server and other conflicts. To avoid such a situation, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to prevent an application from being installed on a device managed by another Administration Server.
You can also use the Managed by a different Administration Server property as a criterion for the following purposes:
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console uses heuristics to determine whether a client device is managed by the Administration Server you are working with or by a different Administration Server.
Page topCreating Administration Server connection profiles
To allow out-of-office users to change the method of connecting Network Agent to Administration Server, you have to configure Administration Server connection profiles.
Connection profiles are supported only for devices running Windows and macOS.
To create a connection profile:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices), and do one of the following:
- If you want to create a connection profile for a group of managed devices, click Policies & profiles, and then click Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent.
- If you want to create a connection profile for a specific managed device, click Managed devices, and then click the name of the device. In the window that opens, go to the Applications tab, and then click Kaspersky Security Center Network Agent.
The properties window of the Network Agent policy opens.
- Go to the Application settings tab, and then go to the Connectivity section.
- In the Connection profiles section, click the Settings button.
The Administration Server connection profiles subsection displays the table of connection profiles.
You cannot view, modify, or delete the Home Administration Server and Offline mode connection profiles.
- Click the Add button, and then in the window that opens, specify the profile name.
The name must be unique. You cannot use the same name for several profiles.
- If necessary, select the check boxes in the following fields:
- Enable out-of-office mode when Administration Server is not available.
- Use proxy server.
If you select this option, do the following:
- Specify information in the Address and the Port number fields.
- If necessary, select the Proxy server authentication check box, and then specify the user name and the password in the corresponding fields.
- Click the Save button.
The new profile is displayed in the table of connection profiles. You can use it when configuring the Network location settings.
You can edit and delete connection profiles.
To edit a connection profile:
- In the table of connection profiles click the name of the connection profile that you want to edit.
- Make all necessary changes, and then click the Save button.
The changes are applied to the connection profile.
To delete a connection profile:
- In the table of connection profiles select the check boxes next to the connection profiles that you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button.
The selected connection profiles are deleted.
Page topAbout clusters and server arrays
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console supports cluster technology. If Network Agent sends information to Administration Server confirming that an application installed on a client device is part of a server array, this client device becomes a cluster node.
If an administration group contains clusters or server arrays, the Managed devices page displays two tabs—one for individual devices, and one for clusters and server arrays. After the managed devices are detected as cluster nodes, the cluster is added as an individual object to the Clusters and server arrays tab.
The cluster or server array nodes are listed on the Devices tab, along with other managed devices. You can view properties of the nodes as individual devices and perform other operations, but you cannot delete a cluster node or move it to another administration group separately from its cluster. You can only delete or move an entire cluster.
You can perform the following operations with clusters or server arrays:
- View properties
- Move the cluster or server array to another administration group
When you move a cluster or server array to another group, all of its nodes move with it, because a cluster and any of its nodes always belong to the same administration group.
- Delete
It is reasonable to delete a cluster or server array only when the cluster or server array does not exist in the organization network any longer. If a cluster is still visible on your network and Network Agent and the Kaspersky security application are still installed on the cluster nodes, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console returns the deleted cluster and its nodes back to the list of managed devices automatically.
Properties of a cluster or server array
To view the settings of a cluster or server array:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → Clusters and server arrays.
The list of clusters and server arrays is displayed.
- Click the name of the required cluster or server array.
The properties window of the selected cluster or server array is displayed.
General
The General section displays general information about the cluster or server array. Information is provided on the basis of data received during the last synchronization of the cluster nodes with the Administration Server:
- Name
- Description
- Windows domain
- NetBIOS name
- DNS name
Tasks
In the Tasks tab, you can manage the tasks assigned to the cluster or server array: view the list of existing tasks; create new ones; remove, start, and stop tasks; modify task settings; and view execution results. The listed tasks relate to the Kaspersky security application installed on the cluster nodes. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console receives the task list and the task status details from the cluster nodes. If a connection is not established, the status is not displayed.
Nodes
This tab displays a list of nodes included into the cluster or server array. You can click a node name to view the device properties window.
Kaspersky application
The properties window may also contain additional tabs with the information and settings related to the Kaspersky security application installed on the cluster nodes.
Device tags
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console enables you to tag devices. A tag is the label of a device that can be used for grouping, describing, or finding devices. Tags assigned to devices can be used for creating selections, for finding devices, and for distributing devices among administration groups.
You can tag devices manually or automatically. You may use manual tagging when you want to tag an individual device. Auto-tagging is performed by Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console in accordance with the specified tagging rules.
Devices are tagged automatically when specified rules are met. An individual rule corresponds to each tag. Rules are applied to the network properties of the device, operating system, applications installed on the device, and other device properties. For example, if your network includes devices running Windows, Linux, and macOS, you can set up a rule that will assign the [Linux] tag to all Linux-based devices. Then, you can use this tag when creating a device selection; this will help you sort all Linux-based devices and assign them a task. A tag is automatically removed from a device in the following cases:
- When the device stops meeting conditions of the rule that assigns the tag.
- When the rule that assigns the tag is disabled or deleted.
The list of tags and the list of rules on each Administration Server are independent of all other Administration Servers, including a primary Administration Server or subordinate virtual Administration Servers. A rule is applied only to devices from the same Administration Server on which the rule is created.
Creating a device tag
To create a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click Add.
A new tag window opens.
- In the Tag field, enter the tag name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The new tag appears in the list of device tags.
Page topRenaming a device tag
To rename a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click the name of the tag that you want to rename.
A tag properties window opens.
- In the Tag field, change the tag name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The updated tag appears in the list of device tags.
Page topDeleting a device tag
To delete a device tag:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- In the list, select the device tag that you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button.
- In the window that opens, click Yes.
The device tag is deleted. The deleted tag is automatically removed from all of the devices to which it was assigned.
The tag that you have deleted is not removed automatically from auto-tagging rules. After the tag is deleted, it will be assigned to a new device only when the device first meets the conditions of a rule that assigns the tag.
The deleted tag is not removed automatically from the device if this tag is assigned to the device by an application or Network Agent. To remove the tag from your device, use the klscflag utility.
Page topViewing devices to which a tag is assigned
To view devices to which a tag is assigned:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags.
- Click the View devices link next to the tag for which you want to view assigned devices.
You will be redirected to the Managed devices section of the main menu, with the devices filtered by the tag for which you clicked the View devices link.
- If you want to return to the list of device tags, click the Back button of your browser.
After you view the devices to which the tag is assigned, you can either create and assign a new tag or assign the existing tag to other devices. In this case, you have to remove the filter by tag, select the devices, and then assign the tag.
Page topViewing tags assigned to a device
To view tags assigned to a device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device whose tags you want to view.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Tags tab.
The list of tags assigned to the selected device is displayed. In the Tag assigned column you can view how the tag was assigned.
You can assign another tag to the device or remove an already assigned tag. You can also view all device tags that exist on the Administration Server.
You can also view tags assigned to a device in the command line, by using the klscflag utility.
To view tags assigned to a device in the command line, run the following command:
klscflag -ssvget -pv 1103/1.0.0.0 -s KLNAG_SECTION_TAGS_INFO -n KLCONN_HOST_TAGS -svt ARRAY_T -ss "|ss_type = \"SS_PRODINFO\";"
Tagging devices manually
To assign a tag to a device:
- View tags assigned to the device to which you want to assign another tag.
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, do one of the following:
- To create and assign a new tag, select Create new tag, and then specify the name of the new tag.
- To select an existing tag, select Assign existing tag, and then select the necessary tag in the drop-down list.
- Click OK to apply the changes.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The selected tag is assigned to the device.
To assign a tag to several devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Select the devices to which you want to assign a tag.
- Click Tags, and then select Assign from the drop-down list.
- In the window that opens, select a tag from the drop-down list.
If necessary, you can select several tags.
You can also do the following:
- Edit the name of a tag by clicking the Edit (
) icon.
Specify the new name of the tag, and then click the Save button.
Note that the tag will also be renamed in the list of device tags.
- Delete a tag by clicking the Delete (
) icon.
In the window that opens, click Delete.
Note that the tag will also be deleted from the Administration Server.
- Edit the name of a tag by clicking the Edit (
- Click the Save button.
The tags are assigned to the selected devices. You can remove the assigned tags.
Page topRemoving assigned tags from devices
The unassigned device tag is not deleted. If you want, you can delete it manually.
You cannot manually remove tags assigned to the device by applications or Network Agent. To remove these tags, use the klscflag utility.
To remove a tag from a device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device whose tags you want to view.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Tags tab.
- Select the check box next to the tag that you want to remove.
- At the top of the list, click the Unassign tag? button.
- In the window that opens, click Yes.
The tag is removed from the device.
To remove tags from several devices:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Select the devices whose tags you want to remove.
- Click Tags, and then select Unassign from the drop-down list.
- In the window that opens, select the check boxes next to the tags that you want to remove.
The window displays all tags assigned to all the devices that you selected at step 2.
- Click the Save button.
The tags are removed from the devices.
Page topViewing rules for tagging devices automatically
To view rules for tagging devices automatically,
Do any of the following:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Auto-tagging rules.
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Tags → Device tags, and then click the Set up auto-tagging rules link.
- View tags assigned to a device and then click the Settings button.
The list of rules for auto-tagging devices appears.
Page topEditing a rule for tagging devices automatically
To edit a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Click the name of the rule that you want to edit.
A rule settings window opens.
- Edit the general properties of the rule:
- In the Rule name field, change the rule name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- Do any of the following:
- Enable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule enabled.
- Disable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule disabled.
- In the Rule name field, change the rule name.
- Do any of the following:
- If you want to add a new condition, click the Add button, and specify the settings of the new condition in the window that opens.
- If you want to edit an existing condition, click the name of the condition that you want to edit, and then edit the condition settings.
- If you want to delete a condition, select the check box next to the name of the condition that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
- Click OK in the conditions settings window.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The edited rule is shown in the list.
Page topCreating a rule for tagging devices automatically
To create a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Click Add.
A new rule settings window opens.
- Configure the general properties of the rule:
- In the Rule name field, enter the rule name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- Do one of the following:
- Enable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule enabled.
- Disable the rule by switching the toggle button to Rule disabled.
- In the Tag field, enter the new device tag name or select one of the existing device tags from the list.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long.
- In the Rule name field, enter the rule name.
- In the conditions section, click the Add button to add a new condition.
A new condition settings window open.
- Enter the condition name.
The name cannot be more than 256 characters long. The name must be unique within a rule.
- Set up the triggering of the rule according to the following conditions. You can select multiple conditions.
- Network—Network properties of the device, such as the device name on the Windows network, or device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
If case sensitive collation is set for the database that you use for Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, keep case when you specify a device DNS name. Otherwise, the auto-tagging rule will not work.
- Applications—Presence of Network Agent on the device, operating system type, version, and architecture.
- Virtual machines—Device belongs to a specific type of virtual machine.
- Active Directory—Presence of the device in an Active Directory organizational unit and membership of the device in an Active Directory group.
- Applications registry—Presence of applications of different vendors on the device.
- Network—Network properties of the device, such as the device name on the Windows network, or device inclusion in a domain or an IP subnet.
- Click OK to save the changes.
If necessary, you can set multiple conditions for a single rule. In this case, the tag will be assigned to a device if it meets at least one condition.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The newly created rule is enforced on devices managed by the selected Administration Server. If the settings of a device meet the rule conditions, the device is assigned the tag.
Later, the rule is applied in the following cases:
- Automatically and periodically, depending on the server workload
- After you edit the rule
- When you run the rule manually
- After the Administration Server detects a change in the settings of a device that meets the rule conditions or the settings of a group that contains such device
You can create multiple tagging rules. A single device can be assigned multiple tags if you have created multiple tagging rules and if the respective conditions of these rules are met simultaneously. You can view the list of all assigned tags in the device properties.
Page topRunning rules for auto-tagging devices
When a rule is run, the tag specified in properties of this rule is assigned to devices that meet conditions specified in properties of the same rule. You can run only active rules.
To run rules for auto-tagging devices:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Select check boxes next to active rules that you want to run.
- Click the Run rule button.
The selected rules are run.
Page topDeleting a rule for tagging devices automatically
To delete a rule for tagging devices automatically:
- View rules for tagging devices automatically.
- Select the check box next to the rule that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click Delete again.
The selected rule is deleted. The tag that was specified in properties of this rule is unassigned from all of the devices that it was assigned to.
The unassigned device tag is not deleted. If you want, you can delete it manually.
Page topQuarantine and Backup
Kaspersky anti-virus applications installed on client devices may place files in Quarantine or Backup during device scan.
Quarantine is a special repository for storing files that are probably infected with viruses and files that cannot be disinfected at the time when they are detected.
Backup is designed for storing backup copies of files that have been deleted or modified during the disinfection process.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console creates a summarized list of files placed in Quarantine or Backup by Kaspersky applications on the devices. Network Agents on client devices transmit information about the files in Quarantine and Backup to the Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console does not copy files from repositories to Administration Server. All files are stored in repositories on the devices.
Downloading a file from repositories
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console enables you to download copies of files that a security application placed in Quarantine or Backup on a client device. Files are copied to the destination that you specify.
You can download files only if one of the following conditions is met: the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, a push server is in use, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, downloading is not possible.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
To save a copy of file from Quarantine or Backup to a hard drive:
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to save a copy of file from Quarantine, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Quarantine.
- If you want to save a copy of file from Backup, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Backup.
- In the window that opens, select a file that you want to download and click Download.
The download starts. A copy of the file that had been placed in Quarantine on the client device is saved to the specified folder.
Deleting files from repositories
To delete a file from Quarantine or Backup:
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to save a copy of file from Quarantine, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Quarantine.
- If you want to save a copy of file from Backup, in the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Backup.
- In the window that opens, select a file that you want to delete and click Delete.
- Confirm that you want to delete the file.
The security application on the client device that had placed files in the repository (Quarantine or Backup) deletes the same files from this repository.
Remote diagnostics of client devices
You can use remote diagnostics for remote execution of the following operations on Windows-based and Linux-based client devices:
- Enabling and disabling tracing, changing the tracing level, and downloading the trace file
- Downloading system information and application settings
- Downloading event logs
- Generating a dump file for an application
- Starting diagnostics and downloading diagnostics reports
- Starting, stopping, and restarting applications
You can use event logs and diagnostics reports downloaded from a client device to troubleshoot problems on your own. Also, if you contact Kaspersky Technical Support, a Technical Support specialist might ask you to download trace files, dump files, event logs, and diagnostics reports from a client device for further analysis at Kaspersky.
Opening the remote diagnostics window
To perform remote diagnostics on Windows-based and Linux-based client devices, you first have to open the remote diagnostics window.
To open the remote diagnostics window:
- To select the device for which you want to open the remote diagnostics window, perform one of the following:
- If the device belongs to an administration group, in the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Groups → <group name> → Managed devices.
- If the device belongs to the Unassigned devices group, in the main menu, go to Discovery & deployment → Unassigned devices.
- Click the name of the required device.
- In the device properties window that opens, select the Advanced tab.
- In the window that opens, click Remote diagnostics.
This opens the Remote diagnostics window of a client device. If connection between Administration Server and the client device is not established, the error message is displayed.
Alternatively, if you need to obtain all diagnostic information about a Linux-based client device at once, you can run the collect.sh script on this device.
Page topEnabling and disabling tracing for applications
You can enable and disable tracing for applications, including Xperf tracing.
Enabling and disabling tracing
To enable or disable tracing on a remote device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the application list, select the application for which you want to enable or disable tracing.
The list of remote diagnostics options opens.
- If you want to enable tracing:
- In the Tracing section, click Enable tracing.
- In the Modify tracing level window that opens, we recommend that you keep the default values of the settings. When required, a Technical Support specialist will guide you through the configuration process. The following settings are available:
- Tracing level
- Rotation-based tracing
This setting is available for Kaspersky Endpoint Security only.
- Click Save.
The tracing is enabled for the selected application. In some cases, the security application and its task must be restarted in order to enable tracing.
On Linux-based client devices, tracing for the Updater of Kaspersky Security Agent component is regulated by the Network Agent settings. Therefore, the Enable tracing and Modify tracing level options are disabled for this component on client devices running Linux.
- If you want to disable tracing for the selected application, click Disable tracing.
The tracing is disabled for the selected application.
Enabling Xperf tracing
For Kaspersky Endpoint Security, a Technical Support specialist may ask you to enable Xperf tracing for information about the system performance.
To enable and configure Xperf tracing or disable it:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
The list of remote diagnostics options for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows displays.
- In the Xperf tracing section, click Enable Xperf tracing.
If Xperf tracing is already enabled, the Disable Xperf tracing button is displayed instead. Click this button if you want to disable Xperf tracing for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- In the Change Xperf tracing level window that opens, depending on the request from the Technical Support specialist, do the following:
- Select one of the following tracing levels:
- Select one of the following Xperf tracing types:
You may also be asked to enable the Rotation file size, in MB option to prevent excessive increase in the size of the trace file. Then specify the maximum size of the trace file. When the file reaches the maximum size, the oldest tracing information is overwritten with new information.
- Define the rotation file size.
- Click Save.
Xperf tracing is enabled and configured.
- If you want to disable Xperf tracing for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, click Disable Xperf tracing in the Xperf tracing section.
Xperf tracing is disabled.
Downloading trace files of an application
You can download trace files from a client device only if one of the following conditions is met: the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, a push server is in use, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, downloading is not possible.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
To download a trace file of an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application for which you want to download a trace file.
- In the Tracing section, click the Trace files button.
This opens the Device tracing logs window, where a list of trace files is displayed.
- In the list of trace files, select the file that you want to download.
- Do one of the following:
- Download the selected file by clicking the Download. You can select one or several files for downloading.
- Download a portion of the selected file:
- Click Download a portion.
You cannot download portions of several files at the same time. If you select more than one trace file, the Download a portion button will be disabled.
- In the window that opens, specify the name and the file portion to download, according to your needs.
For Linux-based devices, editing the file portion name is not available.
- Click Download.
- Click Download a portion.
The selected file, or its portion, is downloaded to the location that you specify.
Page topDeleting trace files
You can delete trace files that are no longer needed.
To delete a trace file:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window that opens, select the Event logs tab.
- In the Trace files section, click Windows Update logs or Remote installation logs, depending on which trace files you want to delete.
This opens the Device tracing logs window, where a list of trace files is displayed.
- In the list of trace files, select one or several files that you want to delete.
- Click the Remove button.
The selected trace files are deleted.
Page topDownloading application settings
You can download application settings from a client device only if one of the following conditions is met: the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, a push server is in use, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, downloading is not possible.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
To download application settings from a client device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
- In the Application settings section, click the Download button to download information about the settings of the applications installed on the client device.
The ZIP archive with information is downloaded to the specified location.
Page topDownloading system information from a client device
You can download system information to your device from a client device only if one of the following conditions is met: the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, a push server is in use, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, downloading is not possible.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
To download system information from a client device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the System information tab.
- Click the Download button to download the system information about the client device.
The file with information is downloaded to the specified location.
Page topDownloading event logs
You can download event logs to your device from a client device only if one of the following conditions is met: the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled in the settings of the device, a push server is in use, or a connection gateway is in use. Otherwise, downloading is not possible.
The maximum total number of devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option selected is 300.
To download an event log from a remote device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, on the Event logs tab, click All device logs.
- In the All device logs window, select one or several relevant logs.
- Do one of the following:
- Download the selected log by clicking Download entire file.
- Download a portion of the selected log:
- Click Download a portion.
You cannot download portions of several logs at the same time. If you select more than one event log, the Download a portion button will be disabled.
- In the window that opens, specify the name and the log portion to download, according to your needs.
- Click Download.
- Click Download a portion.
The selected event log, or a portion of it, is downloaded to the specified location.
Page topStarting, stopping, restarting the application
You can start, stop, and restart applications on a client device.
To start, stop, or restart an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application that you want to start, stop, or restart.
- Select an action by clicking one of the following buttons:
- Stop application
This button is available only if the application is currently running.
- Restart application
This button is available only if the application is currently running.
- Start application
This button is available only if the application is not currently running.
- Stop application
Depending on the action that you have selected, the required application is started, stopped, or restarted on the client device.
If you restart the Network Agent, a message is displayed stating that the current connection of the device to the Administration Server will be lost.
Page topRunning the remote diagnostics of an application and downloading the results
To start diagnostics for an application on a remote device and download the results:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Kaspersky applications tab.
In the Application management section, the list of Kaspersky applications installed on the device displays.
- In the list of applications, select the application for which you want to run remote diagnostics.
The list of remote diagnostics options opens.
- In the Diagnostics report section, click the Run diagnostics button.
This starts the remote diagnostics process and generates a diagnostics report. When the diagnostics process is complete, the Download diagnostics report button becomes available.
- Click the Download diagnostics report button to download the report.
The report is downloaded to the specified location.
Page topRunning an application on a client device
You may have to run an application on the client device, if a Kaspersky support specialist requests it. You do not have to install the application on that device.
To run an application on the client device:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select the Running a remote application tab.
- In the Running a remote application section, click the Upload button to select a ZIP archive containing the application that you want to run on the client device.
The ZIP archive must include the utility folder. This folder contains the executable file to be run on a remote device.
You can specify the executable file name and the command-line arguments, if necessary. To do this, fill in the Executable file in an archive to be run on a remote device and Command line arguments fields.
- Click the Upload and run button to run the specified application on a client device.
- Follow the instructions of the Kaspersky support specialist.
Generating a dump file for an application
An application dump file allows you to view parameters of the application running on a client device at a point in time. This file also contains information about modules that were loaded for an application.
Generating dump files is available only for 32-bit processes running on Windows-based client devices. For client devices running Linux and for 64-bit processes this feature is not supported.
To create a dump file for an application:
- Open the remote diagnostics window of a client device.
- In the remote diagnostics window, select click the Running a remote application tab.
- In the Generating the process dump file section, specify the executable file of the application for which you want to generate a dump file.
- Click the Download button to save the dump file for the specified application.
If the specified application is not running on the client device, the error message will be displayed.
Remotely connecting to the desktop of a client device
You can obtain remote access to the desktop of a client device through a Network Agent installed on the device. Remote connection to a device through the Network Agent is possible even if the TCP and UDP ports of the client device are closed.
Upon establishing the connection with the device, you gain full access to information stored on this device and can manage applications installed on it.
Remote connection must be allowed in the operating system settings of the target managed device. For example, in Windows 10, this option is called Allow Remote Assistance connections to this computer (you can find this option at Control Panel → System and Security → System → Remote settings). If you have a license for the Vulnerability and patch management feature, you can enable this option forcibly when you establish connection to a managed device. If you do not have the license, enable this option locally on the target managed device. If this option is disabled, remote connection is not possible.
To establish remote connection to a device, you must have two utilities:
- Kaspersky utility named klsctunnel. This utility must be stored on your workstation. You use this utility for tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
Connection tunneling between a remote client device and Administration Server is required if the port used for connection to Administration Server is not available on the device. The port on the device may be unavailable in the following cases:
- The remote device is connected to a local network that uses the NAT mechanism.
- The remote device is part of the local network of Administration Server, but its port is closed by a firewall.
- Standard Microsoft Windows component named Remote Desktop Connection. Connection to a remote desktop is established through the standard Windows utility mstsc.exe in accordance with the utility's settings.
Connection to the current remote desktop session of the user is established without the user's knowledge. Once you connect to the session, the device user is disconnected from the session without an advance notification.
To connect to the desktop of a client device, one of the following conditions must be met:
- Client device is a member of an administration group that has a distribution point with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option enabled.
- In the client device settings, the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option is enabled.
The maximum total number of client devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option enabled is 300.
To connect to the desktop of a client device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Select the check box next to the name of the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Click the Connect to Remote Desktop button.
The Connect to Remote Desktop window opens.
- Click the Download button to download the klsctunnel utility.
- Click the Copy to clipboard button to copy the text from the text field. This text is a Binary Large Object (BLOB) that contains settings required to establish connection between the Administration Server and the managed device.
A BLOB is valid for 3 minutes. If it has expired, reopen the Connect to Remote Desktop window to generate a new BLOB.
- Run the klsctunnel utility.
The utility window opens.
- Paste the copied text into the text field.
- If you use a proxy server, select the Use proxy server check box, and then specify the proxy server connection settings.
- Click the Open port button.
The Remote Desktop Connection login window opens.
- Specify the credentials of the account under which you are currently logged in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- Click the Connect button.
When connection to the device is established, the desktop is available in the Remote Desktop Connection window of Microsoft Windows.
Connecting to devices through Windows Desktop Sharing
You can obtain remote access to the desktop of a client device through a Network Agent installed on the device. Remote connection to a device through the Network Agent is possible even if the TCP and UDP ports of the client device are closed.
You can connect to an existing session on a client device without disconnecting the user in this session. In this case, you and the session user on the device share access to the desktop.
To establish remote connection to a device, you must have two utilities:
- Kaspersky utility named klsctunnel. This utility must be stored on your workstation. You use this utility for tunneling the connection between a client device and the Administration Server.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows tunneling TCP connections from Administration Console via the Administration Server and then via Network Agent to a specified port on a managed device. Tunneling is designed for connecting a client application on a device with Administration Console installed to a TCP port on a managed device—if no direct connection is possible between Administration Console and the target device.
Connection tunneling between a remote client device and Administration Server is required if the port used for connection to Administration Server is not available on the device. The port on the device may be unavailable in the following cases:
- The remote device is connected to a local network that uses the NAT mechanism.
- The remote device is part of the local network of Administration Server, but its port is closed by a firewall.
- Windows Desktop Sharing. When connecting to an existing session of the remote desktop, the session user on the device receives a connection request from you. No information about remote activity on the device and its results will be saved in reports created by Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
You can configure an audit of user activity on a remote client device. During the audit, the application saves information about files on the client device that have been opened and/or modified by the administrator.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing, the following conditions must be met:
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on your workstation.
To check whether the Windows Desktop Sharing feature is included in your Windows edition, make sure that CLSID {32BE5ED2-5C86-480F-A914-0FF8885A1B3F} is included in the 32-bit registry.
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the client device.
- Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console uses a license for Vulnerability and patch management.
- The client device is a member of an administration group that has a distribution point with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option enabled, or this option is enabled in the client device settings.
Note that the maximum total number of client devices with the Do not disconnect from the Administration Server option enabled is 300.
To connect to the desktop of a client device through Windows Desktop Sharing:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Select the check box next to the name of the device to which you want to obtain access.
- Click the Windows Desktop Sharing button.
The Windows Desktop Sharing wizard opens.
- Click the Download button to download the klsctunnel utility, and wait for the download process to complete.
If you already have the klsctunnel utility, skip this step.
- Click the Next button.
- Select the session on the device to which you want to connect, and then click the Next button.
- On the target device, in the dialog box that opens, the user must allow a desktop sharing session. Otherwise, the session is not possible.
After the device user confirms the desktop sharing session, the next page of the wizard opens.
- Click the Copy to clipboard button to copy the text from the text field. This text is a Binary Large Object (BLOB) that contains settings required to establish connection between the Administration Server and the managed device.
A BLOB is valid for 3 minutes. If it has expired, generate a new BLOB.
- Run the klsctunnel utility.
The utility window opens.
- Paste the copied text into the text field.
- If you use a proxy server, select the Use proxy server check box, and then specify the proxy server connection settings.
- Click the Open port button.
Desktop sharing starts in a new window. If you want to interact with the device, click the menu icon (![]() ) in the upper-left corner of the window, and then select Interactive mode.
) in the upper-left corner of the window, and then select Interactive mode.
Triggering of rules in Smart Training mode
This section provides information about the detections performed by the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows on client devices.
The rules detect anomalous behavior on client devices and may block it. If the rules work in Smart Training mode, they detect anomalous behavior and send reports about every such occurrence to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console Administration Server. This information is stored as a list in the Rule triggers in Smart Training state subfolder of the Repositories folder. You can confirm detections as correct or add them as exclusions, so that this type of behavior is not considered anomalous anymore.
Information about detections is stored in the event log on the Administration Server (along with other events) and in the Adaptive Anomaly Control report.
For more information about Adaptive Anomaly Control, the rules, their modes and statuses, refer to Kaspersky Endpoint Security Help.
Viewing the list of detections performed using Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
To view the list of detections performed by Adaptive Anomaly Control rules:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories.
- Click the Rule triggers in Smart Training state link.
The list displays the following information about detections performed using Adaptive Anomaly Control rules:
To view properties of each information element:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories.
- Click the Rule triggers in Smart Training state link.
- In the window that opens, select the object that you want.
- Click the Properties link.
The properties window of the object opens and displays information about the selected element.
You can confirm or add to exclusions any element in the list of detections of Adaptive Anomaly Control rules.
To confirm an element,
Select an element (or several elements) in the list of detections and click the Confirm button.
The status of the element(s) will be changed to Confirming.
Your confirmation will contribute to the statistics used by the rules (for more information, refer to Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation).
To add an element as an exclusion,
Select an element (or several elements) in the list of detections and click the Exclude button.
The Add exclusion wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
If you reject or confirm an element, it will be excluded from the list of detections after the next synchronization of the client device with the Administration Server, and will no longer appear in the list.
Adding exclusions from the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules
The Add exclusion wizard enables you to add exclusions from the Adaptive Anomaly Control rules for Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To start the Add exclusion wizard through the Adaptive Anomaly Control node:
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Repositories → Rule triggers in Smart Training state.
- In the window that opens, select an element (or several elements) in the list of detections, and then click the Exclude button.
You can add up to 1000 exclusions at a time. If you select more elements and try to add them to exclusions, an error message is displayed.
The Add exclusion wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
Managing administration groups
This section provides information about how to manage administration groups.
You can perform the following actions on administration groups:
- Add any number of nested groups at any level of hierarchy to administration groups.
- Add devices to administration groups.
- Change the hierarchy of administration groups by moving individual devices and entire groups to other groups.
- Remove nested groups and devices from administration groups.
- Add secondary and virtual Administration Servers to administration groups.
- Move devices from the administration groups of an Administration Server to those of another Server.
- Define which Kaspersky applications will be automatically installed on devices included in a group.
You can perform these actions only if you have the Modify permission in the Management of administration groups area for the administration groups you want to manage or for the Administration Server to which these groups belong.
Creating administration groups
Initially, the hierarchy of administration groups contains only one administration group called Managed devices group. You can add devices and subgroups into the Managed devices group.
To create an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the hierarchy, select the administration group that is to include the new administration group.
- Click the Add button.
- In the window that opens, enter a name for the group and click Add.
A new administration group with the specified name appears in the administration group hierarchy.
The application allows creating a hierarchy of administration groups based on the structure of Active Directory or the domain network's structure. Also, you can create a structure of groups from a text file.
To create a structure of administration groups:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- Click the Import button.
The New administration group structure wizard starts. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
Automatic installation of applications on devices in an administration group
You can specify which installation packages must be used for automatic remote installation of Kaspersky applications to client devices in an administration group.
To configure automatic installation of applications on the devices in an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups, and click the name of the required administration group.
- In the properties window that opens, go to the Automatic installation tab.
- Select the installation packages of the applications to be installed on the devices, and then click the Save button.
If you select several installation packages of the same application that differ only in their versions, the installation package with the latest version is saved.
After you select the installation packages, a group tasks for installation of the applications on the devices in the administration group is created for each of the application. These tasks are run on the client devices immediately after they are added to the administration group.
Page topMoving administration groups
You can move nested administration groups within the groups hierarchy.
An administration group is moved together with all nested groups, secondary Administration Servers, devices, group policies, and tasks. The application applies to the group all the settings that correspond to its new position in the hierarchy of administration groups.
The name of the group must be unique within one level of the hierarchy. If a group with the same name already exists in the folder into which you move the administration group, you must change the name of the latter. If you have not changed the name of the moved group, an index in (<next sequence number>) format is automatically added to its name when it is moved, for example: (1), (2).
You cannot rename and move the Managed devices group.
To move an administration group to another level of the administration groups hierarchy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups, and then select the check box next to the administration group that you want to move.
- On the toolbar, click the Move button.
- In the window that opens, select where you want to move the administration group, and then click the Move button.
The window is closed, and the administration group is moved to another level of the groups hierarchy.
Page topDeleting administration groups
If you delete an administration group that contains secondary Administration Servers, nested groups, client devices, group tasks, or policies created for this group, all of them will also be deleted.
Before deleting an administration group, you must delete all secondary Administration Servers, nested groups, and client devices from that group.
To delete an administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups, and then select the check box next to the administration group that you want to delete.
- On the toolbar, click the Delete button.
The administration group is deleted.
Page topPolicies and policy profiles
In Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, you can create policies for Kaspersky applications. This section describes policies and policy profiles, and provides instructions for creating and modifying them.
About policies
A policy is a set of Kaspersky application settings that are applied to an administration group and its subgroups. You can install several Kaspersky applications on the devices of an administration group. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console provides a single policy for each Kaspersky application in an administration group. A policy has one of the following statuses (see the table below):
The status of the policy
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
Active |
The current policy that is applied to the device. Only one policy may be active for a Kaspersky application in each administration group. Devices apply the settings values of an active policy for a Kaspersky application. |
Inactive |
A policy that is not currently applied to a device. |
Out-of-office |
If this option is selected, the policy becomes active when the device leaves the corporate network. |
Policies function according to the following rules:
- Multiple policies with different values can be configured for a single application.
- Only one policy can be active for the current application.
- You can activate an inactive policy when a specific event occurs. For example, you can enforce stricter anti-virus protection settings during virus outbreaks.
- A policy can have child policies.
Generally, you can use policies as preparations for emergency situations, such as a virus attack. For example, if there is an attack via flash drives, you can activate a policy that blocks access to flash drives. In this case, the current active policy automatically becomes inactive.
In order to prevent maintaining multiple policies, for example, when different occasions assume changing of several settings only, you may use policy profiles.
A policy profile is a named subset of policy settings values that replaces the settings values of a policy. A policy profile affects the effective settings formation on a managed device. Effective settings are a set of policy settings, policy profile settings, and local application settings that are currently applied for the device.
Policy profiles function according to the following rules:
- A policy profile takes an effect when a specific activation condition occurs.
- Policy profiles contain values of settings that differ from the policy settings.
- Activation of a policy profile changes the effective settings of the managed device.
- A policy can include a maximum of 100 policy profiles.
You cannot create an Administration Server policy.
About lock and locked settings
Each policy setting has a lock button icon ( ). The table below shows lock button statuses:
). The table below shows lock button statuses:
Lock button statuses
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
|
If an open lock is displayed next to a setting and the toggle button is disabled, the setting is not specified in the policy. A user can change these settings in the managed application interface. These type of settings are called unlocked. |
|
If a closed lock is displayed next to a setting and the toggle button is enabled, the setting is applied to the devices where the policy is enforced. A user cannot modify the values of these settings in the managed application interface. These type of settings are called locked. |
We highly recommend that you close locks for the policy settings that you want to apply on the managed devices. The unlocked policy settings can be reassigned by Kaspersky application settings on a managed device.
You can use a lock button for performing the following actions:
- Locking settings for an administration subgroup policy
- Locking settings of a Kaspersky application on a managed device
Thus, a locked setting is used for implementing effective settings on a managed device.
A process of effective settings implementation includes the following actions:
- Managed device applies settings values of Kaspersky application.
- Managed device applies locked settings values of a policy.
A policy and managed Kaspersky application contain the same set of settings. When you configure policy settings, the Kaspersky application settings change values on a managed device. You cannot adjust locked settings on a managed device (see the figure below):
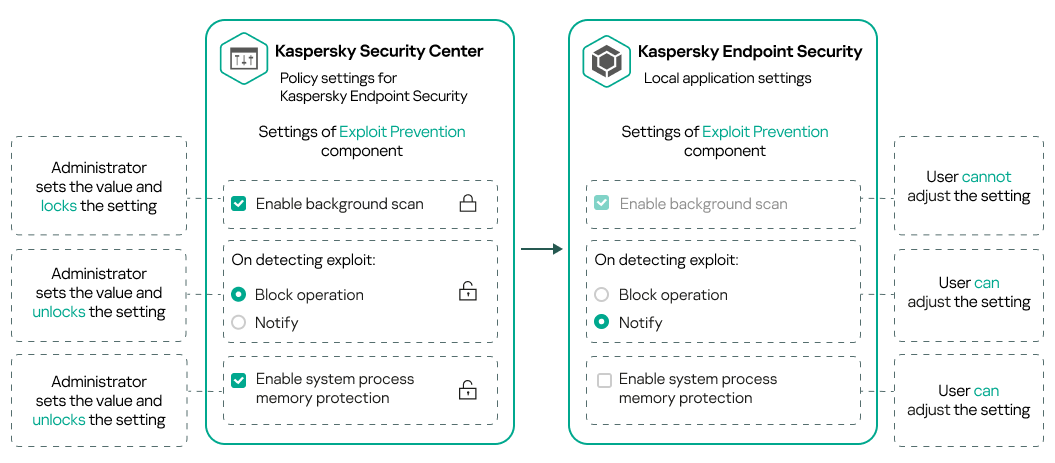
Locks and Kaspersky application settings
Inheritance of policies and policy profiles
This section provides information about the hierarchy and inheritance of policies and policy profiles.
Hierarchy of policies
If different devices need different settings, you can organize devices into administration groups.
You can specify a policy for a single administration group. Policy settings can be inherited. Inheritance means receiving policy settings values in subgroups (child groups) from a policy of a higher-level (parent) administration group.
Hereinafter, a policy for a parent group is also referred to as a parent policy. A policy for a subgroup (child group) is also referred to as a child policy.
By default, at least one managed devices group exists on Administration Server. If you want to create custom groups, they are created as subgroups (child groups) within the managed devices group.
Policies of the same application act on each other, according to a hierarchy of administration groups. Locked settings from a policy of a higher-level (parent) administration group will reassign policy settings values of a subgroup (see the figure below).
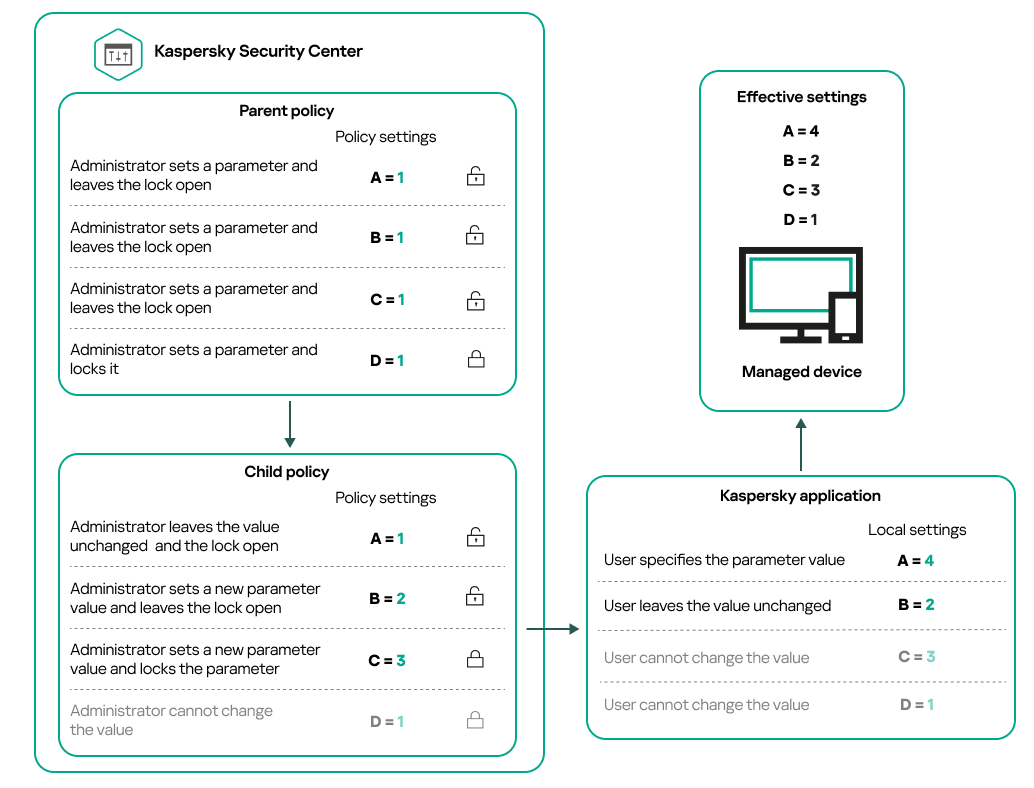
Hierarchy of policies
Page topPolicy profiles in a hierarchy of policies
Policy profiles have the following priority assignment conditions:
- A profile's position in a policy profile list indicates its priority. You can change a policy profile priority. The highest position in a list indicates the highest priority (see the figure below).
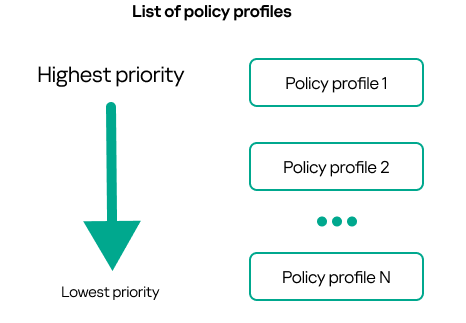
Priority definition of a policy profile
- Activation conditions of policy profiles do not depend on each other. Several policy profiles can be activated simultaneously. If several policy profiles affect the same setting, the device takes the setting value from the policy profile with the highest priority (see the figure below).

Managed device configuration fulfills activation conditions of several policy profiles
Policy profiles in a hierarchy of inheritance
Policy profiles from different hierarchy level policies comply with the following conditions:
- A lower-level policy inherits policy profiles from a higher-level policy. A policy profile inherited from a higher-level policy obtains higher priority than the original policy profile's level.
- You cannot change a priority of an inherited policy profile (see the figure below).
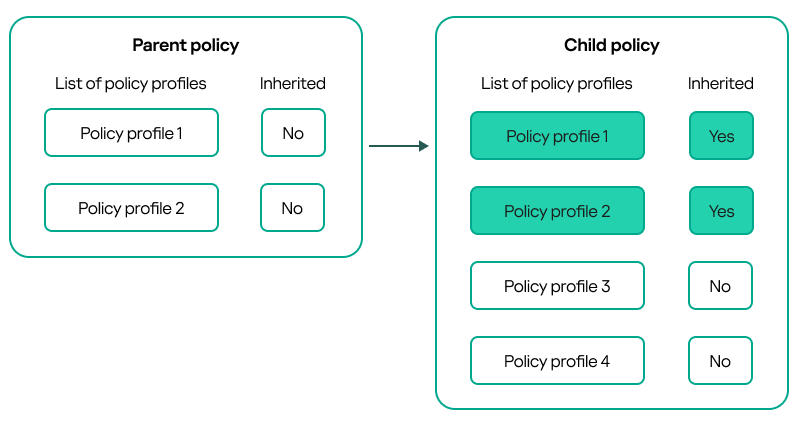
Inheritance of policy profiles
Policy profiles with the same name
If there are two policies with the same names in different hierarchy levels, these policies function according to the following rules:
- Locked settings and the profile activation condition of a higher-level policy profile changes the settings and profile activation condition of a lower-level policy profile (see the figure below).
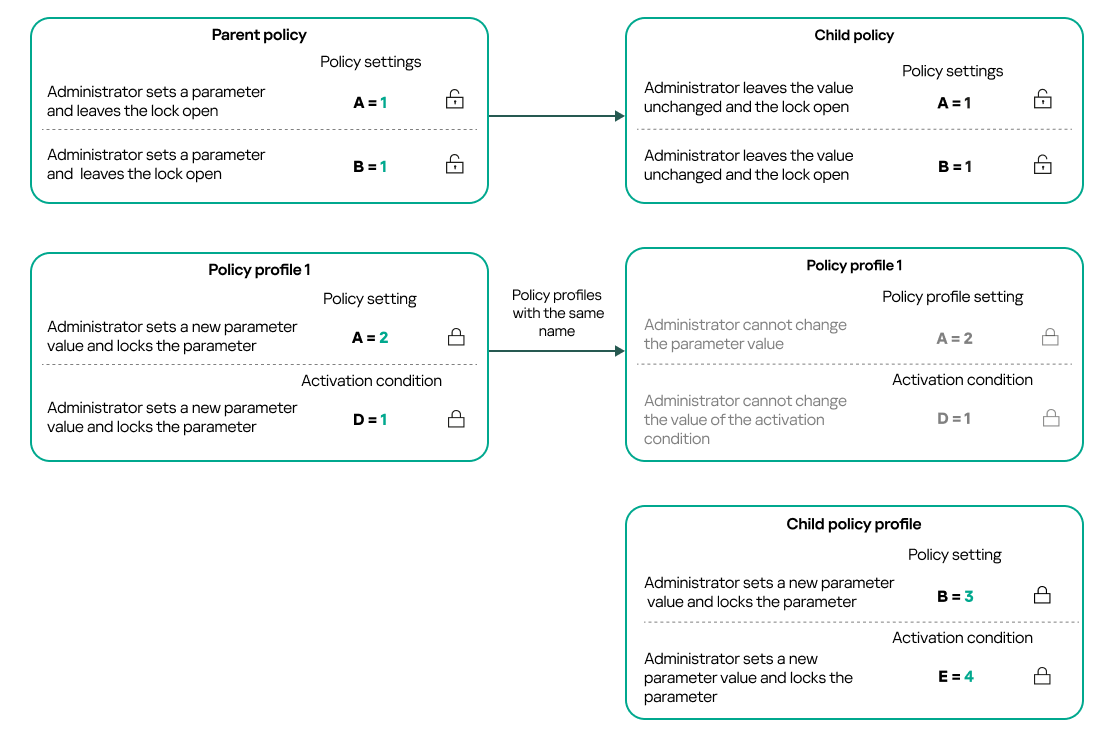
Child profile inherits settings values from a parent policy profile
- Unlocked settings and the profile activation condition of a higher-level policy profile do not change the settings and profile activation condition of a lower-level policy profile.
How settings are implemented on a managed device
Implementation of effective settings on a managed device can be described as follows:
- The values of all settings that have not been locked are taken from the policy.
- Then they are overwritten with the values of managed application settings.
- And then the locked settings values from the effective policy are applied. Locked settings values change the values of unlocked effective settings.
Managing policies
This section describes managing policies and provides information about viewing the list of policies, creating a policy, modifying a policy, copying a policy, moving a policy, forced synchronization, viewing the policy distribution status chart, and deleting a policy.
Viewing the list of policies
You can view lists of policies created for the Administration Server or for any administration group.
To view a list of policies:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups.
- In the administration group structure, select the administration group for which you want to view the list of policies.
The list of policies appears in tabular format. If there are no policies, the table is empty. You can show or hide the columns of the table, change their order, view only lines that contain a value that you specify, or use search.
Creating a policy
You can create policies; you can also modify and delete existing policies.
You cannot create an Administration Server policy.
To create a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click Add.
The Select application window opens.
- Select the application for which you want to create a policy.
- Click Next.
The new policy settings window opens with the General tab selected.
- If you want, change the default name, default status, and default inheritance settings of the policy.
- Click the Application settings tab.
Or, you can click Save and exit. The policy will appear in the list of policies, and you can edit its settings later.
- On the Application settings tab, in the left pane select the category that you want and in the results pane on the right, edit the settings of the policy. You can edit policy settings in each category (section).
The application settings depend on the application for which you create a policy. For details, refer to the following:
- Administration Server configuration
- Network Agent policy settings
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation
For details about settings of other security applications, refer to the documentation for the corresponding application.
When editing the settings, you can click Cancel to cancel the last operation.
- Click Save to save the policy.
The policy will appear in the list of policies.
Modifying a policy
To modify a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy that you want to modify.
The policy settings window opens.
- Specify the general settings and settings of the application for which you create a policy. For details, refer to the following:
- Administration Server configuration
- Network Agent policy settings
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows documentation
For details about settings of other security applications, refer to the documentation for that application.
- Click Save.
The changes made to the policy will be saved in the policy properties, and will appear in the Revision history section.
General policy settings
General
On the General tab, you can modify the policy status and specify the inheritance of policy settings:
- In the Policy status block, you can select one of the policy modes:
- Active
- Out-of-office
- Inactive
- In the Settings inheritance settings group, you can configure the policy inheritance:
Event configuration
The Event configuration tab enables you to configure event logging and event notification. Events are distributed by importance level on the following tabs:
- Critical
The Critical section is not displayed in the Network Agent policy properties.
- Functional failure
- Warning
- Info
In each section, the list shows the types of events and the default event storage term on the Administration Server (in days). Clicking an event type lets you specify the following settings:
- Event registration
You can specify how many days to store the event and select where to store the event:
- Store in the Administration Server database for (days)
- Store in the OS event log on device
- Event notifications
You can select if you want to be notified about the event by email.
By default, the notification settings specified on the Administration Server properties tab (such as recipient address) are used. If you want, you can change these settings on the Email tab.
Also, the Event configuration tab displays a notification when new event types are added (for example, in a new version of the product) and enables you to apply the new settings by clicking the Save or Save and close button.
Revision history
The Revision history tab enables you to view the list of the policy revisions and roll back changes made to the policy, if necessary.
Enabling and disabling a policy inheritance option
To enable or disable the inheritance option in a policy:
- Open the required policy.
- Open the General tab.
- Enable or disable policy inheritance:
- If you enable Inherit settings from parent policy in a child policy and an administrator locks some settings in the parent policy, then you cannot change these settings in the child policy.
- If you disable Inherit settings from parent policy in a child policy, then you can change all of the settings in the child policy, even if some settings are locked in the parent policy.
- If you enable Force inheritance of settings in child policies in the parent group, this enables the Inherit settings from parent policy option for each child policy. In this case, you cannot disable this option for any child policy. All of the settings that are locked in the parent policy are forcibly inherited in the child groups, and you cannot change these settings in the child groups.
- Click the Save button to save changes or click the Cancel button to reject changes.
By default, the Inherit settings from parent policy option is enabled for a new policy.
If a policy has profiles, all of the child policies inherit these profiles.
Copying a policy
You can copy policies from one administration group to another.
To copy a policy to another administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy (or policies) that you want to copy.
- Click the Copy button.
On the right side of the screen, the tree of the administration groups appears.
- In the tree, select the target group, that is, the group to which you want to copy the policy (or policies).
- Click the Copy button at the bottom of the screen.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The policy (policies) will be copied to the target group with all its profiles. The status of each copied policy in the target group will be Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy with the name identical to that of the newly moved policy already exists in the target group, the name of the newly moved policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1).
Moving a policy
You can move policies from one administration group to another. For example, you want to delete a group, but you want to use its policies for another group. In this case, you may want move the policy from the old group to the new one before deleting the old group.
To move a policy to another administration group:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy (or policies) that you want to move.
- Click the Move button.
On the right side of the screen, the tree of the administration groups appears.
- In the tree, select the target group, that is, the group to which you want to move the policy (or policies).
- Click the Move button at the bottom of the screen.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
If a policy is not inherited from the source group, it is moved to the target group with all its profiles. The status of the policy in the target group is Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy is inherited from the source group, it remains in the source group. It is copied to the target group with all its profiles. The status of the policy in the target group is Inactive. You can change the status to Active at any time.
If a policy with the name identical to that of the newly moved policy already exists in the target group, the name of the newly moved policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1).
Exporting a policy
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to save a policy, its settings, and the policy profiles to a KLP file. You can use this KLP file to import the saved policy both to Kaspersky Security Center Windows and Kaspersky Security Center Linux.
To export a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy that you want to export.
You cannot export multiple policies at the same time. If you select more than one policy, the Export button will be disabled.
- Click the Export button.
- In the opened Save as window, specify the policy file name and path. Click the Save button.
The Save as window is displayed only if you use Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Opera. If you use another browser, the policy file is automatically saved in the Downloads folder.
Importing a policy
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to import a policy from a KLP file. The KLP file contains the exported policy, its settings, and the policy profiles.
To import a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the Import button.
- Click the Browse button to choose a policy file that you want to import.
- In the opened window, specify the path to the KLP policy file, and then click the Open button. Note that you can select only one policy file.
The policy processing starts.
- After the policy is processed successfully, select the administration group to which you want to apply the policy.
- Click the Complete button to finish the policy import.
The notification with the import results appears. If the policy is imported successfully, you can click the Details link to view the policy properties.
After a successful import, the policy is displayed in the policy list. The settings and profiles of the policy are also imported. Regardless of the policy status that was selected during the export, the imported policy is inactive. You can change the policy status in the policy properties.
If the newly imported policy has a name identical to that of an existing policy, the name of the imported policy is expanded with the (<next sequence number>) index, for example: (1), (2).
Page topViewing the policy distribution status chart
In Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, you can view the status of policy application on each device in a policy distribution status chart.
To view the policy distribution status on each device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select check box next to the name of the policy for which you want to view the distribution status on devices.
- In the menu that appears, click the Distribution link.
The <Policy name> distribution results window opens.
- In the <Policy name> distribution results window that opens, the Status description (if available) of the policy is displayed.
You can change number of results displayed in the list with policy distribution. The maximum number of devices is 100,000.
To change the number of devices displayed in the list with policy distribution results:
- In the main menu, go to your account settings, and then select Interface options.
- In the Maximum number of devices displayed in policy distribution results, enter the number of devices (up to 100,000).
By default, the number is 5000.
- Click Save.
The settings are saved and applied.
Activating a policy automatically at the Virus outbreak event
To make a policy perform automatic activation at a Virus outbreak event:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens, with the General tab selected.
- Select the Virus outbreak section.
- In the right pane, click the Configure policies to activate when a virus outbreak event occurs link.
The Policy activation window opens.
- In the section relating to the component that detects a virus outbreak—Anti-Virus for workstations and file servers, Anti-Virus for mail servers, or Anti-Virus for perimeter defense—select the option button next to the entry you want, and then click Add.
A window opens with the Managed devices administration group.
- Click the chevron icon (
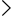 ) next to Managed devices.
) next to Managed devices.A hierarchy of administration groups and their policies is displayed.
- In the hierarchy of administration groups and their policies, click the name of a policy or policies that are activated when a virus outbreak is detected.
To select all policies in the list or in a group, select the check box next to the required name.
- Click the Save button.
The window with the hierarchy of administration groups and their policies is closed.
The selected policies are added to the list of policies that are activated when a virus outbreak is detected. The selected policies are activated at the virus outbreak, independent whether they are active or inactive.
If a policy has been activated on the Virus outbreak event, you can return to the previous policy only by using the manual mode.
Forced synchronization
Although Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console automatically synchronizes the status, settings, tasks, and policies for managed devices, in some cases you need to know for certain, at a given moment, whether synchronization has already been performed for a specified device.
Synchronizing a single device
To force synchronization between the Administration Server and a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
A property window opens with the General section selected.
- Click the Force synchronization button.
The application synchronizes the selected device with the Administration Server.
Synchronizing multiple devices
To force synchronization between the Administration Server and multiple managed devices:
- Open the device list of an administration group or a device selection:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices → Groups, and then select the administration group that contains devices to synchronize.
- Run a device selection to view the device list.
- Select the check boxes next to the devices that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
- Click the Force synchronization button.
The application synchronizes the selected devices with the Administration Server.
- In the device list, check that the time of last connection to the Administration Server has changed, for the selected devices, to the current time. If the time has not changed, update the page content by clicking the Refresh button.
The selected devices are synchronized with the Administration Server.
Viewing the time of a policy delivery
After changing a policy for a Kaspersky application on the Administration Server, you can check whether the changed policy has been delivered to a specific managed device. A policy can be delivered during a regular synchronization or a forced synchronization.
To view the date and time that an application policy was delivered to a managed device:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Managed devices.
- Click the name of the device that you want to synchronize with the Administration Server.
A property window opens with the General section selected.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Select the application for which you want to view the policy synchronization date.
The application policy window opens with the General section selected and the policy delivery date and time displayed.
Deleting a policy
You can delete a policy if you do not need it anymore. You can delete only a policy that is not inherited in the specified administration group. If a policy is inherited, you can only delete it in the upper-level group for which it was created.
To delete a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Select the check box next to the policy that you want to delete, and click Delete.
The Delete button becomes unavailable (dimmed) if you select an inherited policy.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The policy is deleted together with all its profiles.
Managing policy profiles
This section describes managing policy profiles and provides information about viewing the profiles of a policy, changing a policy profile priority, creating a policy profile, modifying a policy profile, copying a policy profile, creating a policy profile activation rule, and deleting a policy profile.
Viewing the profiles of a policy
To view profiles of a policy:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the name of the policy whose profiles you want to view.
The policy properties window opens with the General tab selected.
- Open the Policy profiles tab.
The list of policy profiles appears in tabular format. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
Changing a policy profile priority
To change a policy profile priority:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the check box next to the policy profile for which you want to change priority.
- Set a new position of the policy profile in the list by clicking Prioritize or Deprioritize.
The higher a policy profile is located in the list, the higher its priority.
- Click the Save button.
Priority of the selected policy profile is changed and applied.
Creating a policy profile
To create a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of the policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
- Click Add.
- If you want, change the default name and default inheritance settings of the profile.
- Select the Application settings tab.
Alternatively, you can click Save and exit. The profile that you have created appears in the list of policy profiles, and you can edit its settings later.
- On the Application settings tab, in the left pane, select the category that you want and in the results pane on the right, edit the settings for the profile. You can edit policy profile settings in each category (section).
When editing the settings, you can click Cancel to cancel the last operation.
- Click Save to save the profile.
The profile will appear in the list of policy profiles.
Modifying a policy profile
The capability to edit a policy profile is only available for policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
To modify a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, click the policy profile that you want to modify.
The policy profile properties window opens.
- Configure the profile in the properties window:
- If necessary, on the General tab, change the profile name and enable or disable the profile.
- Edit the profile activation rules.
- Edit the application settings.
For details about settings of security applications, please see the documentation of the corresponding application.
- Click Save.
The modified settings will take effect either after the device is synchronized with the Administration Server (if the policy profile is active), or after an activation rule is triggered (if the policy profile is inactive).
Copying a policy profile
You can copy a policy profile to the current policy or to another, for example, if you want to have identical profiles for different policies. You can also use copying if you want to have two or more profiles that differ in only a small number of settings.
To copy a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears. If the policy does not have profiles, an empty table appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the policy profile that you want to copy.
- Click Copy.
- In the window that opens, select the policy to which you want to copy the profile.
You can copy a policy profile to the same policy or to a policy that you specify.
- Click Copy.
The policy profile is copied to the policy that you selected. The newly copied profile gets the lowest priority. If you copy the profile to the same policy, the name of the newly copied profile will be expanded with the () index, for example: (1), (2).
Later, you can change the settings of the profile, including its name and its priority; the original policy profile will not be changed in this case.
Creating a policy profile activation rule
To create a policy profile activation rule:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, click the policy profile for which you need to create an activation rule.
If the list of policy profiles is empty, you can create a policy profile.
- On the Activation rules tab, click the Add button.
The window with policy profile activation rules opens.
- Specify a name for the rule.
- Select the check boxes next to the conditions that must affect activation of the policy profile that you are creating:
- General rules for policy profile activation
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for specific device owner
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for hardware specifications
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for role assignment
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for tag usage
For this option, specify at the next step:
- Rules for Active Directory usage
For this option, specify at the next step:
The number of additional pages of the wizard depends on the settings that you select at the first step. You can modify policy profile activation rules later.
- General rules for policy profile activation
- Check the list of the configured parameters. If the list is correct, click Create.
The profile will be saved. The profile will be activated on the device when activation rules are triggered.
Policy profile activation rules created for the profile are displayed in the policy profile properties on the Activation rules tab. You can modify or remove any policy profile activation rule.
Multiple activation rules can be triggered simultaneously.
Deleting a policy profile
To delete a policy profile:
- Proceed to the list of profiles of a policy that you want.
The list of policy profiles appears.
- On the Policy profiles tab, select the check box next to the policy profile that you want to delete, and click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click Delete again.
The policy profile is deleted. If the policy is inherited by a lower-level group, the profile remains in that group, but becomes the policy profile of that group. This is done to eliminate significant change in settings of the managed applications installed on the devices of lower-level groups.
Data encryption and protection
Data encryption reduces the risk of unintentional leakage in case your laptop or hard drive is stolen or lost, or upon access by unauthorized users and applications.
The following Kaspersky applications support encryption:
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
- Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
You can show or hide some of the interface elements related to the encryption management feature by using the user interface settings.
Encryption of data in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows
You can manage the BitLocker Drive Encryption technology on devices running a Windows operating system for servers or workstations.
By using these components of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, you can, for example, enable or disable encryption, view the list of encrypted drives, or generate and view reports about encryption.
You configure encryption by defining policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows performs encryption and decryption according to the active policy. For detailed instructions on how to configure rules and a description of encryption features, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
Encryption of data in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac
You can use FileVault encryption on devices running macOS. While working with Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac, you can enable or disable this encryption.
You configure encryption by defining policies of Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac performs encryption and decryption according to the active policy. For a detailed description of encryption features, see the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Mac Help.
Viewing the list of encrypted drives
In Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, you can view details about encrypted drives and devices that are encrypted at the drive level. After the information on a drive is decrypted, the drive is automatically removed from the list.
To view the list of encrypted drives,
In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection → Encrypted drives.
If the section is not on the menu, this means that it is hidden. In the user interface settings, enable the Show data encryption and protection option to display the section.
You can export the list of encrypted drives to a CSV or TXT file. To do this, click the Export to CSV or Export to TXT button.
Creating and viewing encryption reports
You can generate the following reports:
- Report on encryption status of managed devices. This report provides details about the data encryption of various managed devices. For example, the report shows the number of devices to which the policy with configured encryption rules applies. Also, you can find out, for instance, how many devices need to be rebooted. The report also contains information about the encryption technology and algorithm for every device.
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices. This report contains similar information as the report on the encryption status of managed devices, but it provides data only for mass storage devices and removable drives.
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives. This report shows which user accounts have access to encrypted drives.
- Report on file encryption errors. This report contains information about errors that occurred when the data encryption or decryption tasks were run on devices.
- Report on blockage of access to encrypted files. This report contains information about blocking application access to encrypted files. This report is helpful if an unauthorized user or application tries to access encrypted files or drives.
You can generate any report in the Monitoring & reporting → Reports section. Alternatively, in the Operations → Data encryption and protection section, you can generate the following encryption reports:
- Report on encryption status of mass storage devices
- Report on rights to access encrypted drives
- Report on file encryption errors
To generate an encryption report in the Data encryption and protection section:
- Make sure that you enabled the Show data encryption and protection option in the Interface options.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection.
- Open the Encrypted drives section to generate the report on encryption status of mass storage devices or the report on rights to access encrypted drives.
- Click the name of the report that you want to generate.
The report generation starts.
Granting access to an encrypted drive in offline mode
A user can request access to an encrypted device, for example, when Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows is not installed on the managed device. After you receive the request, you can create an access key file and send it to the user. All of the use cases and detailed instructions are provided in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help.
To grant access to an encrypted drive in offline mode:
- Get a request access file from a user (a file with the FDERTC extension). Follow the instructions in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help to generate the file in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows.
- In the main menu, go to Operations → Data encryption and protection → Encrypted drives.
A list of encrypted drives appears.
- Select the drive to which the user requested access.
- Click the Grant access to the device in offline mode button.
- In the window that opens, select the plug-in corresponding to the Kaspersky application that was used to encrypt the selected drive.
If a drive is encrypted with a Kaspersky application that is not supported by Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, use Microsoft Management Console-based Administration Console to grant the offline access.
- Follow the instructions provided in the Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows Help (see expanding blocks at the end of the section).
After that, the user applies the received file to access the encrypted drive and read data stored on the drive.
Users and user roles
This section describes users and user roles, and provides instructions for creating and modifying them, for assigning roles and groups to users, and for associating policy profiles with roles.
About user accounts
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to manage user accounts and groups of accounts. The application supports two types of accounts:
- Accounts of organization employees. Administration Server retrieves data of the accounts of those local users when polling the organization's network.
- Accounts of internal users of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. You can create accounts of internal users. These accounts are used only within Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
To view tables of user accounts and security groups:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups.
- Select the Users or the Groups tab.
The table of users or security groups opens. By default, the opened table is filtered by the Subtype and Has assigned roles columns. The table displays internal users or groups that have assigned roles.
If you want to view the table with only the accounts of local users, set the Subtype filter criteria to Local.
If you switch to a secondary Administration Server version 14.2 or earlier, and then open the list of users or security groups, the opened table will be filtered only by the Subtype column. The filter by the Has assigned roles column will not be applied by default. The filtered table will contain all internal users or security groups with the assigned role and without it.
Page topAdding an account of an internal user
If you want, you can add internal users of your workspace on the portal. After you add an internal user, you can assign a role to him or her in the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
Page topAbout user roles
A user role (also referred to as a role) is an object containing a set of rights and privileges. A role can be associated with settings of Kaspersky applications installed on a user device. You can assign a role to a set of users or to a set of security groups at any level in the hierarchy of administration groups, Administration Servers, or at the level of specific objects.
If you manage devices through a hierarchy of Administration Servers that includes virtual Administration Servers, note that you can create, modify, or delete user roles only from a physical Administration Server. Then, you can propagate the user roles to secondary Administration Servers, including virtual ones.
You can associate user roles with policy profiles. If a user is assigned a role, this user gets security settings necessary to perform job functions.
A user role can be associated with users of devices in a specific administration group.
User role scope
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
Advantage of using roles
An advantage of using roles is that you do not have to specify security settings for each of the managed devices or for each of the users separately. The number of users and devices in a company may be quite large, but the number of different job functions that require different security settings is considerably smaller.
Differences from using policy profiles
Policy profiles are properties of a policy that is created for each Kaspersky application separately. A role is associated with many policy profiles created for different applications. Therefore, a role is a method of uniting settings for a certain user type in one place.
Configuring access rights to application features. Role-based access control
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console provides facilities for role-based access to the features of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console and of managed Kaspersky applications.
You can configure access rights to application features for Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console users in one of the following ways:
- By configuring the rights for each user or group of users individually.
- By creating standard user roles with a predefined set of rights and assigning those roles to users depending on their scope of duties.
Application of user roles is intended to simplify and shorten routine procedures of configuring users' access rights to application features. Access rights within a role are configured in accordance with the standard tasks and the users' scope of duties.
User roles can be assigned names that correspond to their respective purposes. You can create an unlimited number of roles in the application.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself.
Access rights to application features
The table below shows the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console features with the access rights to manage the associated tasks, reports, settings, and perform the associated user actions.
To perform the user actions listed in the table, a user has to have the right specified next to the action.
Read, Write, and Execute rights are applicable to any task, report, or setting. In addition to these rights, a user has to have the Perform operations on device selections right to manage tasks, reports, or settings on device selections.
The General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs functional area is intended for audit purposes. When users are granted Read rights in this functional area, they get full Read access to all objects and are able to execute any created tasks on selections of devices connected to the Administration Server via Network Agent with local administrator rights (root for Linux). We recommend granting these rights carefully and to a limited set of users who need them to perform their official duties.
All tasks, reports, settings, and installation packages that are missing in the table belong to the General features: Basic functionality functional area.
Access rights to application features
Functional area |
Right |
User action: right required to perform the action |
Task |
Report |
Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
General features: Management of administration groups |
Write |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs |
Read |
Get read access to all objects: Read |
None |
None |
Access is granted regardless of other rights, even if they prohibit read access to specific objects. |
General features: Basic functionality |
|
|
|
|
None |
General features: Deleted objects |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Event processing |
|
|
None |
None |
Settings:
|
General features: Kaspersky software deployment |
|
Approve or decline installation of the patch: Manage Kaspersky patches |
None |
|
Installation package: "Kaspersky" |
General features: License key management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Enforced report management |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
Register, update, or delete secondary Administration Servers: Configure hierarchy of Administration Servers |
None |
None |
None |
General features: User permissions |
Modify object ACLs |
|
None |
None |
None |
General features: Virtual Administration Servers |
|
|
None |
"Report on results of installation of third-party software updates" |
None |
General features: Encryption Key Management |
Write |
Import the encryption keys: Write |
None |
None |
None |
System management: Connectivity |
|
|
None |
"Report on device users" |
None |
System management: Hardware inventory |
|
|
None |
|
None |
System management: Network access control |
|
|
None |
None |
None |
System management: Operating system deployment |
|
|
"Create installation package upon reference device OS image" |
None |
Installation package: "OS Image" |
System management: Vulnerability and patch management
|
|
|
|
"Report on software updates" |
None |
System management: Remote installation |
|
|
None |
None |
Installation packages:
|
System management: Software inventory |
|
None |
None |
|
None |
Predefined user roles
User roles assigned to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console users provide them with sets of access rights to application features.
Users created on a virtual Server cannot be assigned a role on the Administration Server.
You can use the predefined user roles with already configured set of rights, or create new roles and configure the required rights yourself. Some of the predefined user roles available in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console can be associated with specific job positions, for example, Auditor, Security Officer, Supervisor (these roles are present in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console starting from the version 11). Access rights of these roles are pre-configured in accordance with the standard tasks and scope of duties of the associated positions. The table below shows how roles can be associated with specific job positions.
Examples of roles for specific job positions
Role |
Comment |
Auditor |
Permits all operations with all types of reports, all viewing operations, including viewing deleted objects (grants the Read and Write permissions in the Deleted objects area). Does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Supervisor |
Permits all viewing operations; does not permit other operations. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Security Officer |
Permits all viewing operations, permits reports management; grants limited permissions in the System management: Connectivity area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
The table below shows the access rights assigned to each predefined user role.
Access rights of predefined user roles
Role |
Description |
|---|---|
Administration Server Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Administration Server Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Auditor |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas, in General features:
You can assign this role to a person who performs the audit of your organization. |
Installation Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants Read and Execute rights in the General features: Virtual Administration Servers functional area. |
Installation Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Main Administrator |
Permits all operations in functional areas, except for the following areas in General features:
Grants the Read and Write rights in the General features: Encryption key management functional area. |
Main Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in all of the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Administrator |
Permits all operations in the following functional areas:
|
Mobile Device Management Operator |
Grants the Read and Execute rights in the General features: Basic functionality functional area. Grants Read and Send only information commands to mobile devices in the Mobile Device Management: General functional area. |
Security Officer
|
Permits all operations in the following functional areas, in General features:
Grants the Read, Write, Execute, Save files from devices to the administrator's workstation, and Perform operations on device selections rights in the System management: Connectivity functional area. You can assign this role to an officer in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Senior Security Analyst |
Grants the Read right in the General features: Basic functionality functional area. Grants the Read, Write, Execute, Save files from devices to the administrator's workstation, and Perform operations on device selections rights in the System management: Connectivity functional area. Grants the access rights to the Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response Expert solution. |
Self Service Portal User |
Permits all operations in the Mobile Device Management: Self Service Portal functional area. This feature is not supported in Kaspersky Security Center 11 and later. |
Supervisor |
Grants the Read right in the General features: Access objects regardless of their ACLs and General features: Enforced report management functional area. You can assign this role to a security officer and other managers in charge of the IT security in your organization. |
Vulnerability and patch management administrator |
Permits all operations in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Vulnerability and patch management operator |
Grants the Read and Execute (where applicable) rights in the General features: Basic functionality and System management (including all features) functional areas. |
Assigning access rights to specific objects
In addition to assigning access rights at the server level, you can configure access to specific objects, for example, to a specific task. The application allows you to specify access rights to the following object types:
- Administration groups
- Tasks
- Reports
- Device selections
- Event selections
To assign access rights to a specific object:
- Depending on the object type, in the main menu, go to the corresponding section:
- Assets (Devices) → Hierarchy of groups
- Assets (Devices) → Tasks
- Monitoring & reporting → Reports
- Assets (Devices) → Device selections
- Monitoring & reporting → Event selections
- Open the properties of the object to which you want to configure access rights.
To open the properties window of an administration group or a task, click the object name. Properties of other objects can be opened by using the button on the toolbar.
- In the properties window, open the Access rights section.
The user list opens. The listed users and security groups have access rights to the object. By default, if you use a hierarchy of administration groups or Servers, the list and access rights are inherited from the parent administration group or primary Server.
- To be able to modify the list, enable the Use custom permissions option.
- Configure access rights:
- Use the Add and Delete buttons to modify the list.
- Specify access rights for a user or security group. Do one of the following:
- If you want to specify access rights manually, select the user or security group, click the Access rights button, and then specify the access rights.
- If you want to assign a user role to the user or security group, select the user or security group, click the Roles button, and then select the role to assign.
- Click the Save button.
The access rights to the object are configured.
Assigning access rights to users and security groups
You can give users and security groups access rights to use different features of Administration Server, for example, Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Linux.
To assign access rights to a user or a security group:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Access rights tab, select the check box next to the name of the user or the security group to whom to assign rights, and then click the Access rights button.
You cannot select multiple users or security groups at the same time. If you select more than one item, the Access rights button will be disabled.
- Configure the set of rights for the user or group:
- Expand the node with features of Administration Server or other Kaspersky application.
- Select the Allow or Deny check box next to the feature or the access right that you want.
Example 1: Select the Allow check box next to the Application integration node to grant all available access rights to the Application integration feature (Read, Write, and Execute) for a user or group.
Example 2: Expand the Encryption key management node, and then select the Allow check box next to the Write permission to grant the Write access right to the Encryption key management feature for a user or group.
- After you configure the set of access rights, click OK.
The set of rights for the user or group of users will be configured.
The permissions of the Administration Server (or the administration group) are divided into the following areas:
- General features:
- Management of administration groups
- Access objects regardless of their ACLs
- Basic functionality
- Deleted objects
- Encryption Key Management
- Event processing
- Operations on Administration Server (only in the property window of Administration Server)
- Device tags
- Kaspersky application deployment
- License key management
- Application integration
- Enforced report management
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers
- User permissions
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Mobile Device Management:
- General
- Self Service Portal
- System Management:
- Connectivity
- Execute scripts remotely
- Hardware inventory
- Network Access Control
- Operating system deployment
- Vulnerability and patch management
- Remote installation
- Software inventory
If neither Allow nor Deny is selected for an access right, then the access right is considered undefined: it is denied until it is explicitly denied or allowed for the user.
The rights of a user are the sum of the following:
- User's own rights
- Rights of all the roles assigned to this user
- Rights of all the security group to which the user belongs
- Rights of all the roles assigned to the security groups to which the user belongs
If at least one of these sets of rights has Deny for a permission, then the user is denied this permission, even if other sets allow it or leave it undefined.
You can also add users and security groups to the scope of a user role to use different features of Administration Server. Settings associated with a user role will only apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
Page topAssigning a role to a user or a security group
To assign a role to a user or a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users or the Groups tab.
- Select the name of the user or the security group to whom to assign a role.
You can select multiple names.
- On the menu line, click the Assign role button.
The Role assignment wizard starts.
- Follow the instructions of the wizard: select the role that you want to assign to the selected users or security groups, and then select the scope of role.
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
The role with a set of rights for working with Administration Server is assigned to the user (or users, or the security group). In the list of users or security groups, a check box appears in the Has assigned roles column.
Page topCreating a user role
To create a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click Add.
- In the New role name window that opens, enter the name of the new role.
- Click OK to apply the changes.
- In the role properties window that opens, change the settings of the role:
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
You cannot edit the name of a predefined role.
- On the Settings tab, edit the role scope and policies and profiles associated with the role.
- On the Access rights tab, edit the rights for access to Kaspersky applications.
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The new role appears in the list of user roles.
Editing a user role
To edit a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role that you want to edit.
- In the role properties window that opens, change the settings of the role:
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
You cannot edit the name of a predefined role.
- On the Settings tab, edit the role scope and policies and profiles associated with the role.
- On the Access rights tab, edit the rights for access to Kaspersky applications.
- On the General tab, edit the role name.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The updated role appears in the list of user roles.
Editing the scope of a user role
A user role scope is a combination of users and administration groups. Settings associated with a user role apply only to devices that belong to users who have this role, and only if these devices belong to groups associated with this role, including child groups.
To add users, user groups, and administration groups to the scope of a user role, you can use either of the following methods:
Method 1:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users or the Groups tab.
- Select check boxes next to the users or user groups that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button.
The Role assignment wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Select role step, select the user role that you want to assign.
- On the Define scope step, select the administration group that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button to close the window.
The selected users or user groups and the selected administration group are added to the scope of the user role.
Method 2:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role for which you want to define the scope.
- In the role properties window that opens, select the Settings tab.
- In the Role scope section, click Add.
The Role assignment wizard starts. Proceed through the wizard by using the Next button.
- On the Define scope step, select the administration group that you want to add to the user role scope.
- On the Select users step, select users and user groups that you want to add to the user role scope.
- Click the Assign role button to close the window.
- Close the role properties window.
The selected users or user groups and the selected administration group are added to the scope of the user role.
Method 3:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the Access rights tab, select the check box next to the name of the user or the security group that you want to add to the user role scope, and then click the Roles button.
You cannot select multiple users or security groups at the same time. If you select more than one item, the Roles button will be disabled.
- In the Roles window, select the user role that you want to assign, and then click OK and save changes.
The selected users or security groups are added to the scope of the user role.
Deleting a user role
To delete a user role:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Select the check box next to the name of the role that you want to delete.
- Click Delete.
- In the window that opens, click OK.
The user role is deleted.
Associating policy profiles with roles
You can associate user roles with policy profiles. In this case, the activation rule for this policy profile is based on the role: the policy profile becomes active for a user that has the specified role.
For example, the policy bars any GPS navigation software on all devices in an administration group. GPS navigation software is necessary only on a single device in the Users administration group—the device owned by a courier. In this case, you can assign a "Courier" role to its owner, and then create a policy profile allowing GPS navigation software to run only on the devices whose owners are assigned the "Courier" role. All the other policy settings are preserved. Only the user with the role "Courier" will be allowed to run GPS navigation software. Later, if another worker is assigned the "Courier" role, the new worker also can run navigation software on your organization's device. Running GPS navigation software will still be prohibited on other devices in the same administration group.
To associate a role with a policy profile:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Roles.
- Click the name of the role that you want to associate with a policy profile.
The role properties window opens with the General tab selected.
- Select the Settings tab, and scroll down to the Policies & profiles section.
- Click Edit.
- To associate the role with:
- An existing policy profile—Click the chevron icon (
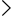 ) next to the required policy name, and then select the check box next to the profile with which you want to associate the role.
) next to the required policy name, and then select the check box next to the profile with which you want to associate the role. - A new policy profile:
- Select the check box next to the policy for which you want to create a profile.
- Click New policy profile.
- Specify a name for the new profile and configure the profile settings.
- Click the Save button.
- Select the check box next to the new profile.
- An existing policy profile—Click the chevron icon (
- Click Assign to role.
The profile is associated with the role and appears in the role properties. The profile applies automatically to any device whose owner is assigned the role.
Creating a security group
To create a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Groups tab.
- Click New group.
- In the New group window, specify the following settings for the new security group:
- Name
- Description
- Click OK to save the changes.
A new security group is added to the security group list.
Editing a security group
To edit a security group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Groups tab.
- Click the name of the security group that you want to edit.
- In the group settings window that opens, change the settings of the security group:
- On the General tab, you can change the Name and Description settings. These settings are available only for internal security groups.
- On the Users tab, you can add users to the security group. This setting is available only for internal users and internal security groups.
- On the Roles tab, you can assign a role to the security group.
- Click Save to save the changes.
The changes are applied to the security group.
Adding user accounts to an internal group
You can add only accounts of internal users to an internal group.
To add user accounts to an internal group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
- Select check boxes next to user accounts that you want to add to a group.
- Click the Assign group button.
- In the Assign group window that opens, select the group to which you want to add user accounts.
- Click the Assign button.
The user accounts are added to the group. You can also add internal users to a group by using the group settings.
Deleting a security group
You can delete only internal security groups.
To delete a user group:
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Groups tab.
- Select the check box next to the user group that you want to delete.
- Click Delete, and then confirm the deletion in the opened window.
The user group is deleted.
Configuring ADFS integration
To allow the users registered in Active Directory (AD) in your organization to sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, you must configure integration with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS).
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console supports ADFS 3 (Windows Server 2016) or a later version. ADFS must be published and available on the internet. As the service communication certificate ADFS uses publicly trusted certificate.
To change ADFS integration settings, you must have the access right to change user permissions.
Before you proceed, make sure that you completed Active Directory polling.
To configure ADFS integration:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the ADFS integration settings section.
- Copy the callback URL.
You will need this URL to configure the integration in ADFS Management Console.
- In ADFS Management Console, add a new application group, and then add a new application by selecting the Server application template (the names of the Microsoft interface elements are provided in English.).
ADFS Management Console generates client ID for the new application. You will need the client ID to configure the integration in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- As a redirect URI, specify the callback URL that you copied in the Administration Server properties window.
- Generate a client secret. You will need the client secret to configure the integration in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- Save the properties of the added application.
- Add a new application to the created application group. This time select the Web API template.
- On the Identifiers tab, to the Relying party identifiers list, add the client ID of the server application that you added before.
- On the Client Permissions tab, in the Permitted scopes list, select the allatclaims and openid scopes.
- On the Issuance Transform Rules tab, add a new rule by selecting the Send LDAP Attributes as Claims template:
- Name the rule. For example, you can name it 'Group SID'.
- Select Active Directory as an attribute store, and then map Token-Groups as SIDs as a LDAP attribute to 'Group SID' as an outgoing claim type.
- On the Issuance Transform Rules tab, add a new rule by selecting the Send Claims Using a Custom Rule template:
- Name the rule. For example, you can name it 'ActiveDirectoryUserSID'.
- In the Custom rule field, type:
c:[Type == "http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/windowsaccountname", Issuer == "AD AUTHORITY"] => issue(store = "Active Directory", types = ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/primarysid"), query = ";objectSID;{0}", param = c.Value);
- In Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, open again the ADFS integration settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the ADFS integration Enabled position.
- Click the Settings link, and then specify the file that contains the certificate or several certificates for the federation server.
- Click the ADFS integration settings link, and then specify the following settings:
- Click the Save button.
The integration with ADFS is complete. To sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console with an AD account credentials, use the link provided in the ADFS integration settings section (Login link to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console with ADFS).
When you sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console through ADFS for the first time, the console might respond with a delay.
Page topConfiguring integration with Microsoft Entra ID
You have to configure integration with Microsoft Entra ID to allow the users in your organization to sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console with their Microsoft Entra ID account credentials.
Integration with Microsoft Entra ID is available for the primary Administration Server only. You cannot configure the integration for secondary or virtual Administration Servers.
To configure integration with Microsoft Entra ID:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Microsoft Entra ID section.
- Turn on the Microsoft Entra ID integration toggle button.
- Copy the links from the following fields:
- Callback URL
- Front-channel logout URL
You will need these URLs to register Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console in the Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- Login URL
You will need this URL to allow users to sign in to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console workspace with their Microsoft Entra ID credentials after the integration with Microsoft Entra ID is complete.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center, and then select the tenant of your organization.
You must have the Global administrator or the Application administrator role in the tenant.
- In the main menu, go to Identity → Applications → App registrations, and then click the New registration button.
- In the window that opens, do the following:
- Specify a name for the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application.
- In the Supported account types section, select the Accounts in this organizational directory only (<tenant_name> only - Single tenant) option.
- In the Redirect URI section, select Web from the drop-down list, and then enter the callback URL that you copied from Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console at step 4.
- Click the Register button.
The Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application is registered in Microsoft Entra ID, and the application overview page opens.
- If necessary, add Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console to the list of applications.
The users will be able to open Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console by clicking its name in the list of applications in My Apps and Office 365 Launcher, without using the login URL.
- Copy the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID, and save them in any convenient way.
You will need these IDs when filling in the mandatory fields in Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console at step 14.
- In the menu of the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application, go to the Authentication section, and then enter the URLs that you copied from Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console at step 4:
- In the Web section, click the Add URI button, and then enter the login URL.
- In the Front-channel logout URL section, enter the front-channel logout URL.
- In the menu of the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application, go to the Certificates & secrets section, and then do the following:
- Go to the Client secrets tab, and then click the New client secret button.
- In the window that opens, specify any description for the client secret, and then select the period after which the secret expires.
We recommend that you copy the date after which the secret expires, in any convenient way, to rotate the secrets in a timely manner.
- Click the Add button.
The created secret is displayed on the Client secrets tab.
- Copy the information from the Value column.
We strongly recommend that you copy the information immediately after creating the client secret.
- In the menu of the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application, go to the Token configuration section, and then do the following:
- Add the onprem_sid optional claim:
- Click the Add optional claim button.
- In the window that opens, select the ID token type, and then in the Claim column, select the check box next to the onprem_sid.
- Click the Add button.
The onprem_sid optional claim is displayed on the Optional claims page.
- Add the preferred_username optional claim:
- Click the Add optional claim button.
- In the window that opens, select the Access token type, and then in the Claim column, select the check box next to the preferred_username.
- Click the Add button.
The preferred_username optional claim is displayed on the Optional claims page.
- Add the onprem_sid optional claim:
- In the menu of the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application, go to the API permissions section, and then add the permissions:
- User.Read.All
- User.Export.All
- GroupMember.Read.All
- Directory.Read.All
To add a permission, do the following:
- Click the Add a permission button, and then select the Microsoft APIs tab.
- Select Microsoft Graph → Application permissions, and then select the permission you want to add.
- Click the Add permission button.
The four permissions are added and displayed on the Configured permissions page.
- Click the Grant admin consent for <tenant_name> button, and then in the window that opens, click Yes to confirm the granting of consent for the permissions you added.
- Go back to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, and on the General tab, fill in the following mandatory fields:
- Tenant ID. The Directory (tenant) ID that you copy at step 10.
- Client ID. The Application (client) ID that you copy at step 10.
- Client secret. The value that you copy at step 12.
- Click the Check connection button to check if the settings are correct, and then after the Connected status is displayed, click the Save button.
The integration settings are saved, and the integration with Microsoft Entra ID is configured.
After you configure the integration with Microsoft Entra ID, you have to do the following:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups to make sure that the users and groups from Microsoft Entra ID are added to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
If the users and groups in your Microsoft Entra ID tenant are synchronized from the Active Directory of your organization, and Active Directory polling is configured, then the users and groups are already added to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console as a result of Active Directory polling.
Otherwise, you have to enable and run Microsoft Entra ID polling to add the users and groups from your Microsoft Entra ID tenant to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- Assign necessary roles to the users and groups.
When assigning roles to a user on a virtual Administration Server, in the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab. If you select the Groups tab, and then assign roles to the group where the user is a member, the user will not be able to log in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
- Send the login URL that you copied at step 4 to the users. They will enter this URL to sign in to the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console workspace by using their Microsoft Entra ID credentials.
To sign in to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console with Microsoft Entra ID account credentials, users must be able to sign in to their Microsoft Entra ID account.
Page topEnabling Microsoft Entra ID polling
You have to enable Microsoft Entra ID polling to add the users from your Microsoft Entra ID to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
To enable Microsoft Entra ID polling:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server.The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the Microsoft Entra ID section.
- In the User discovery section, turn on the Microsoft Entra ID polling toggle button.
- If you want to change the default polling schedule, click the Schedule settings button, specify the polling frequency and time in the window that opens, and then click the Save button.
Microsoft Entra ID polling will run according to the schedule that you configure.
- If you want to run Microsoft Entra ID polling immediately, click the Run now button.
The users are loading. When the users are loaded, the Microsoft Entra ID polling is finished.
- Click the Save button.
The Microsoft Entra ID polling is complete, and the users from your Microsoft Entra ID are added to Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
Page topAdding Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console to the list of applications
You can allow users to open Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console by clicking its name in the list of applications, without entering the login URL. The application list is available in My Apps and Office 365 Launcher.
To add Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console to the list of applications:
- In the Microsoft Entra admin center main menu, go to Identity → Applications → App registrations, and then on the All applications tab, select the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console application that you have previously registered in Microsoft Entra ID.
- In the menu of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, select the Branding & properties section, and then do the following:
- In the Home page URL field, enter the login URL.
- If necessary, in the Upload new logo field, add an image that will be used as the application icon in the list of applications.
- Click the Save button.
- In the Microsoft Entra admin center main menu, go to Identity → Applications → Enterprise applications, and then select Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console.
The application overview page opens.
- In the menu of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, select the Properties section, and then do the following:
- Set the following options to Yes:
- Enabled for users to sign-in?
This action is necessary only if the option is not set to Yes by default.
- Visible to users?
- Enabled for users to sign-in?
- Click the Save button.
- Set the following options to Yes:
- In the menu of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, select the Users and groups section, and then do the following:
- Click the Add user/group button, and then click the link below Users and groups.
- In the window that opens, select users and groups, and then click the Save button.
The window is closed.
- Click the Assign button.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console is available in My Apps and Office 365 Launcher for the selected users. The users can open Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console by clicking its name in the list, without entering the login URL.
Page topAssigning a user as a device owner
For information about assigning a user as a mobile device owner, see Kaspersky Security for Mobile Help.
To assign a user as a device owner:
- If you want to assign an owner of a device connected to a virtual Administration Server, first switch to the virtual Administration Server:
- In the main menu, click the chevron icon (
 ) to the right of the current Administration Server name.
) to the right of the current Administration Server name. - Select the required Administration Server.
- In the main menu, click the chevron icon (
- In the main menu, go to Users & roles → Users & groups, and then select the Users tab.
A user list opens. If you are currently connected to a virtual Administration Server, the list includes users from the current virtual Administration Server and the primary Administration Server.
- Click the name of the user account that you want to assign as a device owner.
- In the user settings window that opens, select the Devices tab.
- Click Add.
- From the device list, select the device that you want to assign to the user.
- Click OK.
The selected device is added to the list of devices assigned to the user.
You can perform the same operation at Assets (Devices) → Managed devices, by clicking the name of the device that you want to assign, and then clicking the Manage device owner link.
Assigning a user as a Linux device owner after installation of Network Agent
To allow the user to register as a Linux device owner:
- In the Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console, go to Discovery & deployment → Deployment & assignment → Installation packages.
The list of installation packages opens.
- Click on the installation package of Network Agent.
The properties window of the installation package opens.
- In the installation package properties window, click Settings → Advanced.
- In the User registration as a device owner (Linux only) section, turn on the Allow running the user registration utility after Network Agent installation option and click Save.
The utility for registering the user as a device owner can be run via the command line on the client device.
To register a user as a Linux device owner on the client device:
- Execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
$ /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/nagregister -set_owner - Enter the login and password, if prompted.
If the login and the password are included in the answer file or installation package of Network Agent, execute the following command in the command line on the client device:
$ /opt/kaspersky/klnagent64/bin/nagregister -set_owner -unattended
If the user is included in an internal security group, the login must contain the user name.
If the user is included in an Active Directory security group, the login must contain the user name and domain name.
The user will be registered as a device owner.
Page topManaging object revisions
This section contains information about object revision management. Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to track object modification. Every time you save changes made to an object, a revision is created. Each revision has a number.
Objects that support revision management include:
- Administration Server properties
- Policies
- Tasks
- Administration groups
- User accounts
- Installation packages
You can perform the following actions on object revisions:
- View a selected revision (available only for policies)
- Roll back changes made to an object to a selected revision
- Save revisions as a JSON file (available only for policies)
In the properties window of any object that supports revision management, the Revision history section displays a list of object revisions with the following details:
- Revision—Object revision number.
- Time—Date and time the object was modified.
- User—Name of the user who modified the object.
- User device IP address—IP address of the device from which the object was modified.
- Web Console IP address—IP address of Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console with which the object was modified.
- Action—Action performed on the object.
- Description—Description of the revision related to the change made to the object settings.
By default, the object revision description is blank. To add a description to a revision, select the relevant revision and click the Edit description button. In the opened window, enter some text for the revision description.
Rolling back changes
You can roll back changes made to an object, if necessary. For example, you may have to revert the settings of a policy to their state on a specific date.
To roll back changes made to an object:
- In the object's properties window, open the Revision history tab.
- In the list of object revisions, select the number of the revision to which you have to roll back changes.
- Click the Roll back button.
- Click OK to confirm the operation.
The object is now rolled back to the selected revision. The list of object revisions displays a record of the action that was taken. The revision description displays information about the number of the revision to which you reverted the object.
Adding a revision description
You can add a description for the revision to simplify the search for revisions in the list.
To add a description for a revision:
- In the object's properties window, open the Revision history tab.
- In the list of object revisions, select the revision for which you need to add a description.
- Click the Edit description button.
The Description window opens.
- In the Description window, enter some text for the revision description.
By default, the object revision description is blank.
- Save the revision description.
The description is added for the revision of the object.
Viewing and saving a policy revision
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console allows you to view which modifications were made to a policy over a certain period, as well as save information about these modifications in a file.
Viewing and saving a policy revision are available if the corresponding management web plug-in supports this functionality.
To view a policy revision:
- In the main menu, go to Assets (Devices) → Policies & profiles.
- Click the policy for the revision that you want to view, and then go to the Revision history section.
- In the list of policy revisions, click the number of the revision that you want to view.
If the revision size is more than 10 MB, you will not be able to view it by using Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. You will be prompted to save the selected revision to a JSON file.
If the revision size does not exceed 10 MB, a report in the HTML format with the settings of the selected policy revision is displayed. Since the report is displayed in a pop-up window, ensure that pop-ups are allowed in your browser.
To save a policy revision to a JSON file,
In the list of policy revisions, select the revision that you want to save, and then click Save to file.
The revision is saved to a JSON file.
Page topKaspersky Security Network (KSN)
This section describes how to use an online service infrastructure named Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). The section provides the details on KSN, as well as instructions on how to enable KSN, configure access to KSN, and view the statistics of the use of KSN proxy server.
Updates functionality (including providing anti-virus signature updates and codebase updates), as well as KSN functionality may not be available in the software in the U.S.
About KSN
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is an online service infrastructure that provides access to the online Knowledge Base of Kaspersky, which contains information about the reputation of files, web resources, and software. The use of data from Kaspersky Security Network ensures faster responses by Kaspersky applications to threats, improves the effectiveness of some protection components, and reduces the risk of false positives. KSN enables you to use Kaspersky reputation databases to retrieve information about applications installed on client devices.
If you participate in KSN, you agree to send to Kaspersky, in automatic mode, information about the operation of Kaspersky applications installed on client devices that are managed through Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. Information is transferred in accordance with the current KSN access settings. Kaspersky analysts additionally analyze received information, and include it in the reputation and statistical databases of Kaspersky Security Network.
The application prompts you to join KSN while running the Quick Start Wizard. You can start or stop using KSN at any moment when using the application.
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is displayed to you when you update or upgrade Administration Server. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you keep using KSN in accordance with the previous version of KSN Statement that you accepted before.
When KSN is enabled, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console checks if the KSN servers are accessible. If access to the servers using system DNS is not possible, the application uses public DNS servers. This is necessary to make sure the level of security is maintained for the managed devices.
Client devices managed by the Administration Server interact with KSN through KSN proxy server. KSN proxy server provides the following features:
- Client devices can send requests to KSN and transfer information to KSN even if they do not have direct access to the internet.
- The KSN proxy server caches processed data, thus reducing the load on the outbound channel and the time period spent for waiting for information requested by a client device.
You can enable KSN proxy server on the distribution point side to make the device act as a KSN proxy server. In this case, the KSN proxy service (ksnproxy) is run on the device.
Page topEnabling and disabling KSN
To enable KSN:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Security Network Enabled position.
KSN is enabled.
If the toggle button is enabled, client devices send patch installation results to Kaspersky. When enabling this toggle button, you should read and accept the terms of the KSN Statement.
- Click the Save button.
To disable KSN:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the required Administration Server.
) next to the name of the required Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN settings section.
- Switch the toggle button to the Use Kaspersky Security Network Disabled position.
KSN is disabled.
If this toggle button is disabled, client devices will send no patch installation results to Kaspersky.
- Click the Save button.
Viewing the accepted KSN Statement
When you enable Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), you must read and accept the KSN Statement. You can view the accepted KSN Statement at any time.
To view the accepted KSN Statement:
- In the main menu, click the settings icon (
 ) next to the name of the Administration Server.
) next to the name of the Administration Server. The Administration Server properties window opens.
- On the General tab, select the KSN settings section.
- Click the View Kaspersky Security Network Statement link.
In the window that opens, you can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement.
Page topAccepting an updated KSN Statement
You use KSN in accordance with the KSN Statement that you read and accept when you enable KSN. If the KSN Statement is updated, it is automatically displayed when you open Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console. You can accept the updated KSN Statement or decline it. If you decline it, you will continue using KSN in accordance with the version of the KSN Statement that you previously accepted. You can view and accept the updated KSN Statement later.
To view, and then accept or decline an updated KSN Statement:
- Click the View notifications link in the upper-right corner of the main application window.
The Notifications window opens.
- Click the View the updated KSN Statement link.
The Kaspersky Security Network Statement update window opens.
- Read the KSN Statement, and then make your decision by clicking one of the following buttons:
- I accept the updated KSN Statement
- Use KSN under the old Statement
Depending on your choice, KSN keeps working in accordance with the terms of the current or updated KSN Statement. You can view the text of the accepted KSN Statement in the properties of Administration Server at any time.
Page topChecking whether the distribution point works as KSN proxy server
On a managed device assigned to work as a distribution point, you can enable KSN proxy server. A managed device works as KSN proxy server when the ksnproxy service is running on the device. You can check, turn on, or turn off this service on the device locally.
You can assign a Windows-based or a Linux-based device as a distribution point. The method of distribution point checking depends on the operating system of this distribution point.
To check whether the Windows-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, in Windows, open Services (All Programs → Administrative Tools → Services).
- In the list of services, check whether the ksnproxy service is running.
If the ksnproxy service is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
If you want, you may turn off the ksnproxy service. In this case, Network Agent on the distribution point stops participating in Kaspersky Security Network. This requires local administrator rights.
To check whether the Linux-based distribution point works as KSN proxy server:
- On the distribution point device, display the list of running processes.
- In the list of running processes, check whether the
/opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxyprocess is running.
If /opt/kaspersky/ksc64/sbin/ksnproxy process is running, then Network Agent on the device participates in Kaspersky Security Network and works as the KSN proxy server for the managed devices included in the scope of the distribution point.
Deletion of objects
You can delete objects, including the following:
- Policies
- Tasks
- Installation packages
- Virtual Administration Servers
- Users
- Security groups
- Administration groups
When you delete an object, information about it remains in the database. The storage term for information about the deleted objects is the same as the storage term for object revisions (the recommended term is 90 days). You can change the storage term only if you have the Modify permission in the Deleted objects area of rights.
About deletion of client devices
When you delete a managed device from an administration group, the application moves the device to the Unassigned devices group. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications—Network Agent and any security application, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security—remain on the device.
Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console handles the devices in the Unassigned devices group according to the following rules:
- If you have configured device moving rules and a device meets the criteria of a moving rule, the device is automatically moved to an administration group according to the rule.
- The device is stored in the Unassigned devices group and automatically removed from the group according to the device retention rules.
The device retention rules do not affect the devices that have one or more drives encrypted with full disk encryption. Such devices are not deleted automatically—you can only delete them manually. If you need to delete a device with an encrypted drive, first decrypt the drive, and then delete the device.
When you delete a device with encrypted drive, the data required to decrypt the drive is also deleted. If you select the I understand the risk and want to delete device(s) check box in the confirmation window that opens when you delete such devices (either from the Unassigned devices or the Managed Devices group), it means that you are aware of the subsequent data deletion.
To decrypt the drive, the following conditions must be met:
- The device is reconnected to Administration Server to restore the data required to decrypt the drive.
- The device user remembers the decryption password.
- The security application that was used to encrypt the drive, for example Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Windows, is still installed on the device.
If the drive was encrypted by Kaspersky Disk Encryption technology, you can also try recovering data by using the FDERT Restore Utility.
When you delete a device from the Unassigned devices group manually, the application removes the device from the list. After device deletion, the installed Kaspersky applications (if any) remain on the device. Then, if the device is still visible to Administration Server and you have configured regular network polling, Kaspersky Security Center Cloud Console discovers the device during the network polling and adds it back to the Unassigned devices group. Therefore, it is reasonable to delete a device manually only if the device is invisible to Administration Server.

