"Events" widget
You can use the Events widget to get analytics based on SQL queries.
When creating this type of widget, you must set values for the following settings:
General tab:
- Graph is the type of the graph. The following graph types are available:
- Pie chart.
- Bar chart.
- Counter.
- Line chart.
- Table.
- Date Histogram.
Tenant is the tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings.
- Period is the period for which data is displayed in the widget. The following periods are available:
- As layout means data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. The default value.
- 1 hour—data is displayed for the previous hour.
- 1 day—data is displayed for the previous day.
- 7 days—data is displayed for the previous 7 days.
- 30 days—data is displayed for the previous 30 days.
- In period—data is displayed for a custom time period. If you select this option, use the opened calendar to select the start and end dates of the period and click Apply Filter. The date and time format depends on your operating system's settings. You can manually change the date values if necessary.
The upper boundary of the period is not included in the time slice defined by it. In other words, to receive analytics for a whole day, you must configure the period as <Day 1>, 00:00:00 – <Day 2>, 00:00:00 instead of <Day 1>, 00:00:00 – <Day 1>, 23:59:59.
- Show data for previous period—enable the display of data for two periods at the same time: for the current period and for the previous period.
- Storage is the storage that is searched for events.
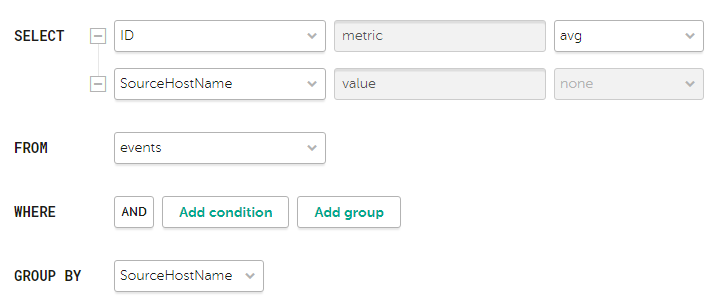
- SQL query field (
 ) is the query for manually filtering and searching for events. You can create a query in Builder by clicking
) is the query for manually filtering and searching for events. You can create a query in Builder by clicking  .
.How to create a query in Builder
Example of search conditions in the query builder
The following limitations apply:
- The
metricandvaluealiases in SQL queries cannot be edited for any type of event analytics widget, except tables. - Aliases in widgets of the Table type can contain Latin and Cyrillic characters, as well as spaces. When using spaces or Cyrillic, the alias must be enclosed in quotation marks:
"An alias with a space",`Another alias`. ARRAY JOINSQL queries are not supported.- When displaying data for the previous period, sorting by the
count(ID)parameter may not work correctly. We recommend sorting by themetricparameter. For example,SELECT count(ID) AS "metric", Name AS "value" FROM `events` GROUP BY Name ORDER BY metric ASC LIMIT 250. - In widgets of the Counter type, you must specify the method of data processing for the values of the
SELECTfunction:count,max,min,avg,sum.
- The
Axes tab:
The tab is displayed if on the  tab in the Graph field you have selected one of the following values: Bar chart, Line chart, Date Histogram.
tab in the Graph field you have selected one of the following values: Bar chart, Line chart, Date Histogram.
- The Y-min and Y-max values set the scale of the Y axis.
- The X-min and X-max values set the scale of the X axis.
Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto.
- Line-width is the width of the line on the graph. This field is displayed for the "Line chart" graph type.
- Point size is the size of the pointer on the graph. This field is displayed for the "Line chart" graph type.
Appearance tab:
- Name is the name of the widget.
- Description is the description of the widget.
- Color is the color used for displaying the information:
- default for your browser's default font color
- green
- red
- blue
- yellow
- Horizontal makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical.
When this option is enabled, when a widget displays a large amount of data, horizontal scrolling is not available and all available information is fit into the fixed size of the widget. If there is a lot of data to display, it is recommended to increase the widget size.
- Show total shows sums total of the values.
- Legend displays a legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default.
Show nulls in legend displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default.
- Decimals is the number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off.
- Period segments length (available for graphs of the Date Histogram type) sets the length of segments into which you want to divide the period.
 .
.