Channel groups
The channels in which an entity serves as a server may be combined into one or more groups.
Each group of channels has its own listener handle.
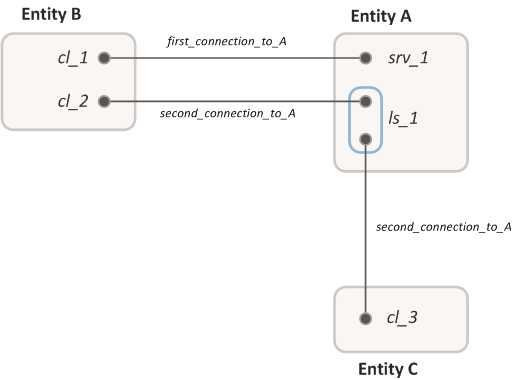
Two IPC channels have the same name, "second_connection_to_A", and are combined into a group. Another channel, named "first_connection_to_A", is not included in this group. Designations: cl_1, cl_2, cl_3 – client IPC handles; srv_1 – server IPC handle; ls_1 – listener IPC handle.
The listener handle allows the server to receive requests immediately over all channels in the group. There is no need to create a separate thread for each channel. It is enough to execute one Recv() system call in one server thread by specifying a listener handle.
Creating a group of channels using an init description
For channels to form a group, they must connect to the same server entity and have identical names. For example, to produce the system of channels depicted above, the following init description can be used:
init.yaml
entities:
# Entity A acts as a server, so its list of connections is empty.
- name: A
# Entity B will be connected with entity A via two different channels.
- name: B
connections:
- target: A
id: first_connection_to_A
- target: A
id: second_connection_to_A
# Entity C will be connected with entity A via a channel named
# "second_connection_to_A". Two channels with identical names will be combined
# into a group: on the entity A side, they will have the same
# IPC handle (listener handle ls_1).
- name: C
connections:
- target: A
id: second_connection_to_A
Messaging within a channel group
Let us look at how messages are exchanged for the group of channels described above.
The client entities B and C receive a client handle value based on the name of the first_connection_to_A connection and send a request:
entity_B.c, entity_C.c
…
// Receive client IPC handle cl corresponding to "second_connection_to_A".
Handle cl = ServiceLocatorConnect("second_connection_to_A");
…
// Send request
Call(cl, &RequestBuffer, &ResponseBuffer);
…
Both channels being used have the same name: second_connection_to_A. However, by this name the entities B and C will receive different handle values for that name: entity B will receive the value cl_2, whereas entity C will receive the value cl_3.
Server entity A receives the listener handle value ls_1. Entity A awaits requests over two channels at the same time (from B and from C), using the ls_1 handle. After receiving and processing the request, entity A sends a response using the ls_1 handle. The response will be sent to the client that initiated the request:
entity_A.c
…
nk_iid_t iid;
// Receive listener handle ls_1 corresponding to
"second_connection_to_A"
Handle ls_1 = ServiceLocatorRegister("second_connection_to_A", NULL, 0, &iid);
…
// Wait for the request from entity B or C
Recv(ls_1, &RequestBuffer);
…
// Process received request
…
// Send response to client from which request was received
Reply(ls_1, &ResponseBuffer);
…