Kaspersky MLAD components
Kaspersky MLAD includes the following components:
ML model
An ML model is a model created by Kaspersky experts or by a certified integrator for a specific facility based on machine learning algorithms and/or diagnostic rules using telemetry data from this facility. The ML model detects incidents.
An ML model is not included in the application distribution kit but is provided as part of the Kaspersky MLAD Model-building and Deployment Service.
Kaspersky MLAD services
Kaspersky MLAD services comprise the set of main application components supplied to each monitored asset. Kaspersky MLAD includes the following services:
- Anomaly Detector. Uses an ML model to process data and detect anomalies.
- Event Processor. Uses machine learning methods based on a semantic neural network to identify patterns and anomalous sequences of events.
- Stream Processor. Brings telemetry data received from the monitored asset at arbitrary real-time moments to a uniform temporal grid.
- Model Trainer. Performs repeated or additional training of an existing ML model based on the new telemetry data obtained by Kaspersky MLAD for a specific monitored asset.
- Similar Anomaly. Identifies and groups together similar incidents.
- Message Broker. Performs data exchange between Kaspersky MLAD components.
- Time Series Database. Stores time series of observed tag values, tag values predicted by the ML model, and prediction errors.
- Keeper. Performs routing of the telemetry data that should be saved in the database.
- Database. Stores all configuration settings of Kaspersky MLAD.
- API Server. Supports operation of the internal interfaces of Kaspersky MLAD.
- Web Server. Supports operation of the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
- Logger. Stores Kaspersky MLAD operation logs.
- Mail Notifier. Sends emails with incident registration notifications.
Connectors
Connectors are services that facilitate the exchange of data with external systems. For each protection object, you must select one of the following connectors:
- KICS Connector. Supports interaction with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
- OPC UA Connector. Receives tags from industrial process control systems (ICS) according to the protocol described in the OPC Unified Architecture specification.
- CEF Connector. Receives events from external sources (Industrial Internet of Things, network devices and applications) and returns messages in CEF (Common Event Format) registered by event analysis monitors.
- MQTT Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via the MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) protocol.
- AMQP Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol).
- WebSocket Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via the WebSocket protocol.
- HTTP Connector. Receives telemetry data from ICS in CSV files via HTTP POST requests.
The figure below shows a diagram of interaction between the components of Kaspersky MLAD.
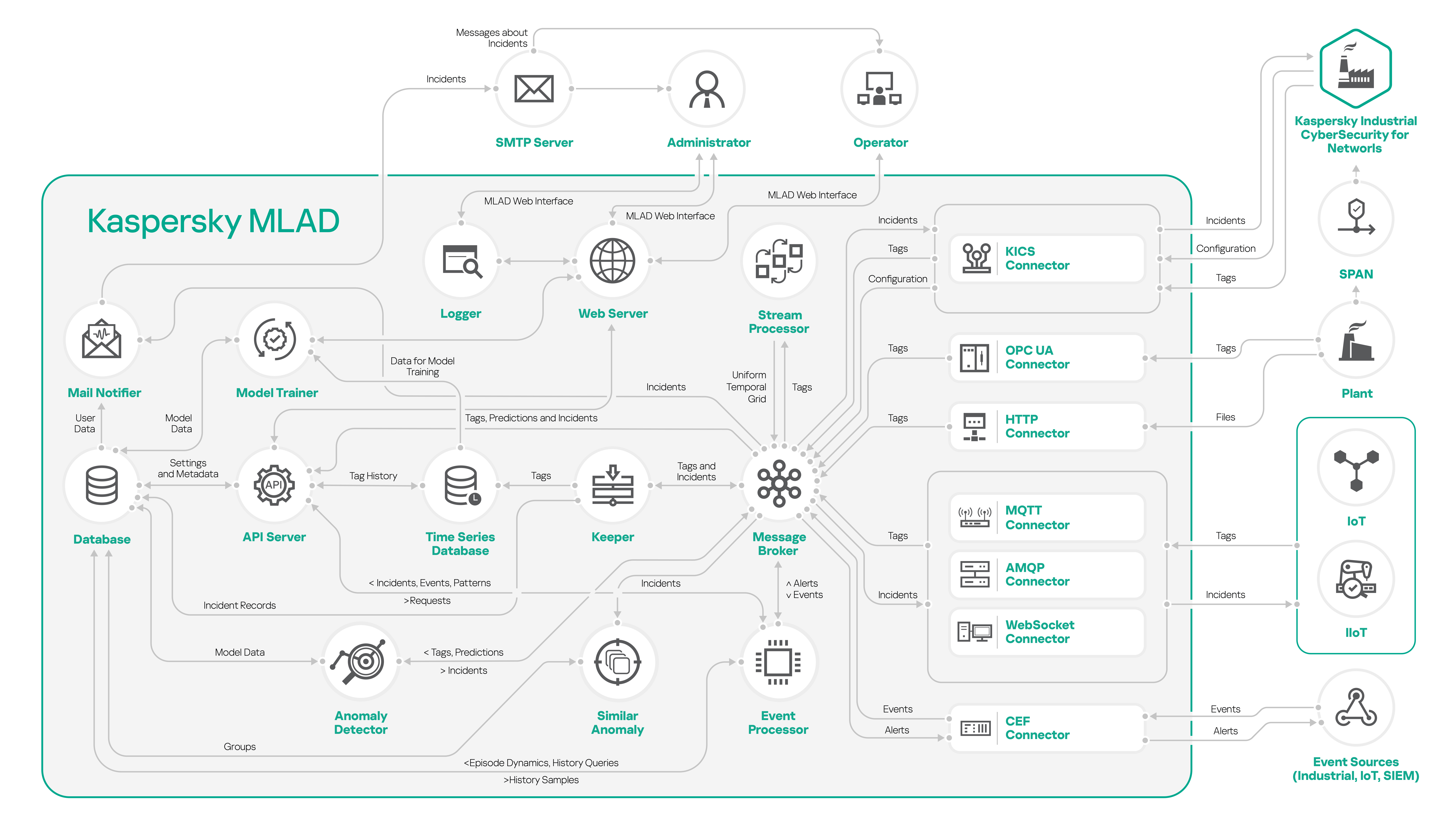
Diagram of interaction of Kaspersky MLAD components
Page top