messagebus example
This example demonstrates use of the MessageBus component in KasperskyOS.
In this example, the Publisher, SubscriberA and SubscriberB programs use the MessageBus component to exchange messages:
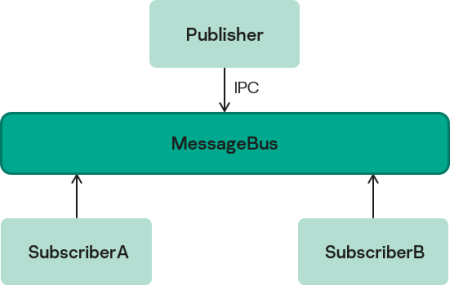
Example of using the MessageBus component in a KasperskyOS-based solution
The MessageBus component implements the message bus that ensures receipt, distribution, and delivery of messages between programs. Use of a message bus in KasperskyOS-based solutions lets you easily scale the distribution of messages for a large number of subscribers, for example. The message bus can process large volumes of messages and effectively distribute them between recipients.
The log level of the MessageBus component is set by the LOG_LEVEL environment variable defined in the ./einit/CMakeLists.txt file. This variable can have the following values:
- LOG_TRACE
- LOG_DEBUG
- LOG_INFO (default value)
- LOG_WARNING
- LOG_ERROR
- LOG_CRITICAL
- LOG_OFF
The Publisher program is the publisher that transfers messages to the bus:
- The
IProviderFactory::CreateBusControl()method is used to get the interface for registering a publisher in the message bus. - The
IProviderFactory::CreateBus()method is used to get the interface containing the methods enabling the publisher to send messages to the bus. - The
IProviderControl::RegisterPublisher()method is used to register the publisher in the message bus. - The
IProvider::Push()method is used to send messages to the bus. - The
IProviderControl::UnregisterPublisher()method is used to deregister a publisher in the message bus.
The SubscriberA and SubscriberB programs are the subscribers that receive messages from the bus:
- The
IProviderFactory::CreateBusControl()method is used to get the interface for registering a subscriber in the message bus. - The
IProviderFactory::CreateSubscriberRunner()method is used to get the interfaces containing the methods enabling the subscriber to receive messages from the bus. - The
IProviderControl::RegisterSubscriber()method is used to register the subscriber in the message bus. - The
ISubscriberRunner::Run()method is used to switch a subscriber to standby mode to wait for a message from the bus. - The
ISubscriber::OnMessage()method is called when a message is received from the bus. - The
IProviderControl::UnregisterSubscriber()method is used to deregister a subscriber in the message bus.
The example also demonstrates the use of various virtual file systems (VFS) in a single solution. The example uses different VFS to access the functions for working with the file system and functions for working with the network:
- The
VfsNetprogram is used for working with the network. - The
VfsSdCardFsprogram is used to work with the file system.
The kl.Ntpd program is included in KasperskyOS Community Edition and is an implementation of an NTP client, which gets time parameters from external NTP servers in the background and passes them to the KasperskyOS kernel.
The kl.rump.Dhcpcd program is included in KasperskyOS Community Edition and is an implementation of a DHCP client, which gets the parameters of network interfaces from an external DHCP server in the background and passes them to the virtual file system.
The CMake system, which is included with KasperskyOS Community Edition, is used to build and run the example.
Example files
The code of the example and build scripts are available at the following path:
/opt/KasperskyOS-Community-Edition-<version>/examples/messagebus
Building and running example
See Building and running examples section.
To ensure that the messagebus example will correctly run in Raspberry Pi, you must do the following after building the example and preparing your bootable SD card:
- Create the
/libdirectory on the bootable SD card if this directory doesn't already exist. - Open the
build/hdd/libdirectory that was generated when building the example and copy the directory contents to the/libdirectory on the bootable SD card.