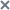Contents
- About Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection
- What's new
- Basic concepts of Kaspersky MLAD
- Kaspersky MLAD components
- Common deployment scenarios
- Telemetry and event data flow diagram
- Administering Kaspersky MLAD
- Installing the application
- Updating the application and rolling back to the previous installed version
- Getting started
- Starting and stopping Kaspersky MLAD
- Updating Kaspersky MLAD certificates
- First startup of Kaspersky MLAD
- Configuring Kaspersky MLAD
- Configuring the main settings of Kaspersky MLAD
- Configuring the Anomaly Detector service
- Configuring the Keeper service
- Configuring the Mail Notifier service
- Configuring the Similar Anomaly service
- Configuring the Stream Processor service
- Configuring the HTTP Connector
- Configuring the MQTT Connector
- Configuring the AMQP Connector
- Configuring the OPC UA Connector
- Configuring the KICS Connector
- Configuring the CEF Connector
- Configuring the WebSocket Connector
- Configuring the Event Processor service
- Configuring the statuses and causes of incidents
- Configuring logging of Kaspersky MLAD services
- Configuring time intervals for displaying data
- Configuring how the Kaspersky MLAD main menu is displayed
- Exporting and importing a configuration file for Kaspersky MLAD components
- Starting, stopping, and restarting services
- Managing tags
- Managing ML models and templates
- Configuring settings in the Event Processor section
- Managing user accounts
- Managing incident notifications
- Removing the application
- Connecting to Kaspersky MLAD and closing the session
- Kaspersky MLAD web interface
- Licensing the application
- Processing and storing data in Kaspersky MLAD
- Performing common tasks
- Scenario: Working with Kaspersky MLAD
- Viewing summary data in the Dashboard section
- Viewing incoming data in the Monitoring section
- Viewing data in the History section
- Viewing data in the Time slice section
- Viewing data for a specific preset in the Time slice section
- Selecting a specific branch of the ML model in the Time slice section
- Selecting a date and time interval in the Time slice section
- Navigating through time in the Time slice section
- Configuring how graphs are displayed in the Time slice section
- Working with events and patterns
- Working with incidents and groups of incidents
- Scenario: Analysis of incidents
- Viewing incidents
- Viewing the technical specifications of a registered incident
- Viewing incident groups
- Studying the behavior of the monitored asset at the moment when an incident was detected
- Adding a status, cause, expert opinion or note to an incident or incident group
- Exporting incidents to a file
- Working with ML models and templates
- Managing presets
- Viewing the status of a service
- Troubleshooting
- When connecting to Kaspersky MLAD, the browser displays a certificate warning
- The hard drive has run out of free space
- The operating system restarted unexpectedly
- Cannot connect to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface
- Graphs are not displayed in the History and Monitoring sections
- Events are not transmitted between Kaspersky MLAD and external systems
- Cannot load data to view in the Event Processor section
- Data is incorrectly processed in the Event Processor section
- Events are not displayed in the Event Processor section
- Previously created monitors and the specified attention settings are not displayed in the Event Processor section
- The localization language for Help needs to be changed before connecting to the application
- Contacting Technical Support
- Appendix
- Glossary
- Information about third-party code
- Trademark notices
About Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection
The early anomaly detection system known as Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection 3.0.0 (hereinafter also referred to as Kaspersky MLAD or "the application") is specialized software designed to prevent failures, accidents or degradation of industrial installations, technological processes, and complex cyber-physical systems. By analyzing telemetry data using machine learning techniques (artificial intelligence), Kaspersky MLAD detects signs of an abnormal situation before it is detected by traditional monitoring systems.
Kaspersky MLAD detects anomalies in industrial processes regardless of their causes. Anomalies may be caused by the following:
- Physical factors, such as damage to equipment or malfunctioning sensors.
- Human factors (such as intentional or inadvertent inappropriate actions of the operator, hardware configuration, change of operating modes or equipment, or switch to manual control).
- Cyberattacks.
Main capabilities of Kaspersky MLAD:
- Detects abnormal behavior of the monitored asset in real time.
- Identifies signals that display the largest deviations from normal behavior.
- Allows you to analyze incidents taking into account information about similar incidents.
- Allows expert classification and annotation of incidents.
- Allows you to alert the users about the detected incidents using the web interface, by email, by sending messages in Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks, and using industrial data transfer protocols.
- Allows you to use models based on both machine learning and arbitrary rules for anomaly detection.
- Displays observed and predicted tag values and prediction errors as the graphs both in the online monitoring mode and in the retrospective analysis of telemetry history mode.
- Lets you manage the log of detected incidents.
- Allows you to perform retraining and additional training of the ML model being used.
- Allows to create templates based on the added ML models and add ML models to Kaspersky MLAD based on the created templates.
- Allows you to receive telemetry data over HTTP, OPC UA, MQTT, AMQP, CEF, and WebSocket protocols, and via a specialized protocol over HTTPS from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- Displays historical and real-time data as graphs according to the specified sets of tags.
- Detects and handles terminations and interruptions of the incoming data stream, and restores missed observations.
- Based on data on events received from external systems, recognizes principles as repeated events or patterns, and identifies new events and patterns in the event stream.
- Displays the detected events as a graph and a table, and shows detected patterns as a layered hierarchy of nested items.
- Sends alerts about the detection of certain events, patterns, or values of the event parameters received by the Event Processor in the data stream from the monitored asset.
Distribution kit
Kaspersky MLAD is delivered as an archive file named mlad-3.0.0-<build number>.tar.xz, which contains the following files:
- Installation script and all files required for system installation.
- Files containing the text of the End User License Agreement in English and in Russian.
- Files containing information about the application (Release Notes) in English and in Russian.
- File containing information about third-party code (legal_notices.txt) in English.
After you unpack the archive, the "legal" folder will contain a text file named license_en.txt in which you can view the End User License Agreement. The End User License Agreement specifies the terms of use of the application.
Page top
Hardware and software requirements
The hardware requirements for each protected facility must be adjusted considering the model being used, the number of processed tags and events, the average speed of data acquisition (number of observations per second), and the volume of stored data. The more data is processed and the more sophisticated the used ML model is, the more hardware resources are required for installing the server part of Kaspersky MLAD.
To ensure proper operation of Kaspersky MLAD, your computer must meet the following minimum requirements.
Requirements for Kaspersky MLAD server
List of supported processors:
- Intel Xeon E3 v3, v4, v5, v6
- Intel Xeon E5 v3, v4
- Intel Xeon E7 v3, v4
- Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- The 2nd and 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- Intel Xeon E
- Intel Xeon W
- Intel Xeon D
- The 4th generation and later Intel Core i5, i7
- Intel Core i9 processor
- Intel Core M
Minimum hardware requirements:
- 8 cores
- 32 GB of RAM
- 1 TB of free space on the hard drive (SSD recommended)
You can install Kaspersky MLAD on a server with another x86 64-bit processor released in 2013 or later. The processor must meet the minimum hardware requirements listed above and support the following extensions required for the TensorFlow 2.8.3 library:
- Advanced Vector Extensions (avx)
- Advanced Vector Extensions 2 (avx2)
Supported operating system:
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and later
The following software must be installed prior to deployment of Kaspersky MLAD:
- docker 20.10.21 or later
- docker compose 2.12.2 or later
Use the official Docker repository for installation of the software on the Kaspersky MLAD server.
Operator computer requirements
To work with the web interface of Kaspersky MLAD, the operator's computer must meet the following minimum requirements:
- Intel Core i5 CPU;
- 8 GB of RAM;
- Google Chrome browser version 107 or later
- The minimum screen resolution for correct display of the web interface is 1600x900.
Security recommendations
To ensure secure operation of Kaspersky MLAD at an enterprise, it is recommended to restrict and control access to equipment on which the application is running.
Physical security of equipment
When deploying Kaspersky MLAD, it is recommended to take the following measures to ensure secure operations:
- Restrict access to the room housing the server with Kaspersky MLAD installed, and to the equipment of the dedicated network. Access to the room must be granted only to trusted persons, such as personnel who are authorized to install and configure the application.
- Employ technical resources or a security service to monitor physical access to equipment on which the application is running.
- Use security alarm equipment to monitor access to restricted rooms.
- Conduct video surveillance in restricted rooms.
Information security
Important! ML model parameters directly impact the detection of anomalies, therefore they can only be changed by Kaspersky MLAD administrators. The date of last modification to the ML model (activation, or change of the name, threshold MSE value or MSE weights) is available in the Models section. The change history is available only in logs, which are saved for only a limited amount of time.
When using the web interface, it is recommended to also take the following measures to ensure the data security of the intranet system:
- Provide users with access to the application through the web interface only.
- Install certificates to users' computers for authorization of the Kaspersky MLAD server with their browser. To use a trusted certificate, you need to contact your administrator.
- Ensure protection of traffic within the intranet system.
- Ensure protection of connections to external networks.
- For connections through the web interface, use passwords that contain at least 8 characters, including letters and numerals. Ensure that passwords are confidential and unique. If a password has been potentially compromised, change the password (in the current version of the application, only an administrator can change a password).
- Set a time limit for a user web session.
- After you are finished working in the browser, manually terminate the application connection session using the Sign out option in the web interface.
- Periodically install updates for the operating system on the server where Kaspersky MLAD is deployed.
- Use access permission control to restrict user access to application functions.
Data security
While working with Kaspersky MLAD, it is recommended to also take the following measures to ensure data security:
- Perform periodic data backups of the server that has Kaspersky MLAD installed in accordance with the internal company procedure.
- Periodically test the performance of the interface and services of the application. Special attention should be directed to the notification service and logging system.
- Check communication channels to make sure they are secure and working properly.
- Periodically test the performance of the server:
- SMART disk check
- Availability of sufficient free space and memory
- RAM utilization
- Use the monitoring system to make sure that there are no problems with the server protocols.
- Store the activation code and sensitive data in a secure storage location.
Managing access to application functions
This section describes user access restrictions for application functions.
In Kaspersky MLAD, you can use common roles to restrict user access to application functions depending on the tasks performed by specific users.
A role is a set of rights to access application functions that you can assign to a user.
Available functions of the application depending on the user role
Application function |
Administrator |
Operator |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Viewing the roles and rights of users |
|
|
|
|
|
Receiving and processing incident notifications |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Viewing historical data (including the capability to select the date and scale). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring attention settings and display of event parameters |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
View Kaspersky MLAD logs. |
|
|
You can view the available user roles under Settings → Roles. The Roles section contains a table that provides information about each role.
You can view application functionality access rights under Settings → Permissions. The Permissions section contains a table that provides information about users' permissions to access application functions.
User roles and access rights can be viewed only by users that have administrator privileges.
Page top
What's new
Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection 3.0.0 introduces the following features and improvements:
- Models section of the web interface – the functionality for creating templates based on ML models and adding ML models based on the created templates is implemented. ML model templates preserve the algorithm structure, set of elements, and the training state of the ML model used to create the template.
- Stream Processor service – a new component is added for converting telemetry data received from the monitored asset at arbitrary real-time moments to a uniform temporal grid (UTG). The Stream Processor component considers possible data losses and processes observations received by Kaspersky MLAD too early or too late. In such cases, Stream Processor registers incidents.
- Event Processor service – the functionality that switches the Event Processor to the sleep mode according to a specified schedule is implemented. In the sleep mode, the Event Processor analyses sequences of events processed in the online mode once again to improve the quality of previously detected patterns and their structure. A mechanism for saving the Event Processor service state in the database after processing each episode of events is implemented. This mechanism ensures that the data is saved up to the last processed episode and reduces the need for computational resources required to save the full state of the Event Processor service. The functionality is added that allows you to view the structure of patterns as a layered hierarchy of nested elements, including the time intervals between the elements within the pattern.
- WebSocket Connector – a new connector is added that allows you to receive telemetry data from ICS systems and send messages about incident registration via the WebSocket protocol.
- System parameters section of the web interface – the functionality for managing logging levels of Kaspersky MLAD services, statuses and causes of incidents, and time intervals for displaying data on graphs in the Monitoring, History, and Time slice sections is implemented. The functionality for managing the user account blocking settings is added.
- Tags section of the web interface – the function is implemented to automatically add unknown tags received from external assets via the KICS Connector in accordance with the names of tags and assets in Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks 3.0 and later.
Basic concepts of Kaspersky MLAD
This section contains expanded definitions of the basic concepts applied in Kaspersky MLAD.
Tags
Tags are the main objects of observation in Kaspersky MLAD. A tag is a process parameter transmitted within the industrial network (for example, a controlled temperature). Measurements of physical parameters, as well as setpoints, commands, or states of control systems can be transmitted as tags. The values of tags are transmitted and received by the assets over specific protocols. The values of tags are displayed on graphs in the History and Monitoring sections and are also used to detect incidents.
Kaspersky MLAD provides the following types of tags:
Kaspersky MLAD supports several methods for obtaining telemetry data (tags). Depending on the monitored asset attributes and the tag transmission capabilities, you can select one of the following methods for receiving tags:
- Use the connectors of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks that analyze mirrored traffic and send tags to Kaspersky MLAD in online mode. Kaspersky MLAD sends back information about detected incidents.
- Use the OPC UA Connector if the monitored asset provides the capability to transmit tags from ICS over the OPC UA protocol in the online mode.
- Use the MQTT Connector if the monitored asset provides the capability to transmit tags over the MQTT protocol and receive alerts about incident registration in the online mode.
- Use the AMQP Connector if the monitored asset has the capability to transmit tags over the AMQP protocol and receive alerts about incident registration in online mode.
- Use the WebSocket Connector if the monitored asset provides the capability to transmit tags over the WebSocket protocol and receive alerts about incident registration in the online mode.
- Use the CEF Connector if the monitored asset provides the capability to transmit tags using the CEF Connector technology and receive alerts about incident registration in the online mode.
- If the first four methods of tag transmission are not available, you can write a tag export script for using the HTTP Connector to configure a scheduled export of tags as CSV files over HTTP (for example, once per hour or once per minute).
ML models
An ML model is an algorithm based on machine learning methods tasked with analyzing the telemetry of the monitored asset and detecting anomalies.
An ML model is created by Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator for a specific monitored asset while taking into account the specifications of the asset and the characteristics of telemetry data. The general structure of the algorithm (architecture) is formed during creation of the ML model. Then the ML model is trained based on historical telemetry data and is thereby adjusted to the behavior of a specific object.
An ML model loaded into Kaspersky MLAD to work with a monitored asset consists of one or several elements, each of which is an independent ML model. The overall result of the Anomaly Detector service is formed by combining the results of the ML model elements. Normally, the more complex the industrial processes of the monitored asset are, the more elements the ML model will contain.
A Kaspersky MLAD ML model can be built using one or more detectors running in parallel:
In Kaspersky MLAD, an ML model can be imported or created based on a template. In turn, ML model templates are created based on previously added ML models. ML model templates preserve the algorithm structure, set of elements, and the state of the ML model used to create the template. The state of the created ML model will match the training state of the source ML model when the template was created.
Using templates, you can add ML models of the same type to Kaspersky MLAD. These models will analyze data received from equipment of the same type with a similar set of tags. When creating an ML model from a template, you can configure the use of other tags in the ML model by specifying tag IDs that differ from the ones in the source ML model.
Incidents
An incident is a deviation from the expected (normal) behavior of a monitored asset identified by the anomaly detector.
Kaspersky MLAD supports multiple types of anomaly detectors: Forecaster, Rule Detector, and Limit Detector. Each detector analyzes incoming telemetry data received from the monitored asset to identify deviations from normal behavior of the asset.
In addition to detecting deviations from normal object behavior, Kaspersky MLAD monitors the quality of incoming data. If the input data stream is terminated or interrupted for a specific tag, or observations that arrived at the application too soon or too late are detected in the input stream, the Stream Processor service registers incidents.
When a deviation is detected, the corresponding detector records the date, time and relevant deviation parameters, and saves this data as an entry in the Incidents section. If incident notifications for users or external systems are configured in Kaspersky MLAD, information about an incident is sent to the intended recipients via the corresponding components of Kaspersky MLAD.
Incidents detected by the Forecaster detector
An ML model created based on the Forecaster detector is trained on a specific subset of tags and can predict the current behavior of tags. In this case, an incident is any substantial discrepancy between the observed (actual) values of tags and the predicted values of tags resulting from operations of the ML model element. In the model element settings, you can view which tags are analyzed by the neural network (in_tags parameter) and which tags' behavior is predicted (out_tags parameter).
An ML model built based on the Forecaster detector consists of one or several ML model elements that operate in parallel. In the History and Monitoring sections, you can select a specific branch of the ML model to display the incidents registered as a result of a specific model element operation on the MSE graphs. Registered incidents are displayed as color-coded dot indicators in the lower part of the MSE graph.
The MSE graph also displays the predicted tag values and MSEs for the selected element of the ML model. MSE (mean square error) is an indicator of the difference between predicted values from actual values, calculated cumulatively for all tags included in the selected element of the ML model. The higher the MSE value, the more the behavior of tags will differ from the expected (normal) behavior. The MSE threshold is the critical MSE value that, when exceeded, causes the Forecaster detector to register an incident. The MSE threshold on an MSE graph is shown as an orange line.
The MSE graph is displayed in the lower part of the History section (see the figure below).
MSE graph in the History section
For each incident, the application automatically identifies the tags whose behavior had a stronger influence on incident registration. These tags are used to form the Tags for event #N preset, which is available for selection in the History section. Tags that are included in the Tags for event #N preset are sorted in descending order of their deviation from expected behavior. The first, most anomalous tag is also displayed in the incidents table in the Incidents section. The incidents table also indicates the MSE threshold and the actual MSE value at the moment when the incident was registered.
Information obtained when viewing the Tags for event #N preset is not actually diagnostic information for the purposes of identifying the causes of an incident, but you can still use this information when analyzing the values of tags with the largest deviations in behavior. The tag whose behavior was the first to deviate from the norm and caused subsequent deviations in other tags is referred to as the causal tag. In some cases, the causal tag may not be at the top of the list in the Tags for event #N preset and may even be entirely absent from this preset. This could happen due to the following reasons:
- Minor amplitude changes in the behavior of the causal tag had a multiplier effect and caused significant deviations in other tags that were included in the Tags for event #N preset.
- The causal tag is not analyzed by the ML model, and Kaspersky MLAD registers derivative changes in the behavior of tags caused by the deviation of the causal tag.
- Changes in the behavior of the causal tag had a delayed effect, and by the time an anomaly occurred in the operation of the monitored asset, the behavior of the causal tag returned to normal.
Incidents detected by the Rule Detector
An ML model element based on the Rule Detector consists of one or several diagnostic rules. Each diagnostic rule results in a value of an indicator tag that is calculated at each point in time. The name and description of the indicator tag represent the purpose of the diagnostic rule, for example, Sensor X failure, Dirty turbine blades, and Rotor speed drop. You can interpret the values of an indicator tag as follows:
- The value
0was received. The diagnostic rule was not triggered or applied at this moment. - The value
1was received. The diagnostic rule was triggered at this moment. - Intermediate values from
0to1are possible in individual cases. The diagnostic rule was partially triggered at this moment.
Whenever the value of an indicator tag reaches the threshold defined for a diagnostic rule (normally equal to 1), the Rule Detector registers an incident. The indicator tag is displayed in the incidents table in the Incidents section. For each incident registered by the Rule Detector, the application automatically creates the "Tags for event #N" preset, which is available in the History section. This preset includes the indicator tag that invoked the incident, and the tags that are included in the corresponding diagnostic rule.
To display the graphs of indicator tags, you can enable display of predicted tag values in the History section.
Page top
Incidents detected by the Limit Detector
If the Limit Detector is enabled, Kaspersky MLAD automatically monitors all tags having acceptable technical limits specified for the tag values when using any ML model. Technical limits can be defined in a tag configuration imported into Kaspersky MLAD at the start of operations. You can change the technical limits of tag values when editing a tag.
To visually control the position of a tag graph relative to its technical limits, enable the Always show technical limits option. If this option is disabled, the upper or lower limit line is displayed only if the tag values reached the corresponding limit during the time interval displayed on the screen. The Limit Detector identifies and registers events regardless of whether or not the Always show technical limits option is enabled.
When the tag value reaches its upper or lower technical limit, the Limit Detector registers an incident. This tag is displayed in the incidents table in the Incidents section. The incidents table also shows the technical limits of tag values and the actual value of a tag that violated one of these limits. For each incident registered by the Limit Detector, the application automatically creates the "Tags for event #N" preset, available in the History section. This preset includes the only causal tag of the incident.
Page top
Incidents detected by the Stream Processor service
The Stream Processor service gathers real-time telemetry data received from the monitored asset at arbitrary points in time and converts this data to a uniform temporal grid. When gathering incoming data, the Stream Processor service can detect losses of telemetry data and observations that were received by Kaspersky MLAD too early or too late. The Stream Processor service registers an incident in such cases.
Incidents detected by the Stream Processor service are displayed in the incidents table of the Incidents section. Each incident registered by the Stream Processor service is automatically assigned one of the following incident types:
- Monitored asset time failure – observations received by Kaspersky MLAD too early are detected.
- Late receipt of observation – observations received by Kaspersky MLAD too late are detected.
- No data – input data stream for a specific tag was terminated or interrupted.
Anomalies
An anomaly is any deviation in a monitored asset's behavior that is abnormal, not provided for by the current work procedure, and not normally caused by the industrial process.
Kaspersky MLAD registers only incidents. A specific incident can be identified as an anomaly only by an ICS specialist after conducting an analysis of incidents registered by the application. An incident analysis may result in one of the following conclusions:
- The incident is an anomaly that requires certain actions from a responding operator of the monitored asset.
- The incident is not actually an anomaly, but instead was a false positive by the triggered detector.
- The detector utilized in the ML model was correctly triggered but the incident is not an anomaly.
Incidents are analyzed and assessed by a subject-matter expert. In some cases, like when registering incidents detected by diagnostic rules or incidents that occur repeatedly, similar incidents can be automatically grouped and assessed.
The detector utilized in the ML model may fail to detect an actual anomaly. In this case, the anomaly will not be correlated to any registered incidents and will not be reflected in the Kaspersky MLAD history. If according to the expert or operator observations or external sources a detector is repeatedly not triggered, you need to identify the reason for the deteriorating quality of the detector, perform additional configuration, or conduct additional training of the ML model. Additional training of the ML model can be performed only by Kaspersky experts or certified integrators.
New
, , and values of the event parameters detected by the Event Processor service in the stream of incoming events can also indicate an anomaly in the operation of a monitored asset. When new events, patterns or values of event parameters are detected, the Event Processor service does not register incidents. To view new detections in the Event Processor section, you can view the history of registered patterns, filtering them by the New type. You can also create a monitor for tracking new events, patterns, or values of event parameters. The Event Processor service activates the monitor when it detects events, patterns, or event parameter values that match the specified search criteria. When the specified threshold for the number of monitor activations in a sliding window is reached, the Event Processor service sends an alert about the monitor activation to the external system using the CEF Connector.
Event Processor
The Kaspersky MLAD Event Processor is designed to detect regularities in the form of recurring events and patterns in the stream of events received from monitored assets and from the Anomaly Detector service, as well as to detect new events and patterns. New events and patterns may indicate an anomaly in the monitored asset operation.
Events
Data received from monitored assets and from the Anomaly Detector service are processed as events by the Event Processor service. An event is a set of values describing a change in the monitored asset state according to a predefined list of parameters and the time when this change occurred. The set of event parameters depends on the monitored asset and is defined by the administrator in the configuration file for the Event Processor service.
The Event Processor is designed to work only with categorical values of the event parameters. Event parameter values are converted to string type. Kaspersky MLAD uses the Anomaly Detector service to work with numeric values of telemetry data when processing the event stream. The administrator can enable the processing of data received from the Anomaly Detector service when configuring the Event Processor service settings.
An event is a phenomenon distinct from other events. There may also be intervals of time during which no events have occurred. Event registration may be affected by such factors as the actions of personnel, changes in the asset operating mode at the facility, or the execution of ICS commands by a specialist.
Examples of situations that may lead to event registration in Kaspersky MLAD
An event is registered once by the Event Processor service. When an event stream is received, the Event Processor recognizes previously detected events. If events are found that do not match those previously detected, the Event Processor registers new events.
You can view the received events as a graph or a table. To view events, you need to upload them to Event Processor → Event history. Event parameters specified in the configuration file for the Event Processor service may not appear in all events received from the monitored asset. Thus, some parameters may be missing when you view the received events.
Patterns
The Event Processor detects regularities in the stream of events arriving from the monitored asset. These regularities are detected as a hierarchy of stable (persistently recurring) patterns, which can be either simple patterns (sequences of events) or composite patterns (sequences of patterns). The patterns that form a composite pattern are called subpatterns.
A sequence of events or patterns is considered recurrent if its constituent elements follow the same order, and the time intervals between similar elements in different sequences differ from each other by no more than a specific maximum range. The allowable range of intervals between the pattern elements is calculated considering the value of the Coefficient defining the permitted dispersion of the pattern duration parameter. Patterns are the result of the specific facility's adopted practices, prescribed procedures, or technical specifics of the industrial process.
The Event Processor presents the detected regularities as a layered hierarchy of nested elements (pattern structure) down to the event level. Events are the first layer elements, simple patterns are the second layer elements, and composite patterns are the third and higher layer elements. Event parameter values are elements of the null layer.
A pattern is registered once by the Event Processor service. When an event stream is received, the Event Processor recognizes previously detected patterns. If patterns are found that do not match previously detected regularities, the Event Processor registers new patterns.
New patterns also include the sequences of events or patterns with a deviation in the order or composition of subpatterns (for example, turning on an industrial unit before the operator has arrived at the workstation) or with significant changes in the intervals between events or subpatterns even though their sequence is preserved (for example, turning on an industrial unit immediately after or a lot later than the operator arrived at the workstation). Thus, the Event Processor registers patterns with a new structure.
New patterns may indicate an anomaly in the monitored asset operation. You can view the structure of the new pattern and examine its deviations from the structure of previously detected patterns.
If a newly identified sequence of events or patterns begins to repeat in a persistent manner, this sequence is converted to a stable pattern.
Attention directions
The event stream from the monitored asset usually contains many unrelated events. The Event Processor service supports an attention direction mechanism to detect patterns based on a specific subset of events from the entire stream.
Attention is a special configuration of the Event Processor intended to track events and patterns for specific subsets of event history (attention directions). An attention direction is defined by the event parameter value that is common for all events of this direction. The Event Processor detects events and patterns only for the attention directions defined in the attention settings.
You can configure attention directions in the Event Processor section.
Event Processor operating modes
Kaspersky MLAD has the following operating modes of the Event Processor service:
- Online mode. In the online mode, the Event Processor processes the incoming stream as episodes. An episode is a sequence of events from the entire stream that is limited by a specific time period and/or the number of events. An episode is formed when one of the following conditions is fulfilled:
- The episode accumulation time reached the limit defined by the Interval for receiving batch events (sec.) parameter of the Event Processor service.
- The number of accumulated events reached the limit defined by the Batch size in online mode (number of events) parameter of the Event Processor service.
Based on an episode received in the event stream, the Event Processor service detects new and/or repeated (stable) events and patterns for each of the specified attention directions. You can configure attention directions in the Event Processor section.
When an event with the timestamp belonging to a previously processed episode is received, the Event Processor service does not revise the structure of patterns detected during the processing of that episode. The Event Processor service takes into account the events received by Kaspersky MLAD with a delay when detecting patterns during the event history reprocessing in the sleep mode.
- Sleep mode. To improve the quality and structure of the identified patterns, the Event Processor can switch to sleep mode according to the specified schedule. Processing of the event stream in the online mode is paused, and Kaspersky MLAD accumulates incoming events in the internal limited buffer on the server for subsequent processing after the application switches from the sleep mode back to online mode.
In sleep mode, the Event Processor re-analyzes sequences of events that were previously processed in online mode. To detect more complex pattern structures in the sleep mode, the Event Processor processes sequences of events during longer time intervals than the episode accumulation time in the online mode.
In the Event Processor service settings, you can configure a schedule for the sleep mode (for example, at the time when the event stream is least intense) and define a time interval for the events analyzed in the online mode to be forwarded for reprocessing in the sleep mode.
Monitors
A monitor is the source of notifications about patterns, events, or values of event parameters detected by the Event Processor according to the defined monitoring criteria. The monitoring criteria define a sliding time interval, the number of sequential detections, filters for event parameter values, and the condition for detecting new events, patterns, or event parameter values.
You can create monitors for alerts about the following detections in the event stream:
- Values of event parameters. You can create a monitor for alerts about the identification of new or previously encountered values of a specific event parameter. For example, to track new users on a monitored asset, create a monitor with the Parameter values subscription type and configure it to detect new values for the User parameter.
- Events. You can create a monitor for alerts about the identification of new or previously encountered events. You can also focus the attention of the Event Processor on a specific parameter of events. For example, to track new actions of a specific user at the monitored asset, you need to create a monitor with the Events subscription type and specify the name of the user whose actions you want to track in the User event parameter.
- Patterns. You can create a monitor for alerts about the identification of new or previously encountered patterns based on a specific attention direction. For example, to track regularities in the actions of a specific user at the monitored asset, create a monitor with the Patterns subscription type, focus the attention of the Event Processor on the User parameter, and set this parameter to the name of the user whose actions you want to track.
You can set fuzzy filters in the monitoring criteria. For example, you can create a monitor to track situations when a user (monitoring all values of the User parameter) accessed the accounting server (the value of the Server parameter) more than ten times (the value of the Threshold field) in the last five minutes (the value of the sliding time interval).
When events, patterns, or event parameter values matching the monitoring criteria are detected in the stream of incoming data, the Event Processor activates the monitor. Kaspersky MLAD displays information about the number of monitor activations when viewing a monitor, and sends to the external system alerts about the activation of monitors when the specified threshold is reached for a sliding window using the CEF Connector.
The custom monitors are displayed in the Event Processor section on the Monitoring tab.
Kaspersky MLAD components
Kaspersky MLAD includes the following components:
ML model
An ML model is a model created by Kaspersky experts or by a certified integrator for a specific facility based on machine learning algorithms and/or diagnostic rules using telemetry data from this facility. The ML model detects incidents.
An ML model is not included in the application distribution kit but is provided as part of the Kaspersky MLAD Model-building and Deployment Service.
Kaspersky MLAD services
Kaspersky MLAD services comprise the set of main application components supplied to each monitored asset. Kaspersky MLAD includes the following services:
- Anomaly Detector. Uses an ML model to process data and detect anomalies.
- Event Processor. Uses machine learning methods based on a semantic neural network to identify patterns and anomalous sequences of events.
- Stream Processor. Brings telemetry data received from the monitored asset at arbitrary real-time moments to a uniform temporal grid.
- Model Trainer. Performs repeated or additional training of an existing ML model based on the new telemetry data obtained by Kaspersky MLAD for a specific monitored asset.
- Similar Anomaly. Identifies and groups together similar incidents.
- Message Broker. Performs data exchange between Kaspersky MLAD components.
- Time Series Database. Stores time series of observed tag values, tag values predicted by the ML model, and prediction errors.
- Keeper. Performs routing of the telemetry data that should be saved in the database.
- Database. Stores all configuration settings of Kaspersky MLAD.
- API Server. Supports operation of the internal interfaces of Kaspersky MLAD.
- Web Server. Supports operation of the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
- Logger. Stores Kaspersky MLAD operation logs.
- Mail Notifier. Sends emails with incident registration notifications.
Connectors
Connectors are services that facilitate the exchange of data with external systems. For each protection object, you must select one of the following connectors:
- KICS Connector. Supports interaction with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
- OPC UA Connector. Receives tags from industrial process control systems (ICS) according to the protocol described in the OPC Unified Architecture specification.
- CEF Connector. Receives events from external sources (Industrial Internet of Things, network devices and applications) and returns messages in CEF (Common Event Format) registered by event analysis monitors.
- MQTT Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via the MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) protocol.
- AMQP Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol).
- WebSocket Connector. Receives tags from ICS and sends messages about incidents via the WebSocket protocol.
- HTTP Connector. Receives telemetry data from ICS in CSV files via HTTP POST requests.
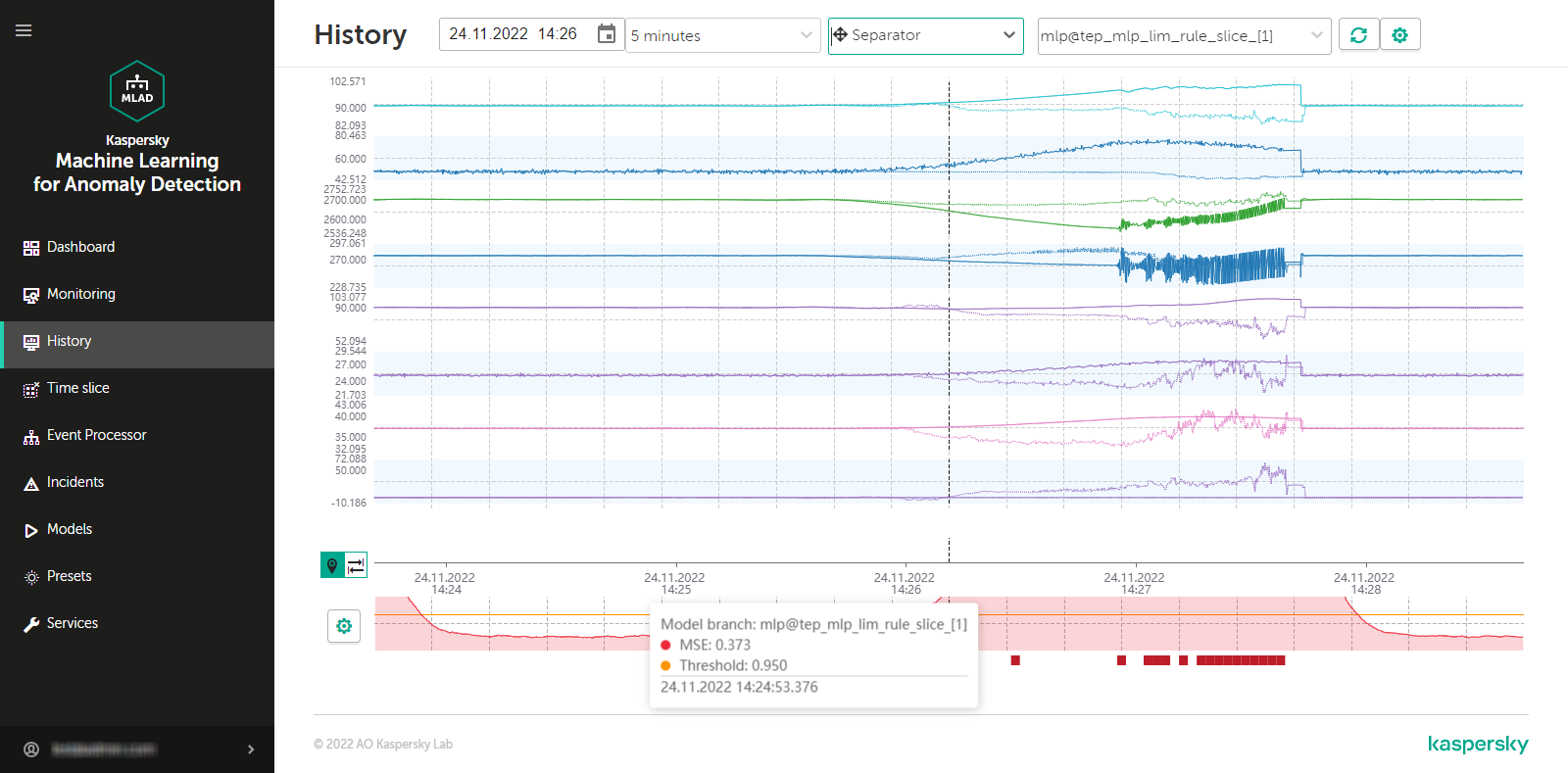
The figure below shows a diagram of interaction between the components of Kaspersky MLAD.
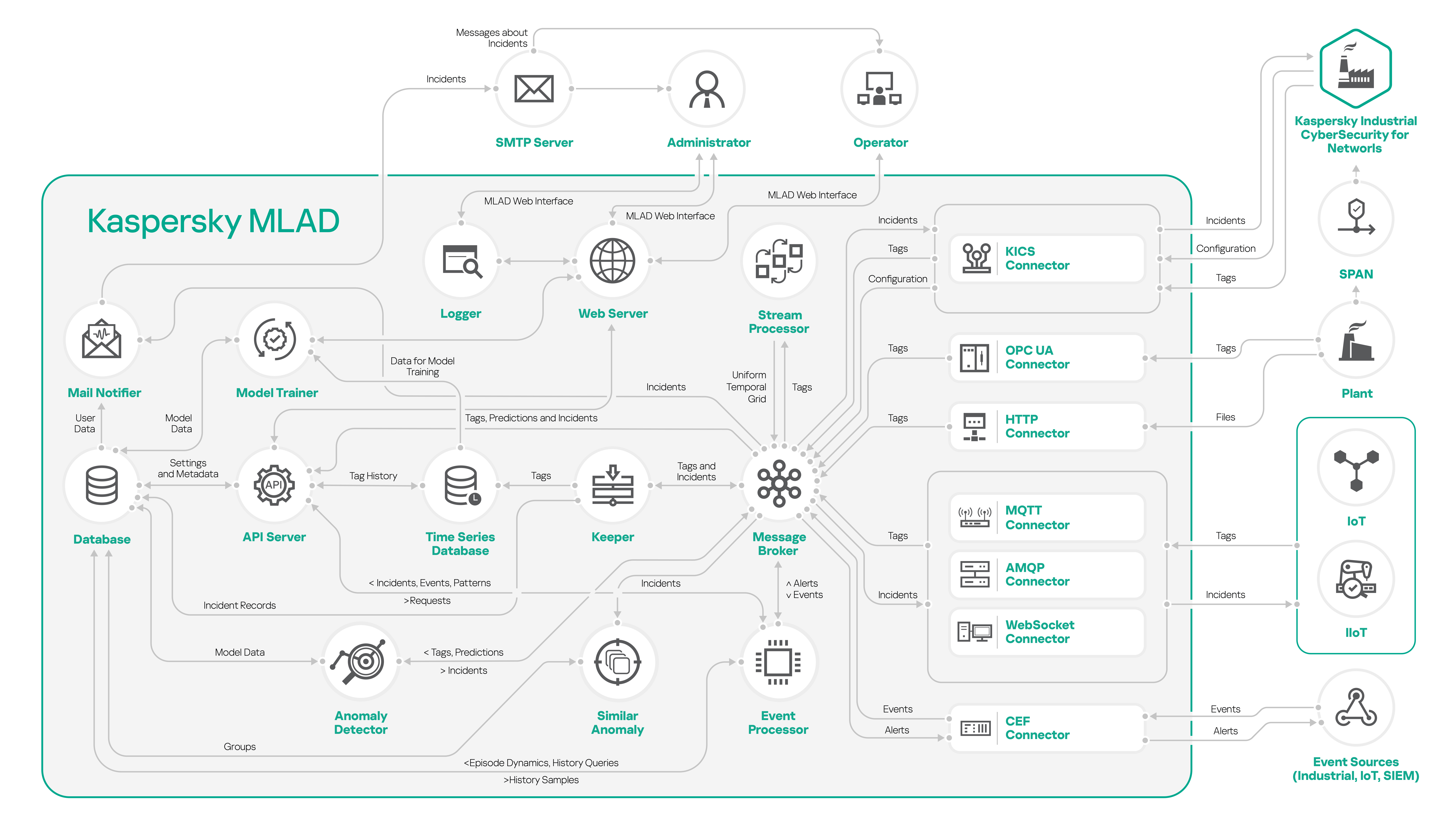
Diagram of interaction of Kaspersky MLAD components
Page top
Common deployment scenarios
This section provides a description of the standard scenarios for deploying Kaspersky MLAD in the network of a monitored asset, and provides special considerations when integrating Kaspersky MLAD with other applications.
Kaspersky MLAD supports the following installation options:
- Standalone installation.
- Installation with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
Standalone installation of Kaspersky MLAD
You can install only Kaspersky MLAD if you plan to use the following connectors as a data provider:
- OPC UA Connector
- MQTT Connector
- AMQP Connector
- CEF Connector
- WebSocket Connector
- HTTP Connector
The figures below show example scenarios for standalone installation of Kaspersky MLAD using the connectors described above. You can use any configurations of connectors that are suitable for your monitored asset.
Standalone installation of Kaspersky MLAD using connectors: OPC UA Connector, MQTT Connector, AMQP Connector, HTTP Connector, WebSocket Connector
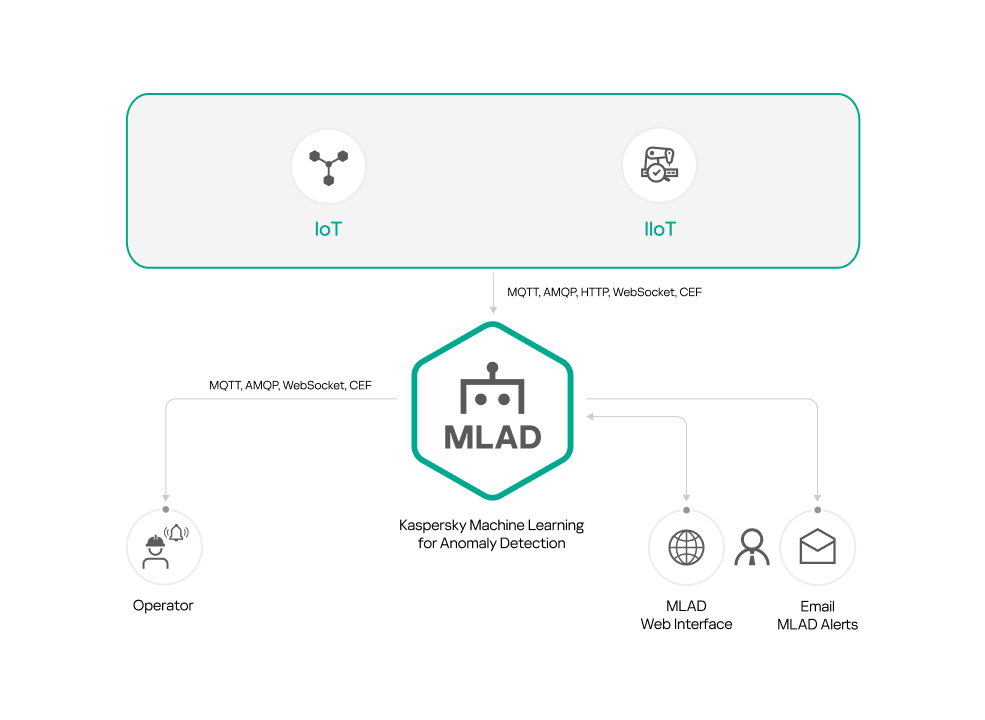
Standalone installation of Kaspersky MLAD using connectors: MQTT Connector, AMQP Connector, HTTP Connector, WebSocket Connector
Installation of Kaspersky MLAD with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks
You can install Kaspersky MLAD and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks if you are planning to use Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks as a data provider (see the figure below).
Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection is compatible with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
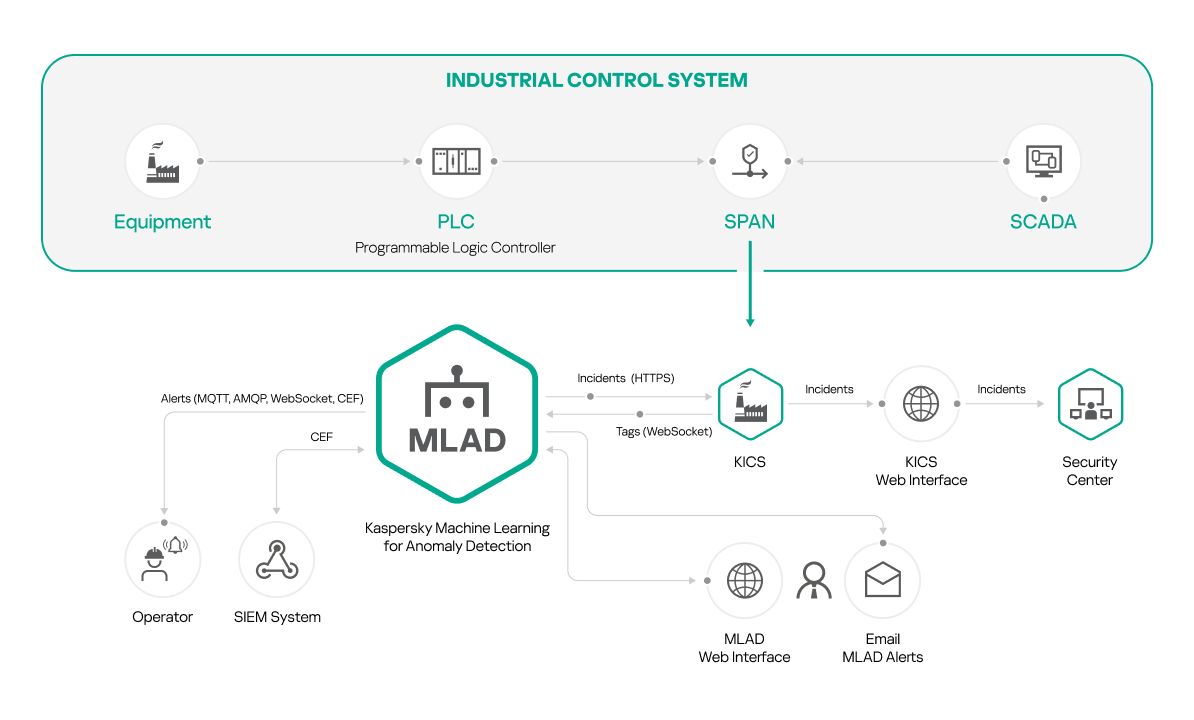
Installation of Kaspersky MLAD with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks
To use this installation option, first install Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks and add a Generic connector. Create a communication data package for the added connector and specify the settings for connecting Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks to Kaspersky MLAD. Upload the obtained communication data package to Kaspersky MLAD when configuring the KICS Connector. For detailed information about creating and adding a connector, please refer to the Adding a connector section of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Help Guide.
Computers with Kaspersky MLAD and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks installed must belong to the same network.
Page top
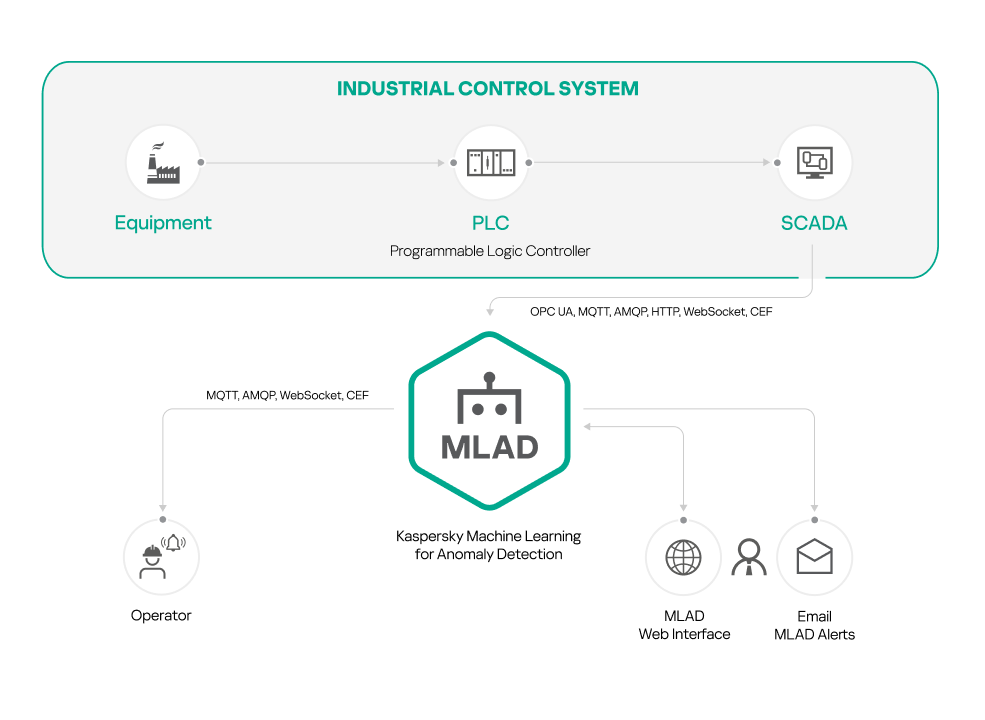
Telemetry and event data flow diagram
In Kaspersky MLAD, data exchange with the external systems is provided by connectors. To receive telemetry data (tags) and/or events from the external systems, you can configure the HTTP Connector, MQTT Connector, AMQP Connector, OPC UA Connector, KICS Connector, CEF Connector, and WebSocket Connector.
The Stream Processor service performs the initial processing of the telemetry data of the monitored asset, converting the received tags to a uniform temporal grid (UTG). When Stream Processor service detects loss of telemetry data and observations received by Kaspersky MLAD too early or too late, it registers incidents.
The Stream Processor service transfers the UTG-converted data to the ML model of the Anomaly Detector service. If the detectors on which the ML model is based detect deviations from the normal behavior of the monitored asset while processing the received data, the Anomaly Detector service registers incidents. When similar incidents are detected, the Similar Anomaly service generates groups of incidents.
You can view registered incidents and groups of incidents in the Incidents section. Kaspersky MLAD also sends incident notifications to the specified email addresses and to external systems using connectors.
Events received by Kaspersky MLAD are processed by the Event Processor service. The Event Processor can also process incidents registered by the Anomaly Detector service. In the stream of events, the Event Processor detects regularities – recurring events and patterns – as well as new events and patterns. When monitors are activated, the Event Processor service sends alerts to external systems about the detection of events, patterns, and event parameter values according to the specified monitoring criteria using the CEF Connector. You can also view information about events, patterns, and monitors in the Event Processor section.
The figure below shows the telemetry and event data stream in Kaspersky MLAD.
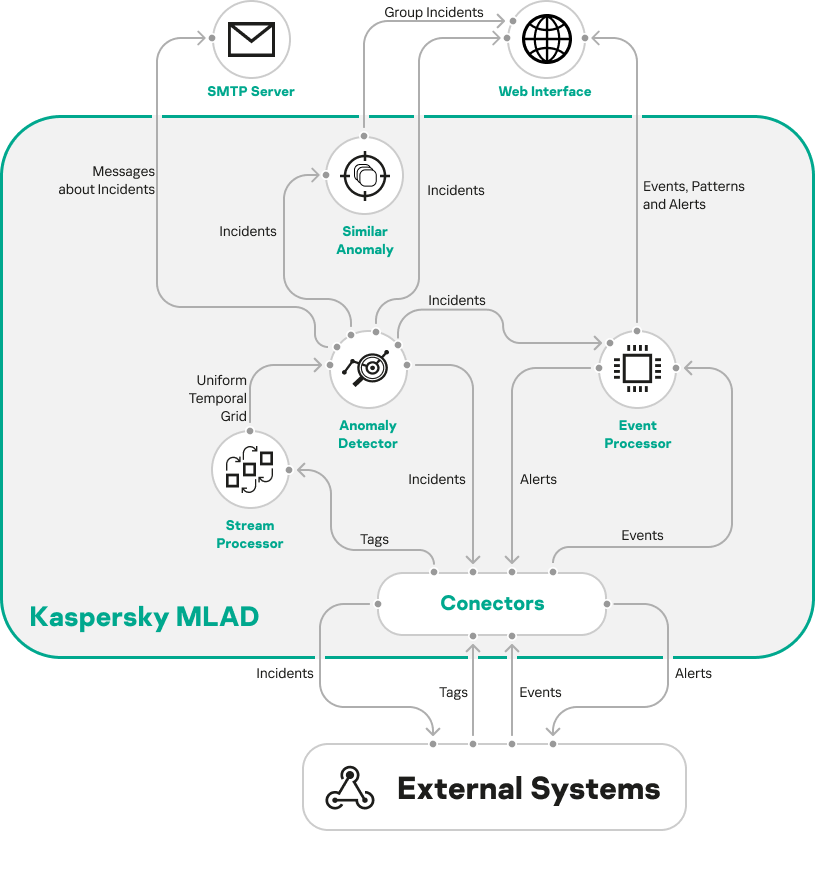
The telemetry and event data stream in Kaspersky MLAD
Page top
Administering Kaspersky MLAD
This section provides information on installing, updating, configuring, and removing the application. This section also provides instructions on managing user accounts and incident notifications.
Installing the application
This section contains options for installing the application (normal mode and silent mode), and a step-by-step description of Kaspersky MLAD installation for each of the options.
Installation of Kaspersky MLAD is performed by a qualified administrator that is employed by the Customer and authorized to accept the End User License Agreement for the application.
To install Kaspersky MLAD from the command line:
- Unpack the archive named mlad-3.0.0-<build number>.tar.xz that is included in the distribution kit:
tar xf mlad-3.0.0-<build number>.tar.xz - Navigate to the directory named mlad-release-3.0.0-<build number>:
cd mlad-release-3.0.0-<build number> - Run the setup.sh installation script:
sudo ./setup.sh - Follow the instructions of the Application Setup Wizard.
To install Kaspersky MLAD in non-interactive mode:
- Unpack the archive named mlad-3.0.0-<build number>.tar.xz that is included in the distribution kit:
tar xf mlad-3.0.0-<build number>.tar.xz - Navigate to the directory named mlad-release-3.0.0-<build number>:
cd mlad-release-3.0.0-<build number> - Run the setup.sh installation script with the following switches:
sudo ./setup.sh -q -e acceptwhere:
-qmeans that the application is installed in non-interactive mode.-e acceptmeans that you accept the terms of the End User License Agreement. You must accept the terms of the End User License Agreement to install the application. If you do not add the-e acceptswitch, installation of the application will not continue.You can read the text of the End User License Agreement in the text file named license_en.txt located in the 'legal' folder.
As a result, the application is installed on the computer.
Updating the application and rolling back to the previous installed version
This section contains a step-by-step description of how to update Kaspersky MLAD, and a description of how to roll back the application to the previous installed version.
Update and rollback of Kaspersky MLAD are possible only for application versions 3.0.0-001 or later. When Kaspersky MLAD is updated, all of the following data that was uploaded, received, or processed by the previous version of Kaspersky MLAD will be saved: tag configurations, presets, ML models, and settings of Kaspersky MLAD.
Kaspersky MLAD must be updated by a qualified administrator who is employed by the Customer and authorized to accept the End User License Agreement for Kaspersky MLAD.
To update Kaspersky MLAD from the command line:
- Unpack the archive named mlad-3.0.0-<new build number>.tar.xz that is included in the distribution kit:
tar xf mlad-3.0.0-<new build number>.tar.xz - Navigate to the folder where you unpacked Kaspersky MLAD:
cd mlad-3.0.0-<new build number> - Run the application update script named upgrade.sh:
sudo ./upgrade.shYou can run the upgrade.sh script with the
-hswitch if you want to call up the assistant in the Kaspersky MLAD update interface:sudo ./upgrade.sh -h - Follow the instructions of the Application Upgrade Wizard.
As a result, Kaspersky MLAD will be updated to the version specified in the build number. All application files are located in the folder where Kaspersky MLAD is installed (mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number> by default). A directory named upgrade_backup-3.0.0-<previous build number> will also be created there and will contain a backup copy of the previous version of Kaspersky MLAD. It is not recommended to move the upgrade_backup-3.0.0-<previous build number> directory to a different directory.
To roll back Kaspersky MLAD to the previous installed version:
- Go to the directory that contains the backup copy of Kaspersky MLAD:
cd upgrade_backup-3.0.0-<previous build number> - Run the application update script named upgrade.sh with the
-rswitch:sudo ./upgrade.sh -r - Follow the instructions of the Application Upgrade Wizard.
When rolling back Kaspersky MLAD to the previous installed version, all data received and processed by Kaspersky MLAD from the moment the application was upgraded to the moment of the rollback to the previous version will be lost. You are advised to verify that you have a full backup copy of all Kaspersky MLAD data.
As a result, Kaspersky MLAD will be rolled back to the previous installed version.
Page top
Getting started
Before starting to work with Kaspersky MLAD, you must make sure that the following conditions are fulfilled:
- The telemetry data source is enabled and configured to send data to Kaspersky MLAD.
- The data transfer network is prepared to deliver telemetry data from the data source to the Kaspersky MLAD server, the network equipment is properly configured, and data transfer is allowed.
- Configuration settings and/or configuration files are prepared for the connector that will be used in Kaspersky MLAD to receive telemetry data or events from external systems. The connector must be configured and activated after Kaspersky MLAD is started.
- Descriptions of tags of received telemetry and (optional) their presets are prepared as a JSON file to be imported into Kaspersky MLAD. This file is created by Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator.
- An ML model or multiple ML models are created, trained on historical telemetry data, and prepared to be imported into Kaspersky MLAD as TAR files. These files are created by Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator.
- The Kaspersky MLAD administrator has been sent the codes for activating ML models. The ML model activation codes are stored in a secure storage location.
Starting and stopping Kaspersky MLAD
Kaspersky MLAD starts automatically immediately after installation.
To start the application after it has been stopped:
- Go to the folder where Kaspersky MLAD is installed (mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number> by default).
- In the command line, run the following command:
./mlad-start.sh
Kaspersky MLAD will be started.
To stop the application:
- Go to the folder where Kaspersky MLAD is installed (mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number> by default).
- In the command line, run the following command:
./mlad-stop.sh
Kaspersky MLAD will be stopped.
Page top
Updating Kaspersky MLAD certificates
The following certificates are used in Kaspersky MLAD:
- Certificates for connecting to Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface.
- Certificates for connecting connectors and services.
It is recommended to update certificates in the following cases:
- Current certificates have been compromised.
- Certificates have expired.
- Certificates need to be updated in accordance with the enterprise information security requirements.
Updating a certificate for connecting to Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface
By default, Kaspersky MLAD uses a self-signed certificate that is automatically generated during the application installation to connect to the web interface. When using a self-signed certificate to connect to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface, the browser displays a warning that the security certificate or the established connection is not trusted.
To use trusted certificates to connect to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface, you can replace the self-signed certificate with a certificate received from a recognized certification authority or with a custom certificate that complies with the security standards of your organization.
By default, Kaspersky MLAD uses the mlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/ssl/nginx/ directory to store certificates for connecting to the web interface.
The certificate for connecting to Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface can be updated by a qualified administrator – a Customer employee authorized to accept the End User License Agreement for the application.
To update certificates for connecting to Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface:
- Obtain a trusted certificate and a key for this certificate to connect to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
A certificate must be received for the IP address and domain name of the server on which Kaspersky MLAD is installed.
- Go to the directory containing the trusted certificate and the key to this certificate.
- In the command line, run the following commands:
sudo chown root:root <new certificate.crt> <new certificate key.key>sudo chmod 640 <new certificate.crt> <new certificate key.key>sudo cp <new certificate.crt> mlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/ssl/nginx/mlad_nginx.crtsudo cp <new certificate key.key> mlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/ssl/nginx/mlad_nginx.keyThe new certificate and its key are saved to the mlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/ssl/nginx/ directory as the mlad_nginx.crt and mlad_nginx.key files respectively.
- Restart Kaspersky MLAD by executing the following commands in the command line:
mlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/mlad-stop.shmlad-3.0.0-<installation build number>/mlad-start.sh
After restarting, Kaspersky MLAD uses the new certificate to connect to the web interface.
Updating a certificate for connecting connectors and services
In Kaspersky MLAD, you can use a secure connection for MQTT Connector, AMQP Connector, WebSocket Connector, and the Mail Notifier service. You can update certificates for connecting these connectors and the Mail Notifier service using a secure connection in the System parameters section of the administrator menu.
The certificate for connecting the KICS connector is contained in the communication data package, which you can update in Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks. You can upload the updated communication data package to Kaspersky MLAD when configuring the KICS Connector. For detailed information about creating a communication data package, please refer to the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Help Guide.
Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection is compatible with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
Page top
First startup of Kaspersky MLAD
This section describes the sequence of application configuration steps that must be performed by the administrator when Kaspersky MLAD is started for the first time.
Kaspersky MLAD starts automatically immediately after installation.
The first startup of Kaspersky MLAD consists of the following steps:
- Starting Kaspersky MLAD
Start Kaspersky MLAD. The following services required for Kaspersky MLAD operation will be started:
- API Server
- Web Server
- Message Broker
- Keeper
- Time Series Database
- Database
- Logger
- Connecting to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface
Open the application web interface in a supported browser and enter the login and password that were created by default. Change the password for your user account. For a secure connection to Kaspersky MLAD web interface, install a trusted certificate.
- Configuring services
In the Settings → System parameters section, configure the services that you need to use for your monitored asset. In the Services section, check the statuses of the services and start them, if necessary. For example, the Anomaly Detector service must be running for correct anomaly detection.
- Uploading a tag configuration to Kaspersky MLAD and creating presets
A tag configuration is created by a Kaspersky expert or integrator while deploying the application and building an ML model. A tag configuration is described in a JSON file. An example configuration description is provided in the Appendix.
For subsequent operation, upload a tag configuration to Kaspersky MLAD. If your tag configuration does not contain presets, create new presets from tags.
- Uploading and activating an ML model
An ML model is not included in the application distribution kit but is provided as part of the Kaspersky MLAD Model-building and Deployment Service.
Upload and activate the ML model. To activate the ML model, you must enter a model activation code.
- Configuring connectors
To work with data, configure the connectors used at your monitored asset. You can configure the following connectors:
- Connecting to a data source
When the above connectors are configured, start the connectors used for your monitored asset. Go to the Dashboard section and make sure that data is being received by Kaspersky MLAD in online mode.
- Configure attention
To work with events and patterns, configure attention settings and display of event parameters. The Event Processor service detects events and patterns only for the attention directions defined in the attention settings.
- Creating user accounts
Create accounts for users of the application and assign the necessary roles to them. Configure incident notifications for users.
Completion of these steps should result in the following:
- Kaspersky Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection is prepared for operation, and the application is receiving and processing data.
- Users can start working with Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface.
Configuring Kaspersky MLAD
This section contains instructions on configuring Kaspersky MLAD settings.
Configuring the main settings of Kaspersky MLAD
Kaspersky MLAD lets you specify the name of the monitored asset, web address and IP address for connecting users to the application web interface, and the frequency of receiving new data from the monitored asset. The name of the monitored asset will be displayed in each section of the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
Configuration of the main parameters of Kaspersky MLAD is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure the main settings of Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Main.
A list of options appears on the right.
- In the Name of monitored object field, specify the name of the monitored asset.
- In the Application web address field, specify the web address of the application.
- In the Application connection IP address field, specify the IP address of the application.
- In the Interval for receiving data from the Message Broker service (ms) field, specify the interval for updating telemetry data in the application web interface.
The higher the specified parameter value, the less frequently the data is updated.
- In the Interval for receiving incident statistics from the database (ms) field, indicate how frequently data on incidents registered by the application should be updated in the application web interface.
- In the Number of authentication attempts field, specify the number of unsuccessful authorization attempts. When this number is reached, Kaspersky MLAD blocks the corresponding user account.
- In the User lock duration (sec) field, specify the period in seconds to block a user account after reaching the specified number of unsuccessful authorization attempts.
- Click the Save button.
Configuring the Anomaly Detector service
In Kaspersky MLAD, an ML model can contain the following detectors:
- Limit Detector detects anomalies whenever the tag value falls below the minimum value or exceeds the maximum value.
- Forecaster predicts the current behavior of an object based on data about its behavior in the recent past.
- XGBoost with a certain probability detects anomalies in the monitored asset data based on the data sample for the examined time interval learned by the XGBoost classifier.
- Rule Detector builds predictions for the tag values during normal operation of the monitored asset and registers incidents whenever one or multiple rules are triggered.
You can configure the procedure for detecting anomalies based on the specific features of your monitored asset by enabling or disabling the necessary detectors in the Anomaly Detector service settings.
Configuration of the Anomaly Detector service is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure the settings of the Anomaly Detector service in Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Anomaly Detector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- Move the Use Limit Detector toggle button to the necessary position to enable or disable use of the Limit Detector.
- Move the Use Forecaster detector toggle button to the necessary position to enable or disable use of the Forecaster detector.
- Move the Use XGBoost detector toggle button to the necessary position to enable or disable use of the XGBoost detector.
- Move the Use Rule Detector toggle button to the necessary position to enable or disable use of the Rule Detector.
- Move the Skip gaps in data toggle button to the necessary position to enable or disable the function for skipping gaps in the incoming data stream.
- In the Maximum number of records requested from the Message Broker service field, enter the number of records that must be requested from the Message Broker service for subsequent processing in the Anomaly Detector.
- In the Number of messages sent in one block to the Message Broker service field, enter the number of incidents that must be sent to the Message Broker service at one time.
- In the Number of simultaneously running models field, enter the maximum number of ML models that can analyze telemetry data at the same time.
For maximum performance of Kaspersky MLAD, the number of ML models running at the same time must not exceed 80% of the number of cores of the server where Kaspersky MLAD is installed.
- Click the Save button.
Configuring the Keeper service
Kaspersky MLAD uses the Keeper service to route telemetry data that should be saved in the database. You can configure the settings that define the rate of incoming data received from connectors and external sources, and the volume of data that is saved in the Kaspersky MLAD database.
Configuration of the Kaspersky MLAD data routing settings is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure the Kaspersky MLAD data routing settings:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Keeper.
A list of options appears on the right.
- Perform one of the following actions:
- To save both known and unknown tags from external sources to the database, turn on the Save all tags toggle.
- To save only the tags that are known to the application, turn off the Save all tags toggle.
- In the Timeout for receiving tags (ms) field, enter the maximum timeout (in milliseconds) for receiving the values of tags.
- In the Timeout for receiving incidents (ms) field, enter the maximum timeout (in milliseconds) for receiving incidents.
- In the Timeout for receiving metrics (ms) field, enter the maximum timeout (in milliseconds) for receiving metrics.
- Click the Save button.
Configuring the Mail Notifier service
Kaspersky MLAD uses the Mail Notifier service to notify users when incidents are registered by the application.
Configuration of the Mail Notifier service is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
Configuring the Mail Notifier service is optional; it is performed if an SMTP server is configured in the monitored asset network.
To configure the Mail Notifier service:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Mail Notifier.
A list of options appears on the right.
- If necessary, move the Use SSL connection toggle button to enable the use of a secure SSL connection.
By default, use of a secure SSL connection is disabled.
- In the SMTP server address field, enter the IP address and port of the SMTP server.
- In the SMTP server user name field, enter the user name for the SMTP server.
- In the SMTP server password field, enter the password for the SMTP server.
- If you are using a secure SSL connection:
- In the SMTP server certificate field, upload the Certification Authority certificate.
- In the Key to SMTP server certificate field, upload the key to the Certification Authority certificate.
To delete the certificate file or certificate key, click the Clear icon (
 ) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon (
) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon ( ) in the corresponding field.
) in the corresponding field. - Click the Save button.
Configuring the Similar Anomaly service
Kaspersky MLAD uses the Similar Anomaly service to identify similar incidents and combine them into groups. In groups, you can view similar incidents that were registered at different times.
Configuration of the Similar Anomaly service is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure the Similar Anomaly service:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Similar Anomaly.
A list of service settings appears on the right.
- In the Minimum number of incidents to group field, enter the minimum number of similar incidents for forming a group.
- In the Maximum number of incidents to group field, enter the maximum number of incidents that can be put into one group.
If you want all incidents to be put into one group, leave this field empty.
- In the Maximum distance between similar incidents field, enter the maximum distance that similar incidents can lag behind each other.
You can specify a value in the range of
0to1. - Click the Save button.
Configuring the Stream Processor service
The Stream Processor service gathers real-time telemetry data (input stream) received from the monitored asset at arbitrary points in time and converts this data to a UTG (output stream). Based on the accumulated data, the Stream Processor service determines the values of tags in the output data stream. After converting data into an output stream, the Stream Processor service forwards this data to the ML model for processing.
When converting incoming telemetry data, the Stream Processor service accounts for potential data losses (for example, if the network of the monitored asset temporarily goes down) and processes observations that were received in Kaspersky MLAD too early or too late. In these cases, the Stream Processor service generates default incidents and/or forwards default tag values to the output data stream.
The Stream Processor service can also compute derivative tags based on incoming telemetry data (for example, to calculate the moving average or average value of a group of tags).
Configuration of the Stream Processor service is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky expert or certified integrator).
To configure the Stream Processor service:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Stream Processor.
- In the Fixed-interval sequence frequency (sec) field, specify the period (in seconds) for which the Stream Processor service will process incoming telemetry data.
- In the Configuration file field, add the file containing the configuration settings for the Stream Processor service.
To delete the configuration file for the Stream Processor service, click Clear (
 ). To save the configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - Click the Save button.
Configuring the HTTP Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the HTTP Connector to receive data from CSV files during scheduled uploads of data using the POST method.
Configuration of the HTTP Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the HTTP Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → HTTP Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- Use the Write data to the Message Broker service toggle button to enable writing data to the Message Broker service.
- If necessary, move the Save received file toggle button to enable the function for saving received CSV files.
- In the Size of written block (tag count) field, specify the number of tags that are written to the Message Broker at one time.
- In the Maximum size of uploaded file (MB) field, specify the maximum size (in megabytes) of a file transmitted to the HTTP Connector.
If you try to download a larger CSV file, the file would not be passed to the HTTP Connector.
If
0is defined, the maximum file size is unlimited. - Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD will receive data from CSV files using the HTTP Connector.
An example of sending a CSV file to the HTTP Connector via cURL using the POST method to port 4999 of the Kaspersky MLAD server:
curl -F "file=@<file name>.csv" -X POST "http://<Kaspersky MLAD server IP address or domain name>:4999/" |
The HTTP Connector accepts CSV files with the following fields:
timestamp;tag_name;value
where:
timestampis the time stamp in the format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.tag_nameis the name of the tag.valueis the tag value.If a tag value contains a fractional portion, use a dot to separate the integer from the fractional portion.
Configuring the MQTT Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the MQTT Connector to receive data and send messages about incident registration via the MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) protocol.
Configuration of the MQTT Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the MQTT Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → MQTT Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- If necessary, move the Use SSL connection toggle button to enable the use of a secure SSL connection.
By default, use of a secure SSL connection is disabled.
- In the MQTT broker (address:port) field, specify the host name and port of the external MQTT broker that the MQTT Connector will interact with.
The default value of this parameter is
mqtt_broker:1883. - In the User name for MQTT connection field, enter the user name.
- In the Password for MQTT connection field, enter the user's password.
- If you enabled the use of a secure SSL connection, add the root certificate for the MQTT broker in the CA certificate field.
To delete the certificate file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - If you need to use client certificates for a secure SSL connection, perform the following actions:
- In the Client certificate field, add the MQTT client application certificate.
- In the Key to client certificate field, add the key for the MQTT client application certificate.
To delete the certificate file or certificate key, click the Clear icon (
 ) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon (
) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon ( ) in the corresponding field.
) in the corresponding field. - In the List of MQTT subscriptions for receiving tags field, enter the name of the list of MQTT subscriptions from which the MQTT Connector will receive tag values.
The default value of this parameter is
tags. - In the MQTT topic for publishing messages field, specify the name of the topic where the MQTT Connector will publish messages about incident registration.
If no value is defined for this setting, messages are not sent.
This setting has no value by default.
- In the Data format drop-down list, select the format to receive data from external systems and send incident alerts.
The following options are available:
JSONBatch,Topic,SmartHome,KISG.The default value of this parameter is
JSONBatch.If none of the incident data and alert formats suits you, you can contact Kaspersky Lab experts to add the required format.
- If you selected
Topicdata type, in the Connector configuration file field, add a configuration file containing the connector settings for this data format.To delete the connector configuration file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - If you need to recalculate the tag values based on the parameter values specified in the preset file, turn on the Scale obtained tag values toggle button.
By default, scaling of the received data is disabled.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD will receive data and send messages about incident registration via the MQTT protocol.
Page top
Configuring the AMQP Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the AMQP Connector to receive data and send messages about incident registration via AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol).
Configuration of the AMQP Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the AMQP Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → AMQP Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- If necessary, move the Use SSL connection toggle button to enable the use of a secure SSL connection.
By default, use of a secure SSL connection is disabled.
- In the AMQP broker (address:port) field, specify the host name and port of the external AMQP broker that the AMQP Connector will interact with.
The default value of this parameter is
rabbitmq:5672. - In the User name for AMQP connection field, enter the user name.
- In the Password for AMQP connection field, enter the user's password.
- If you enabled the use of a secure SSL connection, add the root certificate for the AMQP broker in the CA certificate field.
To delete the certificate file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - If you need to use client certificates for a secure SSL connection, perform the following actions:
- In the Client certificate field, add the AMQP client application certificate.
- In the Key to client certificate field, add the key for the AMQP client application certificate.
To delete the certificate file or certificate key, click the Clear icon (
 ) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon (
) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon ( ) in the corresponding field.
) in the corresponding field. - In the AMQP virtual host field, specify the virtual host for establishing a connection between the AMQP Connector and the external AMQP broker.
The default value of this parameter is
/. - In the AMQP exchange point name for receiving tags field, specify the name of the exchange point to receive tags from an external AMQP broker.
If a value is not defined for this parameter, tags will not be received via the AMQP Connector.
This setting has no value by default.
- In the List of AMQP subscriptions for receiving tags field, specify the name of the list of subscriptions from which the AMQP Connector will receive tag values.
The default value of this parameter is
#. - In the AMQP queue for receiving tags field, specify the name of the queue for the AMQP connector. This field is optional.
- In the AMQP exchange point name for publishing messages field, specify the name of the exchange point for sending messages about events.
If no value is defined for this parameter, messages will not be sent. You can specify the same name that you indicated in step 8 of these instructions.
This setting has no value by default.
- In the AMQP topic for publishing messages field, specify the name of the topic where the AMQP Connector will publish messages about incident registration.
The default value of this parameter is
alert. - In the Data format drop-down list, select the format to receive data from external systems and send incident alerts.
The following options are available:
JSONBatch,Topic,SmartHome,KISG.The default value of this parameter is
JSONBatch.If none of the incident data and alert formats suits you, you can contact Kaspersky Lab experts to add the required format.
- If you selected
Topicdata type, in the Connector configuration file field, add a configuration file containing the connector settings for this data format.To delete the connector configuration file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - If you need to recalculate the tag values based on the parameter values specified in the preset file, turn on the Scale obtained tag values toggle button.
By default, scaling of the received data is disabled.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD will receive data and send messages about incident registration via the AMQP protocol.
Page top
Configuring the OPC UA Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the OPC UA Connector to receive data over a protocol described by the OPC Unified Architecture specification.
Configuration of the OPC UA Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the OPC UA Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → OPC UA Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- In the Connection point field, specify the connection address. For example,
opc.tcp://10.65.48.40:8001/freeopcua/server/. - In the Configuration file field, add the file containing the OPC UA Connector configuration settings.
To delete the connector configuration file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD will receive data using a protocol described by the OPC Unified Architecture specification.
Page top
Configuring the KICS Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the KICS Connector to receive data from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks 3.0 and later and to send back incident registration messages.
The connector for integration with Kaspersky MLAD must be created and added to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks in advance. For detailed information about creating and adding a connector, please refer to the Adding a connector section of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Help Guide.
Integration with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks 3.0 and later is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the KICS Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → KICS Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- In the Communication data package for KICS Connector (zip) field, add the file containing the settings for configuring interaction between Kaspersky MLAD and Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
For detailed information about creating a communication data package, please refer to the Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks Help Guide. The created communication data package must be saved on the computer where Kaspersky MLAD is installed.
To delete a communication data package, in the Communication data package for KICS Connector (zip) field, click the Clear (
 ) icon. To save the communication data package on your computer, click the Download icon (
) icon. To save the communication data package on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - In the Password for KICS Connector field, enter the password that you specified when adding the connector to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- If you need to send incident registration notifications to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks, turn on the Send messages to Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks toggle button.
- In the Tag sampling frequency (Hz) field, specify the frequency (in Hz) at which you need to receive tag values from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
Indicate 0 in this field if data sampling is not required. Data sampling is a method of adjusting a training sample to balance the distribution of classes in the original data set.
- If you need to recalculate the tag values based on the parameter values specified in the preset file, turn on the Scale obtained tag values toggle button.
By default, scaling of the received data is disabled.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD receives data from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks and sends back messages about incident registration.
Page top
Configuring the CEF Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the CEF Connector to receive data from external sources of events (Industrial Internet of Things, network devices and applications) and to return messages regarding incident registration.
To receive events from external sources using the CEF Connector, configure the Event Processor service.
Before configuring the CEF Connector settings in the Kaspersky MLAD web interface, the IP address and port number to be used for connecting to the external event source for receiving events must be specified in the .env file.
Configuration of the CEF Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator.
To configure the CEF Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → CEF Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- If necessary, move the Receive events for the Event Processor service toggle button to enable use of the CEF Connector for receiving events from an external system.
- To send messages about the incidents registered by the Anomaly Detector service to an external system, enable the Send registered incidents to SIEM system option.
- To send messages about the events registered by the Event Processor service to an external system, enable the Send registered events to SIEM system option.
- In the IP address for sending events and incidents to SIEM system field, specify the IP address for connecting to the external system and forwarding events processed by the Event Processor service and incidents registered by the Anomaly Detector service.
- In the Port for sending events and incidents to SIEM system field, specify the port number for connecting to the external system and forwarding events processed by the Event Processor service and incidents registered by the Anomaly Detector service.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD receives data from external sources of events (Industrial Internet of Things, network devices, and applications) and returns messages about the registration of events and incidents.
Page top
Configuring the WebSocket Connector
Kaspersky MLAD uses the WebSocket Connector to receive data and send messages about incident registration via the WebSocket protocol.
Configuration of the WebSocket Connector is performed by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator. The instructions in this section are provided for information purposes.
To configure the WebSocket Connector:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → WebSocket Connector.
A list of options appears on the right.
- In the WebSocket server web address field, specify the web address of the WebSocket server that the WebSocket Connector will interact with.
Indicate the web address in the format
WebSocket protocol://address:port/. - To use a secure connection to connect to the WebSocket server, add the root certificate for the WebSocket server in the CA certificate field.
To delete the certificate file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the certificate file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - To use client certificates for a secure connection to the WebSocket server, do the following:
- In the Client certificate field, add the certificate of the WebSocket client application.
- In the Key to client certificate field, add the key for the WebSocket client application certificate.
To delete the certificate file or certificate key, click the Clear icon (
 ) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon (
) in the corresponding field. To save the certificate file or certificate key on your computer, click the Download icon ( ) in the corresponding field.
) in the corresponding field. - In the Data format drop-down list, select the format to receive data from external systems and send incident alerts.
The following options are available:
JSONBatch,Topic,SmartHome,KISG.The default value of this parameter is
JSONBatch.If none of the incident data and alert formats suits you, you can contact Kaspersky Lab experts to add the required format.
- If you selected
Topicdata type, in the Connector configuration file field, add a configuration file containing the connector settings for this data format.To delete the connector configuration file, click the Clear icon (
 ). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the connector configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
). - If you need to recalculate the tag values based on the parameter values specified in the preset file, turn on the Scale obtained tag values toggle button.
By default, scaling of the received data is disabled.
- To send alerts about the incidents registered in Kaspersky MLAD to a WebSocket server, enable the Submit incidents option.
- Click the Save button.
Kaspersky MLAD will receive data and send messages about incident registration via the WebSocket protocol.
Page top
Configuring the Event Processor service
Kaspersky MLAD uses the Event Processor service to identify patterns and anomalous sequences of events and patterns. You can configure the settings of the Event Processor service.
If Kaspersky MLAD is restarted, you do not need to re-configure the Event Processor service settings. Kaspersky MLAD restores the Event Processor service state from the database or file in bit format. This restoration process may take several minutes if there is a significantly large number of processed events or registered patterns. Until the state of the Event Processor service is restored in the Event Processor section, requests will not be fulfilled, data will not be updated, and data received from the CEF Connector will not be processed. This data is temporarily stored in the system message queue and is processed after the state of the Event Processor service is restored.
The Event Processor service may require a large amount of RAM on the server where Kaspersky MLAD is installed. The amount of RAM usage depends on the rate of the event stream and the volume of events history that is processed. The specific configuration of the Event Processor service also has an effect on the amount of RAM usage.
Configuration of the Event Processor service is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky expert or certified integrator).
To configure the Event Processor service:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Event Processor.
A list of service settings appears on the right.
- In the Online mode section, do the following:
- In the Event processor configuration file field, add the file containing the configuration settings for the Event Processor service.
This configuration file is created by a Kaspersky expert or certified integrator.
To delete the configuration file for the Event Processor service, click Clear (
 ). To save the configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon (
). To save the configuration file on your computer, click the Download icon ( ).
).Changing the configuration file of the Event Processor service results in a complete loss of the service's data.
- If you need to process incidents registered by the Anomaly Detector service, turn on the Process incidents as events toggle button.
- In the Maximum number of network layers field, specify the number of layers of the semantic neural network that will be used.
The default number of network layers for event data that is based on a specific structure is ten layers. In most cases, ten layers are enough for the hierarchical presentation of data in the semantic neural network at the core of the Event Processor. To identify patterns of periodic processes that span an extended period of time, you may need to increase the value of the Maximum number of network layers parameter.
- In the Coefficient defining the permitted dispersion of the pattern duration field, specify the coefficient used to determine the permissible dispersion of intervals between elements in the same pattern.
If the actual dispersion value is less than or equal to one that is specified, the identified sequences of events will be registered as one pattern.
- In the Interval for receiving batch events (sec.) field, specify the time interval (in seconds) for which the Event Processor service forms an episode from incoming events received for processing.
If the rate of incoming events is approximately 1000 events per second, it is recommended to indicate this value as the interval for receiving new events so that you receive a number of events close to the value indicated in the Batch size in online mode (number of events) field during the specified period. If the rate of incoming events is a lot lower than this value, you should adjust the interval for receiving new events to ensure an optimal frequency of event processing.
- In the Batch size in online mode (number of events) field, specify the maximum number of events per episode to be subsequently processed by the Event Processor service.
If the rate of incoming events is approximately 1000 events per second, it is recommended to indicate a value equal to 4096 in this field.
- In the Method of saving the state of the Event Processor service drop-down list, select one of the following options for saving the Event Processor service state:
- Database table – Kaspersky MLAD saves the results from processing each episode in the database table.
- File in bit format – Kaspersky MLAD saves the state of the Event Processor service according to the frequency defined in the Component backup frequency field. The application saves the state of the service to the file specified in the File containing a backup copy of the component state field.
Saving the Event Processor service state to a file in bit format is recommended for debugging and configuring the application settings by Kaspersky employees during the deployment of Kaspersky MLAD.
By default, the Event Processor service saves the results of event stream processing in a database table.
Changing the way of saving the Event Processor service state results in a complete loss of the service's data.
- If you select to store the Event Processor service state in a file in bit format, in the Component backup frequency field, specify how often (in days, hours, and minutes) to perform a backup of the Event Processor service.
- If you select to store the Event Processor service state in a file in bit format, in the File containing a backup copy of the component state field, add the file containing a backup copy of the Event Processor service.
This file will be used if you ever need to restore the state of the Event Processor service. The state of the Event Processor service can be restored by Kaspersky experts as part of their extended technical support.
To delete the file containing a backup copy of the Event Processor service, click Clear (
 ). To save the file containing a backup copy of the service on your computer, click the Download (
). To save the file containing a backup copy of the service on your computer, click the Download ( ) icon.
) icon.
- In the Event processor configuration file field, add the file containing the configuration settings for the Event Processor service.
- In the Sleep mode section, do the following:
- In the Batch size in sleep mode (number of events) field, specify the number of events for forming an episode in sleep mode.
The Event Processor service generates episodes based on the history of events received for reprocessing during the time interval specified in the Events history interval for processing in sleep mode field.
- In the Send alerts when the monitor is activated in sleep mode field, select one of the following values:
- Send alerts when the monitor is activated by any pattern – Kaspersky MLAD sends alerts when the monitor is activated in the sleep mode if the patterns are detected in accordance with the specified monitoring criteria. The number of monitor activations is refreshed in the Event Processor section on the Monitoring tab.
- Do not send alerts when the monitor is activated – Kaspersky MLAD does not send alerts when the monitor is activated in the sleep mode.
- Sends alerts when the monitor is activated by a new pattern – Kaspersky MLAD sends alerts when the monitor is activated in the sleep mode if new patterns are detected in accordance with the specified monitoring criteria. The number of monitor activations is refreshed in the Event Processor section on the Monitoring tab.
- Send alerts when the monitor is activated by a previously registered pattern – Kaspersky MLAD sends alerts when the monitor is activated in the sleep mode if stable patterns are detected in accordance with the specified monitoring criteria. The number of monitor activations is refreshed in the Event Processor section on the Monitoring tab.
- In the Sleep mode frequency field, specify how often (in days) and at what time (according to the UTC standard) the Event Processor service goes to the sleep mode to reprocess events.
It is recommended to specify the time when the event stream is the least intensive as the start time for the sleep mode.
If the specified sleep time has not yet come on the current day, the Event Processor will go to the sleep mode on that day. If the sleep time has already been missed on the current day, the Event Processor will go to the sleep mode at the specified time after the specified number of days.
- In the Sleep mode duration (HH:MM) field, specify the time period (in hours and minutes) during which the Event Processor service processes events in the sleep mode.
- In the Events history interval for processing in sleep mode field, specify the time interval (in days, hours, and minutes) during which the analyzed events must be forwarded for reprocessing in the sleep mode to the Event Processor service.
- In the Batch size in sleep mode (number of events) field, specify the number of events for forming an episode in sleep mode.
- Click the Save button.
Configuring the statuses and causes of incidents
Kaspersky MLAD lets you specify the causes of incidents and the statuses of incidents and groups of incidents.
The status of an incident or a group of incidents is a mark about the status of incident analysis performed by an expert. After installation of Kaspersky MLAD, the following statuses of incidents and incident groups are available by default: Under review, Decision pending, Instructions issued, Problem closed, Cause unknown, Ignore and False positive.
The incident cause is a mark of the cause of the incident added by an expert based on the results of the incident analysis.
You can add causes and statuses for incidents. The created causes and statuses of incidents will become available for selection in the Incidents section. You can also change and delete statuses and causes of incidents.
Configuration of the causes and statuses of incidents is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To add statuses of incidents:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Incidents.
- In the Statuses of incidents section, click the Create button.
The Create element pane will appear on the right.
- In the Value, in Russian field, specify the name of the incident status in Russian.
- In the Value, in English field, specify the name of the incident status in English.
- In the Sort field, indicate the sequence number for which the incident status will be sorted in the Status drop-down list in the Incidents section.
The statuses of incidents will be sorted by their names if the sequence numbers of incident statuses coincide.
- To send incident registration notifications together with the added status and display its indicator in the MSE subsection of the Monitoring and History sections, select the Notify about an incident check box.
- Click the Save button.
To add causes for incidents:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Incidents.
- In the Causes of incidents section, click the Create button.
The Create element pane will appear on the right.
- In the Incident cause field, specify the name of the incident cause.
- In the Sort field, indicate the sequence number for which the incident cause will be sorted in the Incident cause drop-down list in the Incidents section.
The causes of incidents will be sorted by their names if the sequence numbers of incident causes coincide.
- Click the Save button.
To change the statuses or causes of incidents:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Incidents.
- To change the parameters of incidents, do one of the following:
- If you need to change the statuses of incidents or groups of incidents, use the Statuses of incidents settings group to select one or more incident statuses and click the Edit button.
- If you need to change the causes of incidents, use the Causes of incidents settings group to select one or more incident causes and click the Edit button.
- Make the necessary changes.
- Click the Save button.
To remove statuses or causes of incidents:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Incidents.
- To remove parameters of incidents, do one of the following:
- If you need to delete the statuses of incidents or groups of incidents, use the Statuses of incidents settings group to select one or more incident statuses and click the Delete button.
- If you need to delete the causes of incidents, use the Causes of incidents settings group to select one or more incident causes and click the Delete button.
- In the opened window, click Yes to confirm deletion.
Kaspersky MLAD will remove information about the incident statuses and causes from the corresponding tables and will remove them from the information about incidents and incident groups in the Incidents section for which these incident causes or statuses were selected.
Page top
Configuring logging of Kaspersky MLAD services
You can configure the log level for Kaspersky MLAD services to write specific information about the state of the application and display it in the logging system (Grafana). To view how Kaspersky MLAD services are mapped to the names of Docker containers and images, see the Appendix.
Configuration of Kaspersky MLAD service logging is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure the log levels of Kaspersky MLAD services:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Logging.
The list of Kaspersky MLAD services will be displayed on the right.
- If necessary, use the drop-down lists next to the name of the relevant service to change the log level of the service.
The following log levels are available in Kaspersky MLAD:
- Debug – log all information in the application.
- Info – log basic information about application operations.
- General – log important information about application operations.
- Warning – log errors that occur during operation of the application and log events that could lead to errors in application operations.
- Error – log errors that occur in application operations.
- Critical – log critical errors that occur in application operations.
The General log level is used for most services by default. The Info log level is used for the API Server service by default.
- Click the Save button.
Configuring time intervals for displaying data
Kaspersky MLAD lets you specify the time interval (scale) for displaying data on graphs in the Monitoring, History and Time slice sections. After installation of Kaspersky MLAD, the following time intervals are available by default:
- 1, 5, 10, 15, and 30 minutes
- 1, 3, 6, and 12 hours
- 1, 2, 15, and 30 days
- 3 and 6 months
- 1, 2, and 3 years
You can add time intervals for displaying data on graphs. The created time intervals will become available for selection in the Monitoring, History and Time slice sections. You can also edit and delete time intervals.
Configuration of time intervals for displaying data on graphs is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To add time intervals for displaying data:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Graphs.
- In the Time intervals settings group, click the Create button.
The Create element pane will appear on the right.
- In the Time interval (sec.) field, specify the time interval for which you want to display data on graphs.
When a time interval is entered, Kaspersky MLAD automatically breaks down the time interval into specific units of time (years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds) in the Value, in Russian and Value, in English fields.
- If necessary, change the Russian name of the time interval in the Value, in Russian field.
- If necessary, change the English name of the time interval in the Value, in English field.
- In the Sort field, indicate the sequence number for which the time interval will be sorted in the drop-down lists in the Monitoring, History and Time slice section.
- Click the Save button.
To change the time intervals for displaying data:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Graphs.
- In the Time intervals settings group, select one or more time intervals and click the Edit button.
- Make the necessary changes.
- Click the Save button.
To delete time intervals for displaying data:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters → Graphs.
- In the Time intervals settings group, select one or more time intervals and click the Delete button.
- In the opened window, click Yes to confirm deletion.
Information about the time interval will be deleted from the table.
Page top
Configuring how the Kaspersky MLAD main menu is displayed
Configuration of the display settings for the main menu of Kaspersky MLAD is performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
To configure how the main menu and the administrator menu of Kaspersky MLAD are displayed:
- In the user menu, select the Settings section.
You will switch to administrator mode.
- On the opened page, in the menu on the left, select System parameters → Menu.
A list of options appears on the right.
- In the Availability of main menu items settings group, use the toggle button to enable or disable the display of a specific section in the main menu.
- In the Availability of menu items in administrator mode settings group, use the toggle button to enable or disable the display of a specific section in the administrator menu.
- Click the Save button.
Exporting and importing a configuration file for Kaspersky MLAD components
Kaspersky MLAD lets you export and import a configuration file containing the settings for application components that are configured through the web interface. This could substantially reduce the time spent on configuring Kaspersky MLAD if you have to re-deploy the application.
To export a components configuration file from Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters.
- Click the Export button in the upper part of the opened page.
The Kaspersky MLAD components configuration file will be saved as an archive named mlad-settings.tar.gz on the local computer.
To upload a components configuration file to Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the administrator menu, select System parameters.
- Click the Import button in the upper part of the opened page.
- In the opened window, select the archive file containing the necessary configuration of Kaspersky MLAD components.
The Kaspersky MLAD components configuration file will be uploaded to the application.
Page top
Starting, stopping, and restarting services
Kaspersky MLAD lets you start, stop and restart services.
Kaspersky MLAD services can be managed only by users with administrator privileges.
To start, stop, or restart a service:
- In the main menu, select the Services section.
- On the opened page, select one of the following subsections: Machine learning, Main, Connectors or Other.
- Do one of the following for the relevant service:
- To start a service, click Start service (
 ).
). - To stop a service, click Stop service (
 ).
). - To restart a service, click Restart service (
 ).
).
The new status of the service is displayed in the Status column.
- To start a service, click Start service (
Managing tags
Tags management is available only for users with administrator privileges.
In the Settings → Tags section, you can view
and tag groups that were created in or uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. The structure of tags and tag groups is displayed as a tag tree. For each tag, the tree shows the ID, name, and description. You can create tags and tag groups, and edit tag parameters, such as permissible technical limits of tag values or boundaries for displaying tag values on a graph.Kaspersky MLAD can receive data from assets registered in external systems (for example, Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks). Kaspersky MLAD saves the tags received from external assets in the Time Series Database. When saving of all tags is enabled, the Time Series Database also saves IDs and values of unknown tags (not listed in the tag tree). You can compare the current tag structure to the tag structure in the Time Series Database and add missing tags to the current structure, if necessary.
If Kaspersky MLAD detects unknown tags received from external assets via the KICS Connector, these tags are automatically created in the Settings → Tags section in accordance with the names of tags and assets in Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
Kaspersky MLAD is compatible with Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.0 and later.
You can also delete existing tags, import tags from a JSON file, or export them to a JSON file.
Create tag
In Kaspersky MLAD, you can create new tags to describe data received from the monitored asset (source tags) or from the Stream Processor service.
To create a new tag:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the upper part of the page, click the Create button.
The Create tag pane opens on the right.
- In the Tag type drop-down list, select Tag.
- If necessary, click the Choose an icon button and select an icon for the tag in the opened window.
You can upload the tag icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you need to delete the tag icon, click the tag icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- In the Group drop-down list, select the desired tag group to which you want to assign the created tag.
Tag groups must be previously loaded or created manually.
- Specify the tag name in the Name field. If you want to receive tag values from an external system, specify the tag name in the external system.
If the use of the KICS connector is enabled, Kaspersky MLAD automatically fills in the tag name based on the tag name received from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- Enter a description for the tag in the Description field.
- Enter the tag ID in the ID field.
- In the Dimension field, specify the measurement units for the tag.
- In the X, Y, and Z fields, specify the spatial coordinates for the location of the monitored asset's sensor.
You can use an arbitrary point as the origin of the coordinate system.
You can use sensor coordinates to calculate tag values when creating a preset and displaying them on the graph in the Time slice section.
- In the Class to display field, specify the class for displaying the tag.
- In the Technical limits section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper limits for the tag values.
These settings are required for correct operation of the Limit Detector. Whenever the tag value reaches its upper or lower technical limit, the Limit Detector registers an incident.
If the Always show technical limits option is enabled, the vertical scale of the graph will be defined by limit lines drawn at the lower and upper boundaries of the tag graph, provided that the tag values are within the specified range. If the tag values go beyond the specified limits, the vertical scale will be automatically changed to display the tag values exceeding the limits.
- In the Display boundaries section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper boundaries for displaying tag values on graphs.
If tag values go beyond the defined boundaries, they will not be displayed on the tag graph. The permissible boundaries for displaying tag values take priority over the display of technical limits, even if the Always show technical limits function is enabled.
- In the Asset field, specify the name of the asset created in the external system, for which you need to receive tags.
If the use of the KICS connector is enabled, Kaspersky MLAD automatically fills in the asset name based on the asset name for which the tag is received from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- If you need to add additional horizontal threshold lines for this tag on graphs in the Monitoring and History sections, click the Add line button and use the Threshold value field to enter the value that should be displayed on the graph.
Additional horizontal threshold lines help visually evaluate the fluctuations of tag values within certain limits. You can add multiple additional horizontal threshold lines.
- Click the Create button.
The new tag will appear under Tags in the tag tree on the left. If necessary, you can change the position of tags in the tag tree. To do this, drag the required tag up or down in the tag tree by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of its ID.
) to the left of its ID.
Creating a virtual tag
You can create virtual tags in Kaspersky MLAD.
To calculate the real and predicted values of a virtual tag, and the virtual tag error, you can define expressions with simple arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division), calculation of the square root (the sqrt function) and exponentiation (using the ^ character). You can use the following variables in your expressions:
- $tag is the value of the tag based on which the value of the virtual tag is calculated.
- $tagX is the X coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location.
- $tagY is the Y coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location.
- $tagZ is the Z coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location.
For example, you can specify an expression to calculate the Celsius temperature based on the tag that receives the Fahrenheit temperature:
5/9 * ($tag - 32) |
The values of the virtual tag will be displayed on the graphs in the Monitoring and History sections in accordance with the specified expression.
To create a new tag:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the upper part of the page, click the Create button.
The Create tag pane opens on the right.
- In the Tag type drop-down list, select Virtual tag.
- If necessary, click the Choose an icon button and select an icon for the virtual tag in the opened window.
You can upload the tag icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you need to delete the tag icon, click the tag icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- In the Group drop-down list, select the tag group to which you want to assign the created virtual tag.
Tag groups must be previously loaded or created manually.
- in the Name field, specify the virtual tag name.
- In the Description field, specify the virtual tag description.
- In the ID field, specify the virtual tag ID.
- In the Dimension field, specify the measurement units for the virtual tag.
- In the X, Y, and Z fields, specify the spatial coordinates for the location of the monitored asset's sensor.
You can use an arbitrary point as the origin of the coordinate system.
You can use sensor coordinate values to calculate virtual tag values and display them on graphs in the Monitoring and History sections.
- In the Class to display field, specify the class for displaying the virtual tag.
- In the Technical limits section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper limits for the virtual tag values.
These settings are required for correct operation of the Limit Detector. Whenever the tag value reaches its upper or lower technical limit, the Limit Detector registers an incident.
If the Always show technical limits option is enabled, the vertical scale of the graph will be defined by limit lines drawn at the lower and upper boundaries of the tag graph, provided that the tag values are within the specified range. If the tag values go beyond the specified limits, the vertical scale will be automatically changed to display the tag values exceeding the limits.
- In the Display boundaries section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper limits for displaying the virtual tag values on the graphs.
If tag values go beyond the defined boundaries, they will not be displayed on the tag graph. The permissible boundaries for displaying tag values take priority over the display of technical limits, even if the Always show technical limits function is enabled.
- In the Asset field, specify the name of the asset created in the external system, for which you need to calculate the virtual tag values.
- If you need to add additional horizontal threshold lines for this tag on graphs in the Monitoring and History sections, click the Add line button and use the Threshold value field to enter the value that should be displayed on the graph.
Additional horizontal threshold lines help visually evaluate the fluctuations of tag values within certain limits. You can add multiple additional horizontal threshold lines.
- To display the values of a virtual tag on the graphs in the Monitoring and History sections, perform the following actions in the Tag calculation expression group of settings:
- In the Calculation tag ID drop-down list, select the ID of the tag based on which you want to calculate the value of the virtual tag.
- In the Expressions for calculating actual and predicted tag values drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- If you want to use the same expressions to calculate the actual and predicted tag values, select Identical expressions.
- If you want to use different expressions to calculate the actual and predicted tag values, select Different expressions.
- In the Expression for calculating tag values field, specify an expression for calculating tag values.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using the same expressions.
- In the Expression for calculating actual tag values field, specify an expression for calculating actual tag values.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using different expressions.
- If necessary, enter a tag value calculation expression for predicted values in the Expression for calculating predicted tag values field.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using different expressions.
- If necessary, enter an expression for error calculation in the Error calculation expression field.
- Click the Create button.
The new tag will appear under Tags in the tag tree on the left. If necessary, you can change the position of tags in the tag tree. To do this, drag the required tag up or down in the tag tree by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of its ID.
) to the left of its ID.
Creating a group of tags
In Kaspersky MLAD, you can create tag groups and categorize tags as you see fit. For example, you can create tag groups for the assets of the monitored asset from which telemetry data is received.
Tag groups are used to represent the tag structure as a tag tree.
To create a new tag group:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the upper part of the page, click the Create button.
The Create tag pane opens on the right.
- In the Tag type drop-down list, select the Group value.
- If necessary, click the Choose an icon button and select an icon for the tag in the opened window.
You can upload the tag group icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you need to delete the tag group icon, click the icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- In the drop-down list, select the tag group that will be used as the basis for creating a new tag group.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the tag group.
- In the Description field, provide a description for the tag group.
- Click the Create button.
The new tag group will appear under Tags in the tag tree on the left. If necessary, you can change the position of the tag group in the tag tree. To do this, drag the required group of tags up or down in the tag tree holding by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of the tag group name.
) to the left of the tag group name.
Editing a tag
You can edit previously created tags.
To edit a tag:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the tag tree on the left, select the tag you want to edit and click Edit.
You can also switch to the tag edit mode by double-clicking the tag.
The Edit tag pane opens on the right.
- If you need to change the icon of the tag, click the Choose an icon button and select an icon for the tag in the opened window.
You can upload the tag icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you need to delete the tag icon, click the tag icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- If necessary, enter a new name for the tag in the Name field. If you want to receive tag values from an external system, specify the tag name in the external system.
If the use of the KICS connector is enabled, Kaspersky MLAD automatically fills in the tag name based on the tag name received from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- If necessary, enter a new description for the tag in the Description field.
- If necessary, enter new measurement units for the tag in the Dimension field.
- In the X, Y, and Z fields, specify the spatial coordinates for the location of the monitored asset's sensor.
You can use an arbitrary point as the origin of the coordinate system.
You can use sensor coordinate values to calculate virtual tag values and display them on graphs in the Monitoring and History sections. You can also use sensor coordinates to calculate tag values when creating a preset and displaying them on the graph in the Time slice section.
- In the Class to display field, specify the class for displaying the tag.
- In the Technical limits section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper limit boundaries for tag values.
These settings are required for correct operation of the Limit Detector. Whenever the tag value reaches its upper or lower technical limit, the Limit Detector registers an incident.
If the Always show technical limits option is enabled, the vertical scale of the graph will be defined by limit lines drawn at the lower and upper boundaries of the tag graph, provided that the tag values are within the specified range. If the tag values go beyond the specified limits, the vertical scale will be automatically changed to display the tag values exceeding the limits.
- In the Display boundaries section, in the Lower and Upper fields, specify the lower and upper boundaries for displaying tag values on graphs.
If tag values go beyond the defined boundaries, they will not be displayed on the tag graph. The permissible boundaries for displaying tag values take priority over the display of technical limits, even if the Always show technical limits function is enabled.
- In the Asset field, specify the name of the asset created in the external system, for which you need to receive tags.
If the use of the KICS connector is enabled, Kaspersky MLAD automatically fills in the asset name based on the asset name for which the tag is received from Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks.
- If you need to add additional horizontal threshold lines for this tag on graphs in the Monitoring and History sections, click the Add line button and use the Threshold value field to enter the value that should be displayed on the graph.
Additional horizontal threshold lines help visually evaluate the fluctuations of tag values within certain limits. You can add multiple additional horizontal threshold lines.
- If you want to modify the expression used to calculate virtual tag values, do the following in the Tag calculation expression group of settings:
- In the Expressions for calculating actual and predicted tag values drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- If you want to use the same expressions to calculate the actual and predicted tag values, select Identical expressions.
- If you want to use different expressions to calculate the actual and predicted tag values, select Different expressions.
- In the Expression for calculating tag values field, specify an expression for calculating tag values.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using the same expressions.
- In the Expression for calculating actual tag values field, specify an expression for calculating actual tag values.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using different expressions.
- In the Expression for calculating predicted tag values field, specify an expression for calculating predicted tag values.
This field is displayed if you chose to calculate actual and predicted tag values using different expressions.
- In the Error calculation expression field, specify an expression for error calculation.
- In the Expressions for calculating actual and predicted tag values drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- Click the Save button.
The modified tag will appear under Tags in the tag tree on the left. If necessary, you can change the position of tags in the tag tree. To do this, drag the required tag up or down in the tag tree by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of its ID.
) to the left of its ID.
Editing a group of tags
You can edit previously created tag groups.
To edit a tag group:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the tag tree on the left, select the tag group you want to edit and click Edit.
You can also switch to the edit tag group mode by double-clicking the tag group.
The Edit tag group pane opens on the right.
- If you need to change the icon of the group, click the Choose an icon button and select an icon for the tag group in the opened window.
You can upload the tag group icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you need to delete the tag group icon, click the icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- If necessary, enter a new name for the tag group in the Name field.
- If necessary, provide a new description for the tag group in the Description field.
- Click the Save button.
The modified tag group will appear under Tags in the tag tree on the left. If necessary, you can change the position of the tag group in the tag tree. To do this, drag the required group of tags up or down in the tag tree by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of the tag group name.
) to the left of the tag group name.
Removing a tag or group of tags
You can move previously created tags and tag groups from the tag tree to the tag trash bin and permanently delete them from the trash bin. To remove a tag or tag group:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the tag tree or in the trash bin, select the check boxes next to the name of the tag or tag group.
To remove one or several tags from a group, expand the tag group by clicking the right arrow (
 ) and select the required tags. You can also select all tags and groups at the same time by selecting the check box in the table header.
) and select the required tags. You can also select all tags and groups at the same time by selecting the check box in the table header. - Click the Delete button in the upper part of the page.
- In the opened Confirm deletion window, click Yes to confirm deletion.
If the selected tags and tag groups were in the tag tree during deletion, these tags will be moved to the trash bin. To restore tags, select tags and tag groups in the trash bin and drag these tags and groups from the trash bin to the desired location in the tag tree by the three horizontal lines (![]() ) to the left of one of the selected items.
) to the left of one of the selected items.
If the selected tags and tag groups were in the trash bin during deletion, they will be permanently deleted from Kaspersky MLAD.
Page top
Checking the current structure of tags
Kaspersky MLAD saves the tags received from external assets in the Time Series Database. When unknown tags are received via the KICS Connector, the application also automatically creates these tags in the Settings → Tags section.
Kaspersky MLAD allows you to compare the current tag structure displayed in the Settings → Tags section and used for a monitored asset to the one saved for this monitored asset in the Time Series Database. Kaspersky MLAD detects tags that were received from external assets, but are missing in the current tag structure and are not used for the monitored asset. If necessary, you can add these tags to the current tag structure.
To compare the current tag structure with the structure in the Time Series Database:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- In the upper part of the page, click the Compare tags button.
The current tag structure used for the monitored asset is compared with the tag structure stored in the Time Series Database. The comparison result is displayed in the upper part of the page.
If missing tags are detected, Kaspersky MLAD displays a list of these tags with the names in the Tag <tag ID> format.
- To add missing tags, do the following:
- For each detected tag, in the Group field select the group to which you want to assign the tag.
- Click Yes.
Kaspersky MLAD adds the tags to the current tag structure. Only the IDs, names in the Tag <tag ID> format, and the groups to which the tags are assigned are specified for these tags. If necessary, you can change the added tags.
Page top
Uploading a tag configuration to the system
A tag configuration is created while deploying Kaspersky MLAD and building an ML model. A tag configuration is supplied in a JSON file.
To upload a tag configuration to Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- Click the Import button.
- In the opened window, select the JSON file containing the necessary tag configuration.
A tag configuration can be uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. Tags grouped by industrial units are displayed as a tree in the left part of the Tags section.
Saving a tag configuration to a file
You can save the structure of tags and presets to a JSON file for subsequent use.
To save a tag configuration to a JSON file:
- In the administrator menu, select Tags.
- Click the Export button.
The tag configuration will be saved to a file named mlad.json (see the example in the Appendix).
Managing ML models and templates
The Models section provides data on ML models and on the templates created based on the ML models added to Kaspersky MLAD.
ML models and templates can be managed only by the users with administrator privileges.
Models tab
The Models tab shows a table of ML models. You can upload ML models to Kaspersky MLAD or add ML models based on ML model templates.
The following information is displayed for each ML model:
- ID – digital identifier of the ML model.
- Model name – name of the added ML model.
- Creation method – indicator of whether the ML model was imported, created from a template, or created as a result of training on a previously added ML model. If the template used to create the ML model is deleted, the Creation method column shows the Template deleted value. If the ML model used to train the current ML model is deleted, the Creation method column shows the Cloned and trained; original model deleted value.
- State – toggle button allowing you to enable or disable the use of the ML model for the monitored asset. If an ML model is not activated, the State column shows an inactive Unavailable toggle button.
- Action – button for activating the ML model or starting the ML model training process after activation.
Next to each model, there is a vertical menu  , allowing you to create a template based on the existing ML model, view detailed information about the model, or delete the ML model.
, allowing you to create a template based on the existing ML model, view detailed information about the model, or delete the ML model.
Templates tab
The Templates tab provides a table of templates that were created based on ML models added to Kaspersky MLAD. The following information is available for each template:
- ID – digital identifier of the ML model template.
- Template name – name of the ML model template.
- Creation method – name of the ML model used to create the template. If the ML model used to create the template is deleted, the Creation method column shows the Original model was deleted value.
- Action – button for creating an ML model based on a template.
You can use created templates to add new ML models to Kaspersky MLAD. After adding an ML model, you can enable its use for the monitored asset. You can also delete ML model templates.
Editing the parameters of an ML model and its elements
You can edit certain parameters of an ML model and its elements.
The parameters of an ML model and ML model element can be changed only by a Kaspersky employee or certified integrator. It is not recommended to change these parameters on your own.
To change the parameters of an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the vertical menu
 next to the ML model whose parameters you want to change, and select Model details.
next to the ML model whose parameters you want to change, and select Model details.The <ML model name> pane opens on the right showing the Model parameters tab.
- Click the Edit button.
- On the Model parameters tab, edit the relevant parameters of the ML model.
- On the Model elements tab, edit the parameters of the relevant ML model element. If you need to change the relative weights for output tags of an ML model element, do the following:
- In the list of parameters of the ML model element, click the out_tags and mse_weights parameter value.
The Output tags and their relative weights pane is displayed on the right.
- Click the Edit button.
- Change the values of relative weights in the Weight value column for the relevant output tags of the ML model element and click Save.
- Click the Close button.
- In the list of parameters of the ML model element, click the out_tags and mse_weights parameter value.
- Click the Save button.
Uploading an ML model
Kaspersky MLAD lets you upload new ML models. ML model files for uploading are provided by Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator.
Kaspersky MLAD may slow down its operation when uploading an ML model whose size exceeds 1 GB.
To upload an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the Import button.
- In the opened window, select the ML model file.
An ML model file is provided as a TAR archive with a maximum size of 1.5 GB.
The ML model will be uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. The name and state of the ML model are displayed in the table. Activate the ML model after uploading. If you upload an ML model that was previously activated and then deleted, you do not need to reactivate the ML model.
Page top
Activating an ML model
After adding a new ML model to Kaspersky MLAD, you have to activate the model before you can use it.
If the ML model activation code is lost, send a request to Kaspersky to receive a new code.
To activate an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- In the Action column, click Activate.
The Model activation pane appears on the right.
- In the Model activation code field, enter the code received from Kaspersky personnel, and click the Activate button in the lower part of the window.
ML model is activated. You need to enable an ML model to start the analysis of telemetry data received from the monitored asset.
Page top
Changing the status of an ML model
You can enable or disable the use of an ML model for analyzing telemetry data from the monitored asset. After activation, an ML model is disabled by default.
By default, Kaspersky MLAD supports the parallel operation of five ML models. If required, a user with administrator privileges can change the maximum number of simultaneously running models when configuring the Anomaly Detector service.
To change the status of an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Use the toggle button in the State column to enable or disable the use of the relevant ML model.
You can enable or disable the use of an ML model that was previously activated. If an ML model is not activated, the State column shows an inactive Unavailable toggle button.
Training an ML model
Kaspersky MLAD lets you clone an existing ML model built with a Forecaster detector in order to retrain it or perform additional training based on new telemetry data obtained by Kaspersky MLAD for a specific monitored asset.
Training an ML model is a resource-consuming process. Depending on the model complexity and the amount of data, the main Kaspersky MLAD services (data reception, anomaly detection, web interface operation) may slow down. To clarify the rules for training the ML model, it is recommended to consult with Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator.
To train an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- In the Action column, click the Train button located next to the ML model that you want to use as the base for training the new ML model.
The Model cloning and training pane opens on the right.
- If necessary, enter a name for the new ML model in the New model name field.
By default, a new ML model is assigned a name in the following format: <original model name>_Cloned&Retrained_<date and time>.
- In the Start of the data export period field, click the Calendar icon (
 ) and select the start date and time of the data export period for training the model.
) and select the start date and time of the data export period for training the model. - In the End of the data export period field, click the Calendar icon (
 ) and select the end date and time of the data export period for training the model.
) and select the end date and time of the data export period for training the model. - Expand the Additional settings list by clicking the right arrow (
 ), and, if necessary, specify values for the following settings:
), and, if necessary, specify values for the following settings:- In the Number of training epochs field, specify the number of training epochs.
Kaspersky MLAD can finish training the ML model before the specified number of epochs is reached, if it considers that the ML model is trained. The default number is 10000 training epochs.
- To limit the time for training the model, enable the Limit the model training time option and fill in the following fields:
- In the Days field, specify the number of days to train the ML model.
- In the Hours field, specify the number of hours to train the ML model.
- Perform one of the following actions:
- If you want to load the relative weights of the output tags of a previously trained ML model, enable the Load the pre-training state of the original model option.
- If you want to retrain the ML model, disable the Load the pre-training state of the original model option.
This option is disabled by default.
- In the Error resolution window field, specify an MSE smoothing interval (alpha parameter).
By default, this interval is equal to the forecast window size forecast_window_size. If MSE smoothing is not required, enter 0 in the Error resolution window field.
Only Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator can change the error smoothing interval.
- In the Number of training epochs field, specify the number of training epochs.
- Click the Clone and train button.
After training, the new ML model will appear in the models table.
Page top
Removing an ML model
You can remove one or more ML models from Kaspersky MLAD.
After an ML model is removed, the results of the tag values predicted using this model and the calculated MSE are unavailable.
To remove an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- In the model table, select one or more ML models and click Delete.
You can also remove a specific ML model by selecting Delete in the vertical menu
 for the relevant model.
for the relevant model. - Confirm deletion of the ML model.
The selected ML model will be removed from Kaspersky MLAD.
Creating a template based on an ML model
You can create an ML model template based on a previously added ML model. The created templates retain the algorithm structure, set of elements, tag composition, and the training state of the source ML model.
To create a template based on an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the vertical menu
 next to the ML model that you want to use as the basis for creating the template.
next to the ML model that you want to use as the basis for creating the template. - Select Create template.
The Creating a template pane opens on the right.
- Enter the template name in the Template name field.
You can enter up to 100 characters.
- To change the names of the template tags, in the Template tag name column specify the new names for the relevant tags.
If the tags used in the ML model you are using to create the template were loaded or created under Settings → Tags, their names are automatically assigned to the tags in the template. If a tag used in the ML model was not detected in Kaspersky MLAD, this tag will be assigned the default name in the format Test <Model tag ID>.
You can specify a template tag name different from the tag names in the Settings → Tags section. Template tags and tags in the Settings → Tags section are mapped based on the IDs of the ML model tags, which you can specify when creating an ML model from a template.
- Click the Create button.
The created ML model template is displayed on the Templates tab.
Page top
Creating an ML model based on a template
You can create a new ML model based on available templates. When creating an ML model, you can specify the IDs of tags that should be used in the new ML model.
To create an ML model based on a template:
- In the main menu, select the Models section and click Templates.
- In the Action column, click the Create model button in the row of the template you want to use as the basis for creating the ML model.
The Creating a model pane opens on the right.
- Enter a name for the new ML model in the Model name field.
The ML model name must not be longer than 100 characters.
- In the Model tag ID column, select the tag IDs for each tag of the created ML model.
Template tags and tags in the Settings → Tags section are mapped based on the IDs of the ML model tags.
- Click the Create button.
The newly created ML model is displayed on the Models tab. The state of the created ML model will match the training state of the source ML model when the template was created.
Page top
Removing an ML model template
You can remove an ML model template from Kaspersky MLAD.
To remove an ML model template:
- In the main menu, select the Models section and click Templates.
- In the templates table, select one or more ML model templates and click the Delete button.
You can also remove a specific ML model template by selecting Delete from the vertical menu
 in the row of the relevant template.
in the row of the relevant template. - Confirm deletion of the ML model template.
The selected ML model template will be removed from Kaspersky MLAD. Deleting a template does not remove ML models based on this template.
Configuring settings in the Event Processor section
Before events are processed by the Event Processor service, attention settings and display of event parameters must be configured.
Only the users with administrator privileges can manage attention settings and display of event parameters.
A large number of attention directions can slow down the operation of Kaspersky MLAD main services (data reception, anomaly detection, web interface). To clarify the number of attention directions, it is recommended to consult with Kaspersky experts or a certified integrator.
To configure attention settings and display of event parameters:
- In the main menu, select the Event Processor section.
- On the opened page, click the Settings button.
The Event Processor settings pane will appear on the right.
- In the Configure attention section, do one of the following for each event parameter:
- If you need to register patterns for all values of an event parameter, use the drop-down list to select All parameter values.
- To register patterns for a specific event parameter value, select the event parameter value in the drop-down list. As you start typing a value, all matching parameter values are displayed in the list.
If the parameter value is not listed, enter the required value and select Create Value: <event parameter value>.
- If you need to register patterns based on an event parameter value template, turn on the Regular expression toggle button for the relevant event parameter, use the drop-down list to enter the value template with a regular expression, and select Regular expression: <value template>.
You can use special characters of regular expressions to search for patterns based on regular expressions.
Each attention direction is defined by the parameter value that must be present in all events of this direction. When configuring attention directions, you can indicate specific values or templates of values of one or more parameters or define attention directions for all possible values of one or more parameters.
- To configure the display of filters for the event parameters, in the Filters section on the Event history and Patterns history tabs, in the Configure display of event parameter filters section, select the check boxes next to the names of the desired event parameters.
By default, the Configure display of event parameter filters section displays the event parameters from the Anomaly Detector service. To display custom event parameters, load the Event Processor service configuration file. All available event parameters are selected by default.
If necessary, in the Filters section you can change the display order for the event parameters. For this purpose, drag the required event parameter up or down in the Configure display of event parameter filters section.
- To save your changes, click the Apply button.
Managing user accounts
This section contains information about managing Kaspersky MLAD user accounts.
Kaspersky MLAD user accounts can be managed only by users that have administrator privileges.
To ensure a safe user experience with Kaspersky MLAD, install a trusted certificate for connecting to the web interface, create an account for each user, configure and verify sending of incident messages to user emails.
All created user accounts are displayed under Settings → Users. The Users section contains a table that provides information about users.
If necessary, you can also add and edit user accounts. Kaspersky MLAD does not allow you to delete user accounts. To prevent a specific account from accessing Kaspersky MLAD web interface, it is recommended to block this account. You can unblock this user account later if necessary. If an account was locked when the number of unsuccessful login attempts for that user was reached, you can unblock this account before the blocking period expires. You can specify the number of unsuccessful authorization attempts and the account blocking period when configuring the main settings of Kaspersky MLAD.
If necessary, you can also revoke keys for a user account.

Users section
Creating a user account
Kaspersky MLAD user accounts can be managed only by users that have administrator privileges.
To create a user account:
- In the user menu, select the Settings section.
The Users section opens.
- Click the Add user button.
- In the opened Add user window, fill in the following fields:
- Last name refers to the last name of the user.
- First name refers to the first name of the user.
- Middle name refers to the middle name of the user (optional field).
- Email address refers to the user's email address.
- Password refers to the password for the user account.
The password must consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters, and numbers. The minimum password length is eight characters.
- Confirm password means you must type the password again to confirm the password for the user account.
- Click the Add button.
Information about the new user will be displayed in the table. If necessary, you can edit, block or unblock user accounts.
The Administrator or Operator role cannot be assigned to a user while the user account is being created. You can assign the Administrator or Operator role to a user only when editing the user account.
Page top
Editing a user account
Kaspersky MLAD user accounts can be managed only by users that have administrator privileges.
To edit a user account:
- In the user menu, select the Settings section.
The Users section opens.
- Click the edit button
 next to the user account that you want to edit.
next to the user account that you want to edit.The Edit user window opens.
- Make the necessary changes.
- If necessary, assign the Administrator or Operator role to the user account by selecting the corresponding check box.
- If you need to block or unblock a user account, turn on or turn off the Activity toggle button.
Kaspersky MLAD does not allow you to delete user accounts. If you want to prevent a specific user account from accessing Kaspersky MLAD, it is recommended to block this user account.
- Click the Save button.
The updated information about the user will be displayed in the table.
Page top
Revoking keys for a user account
After a user connects to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface, an individualized key is created so that the user authorization in the application can be saved between connection sessions to the application web interface, including when the browser is restarted. If a user is authorized on multiple devices, a key is created for each user session. If necessary, you can revoke keys for a user account at any time. For the user whose keys are revoked, their work session in the application will be closed simultaneously on all devices on which they were authorized. Revoking keys may be useful if you need to immediately terminate application connection sessions for a specific user.
To revoke a key or keys for a user account:
- In the user menu, select the Settings section.
The Users section opens.
- Click the key revocation button
 next to the user account whose keys you want to revoke.
next to the user account whose keys you want to revoke. - In the confirmation window, click Yes.
The user account keys will be revoked, and the user session will be terminated.
Page top
Blocking and unblocking user accounts
You can block or unblock a user account. If an account is blocked, the user cannot log in to Kaspersky MLAD.
If the user was logged in when the account was blocked, the application session is active until one of the following conditions is met:
- The user logged out of the account.
- The application automatically terminated the connection session when the keys for the user account expired.
- An administrator has revoked keys for the user account.
To block or unblock a user account:
- In the user menu, select the Settings section.
The Users section opens.
- Do one of the following for the relevant user:
- To block a user account, turn off the Activity toggle button in the relevant row of the table.
- To unblock a user account, turn on the Activity toggle button in the relevant row of the table.
Managing incident notifications
This section describes how to manage notifications for incident registration. Notifications are emailed to the users for whom these notifications have been configured.
Incident notifications can be managed only by users with administrator privileges.
The Mail Notifier service must be configured and started in advance.
All generated incident notifications are displayed under Settings → Notifications. The Notifications section contains a table that provides information about notifications.
If necessary, you can change the number of notifications displayed on one page.
You can create, edit, and delete notifications regarding specific incidents for Kaspersky MLAD users.
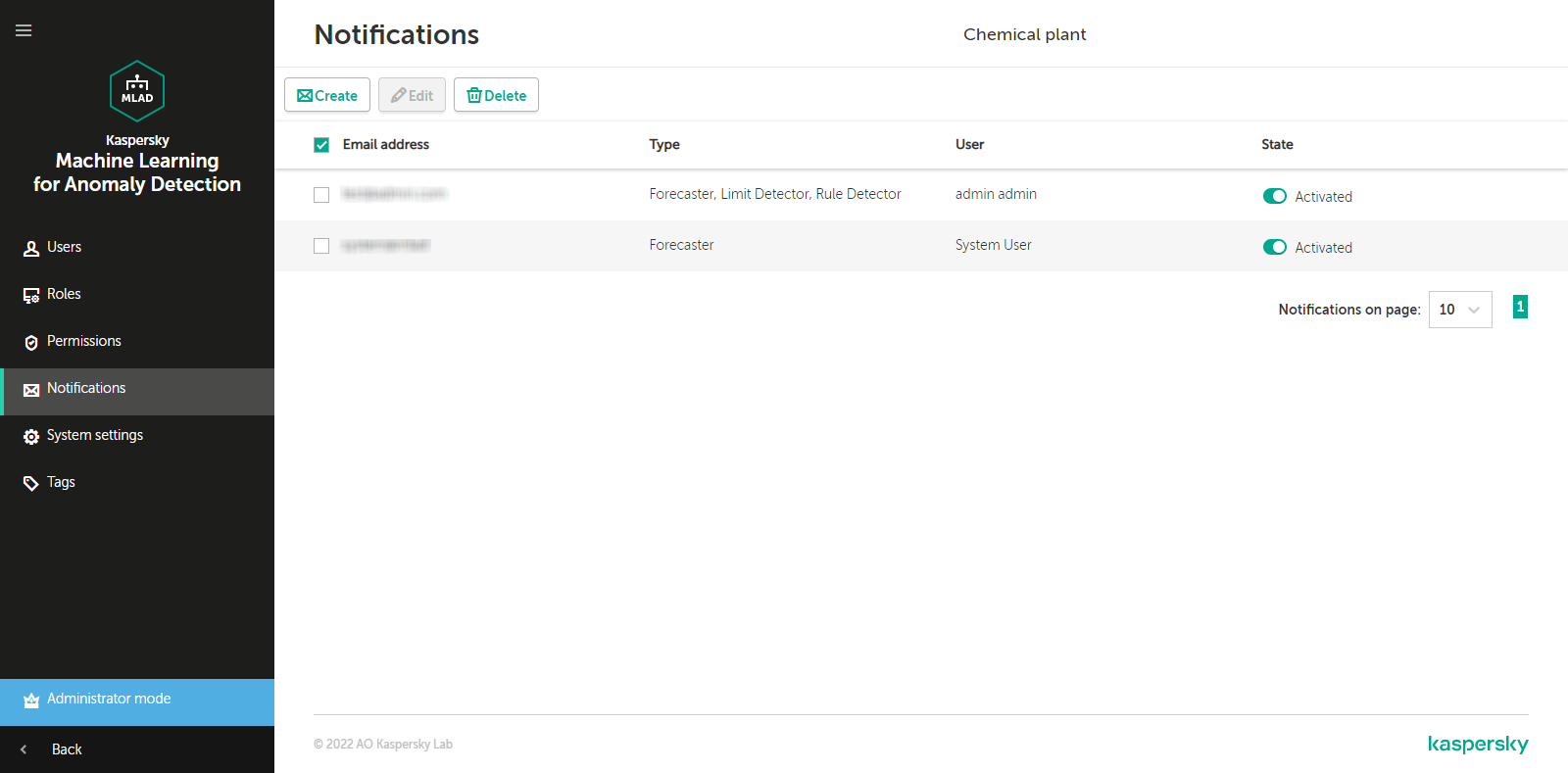
Notifications section
Creating an incident notification
Incident notifications can be managed only by users with administrator privileges.
To create an incident notification for a user:
- In the user menu, select Settings → Notifications.
You will switch to administrator mode.
- On the opened page, click the Create button.
The Create notification window opens.
- In the User drop-down list, select the user for whom you want to create a notification.
The User list displays the last names and first names of users specified when user accounts were created.
- In the Email address field, specify the email address to which incident notifications are sent.
By default, Kaspersky MLAD automatically fills in the Email address field with the address specified for the selected user when the user account was created.
- Specify the types of incidents for which you want to receive notifications:
- If you want to configure a notification about predicted tag values, select the Forecaster check box.
- If you want to configure a notification about a tag value approaching the set limit, select the Limit Detector check box.
- If you want to configure a notification about an indicator tag value reaching the threshold set for a diagnostic rule, select the Rule Detector check box.
- If you want to configure a notification about the termination or interruption of the input data stream for a specific tag, or about the detection of observations that arrived too soon or too late, select the Stream Processor check box.
- In the Delivery language field, select the language of the delivered incident notifications.
By default, the current localization language of the Kaspersky MLAD web interface is used for incident notifications. It is available in English and Russian.
- To enable sending of notifications, switch the State toggle button to the Activated position.
- Click the Create button.
Information about the new notification will be displayed in the table. If necessary, you can edit or delete notifications.
Page top
Editing an incident notification
Incident notifications can be managed only by users with administrator privileges.
To edit an incident notification:
- In the user menu, select Settings → Notifications.
You will switch to administrator mode.
- Select the check box next to the notification that you want to change and click the Edit button.
The Edit button is available if only one notification is selected.
- Make the necessary changes.
- If necessary, enable or disable sending incident notifications using the State toggle button.
- Click the Edit button to save the changes.
The updated information about the notification will be displayed in the table. If necessary, you can delete notifications.
Page top
Enabling and disabling sending notifications about incidents
Kaspersky MLAD allows you to temporarily disable sending of notifications instead of deleting their configuration. Information about notifications is saved in the Notifications section. You can enable forwarding of notifications at any time.
To enable or disable sending of incident notifications:
- In the user menu, select Settings → Notifications.
You will switch to administrator mode.
- Use the toggle button in the State column to enable or disable sending of the desired incident notification.
Deleting an incident notification
Incident notifications can be managed only by users with administrator privileges.
To delete an incident notification:
- In the user menu, select Settings → Notifications.
You will switch to administrator mode.
- Select the check box next to the notification that you want to delete and click the Delete button.
The Delete button is available if at least one notification is selected. You can select multiple notifications at the same time.
- In the opened window, click Yes to confirm deletion.
Information about the notification will be deleted from the table.
Kaspersky MLAD lets you temporarily disable sending of notifications instead of deleting them.
Removing the application
Removal of Kaspersky MLAD must be performed by an administrator (Kaspersky employee or certified integrator).
When Kaspersky MLAD is removed, all Kaspersky MLAD data that was received, uploaded, and processed since the application was installed will be lost. You are advised to verify that you have a full backup copy of all Kaspersky MLAD data. When you update the application, Kaspersky MLAD automatically creates a backup copy of the previous application version.
To remove Kaspersky MLAD:
- Go to the folder where Kaspersky MLAD is installed (mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number> by default).
cd mlad-release-3.0.0-<build number> - Run the setup.sh installation script with the -u switch:
sudo ./setup.sh -u - Confirm removal of Kaspersky MLAD components.
Kaspersky MLAD will be removed.
Page top
Connecting to Kaspersky MLAD and closing the session
Use a supported browser to connect to Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
When a user connects, the application generates a key that is valid for seven days. During this time, the application does not prompt for user account credentials, provided that the connection is used by the same computer, browser, and user account. When the key expires, the application automatically closes the connection session for the user.
To terminate a connection session before the key expires, an authorized user can log out of the account manually. If necessary, a user with administrator permissions can also revoke the account keys from the user. When the user's keys are revoked, their work sessions in the application are terminated simultaneously on all devices on which they are authorized.
The web address, user name (login), and password for signing in to the application must be requested from the Kaspersky MLAD administrator.
Connecting to the web interface
To connect to Kaspersky MLAD using a browser:
- Open a supported browser on your computer.
- In the browser address bar, enter the Kaspersky MLAD server web address received from Kaspersky MLAD administrator.
- On the account credential entry page that opens, enter your login and password.
When connecting to Kaspersky MLAD web interface for the first time, use the default login and password.
- Click the Sign in button or press ENTER.
The Dashboard opens in the browser window.
If you close the browser window without terminating the connection session, the session remains active. An application connection session that is not properly closed remains active for seven days. During this time, the application continues to grant access to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface page without prompting for user account credentials, provided that the connection is used by the same computer, browser, and operating system user account.
In case of unsuccessful authorization, if the number of unsuccessful authorization attempts is reached, Kaspersky MLAD blocks your account for the specified period. The number of unsuccessful authorization attempts and the account blocking period can be specified by a user with administrator rights when the main Kaspersky MLAD settings are configured.
Page for entering the account credentials for Kaspersky MLAD
Page top
Closing a Kaspersky MLAD connection session
When you are done working with Kaspersky MLAD in a browser, you must close the connection session.
To close the connection session:
In the browser window on the Kaspersky MLAD web interface page, open the user menu and select Sign out.
After the application connection session is closed, the browser window shows the page for entering account credentials.
Page top
Kaspersky MLAD web interface
Kaspersky MLAD is managed through a web interface. This section provides a description of the main elements of the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
The main window of the application web interface contains the following items:
- Menu in the left part of the application web interface window
- Workspace in the central part of the application web interface window
The menu consists of a main menu and a user menu, which can be opened by clicking  in the lower-left corner of the page. If necessary, you can also collapse or expand the main menu by clicking
in the lower-left corner of the page. If necessary, you can also collapse or expand the main menu by clicking  in the upper-left corner of the page.
in the upper-left corner of the page.
Users with administrator privileges can access a menu that allows to manage user accounts, configure incident notifications, manage tags, and proceed to the logging system page to view logs.
Main menu
The main menu of Kaspersky MLAD includes the following sections:
|
Opens the section containing information about the latest incidents, services and their statuses. |
|
Opens the section that displays data received by the system in real time. You can also configure the settings for displaying incoming data on a graph. |
|
Opens the section that contains a complete history of data received by the system and the results of its analysis by ML models. You can also configure the settings for displaying historical data on the graph. |
|
Opens the section containing information about the values of process parameters received from sensors at the same point in time. You can also configure the settings for displaying the data on the graph. |
|
Opens the section where you can view information about events received from external systems and patterns detected for them, as well as manage monitors to track specific events, patterns, or event parameter values. |
|
Opens the section that contains the log of detected incidents. As part of the incident analysis, you can also add a status, reason, expert opinion, and comments to an incident or an incident group. |
|
Opens the section enabling you to view information about ML models and ML model templates used in the system, as well as to manage them. |
|
Opens the section enabling you to view information about available presets, edit the preset settings, and create presets. |
|
Services Opens the section enabling you to view information about services and their statuses, as well as to start, stop, and restart services. |
|
|
User menu
The Kaspersky MLAD user menu includes the following elements:
English / Russian Lets you select the localization language for the Kaspersky MLAD web interface. It is available in English and Russian. |
Sign out Signing out of the current user account. |
Settings Opens the administrator menu where you can manage user account credentials, view user roles and permissions, configure incident notifications, and manage tags. The administrator menu is available only for users with administrator privileges. |
Logging Takes you to the logging system (Grafana) in a new browser tab. This section is available only to users with administrator privileges. |
Help Opens the Kaspersky MLAD Help Guide in a new browser tab. |
About Opens the page containing brief information about the application. |
Administrator menu
The Kaspersky MLAD administrator menu is available only to users with administrator permissions and includes the following sections:
|
Opens the section in which you can manage user accounts. |
|
Opens the section containing information about available user roles. |
|
Opens the section containing information about the permissions of users. |
|
Opens the section where you can manage notifications that the application sends to the users when incidents are registered. |
|
Opens the section in which you can manage the settings of Kaspersky MLAD components. |
|
Opens the section in which you can manage tags. |
|
Back Exits administrator mode and switches to the Dashboard section. |
|
|
Licensing the application
This section provides information about general concepts related to licensing of Kaspersky MLAD.
About the End User License Agreement
The End User License Agreement (EULA) is a binding agreement between you and AO Kaspersky Lab that stipulates the terms on which you may use the application.
Please carefully read the terms of the End User License Agreement before using the application.
You can review the terms of the End User License Agreement in the following ways:
- During installation of Kaspersky MLAD.
- By reading the license_en.txt file. This file is included in the application distribution kit.
You accept the terms of the End User License Agreement when you confirm your consent to the End User License Agreement during installation of the application. If you do not accept the terms of the End User License Agreement, you must stop the installation of the application and must not use the application.
About the license
A license is a time-limited right to use the application as granted under the End User License Agreement.
A license entitles you to the following types of services:
- Use of the application in accordance with the terms of the End User License Agreement
- Technical Support
Technical support services are provided if you have an active Technical Support Agreement. The scope of provided technical support services is determined by the current Technical Support Agreement.
Page top
Processing and storing data in Kaspersky MLAD
This section contains information about data provision and folders for storing data.
About data provision
By accepting the terms of the End User License Agreement, you consent to the automatic processing of personal data for the purposes of supporting the operation of the application. For information about how personal data is obtained, processed and stored, please read the text of the End User License Agreement.
The application does not send users' personal data to Kaspersky. Users' personal data is processed on the computers on which the application is installed.
The application processes and saves the following data related to users' personal data:
- Names of user accounts
- User names for connecting through the web interface
- Email addresses of incident notification recipients
- IP addresses or names of computers that were used to connect to the application web interface
The listed data is processed for the purpose of analyzing process violations and for detecting network traffic anomalies that may be signs of attacks.
The last names, first names, middle names and email addresses of application users are saved in plaintext. The confidentiality of this data must be ensured by a qualified application administrator employed by the Customer.
If transmission of events and incidents to recipient systems is configured in the application, the application sends registered events and incidents to recipient systems chosen by the administrator. The application administrator independently selects the recipient systems and the types of events and incidents to transmit to the recipient systems. The recipient system processes and stores the received data according to its functionality and purpose.
The application does not monitor access to the application installation settings file, which may contain personal data. The application monitors startups of application components that involve scanning user account credentials.
The logging system (Grafana) does not transmit personal user data to Kaspersky or to third-party servers. Data may be sent to third-party servers based on user activity. Before starting to work with the logging system, it is recommended to read the Grafana User Guide.
Any received information is protected by Kaspersky in accordance with legally established requirements and applicable regulations of Kaspersky. Data is transmitted over encrypted communication channels.
Page top
Folders for storing application data
Kaspersky MLAD uses the following folders and subfolders for storing data:
- Application directories (by default, mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>):
- . – root directory of the application. It is used to store configuration files, Kaspersky MLAD installation and update logs, scripts for installing, updating, starting, and stopping Kaspersky MLAD, and the distribution package signatures. The root directory of the application contains notes on the current release of Kaspersky MLAD (Release Notes).
- ./data – folder for storing data that is loaded using the HTTP Connector.
- ./containers – folder for storing an archive of containers for Kaspersky MLAD services. Containers of Kaspersky MLAD services are installed to Docker from this archive.
- ./legal – folder for storing the text of the End User License Agreement and the date of its acceptance by the user.
- ./ssl – folder for storing the script for generating a self-signed certificate that provides an HTTPS connection to the Kaspersky MLAD user's browser.
- ./ssl/tokens – folder for storing a JWT (JSON Web Token) key.
- ./ssl/nginx – folder for storing certificates supporting an HTTPS connection with the browser of the Kaspersky MLAD user.
- ./upgrade_backup-<version number>-<build number> – folder for storing the backup copies of Kaspersky MLAD that are created during an update of Kaspersky MLAD. The contents repeat the structure of the root directory where Kaspersky MLAD is installed.
- ./volumes_backup_<date of deletion> – folder for storing backup copies of Docker volumes that are created during removal of Kaspersky MLAD.
- Folder /var/lib/docker/volumes/:
- ./mlad-release-<version number>-<installation build number>_postgres-volume – folder for storing Postgres database files.
- ./mlad-release-<version number>-<installation build number>_inflxdb-volume – folder for storing Time Series Database files.
- ./mlad-release-<version number>-<installation build number>_logger-volume – folder for storing the logging subsystem files.
- ./mlad-release-<version number>-<installation build number>_webstatic-volume – folder for storing static data of the application web interface.
- /etc/hosts – service file describing the mapping between IP addresses and host names of the external servers.
Application files can be modified by a user with application administrator privileges or by the user who unpacked the archive containing the installation script and all the files required for installation of Kaspersky MLAD.
Deleting or modifying any file of Kaspersky MLAD can negatively impact the performance of the application.
Page top
Performing common tasks
This section contains a description of the common user tasks and instructions on how to perform them.
Scenario: Working with Kaspersky MLAD
This section describes the actions of users having operator permissions when working with Kaspersky MLAD.
The scenario for working with the application consists of the following steps:
- Creating presets to monitor the section of the protected facility
For quick and more convenient access to necessary data, it is recommended to create presets that include tags corresponding to units of the industrial plant. If necessary, you can modify existing presets.
- Viewing historical data
Go to the History section to view historical data of process parameters, the results of their processing by Kaspersky MLAD, and the generated predictions and identified incidents. Select the relevant preset and specify the date and time interval for viewing the data. Use the navigation to view historical data.
- Monitoring in online mode
To view the received values of process parameters, their predicted values, and errors in the online mode, go to the Monitoring section. Select the relevant preset and time interval to display the incoming data.
- Viewing data in the Time slice section
To view the values of the process parameters received from the monitored asset's sensors at a certain point in time, go to the Time slice section. Select the relevant preset and specify the date and time interval for viewing the data. Use the navigation to view data.
- Working with incidents
Go to the Incidents section and view information about the registered incidents. Analyze the incidents and add expert opinions or comments where you can indicate if the registered incidents are anomalies.
If you are subscribed to incident notifications, you will receive an email message when an abnormal situation arises. The message will indicate the date and time when the incident began and will provide a link you can use to go to the History section.
- Working with events and patterns
Go to the Event Processor section and view the events and patterns detected by the Event Processor. Create monitors to monitor specific events, patterns, and event parameter values.
Viewing summary data in the Dashboard section
The Dashboard section provides summary information on the number of tags and events received by Kaspersky MLAD, registered incidents, and the status of services.
The information on the page is divided into the following blocks:
- Incoming data is a graph that displays the number of tags and events received by Kaspersky MLAD. You can enable or disable the display of incoming tags and events on the graph by clicking the corresponding data signature legend under the graph. The left scale of the graph displays the range for the number of incoming tags per second. The right scale of the graph displays the range for the number of incoming events per second.
- Latest incidents is a table that contains information about the latest registered incidents.
- Machine learning is a table that displays the status of services used for operation and training of the ML model, and the name of the active ML model.
- Status of services is a table that displays the status of each service.
You can proceed to the History section from the Dashboard section by clicking the date and time of an incident in the Latest incidents table. The History section displays detailed information about the incidents registered by Kaspersky MLAD.
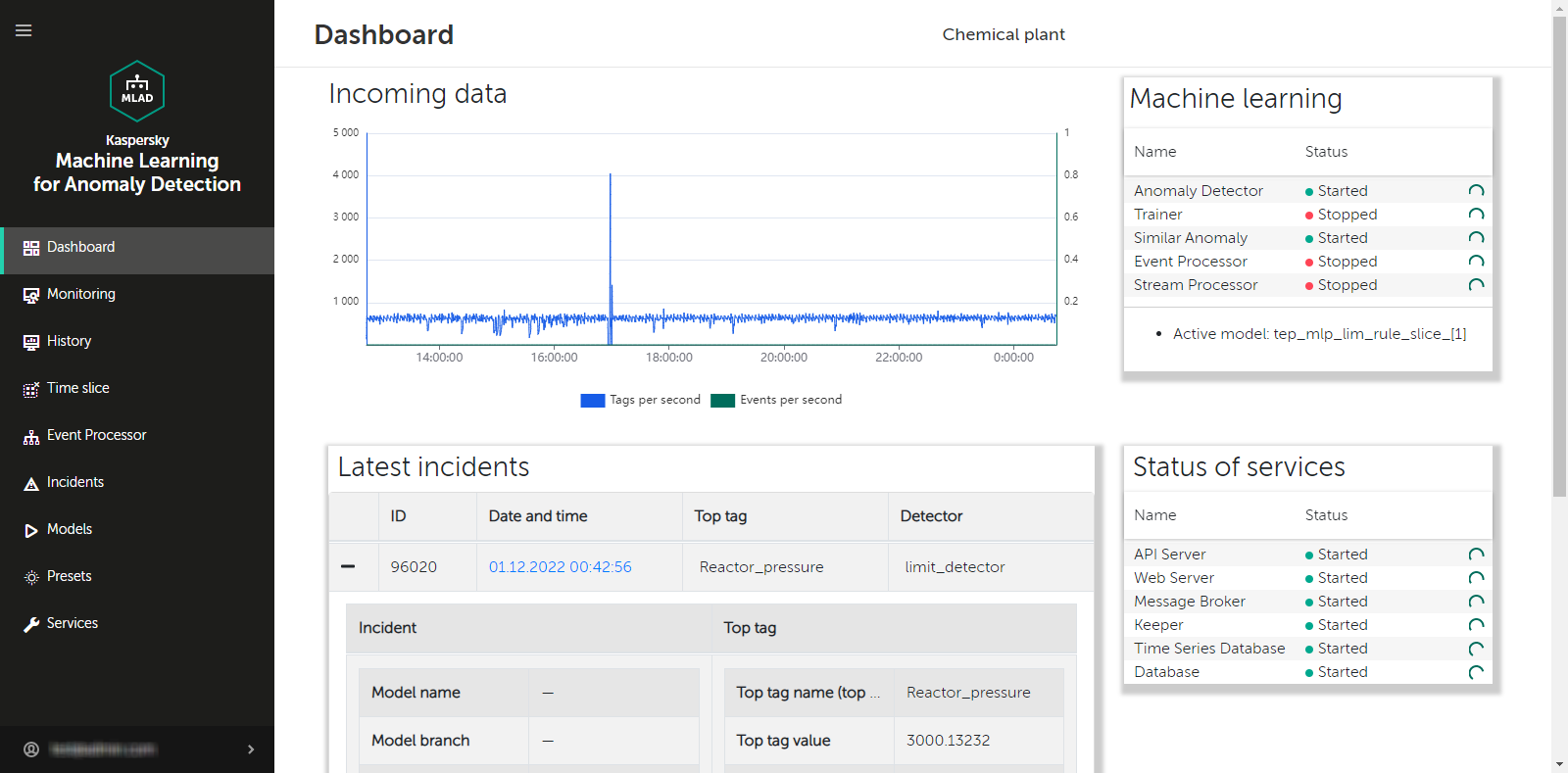
Dashboard section
Page top
Viewing incoming data in the Monitoring section
In the Monitoring section, you can view the real-time values of the tags included in the preset and their predicted values. You can view data on relevant tags by selecting the necessary preset from the drop-down list. This list includes presets that can be created in the Presets section. For each tag included in the selected preset, the incoming values are displayed as a graph. You can customize the display of graphs and select a branch of a specific ML model to view the operating results of this branch. For example, you can view the tag values predicted by the Forecaster Detector and their errors, or the values of indicator tags for diagnostic rules.
The lower part of the page contains a section displaying the cumulative mean square error (also referred to as the "MSE" or "cumulative error"), and the number of registered incidents (color-coded dot indicators). The orange line shows the MSE threshold, above which Kaspersky MLAD registers an incident.
Depending on the selected time scale and the density of incidents, one dot indicator may correspond to one or multiple closely-spaced incidents that were registered by one or multiple different detectors. The color of dot indicators corresponds to the color of the ML model branch that was used to register the incident. Special colors are reserved for dot indicators that correspond to a group of incidents registered by different branches and for incidents registered by the Limit Detector.
Incidents registered by the Rule Detector will not have an MSE value because incident registration occurs when an indicator tag value equal to one is reached. When analyzing these incidents, pay attention to the rule triggering marker (color-coded dot indicator) below the MSE graph for the selected ML model branch.
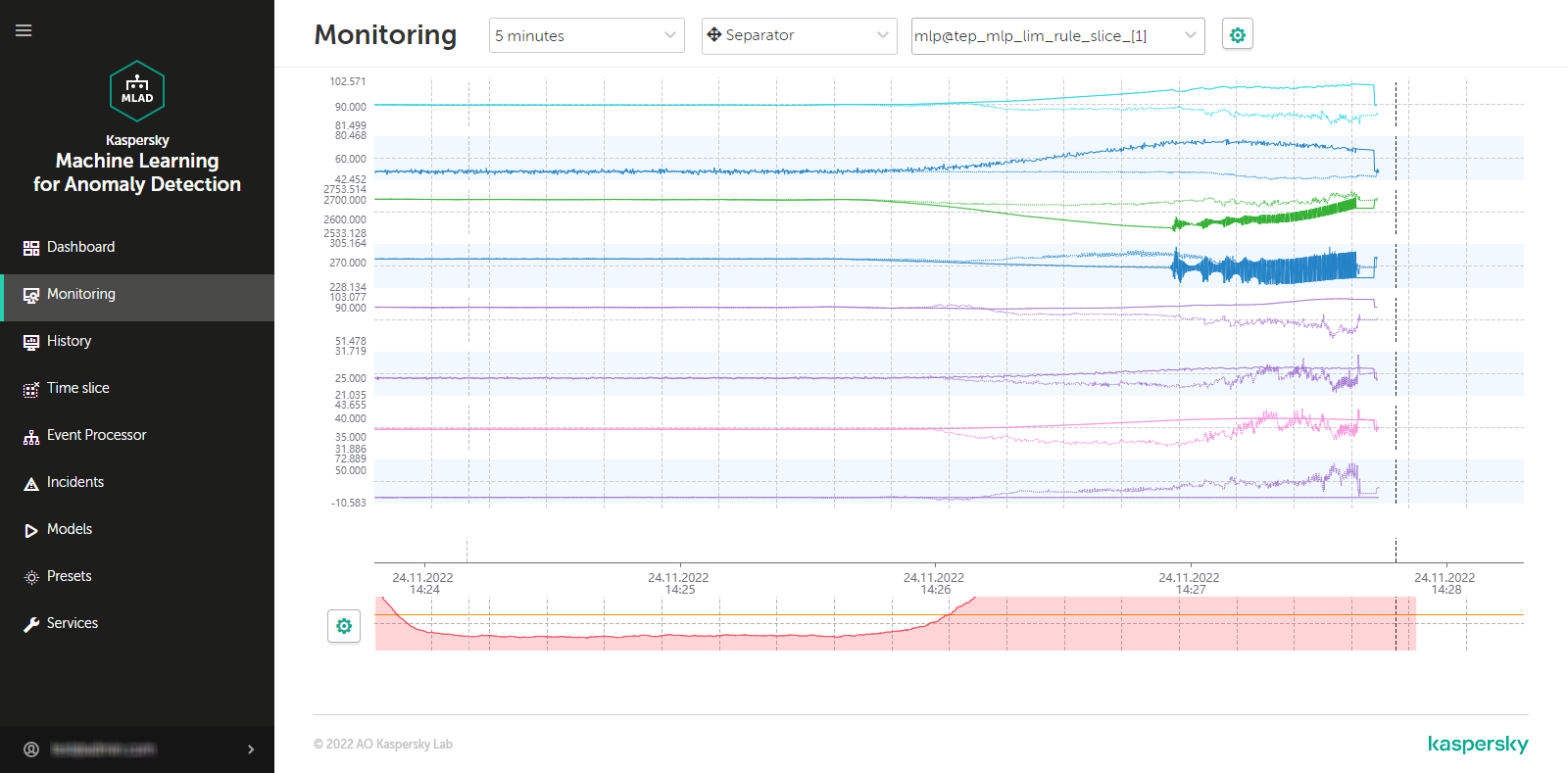
Monitoring section
Viewing data for a specific preset in the Monitoring section
Kaspersky MLAD allows you to select presets for which real-time data is displayed.
To view incoming data for a specific preset in real time:
- In the main menu, select the Monitoring section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant preset from the drop-down list.
The page displays graphs for tags that are included in the selected preset.
If necessary, you can change the time interval for displaying data, customize the display of graphs, or select a specific branch of the ML model. You can also change which tags are displayed by editing the preset.
Page top
Selecting a specific branch of the ML model in the Monitoring section
In the Monitoring section, you can view in real time the incoming values of tags included in the preset, their predicted values, and MSEs.
If the ML model used for a monitored asset has several branches for processing and predicting data, Kaspersky MLAD lets you select a specific branch of the ML model to display the operating results of the corresponding model element:
- For an ML model branch based on the Forecaster Detector, operating results are displayed as predicted values for specific tags, individual errors in the prediction of specific tags, and cumulative MSE and dot indicators of incidents registered by the detector.
- For an ML model branch based on the Rule Detector, operating results are presented as indicator tags and dot indicators of incidents.
- An ML model branch is not created for the Limit Detector. The dot indicators of incidents registered using this detector are displayed if use of the Limit Detector is enabled and the display of indicators for all tags is enabled.
To display the predicted values of a tag on graphs in the Monitoring section, and to display the values of indicator tags for diagnostic rules, you must customize the display of graphs.
To view the operating results of a specific ML model branch:
- In the main menu, select the Monitoring section.
- On the opened page, in the drop-down list, select the check boxes next to the relevant branches of the ML model.
The names of the selected branches are displayed in the field.
The branches belonging to the currently used ML model are located in the upper part of the list. The lower part of the list displays branches of other currently unused ML models that were uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. An ML model branch is displayed in the drop-down list only after Kaspersky MLAD receives data that resulted from operations of the specific branch.
The graphs of the selected preset will display the predicted values of tags or the values of indicator tags depending on the type of detector in the selected ML model branch.
If you need to hide the display of operating results from previously selected ML model branches, clear the check boxes next to these branches (however, one of the branches must remain active for graphs to be displayed in the Monitoring section).
- If you need to display the MSE received as a result of data processing by a specific ML model branch:
- Click the settings button
 below the tag graphs on the left side of the page.
below the tag graphs on the left side of the page. - In the MSE graph display settings pane that appears on the right, select the branch from the Model branch drop-down list. You can select only one ML model branch from the list.
- Click the Close button.
- Click the settings button
The MSE graph displays the MSE values for the selected branch of the ML model. The lower part of the graph displays the dot indicators of incidents that were registered by the selected ML model branches. If the display of indicators for all tags is enabled, the dot indicators of incidents that were registered by all ML model branches will be displayed.
Page top
Selecting a time interval in the Monitoring section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you select the time interval (scale) for displaying incoming data.
To select a time interval:
- In the main menu, select the Monitoring section.
- On the opened page, select the necessary time interval from the drop-down list. The following values are available by default:
- 1, 5, 10, 15, and 30 minutes
- 1, 3, 6, and 12 hours
- 1, 2, 15, and 30 days
- 3 and 6 months
- 1, 2, and 3 years
If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the time intervals.
The page will display graphs of the defined preset for the selected time interval.
Page top
Configuring how graphs are displayed in the Monitoring section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you configure how the graphs of presets are displayed in the Monitoring section.
To configure the display settings for preset graphs:
- In the main menu, select the Monitoring section.
- On the opened page, click the settings button
 in the upper part of the screen.
in the upper part of the screen.The Graph display settings pane will appear on the right.
- In the Graph height drop-down list, select one of the following values: 55 px, 110 px, 145 px, 190 px.
By default, the Graph height parameter is set to 55 px.
- In the To go to the History section, use drop-down list, select the preset whose graphs should be displayed by default when you navigate to the History section.
- If necessary, move the Show graphs in selected color toggle button to enable the display of tag graphs in a specific color and select the color.
- If necessary, move the Predicted tag value toggle button to enable the display of the predicted tag value and values of indicator tags of diagnostic rules on graphs.
- If you need the graphs to display the defined technical limits for a tag:
- Turn on the Technical limits toggle button.
- If you need to always display the defined technical limits, turn on the Always show technical limits toggle button.
If this mode is disabled, the technical limits will be displayed only if the tag value has reached the corresponding limit in the graph area displayed on the screen.
- If necessary, move the Personal tag error toggle button to enable display of the personal tag error on graphs.
- If necessary, move the Tag description and name toggle button to enable display of the tag description and name on graphs.
- If necessary, move the Additional threshold lines toggle button to enable the display of additional threshold lines on the graph.
- If necessary, move the Display indicators for all incidents toggle button to enable display of the dot indicators for incidents registered by all ML model branches.
If this mode is disabled, only the dot indicators for incidents that were registered by the selected ML model branches will be shown.
- Click the Close button to return to viewing graphs in the Monitoring section.
The defined settings for displaying preset graphs in the Monitoring section will be applied.
Page top
Viewing data in the History section
The History section provides access to the history of incoming data, the results of data processing by Kaspersky MLAD, generated predictions, and registered incidents. You can select the necessary preset in the drop-down list. This list includes presets that can be created in the Presets section. For each tag included in the selected preset, the incoming values are displayed as a graph. You can customize the display of graphs, select a time interval for viewing data, and select a branch of a specific ML model to view the operating results of this branch. For example, you can view the tag values predicted by the Forecaster Detector and their errors, or the values of indicator tags for diagnostic rules.
The lower part of the page contains a section displaying the cumulative mean square error (also referred to as the "MSE" or "cumulative error"), and the number of registered incidents (color-coded dot indicators). The orange line shows the MSE threshold, above which Kaspersky MLAD registers an incident.
Depending on the selected time scale and the density of incidents, one dot indicator may correspond to one or multiple closely-spaced incidents that were registered by one or multiple different detectors. The color of dot indicators corresponds to the color of the ML model branch that was used to register the incident. Special colors are reserved for dot indicators that correspond to a group of incidents registered by different branches and for incidents registered by the Limit Detector.
Incidents registered by the Rule Detector will not have an MSE value because incident registration occurs when an indicator tag value equal to one is reached. When analyzing these incidents, pay attention to the rule triggering marker (color-coded dot indicator) below the MSE graph for the selected ML model branch.

History section
Viewing historical data for a specific preset
Kaspersky MLAD allows you to select custom presets for which historical data is displayed. You can also view information about the Tags for event #N dynamic preset if you go to the History section from the Incidents section by clicking the incident registration date. The Tags for event #N dynamic preset contains tags that had the greatest influence on the generation of a registered incident.
To view historical data for a specific preset:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant preset from the drop-down list.
The page displays graphs for tags that are included in the selected preset.
You can use the time navigation function to view the entire history of data. If necessary, you can change the date and time interval. You can also change the composition of tags in a preset, create a new preset, or select a specific branch of the ML model.
Page top
Selecting a specific branch of the ML model in the History section
The History section provides access to the history of incoming data, the results of data processing by Kaspersky MLAD, generated predictions, and registered incidents.
If the ML model used for a monitored asset has several elements for processing data, Kaspersky MLAD lets you select a specific branch of the ML model to display the operating results of the corresponding model element:
- For an ML model branch based on the Forecaster Detector, operating results are displayed as predicted values for specific tags, individual errors in the prediction of specific tags, and cumulative MSE and dot indicators of incidents registered by the detector.
- For an ML model branch based on the Rule Detector, operating results are presented as indicator tags and dot indicators of incidents.
- An ML model branch is not created for the Limit Detector. The dot indicators of incidents registered using this detector are displayed if use of the Limit Detector is enabled and the display of indicators for all tags is enabled.
To display the predicted values of a tag on graphs in the History section, and to display the values of indicator tags for diagnostic rules, you must customize the display of graphs.
To view the operating results of a specific ML model branch:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- On the opened page, in the drop-down list, select the check boxes next to the relevant branches of the ML model.
The names of the selected branches are displayed in the field.
The branches belonging to the currently used ML model are located in the upper part of the list. The lower part of the list displays branches of other currently unused ML models that were uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. An ML model branch is displayed in the drop-down list only after Kaspersky MLAD receives data that resulted from operations of the specific branch.
The graphs of the selected preset will display the predicted values of tags or the values of indicator tags depending on the type of detector in the selected ML model branch.
If you need to hide the operating results from previously selected ML model branches, clear the check boxes next to these branches (however, one of the branches must remain active for graphs to be displayed in the History section).
- If you need to display the MSE received as a result of data processing by a specific ML model branch:
- Click the settings button
 below the tag graphs on the left side of the page.
below the tag graphs on the left side of the page. - In the MSE graph display settings pane that appears on the right, select the branch from the Model branch drop-down list. You can select only one ML model branch from the list.
- Click the Close button.
- Click the settings button
The MSE graph displays the MSE values for the selected branch of the ML model.
The lower part of the graph displays the dot indicators of incidents that were registered by the selected ML model branches. If the display of indicators for all tags is enabled, the dot indicators of incidents that were registered by all ML model branches will be displayed.
Selecting a date and time interval in the History section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you choose the date and a fixed time interval (scale) for displaying historical data or a user-defined time interval (for example, when an incident was detected).
To select the date for displaying historical data:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- Click the calendar icon (
 ) and select the date and time of the historical data to be displayed on the graphs.
) and select the date and time of the historical data to be displayed on the graphs. - Click the Apply button.
The vertical blue line on graphs will indicate the selected date and time (in the center of the graph).
- To select a new date and time (point) on the graph, click the location icon (
 ) on the left of the time axis and select the relevant point on the time axis.
) on the left of the time axis and select the relevant point on the time axis.The selected point will become the new center of the graph. The vertical blue dashed line will indicate the new date and time.
To select a time interval for displaying historical data:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- On the opened page, do one of the following:
- If you need to display data for a fixed time interval, select the relevant time interval from the drop-down list. The following time intervals are available by default:
- 1, 5, 10, 15, and 30 minutes
- 1, 3, 6, and 12 hours
- 1, 2, 15, and 30 days
- 3 and 6 months
- 1, 2, and 3 years
If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the time intervals.
- If you need to display data for an arbitrary time interval, click the interval selection icon (
 ), which is located to the left of the time axis, select the required interval on the time axis and click on
), which is located to the left of the time axis, select the required interval on the time axis and click on  . If you need to change the scale again, repeat this step.
. If you need to change the scale again, repeat this step.
- If you need to display data for a fixed time interval, select the relevant time interval from the drop-down list. The following time intervals are available by default:
The graphs of the defined preset will display the tag values for the selected time interval.
Navigating through time in the History section
Kaspersky MLAD provides the capability to navigate through time for convenient viewing of historical data.
To use time navigation when viewing data:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- On the opened page, select the time interval for the data that you want to view.
- Use the left (
 ) and right arrows (
) and right arrows ( ) in the upper part of the page to move left or right along the time axis.
) in the upper part of the page to move left or right along the time axis.
The time axis for viewing historical data on the graph will shift to the selected time interval.
Navigating through time
On graphs, a vertical blue dashed line indicates the midpoint of the selected time interval and matches the selected date and time. If an interval of 1 day is selected, the graph displays historical data for the 12-hour periods before and after the selected date and time relative to the dashed line. If necessary, you can change the time interval.
Page top
Configuring how graphs are displayed in the History section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you configure the settings for displaying preset graphs in the History section.
To configure the display settings for preset graphs:
- In the main menu, select the History section.
- On the opened page, click the settings button
 in the upper part of the screen.
in the upper part of the screen.The Graph display settings pane will appear on the right.
- In the Graph height drop-down list, select one of the following values: 55 px, 110 px, 145 px, 190 px.
By default, the Graph height parameter is set to 55 px.
- If necessary, move the Show graphs in selected color toggle button to enable the display of tag graphs in a specific color and select the color.
- If necessary, move the Predicted tag value toggle button to enable the display of the predicted tag value and values of indicator tags of diagnostic rules on graphs.
- If you need the graphs to display the defined technical limits for a tag:
- Turn on the Technical limits toggle button.
- If you need to always display the defined technical limits, turn on the Always show technical limits toggle button.
If this mode is disabled, the technical limits will be displayed only if the tag value has reached the corresponding limit in the graph area displayed on the screen.
- If necessary, move the Personal tag error toggle button to enable display of the personal tag error on graphs.
- If necessary, move the Tag description and name toggle button to enable display of the tag description and name on graphs.
- If necessary, move the Additional threshold lines toggle button to enable the display of additional threshold lines on the graph.
- If necessary, move the Display indicators for all incidents toggle button to enable display of the dot indicators for incidents registered by all ML model branches.
If this mode is disabled, only the dot indicators for incidents that were registered by the selected ML model branches will be shown.
- Click the Close button to return to viewing graphs in the History section.
The defined settings for displaying preset graphs in the History section will be applied.
Page top
Viewing data in the Time slice section
In the Time slice section, you can view the values of process parameters received from sensors of the monitored asset at the same point in time. The sensors must be of the same type (have the same dimension) and must be positioned linearly, like pressure sensors in an oil pipeline, for example.
Data is presented in the form of graphs that allow you to see whether an incident was detected at the selected time and where the likely source of the incident is located.
The lower part of the page contains a section displaying the individual errors of tags. The data is presented as a bar graph. The error value for each tag is displayed when the mouse cursor hovers over the relevant column. The MSE graph is located on the right of the preset tag graphs.
In the Time slice section, you can use the drop-down list to select a preset and the date and time when data was received. This list includes special presets that can be created in the Presets section. A special preset should contain only tags of the same type that have defined x-axis coordinates. You can additionally specify expressions dynamically calculated for each tag based on actual and predicted tag values, individual prediction errors, and tag coordinate values and constants defined in expressions.
You can also customize the display of graphs, select a time interval for viewing data, and select a specific element of the ML model to view the personal errors of preset tags obtained as a result of data processing by the selected element of the ML model.
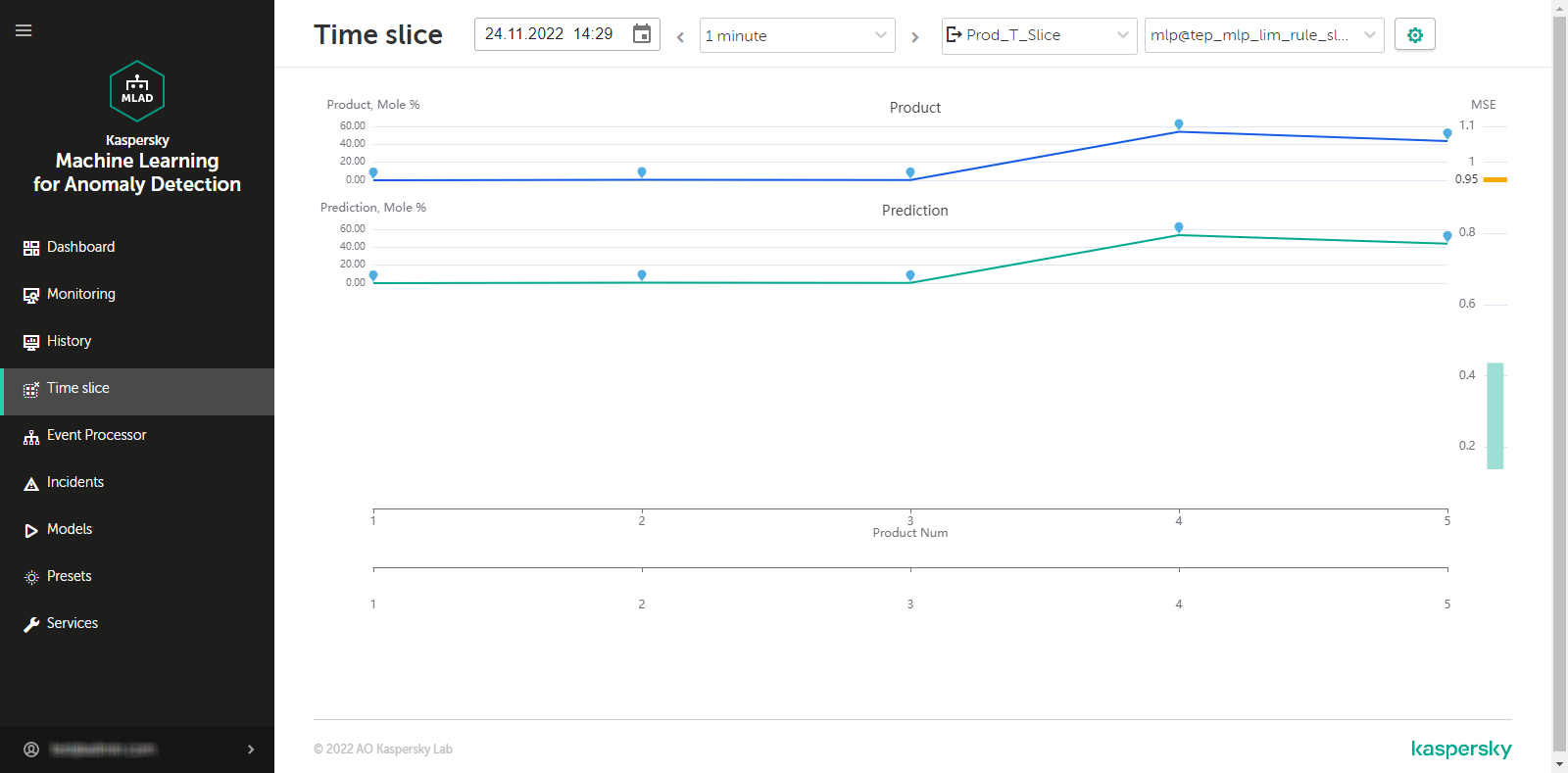
Time slice section
Viewing data for a specific preset in the Time slice section
To view data for a specific preset:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant preset from the drop-down list.
The page displays graphs for tags that are included in the selected preset.
If necessary, you can change the time interval for displaying data, customize the display of a graph, or select a specific branch of the ML model. You can also change which tags are displayed by editing the preset.
Selecting a specific branch of the ML model in the Time slice section
If the ML model used for a monitored asset has several branches for processing and predicting data, Kaspersky MLAD lets you select a specific branch of the ML model to display the personal tag errors obtained as a result of this branch in the Time slice section.
To view the personal tag errors resulting from data processing by a specific ML model branch:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant branch of the ML model from the Model branch drop-down list.
The name of the selected branch will be displayed in the field.
The tag graphs of the selected preset will display the personal tag errors resulting from data processing by the selected branch of the ML model.
Page top
Selecting a date and time interval in the Time slice section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you select a date and time interval (scale) for displaying incoming data.
To select the date for displaying incoming data:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- Click the calendar icon (
 ) and select the date and time for displaying data on the graphs.
) and select the date and time for displaying data on the graphs. - Click the Apply button.
The graphs will display the tag values for the selected date and time.
To select a time interval for displaying incoming data:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- Select the required time interval from the drop-down list in the upper part of the opened page. The following time intervals are available by default:
- 1, 5, 10, 15, and 30 minutes
- 1, 3, 6, and 12 hours
- 1, 2, 15, and 30 days
- 3 and 6 months
- 1, 2, and 3 years
If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the time intervals.
The page will display graphs of the defined preset for the selected time interval.
Page top
Navigating through time in the Time slice section
Kaspersky MLAD provides the capability to navigate through time for convenient viewing of data.
To use time navigation when viewing data:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- On the opened page, select the time interval for the data that you want to view.
- Use the left (
 ) and right arrows (
) and right arrows (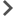 ) in the upper part of the page to move left or right along the time axis.
) in the upper part of the page to move left or right along the time axis.
The time axis for viewing data on the graph will shift to the selected time interval.

Navigating through time
Page top
Configuring how graphs are displayed in the Time slice section
Kaspersky MLAD lets you configure the settings for displaying preset graphs in the Time slice section.
To configure the display settings for preset graphs:
- In the main menu, select the Time slice section.
- On the opened page, click the settings button
 in the upper part of the screen.
in the upper part of the screen.The Graph display settings pane will appear on the right.
- In the Graph height drop-down list, select one of the following values: 55 px, 110 px, 145 px, 190 px.
By default, the Graph height parameter is set to 55 px.
- Click the Close button to return to viewing the graphs.
The configured graph display settings will be applied.
Page top
Working with events and patterns
The Event Processor section provides data on events and the structure of patterns detected by the Event Processor service in the event stream received from external sources or from the Anomaly Detector service.
In the Event Processor section, you can view the history of received events and the registration history of new and/or persistently recurring patterns. You can also configure the display of event parameters and can configure pattern registration settings. On the Monitoring tab, you can monitor specific events, patterns, or values of event parameters received by the Event Processor within the data stream from monitored assets.
If restarted, Kaspersky MLAD restores the state of the Event Processor service and pauses the processing of data received from the CEF Connector. This data is temporarily stored in the internal queue of the application message broker. Until the Event Processor service is restored, the Event Processor section will display a notification informing you that the Event Processor service has stopped. This service restoration process may take several minutes if there is a significantly large number of processed events or registered patterns.

Event Processor section
Working with monitors
In the Event Processor section on the Monitoring tab, you can create monitors for monitoring specific events, patterns, or values of event parameters.
The Monitoring tab displays all monitors created in the application, including the following brief information:
- Monitor name.
- Monitor threshold.
- Sliding window used to track the number of monitor activations.
- Number of monitor activations on the sliding window.
If necessary, you can view detailed information about each monitor by clicking the Information button located next to the name of the relevant monitor in the table.
On the Histogram tab, you can also view brief statistics on the number of registered activations for each created monitor.
Creating a monitor
To create a monitor:
- In the main menu, select the Event Processor section.
- On the opened page, select the Monitoring tab.
- Click the Create monitor button.
The Create monitor pane appears on the right.
- Specify the monitor name in the Name field.
- In the Sliding window (sec.) field, specify the interval (in seconds) from the current point in time back to the time sequence for which the monitor will process incoming values of parameters, events or patterns.
- In the Threshold field, specify the number of monitor activations in the sliding window after which the monitor sends an alert to the external system.
- In the Stack limit field, specify the number of monitor activations that must be displayed when viewing information about the monitor.
- In the Subscription type drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- If you need to process data on the values of event parameters, select Parameter values.
- If you need to process data on events, select Events.
- If you need to process data on detected patterns, select Patterns.
- If you need to track new events, patterns, or values of event parameters, turn on the Only new toggle button in the Filters section.
- To focus the attention of the model on specific directions of events, do one of the following:
- If you selected Events from the Subscription type drop-down list, select Attention for the relevant event parameter. If you need to track events without specifying the attention direction, clear the Attention check box.
- If you selected Patterns from the Subscription type drop-down list, select the Attention check box for the relevant event parameter.
You can select only one attention direction.
- For each event parameter, do one of the following:
- If you need to process data on all values of an event parameter, use the drop-down list to select All parameter values.
This option is displayed if you specified the attention direction for the current event parameter.
- To process data only on the new values of an event parameter, in the drop-down list select New parameter values.
This option is displayed only when the Only new function is enabled for event-based data processing.
- To process data for a specific value of an event parameter, in the drop-down list select the event parameter value. As you start typing a value, all matching parameter values are displayed in the list.
If the parameter value is not listed, enter the required value and select Create Value: <event parameter value>.
- If you need to process data based on an event parameter value template, turn on the Regular expression toggle button for the relevant event parameter, use the drop-down list to enter the value template with a regular expression, and select Regular expression: <value template>.
You can use special characters of regular expressions to search patterns using regular expressions.
- If you need to process data on all values of an event parameter, use the drop-down list to select All parameter values.
- Click the Create button.
The new monitor is created and displayed on the Monitoring tab.
Page top
Deleting a monitor
To delete a monitor:
- In the main menu, select the Event Processor section.
- On the opened page, select the Monitoring tab.
- Click the Delete button in the cell of the monitor whose information you want to delete and confirm your selection.
The monitor will be deleted.
Page top
Viewing the events history
Kaspersky MLAD lets you view the events that were received from external sources of events. To view events, you need to upload them to Event Processor → Event history.
Kaspersky MLAD displays incoming events as a graph of relations between event parameters. The graph nodes correspond to the values of the event parameters, and the arcs between the nodes correspond to the links between the parameter values of incoming events. You can hover the mouse pointer over the event graph and view information about the event parameters and their values. You can also hover the mouse pointer over the event graph arc and view information about the number of links between the values of event parameters.
You can also view information about the detected events as a table.
Each monitored asset has its own specific incoming events and event parameters. The list of event parameters is defined in the configuration file for the Event Processor service. The configuration file is created and uploaded by an administrator (Kaspersky expert or certified integrator) during configuration of the Event Processor service.
To upload data for viewing incoming events:
- In the main menu, select the Event Processor section.
- On the opened page, select the Event history tab.
- In the Filters section, click the calendar icon (
 ) to select the start and end date and time of the period for which you want to load and view events. To configure event parameters, do one of the following:
) to select the start and end date and time of the period for which you want to load and view events. To configure event parameters, do one of the following:- To load events based on the specific values of the event parameters, select the event parameter value in the drop-down lists. As you start typing a value, all matching parameter values are displayed in the lists.
- To load events based on a value template, enable the Regular expression option for the relevant event parameters, in the drop-down lists, specify the value template using a regular expression, and select Regular expression: <value template>.
You can use special characters of regular expressions to perform a search based on regular expressions.
Each monitored asset has its own specific set and names of event parameters.
- Click the Process request button.
Data on the events found by the application will be displayed as a graph in the central part of the page.
- To view the received events as a table, select the Table tab.
The central part of the page displays a table that contains information on the detected events.
Viewing the pattern history
On the Patterns history page, you can find and view the structure of the new and/or persistently recurring patterns. The Event Processor generates patterns only for specific directions that are defined in the attention settings by a user with administrator privileges.
You can also view the structure of the detected patterns down to the event level. The Event Processor represents patterns, events, and values of event parameters as a layered hierarchy of nested elements. For example, a fourth-layer pattern consists of subpatterns of the third layer. A third-layer pattern consists of second-layer patterns, and a second-layer pattern consists of events, which are first-layer elements. Event parameter values are elements of the null terminal layer.
Each monitored asset has its own specific incoming events and event parameters. The list of event parameters is defined in the configuration file for the Event Processor service. The configuration file is created and uploaded by a Kaspersky expert or certified integrator during configuration of the Event Processor service.
To view the registered patterns:
- In the main menu, select the Event Processor section.
- On the opened page, select the Patterns history tab.
- In the Filters section, configure the following settings for displaying patterns on the page:
- In the Start of period field, click the calendar icon (
 ) and select the starting date and time of the period for which you want to view the patterns.
) and select the starting date and time of the period for which you want to view the patterns. - In the End of period field, click the calendar icon (
 ) and select the end date and time of the period for which you want to view the patterns.
) and select the end date and time of the period for which you want to view the patterns. - In the Pattern type drop-down list, select one of the following values:
- Stable refers to patterns that were registered by the Event Processor service two or more times.
- New refers to new patterns registered by the Event Processor service for the first time.
- All includes all patterns that were registered by the Event Processor service.
- To view patterns for a specific attention direction, select Attention for the relevant event parameter.
You must select one of the attention directions that were defined when configuring the attention settings.
- To configure event parameters, do one of the following:
- To view patterns based on specific values of the event parameters, select the event parameter values in the drop-down lists. As you start typing a value, all matching parameter values are displayed in the lists.
- If you need to view patterns based on a value template, turn on the Regular expression toggle button for the relevant event parameters, use the drop-down lists to enter the value template with a regular expression, and select Regular expression: <value template>.
You can use special characters of regular expressions to perform a search based on regular expressions.
For the request to be processed correctly, enter the values for the event parameter that is receiving focused attention from the model. If an event parameter that is receiving focused attention has multiple values defined, the Event Processor will generate patterns for each value of the parameter.
- In the Start of period field, click the calendar icon (
- Click the Process request button.
The central part of the page displays a table containing data on the registered patterns.
- To view the pattern structure, click the desired pattern row.
The page with detailed information on the pattern opens.
- To view the structure of a pattern, do one of the following:
- To view the structure of a particular subpattern, on the Patterns tab in the Nested elements section, click the desired pattern.
You can return to viewing the top-level pattern structure by clicking the ID of the desired pattern above the Pattern info section.
- To view the table of subpatterns at a certain nesting level, select the desired layer on the Patterns tab of the Nested elements section.
- To view the events included in the pattern at the current nesting level, click the Events tab.
Kaspersky MLAD displays the pattern structure from the top nesting level.
- To view the structure of a particular subpattern, on the Patterns tab in the Nested elements section, click the desired pattern.
Working with incidents and groups of incidents
In Kaspersky MLAD, an ML model can simultaneously use multiple types of detectors that analyze incoming telemetry data and detect incidents independent of each other. The Kaspersky MLAD web interface provides the capability to investigate detected incidents. Depending on the type of detector that registered an incident, information about the incident and the methods you can use to investigate it may differ.
You can perform the following actions for any incident:
- Analyze the incident details.
- Find out if any similar incidents were detected previously.
- Study the behavior of the monitored asset at the moment when the incident was detected.
- Leave a note or expert opinion for a registered incident or incident group.
The Incidents section displays a column graph showing the incidents that match the filtering criteria specified under the graph. The graph displays statistics on the registered incidents for the period specified above the graph.
The graph can display up to 60 bars. If the specified period does not exceed 60 days, incidents on the graph are grouped by days. If the specified period is between 60 days and 60 weeks, incidents on the graph are grouped by weeks. If the specified period is longer than 60 weeks, incidents on the graph are grouped by months.
Hovering the mouse pointer over a bar of the graph displays a window showing the number of registered incidents per corresponding time period. Upon clicking a bar, the graph and in the table below display information about the incidents registered during the corresponding time period.
In this section, you can view individual incidents as well as groups of incidents.
Incidents tab
The Incidents tab shows a table of registered incidents. Incidents are sorted by date in descending order, with the newest incidents shown first.
Incidents tab
You can go to the History section by clicking the date and time of the incident.
Groups tab
The Groups tab shows a table of incident groups. Kaspersky MLAD automatically generates groups of similar incidents.
You can change the group name that was assigned automatically and set the status of incidents that belong to this group. You can also provide an expert opinion that contains the recommended actions to take in response to new incidents in this group, for example.
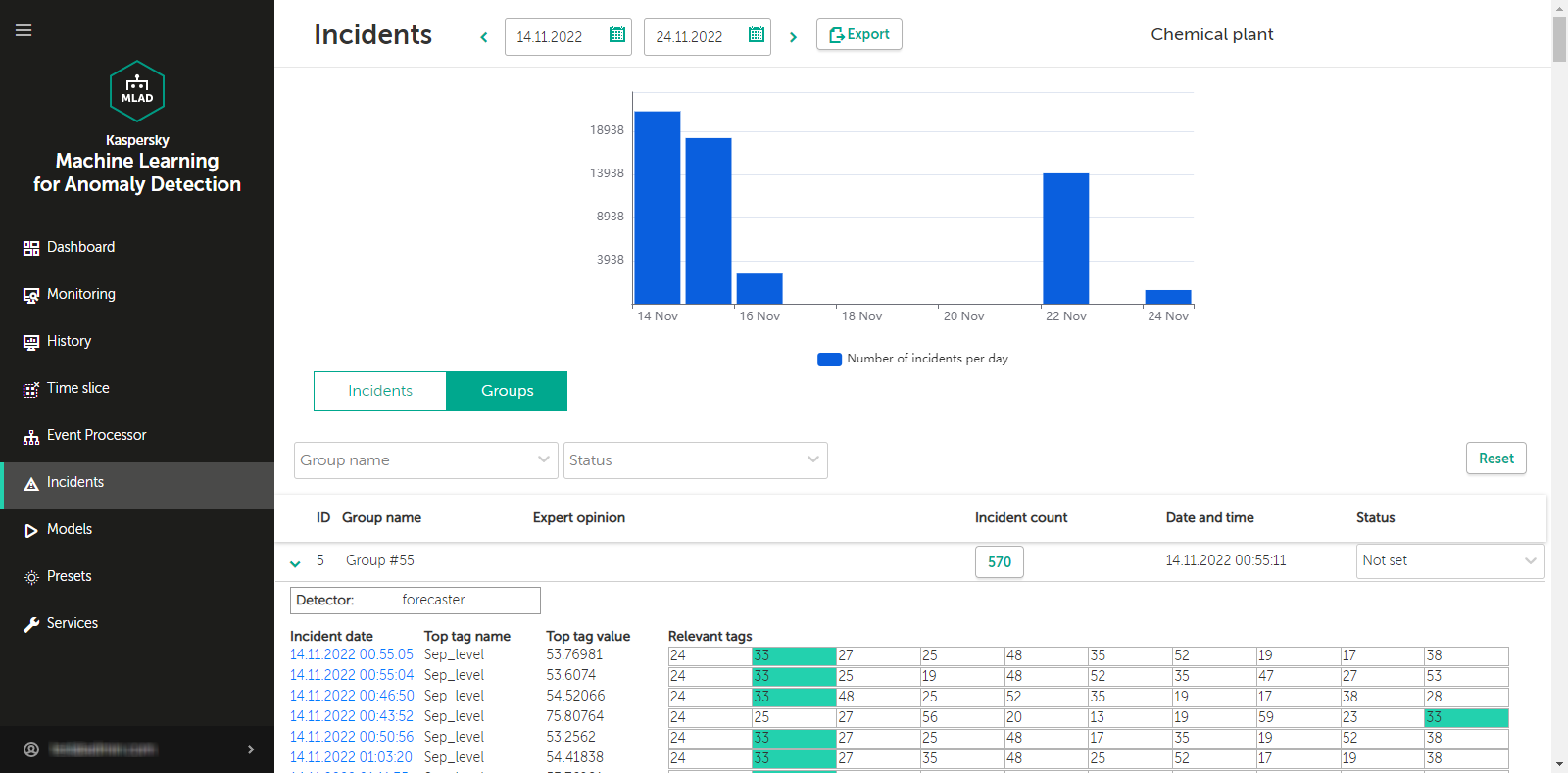
Groups tab
Scenario: Analysis of incidents
This section describes the sequence of actions required when analyzing incidents registered by Kaspersky MLAD.
The incident analysis scenario described in this section is not a precisely regulated procedure. The specific scope and sequence of actions taken to investigate an incident and identify its cause depend on the particular subject area, the knowledge level of the process engineer or ICS expert investigating the incident, and the availability of additional information on the monitored asset.
The incident analysis scenario consists of the following steps:
- Viewing information about a registered incident
The Incidents section displays all incidents registered by Kaspersky MLAD, and provides detailed information about their registration time, the detector that registered the incident, and an expert opinion if one was added. You can proceed to view incident information in one of the following ways:
- Viewing the latest incidents in the Dashboard section
If you want to view a recently detected incident, in the Dashboard section, click the date and time of the relevant incident in the Latest incidents table. In the History section that opens, in the lower part of the page, click the dot indicator in the MSE section to view a specific incident. The Incidents section opens showing only the incidents that were registered in the specific time interval represented by the selected dot indicator (the interval is displayed above the incidents table).
- Viewing incidents in the Incidents section
If you know the date and time when an incident was registered, select the corresponding incident in the Incidents section. You can change the time interval for the displayed incidents by using the bar graph or the date selection field in the upper part of the page.
- Navigating from an incident notification received by email
If an incident notification was created for you, you will receive the notification by email when an incident is registered. The email message contains the time when the incident began, the most anomalous tag, and a link to proceed to the History section in the Kaspersky MLAD web interface. You can use this link to proceed to the start of the incident in the History section. At the bottom of the History page, click on the dot indicator in the MSE section according to the incident start time. The Incidents section opens showing only the incidents that were registered in the specific time interval represented by the selected dot indicator (the interval is displayed above the incidents table).
When you find a record about the required incident, click the right arrow (
 ) to view detailed information about the incident.
) to view detailed information about the incident. - Viewing the latest incidents in the Dashboard section
- Viewing information about similar incidents
When two or more similar incidents are detected, Kaspersky MLAD automatically combines them into a group. In the incidents table in the Incidents section, the group associated with the incident is displayed in the Group column. If nothing is indicated for the selected incident in this column, this means that Kaspersky MLAD has not yet detected incidents similar to this particular incident.
To view all incidents in a group, select the Groups tab and click the right arrow (
 ) next to the relevant group. The table displays information about the incidents assigned to the selected group, as well as an expert opinion if it was added. Read the expert opinions for individual incidents and for the group.
) next to the relevant group. The table displays information about the incidents assigned to the selected group, as well as an expert opinion if it was added. Read the expert opinions for individual incidents and for the group. - Studying the behavior of the monitored asset at the moment when an incident was detected
Study the behavior of the monitored asset at the moment when the incident was detected.
- Analyzing the incident
Analyze the incident while considering the specific details of incident registration depending on the type of detector that registered the incident:
- Forecaster. Based on information obtained when viewing the automatically generated Tags for event #N preset and considering the available expert knowledge on the monitored asset, form a hypothesis regarding which tags could have caused the incident and select the appropriate preset after studying their behavior. Analyze the MSE graph, move back in time from the moment the MSE threshold was reached, and examine the behavior of tags at the moment when the MSE values started to grow.
- Rule Detector. For each incident that was registered by the Rule Detector, the application automatically creates the Tags for event #N preset, which contains the indicator tag that invoked registration of the incident.
- Limit Detector. For each incident that was registered by the Limit Detector, the application automatically creates the Tags for event #N preset, which includes a single causal tag for the incident.
- Stream Processor. The Stream Processor service registers incidents up until telemetry data is transmitted to the ML model for processing. Incidents are registered if data loss is detected or if observations are received by Kaspersky MLAD too early or too late.
- Adding a status, cause, expert opinion or note to an incident or its incident group
For each incident, add an expert opinion or note in which you can specify whether the incident is an anomaly. An expert opinion and note for an incident are displayed only when viewing a specific incident. If necessary, you can specify the status and cause of an incident. The cause of an incident is displayed in the incidents table and when viewing a specific incident. You can also add or edit the status and expert opinion for a group of incidents.
Viewing incidents
To view incidents that were registered on a specific date:
- In the main menu, select the Incidents section.
- In the upper part of the opened page, on the bar graph, click the graph column for the relevant date.
- If necessary, filter incidents by detector, top tag, status, group, or incident cause by selecting relevant values in the corresponding drop-down list.
The table located in the central area of the page shows the incidents registered on that day according to the specified filtering criteria. When you click the Reset button, the table and the bar graph show all registered incidents.
The following information is displayed for each incident in the table:
- ID refers to the ID of the registered incident.
- Date and time refers to the date and time when the incident was registered.
Clicking the incident registration date opens the History section, where you can view information about the "Tags for event #N" preset generated for the registered incident.
- Top tag name refers to the name of the process parameter for which the largest deviation from the prediction was recorded at the time of incident registration.
- Incident cause refers to the cause of the registered incident added by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist) based on the results of the incident analysis.
- Detector refers to the name of the detector that identified an anomaly and registered the incident: Forecaster, Limit Detector, XGBoost, Rule Detector, Stream Processor.
- Group refers to the name of the incident group to which the registered incident belongs.
If two or more similar incidents are detected, they are combined into a group that is created automatically by using the Similar Anomaly component. You can view only those incidents included in the group by selecting the group name from the drop-down list.
- Status refers to the status of a registered incident specified by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist) based on the results of the incident analysis.
You can set the incident status based on analysis results by selecting the appropriate value from the drop-down list. After installation of Kaspersky MLAD, the following statuses of incidents and incident groups are available by default: Under review, Decision pending, Instructions issued, Problem closed, Cause unknown, Ignore and False positive. If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the statuses of incidents.
Viewing the technical specifications of a registered incident
In the Incidents section, you can view the technical specifications of registered incidents. To do so, click the right arrow ( ) next to the relevant incident in the incidents table. The following technical specifications will be displayed for the selected incident:
) next to the relevant incident in the incidents table. The following technical specifications will be displayed for the selected incident:
- Incident is the section containing information about the incident.
- Top tag is the section containing information about the tag for which the incident was registered.
- Stream Processor service incident parameters is a section containing information about the parameters of the incident registered by the Stream Processor service. This group of parameters is displayed if the current incident is registered by the Stream Processor service.
- Incident cause is the field for selecting the cause of the incident. This field is completed by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist). If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete causes of incidents.
- Expert opinion is the field for adding an expert opinion based on an analysis of the registered incident. This field is completed by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist).
- Note is the field for entering a comment for the selected incident. If necessary, you can provide a comment for the incident.
Viewing incident groups
When two or more similar incidents are detected, Kaspersky MLAD automatically combines them into a group (using the Similar Anomaly component). This lets you analyze incidents with consideration of prior history and expert opinions that were generated for similar incidents. In the incidents table in the Incidents section, the group associated with the incident is displayed in the Group column. If nothing is indicated for the incident in this column, this means that Kaspersky MLAD has not yet detected incidents similar to this particular incident. Incidents can be regrouped, and the expert opinions that were added to these incidents are migrated to the new group. The group name is automatically assigned in the format Group #N (N is replaced by the sequence number of the group). If necessary, you can edit a group name.
To view incident groups:
In the main menu, select the Incidents section and click Groups.
All incident groups for your monitored asset are displayed in the table located in the central part of the page.
The following information is displayed for each incident group in the table:
- ID is the incident group identifier.
- Group name refers to the name of the incident group.
- Expert opinion is a conclusion added by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist) based on an analysis of the group of registered incidents.
- Incident count refers to the number of registered incidents included in the group.
You can proceed to view incidents of the group by clicking Incident count.
- Date and time refers to the date and time when the incident group was created.
- Status refers to the status of registered incidents in a group specified by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist) based on the results of the incident analysis.
You can set the incident group status based on analysis results by selecting the appropriate value from the drop-down list. After installation of Kaspersky MLAD, the following statuses of incidents and incident groups are available by default: Under review, Decision pending, Instructions issued, Problem closed, Cause unknown, Ignore and False positive. If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the statuses of incidents.
To view detailed information about an incident group:
- Click the right arrow (
 ) next to the incident group.
) next to the incident group.A list of incidents in this group is displayed. The following technical specifications are displayed for each incident of the group:
- Incident date is the date and time when the incident was registered.
You can go to the History section by clicking the incident registration date.
- Top tag name is the name of the process parameter that had the largest impact when the incident occurred.
- Top tag value is the registered value of the tag that had the largest impact when the incident occurred.
- Relevant tags refers to a table that contains the identifiers of tags that influenced the identification of similar incidents and merging of these incidents into a group.
- Incident date is the date and time when the incident was registered.
- If you need to view the degree of influence a tag had on the formation of similar incidents, click the Relevant tags table cell containing the identifier of the relevant tag.
All table cells containing the selected tag ID are highlighted in green. The closer the green-highlighted cells containing the ID of the selected tag are to the first table column, the more impact that tag has when identifying and grouping similar incidents.
You can also add a status and expert opinion for the incident group.
Page top
Studying the behavior of the monitored asset at the moment when an incident was detected
This section describes the sequence of actions required when studying the behavior of a monitored asset at the moment when an incident was detected.
Studying the behavior of a monitored asset consists of the following steps:
- Viewing the history of tags received for a monitored asset in the History section
You can proceed to view incident information in one of the following ways:
- If you want to view a recently detected incident, in the Dashboard section, click the date and time of the relevant incident in the Latest incidents table.
- In the Incidents section, click the date and time of the relevant incident in the incidents table.
- If an incident notification was created for you, you can proceed to view the incident by clicking the link from the email notification. The email message contains the time when the incident began, the most anomalous tag, and a link to proceed to the History section in the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
In the History section, Kaspersky MLAD displays a graph of tags received from the monitored asset for which the selected incident was registered. The graph displays data on the preset named Tags for event #N (N represents the incident number in the Incidents section), which is generated for the date and time when the selected incident was registered. This preset includes the tags that led to incident registration. Depending on the type of detector that registered an incident, this may involve the following tags:
- Tags whose actual values were deemed the most anomalous by the ML model, if the incident was registered by the Forecaster Detector.
- The indicator tag of the triggered diagnostic rule and the tags included in this rule, if the incident was registered by the Rule Detector.
- The tag whose value was outside the limits of the permissible range of values, if the incident was registered by the Limit Detector.
If necessary, you can select a different preset for displaying data received from the monitored asset at the moment when the incident was registered. The graph uses a vertical blue dashed line to indicate the date and time when the incident was registered.
- Configuring how data is displayed on a graph in the History section
In the History section, you can enable the display of predicted tag values. This lets you assess the difference between actual tag values and predicted tag values. Enabling the display of predicted values will also let you view the values of indicator tags showing the results from applying diagnostic rules. Tag information (name, numerical ID, description, unit of measurement, time, and tag value) is displayed whenever you move your mouse cursor over a tag graph. You can also enable display of the tag name and description for each tag graph.
- Configuring the time settings for displaying data in the History section
When studying the behavior of tags, you can change the scale of the time axis or move forward or backward in time through graphs. When displaying shorter time intervals on tag graphs, the History section may show more details of the behavior of tags that had been averaged when a tag graph for a longer period was displayed.
- Changing the vertical boundaries for displaying data in the History section
The vertical scale of each graph is selected by default based on the minimum and maximum values of a tag in the displayed area. You can control the scale of graphs according to the scale of values on the vertical axis by using one of the following methods:
- If minimum and maximum permissible values (technical limits) are defined for a tag, enable the Always show technical limits function.
If a tag value is within the permissible range, the vertical scale of the graph will be fixed by limit lines derived from the lower and upper boundaries of the tag graph. If tag values go beyond the permissible limits, the vertical scale will be automatically changed to display the tag values exceeding the limits.
- In the tag properties, set the permissible boundaries for displaying tag values on graphs.
If tag values go beyond the defined boundaries, they will not be displayed on the tag graph. The permissible boundaries for displaying tag values take priority over the display of technical limits, even if the Always show technical limits function is enabled.
- If minimum and maximum permissible values (technical limits) are defined for a tag, enable the Always show technical limits function.
Adding a status, cause, expert opinion or note to an incident or incident group
Kaspersky MLAD lets you add an expert opinion or note to a registered incident.
An expert opinion is normally added by an expert (process engineer or ICS specialist) and may contain an incident analysis or recommendations on resolving a problem that is indicated by an identified incident. An expert opinion can be added to an individual incident or to a group of incidents. If expert opinions were previously added to incidents that are later put into a group, these opinions will also be displayed in the group (linked to each specific incident). When incidents are regrouped, the expert opinion for an incident migrates together with the incident to the new group.
Notes are intended to aid discussions between experts or operators of facilities regarding recommended actions for analysis, investigation, and remediation of an incident. Each note includes information stating who added the note and when it was added.
You can also add the cause of the incident and the incident status determined by the expert based on the incident analysis results. A status can be assigned to an individual incident or to a group of incidents. When changing the status of a group of incidents, Kaspersky MLAD changes the status of the incidents that are part of this group.
Before adding a cause, status, note or expert opinion, you must conduct an analysis of the registered incident.
To add an expert opinion, status, cause, or note to an incident:
- In the main menu, select the Incidents section.
- If necessary, change the incident status by selecting one of the following statuses from the Status drop-down list: Under review, Decision pending, Instructions issued, Problem closed, Cause unknown, Ignore, or False positive.
By default, an incident is assigned the Unknown status. If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the statuses of incidents.
- To display detailed technical specifications, click the right arrow (
 ) next to the relevant incident. In the details area that opens, you can do the following:
) next to the relevant incident. In the details area that opens, you can do the following:- If you need to add the cause of an incident, use the Incident cause field to select the cause of the incident.
If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete causes of incidents.
- If you want to add an expert opinion based on an analysis of a registered incident, click the Edit expert opinion (
 ) icon on the right of the Expert opinion field. In the field that opens, enter the opinion, and press ENTER.
) icon on the right of the Expert opinion field. In the field that opens, enter the opinion, and press ENTER.The expert opinion will be added to the selected incident and will appear in the incidents table in the Incidents section.
- If you need to add a note to an incident, enter your message in the Note field and click the Add note button.
You can provide a message up to 512 characters long.
- If you need to add the cause of an incident, use the Incident cause field to select the cause of the incident.
The status, cause, expert opinion, and note will be added to the incident and will be available to other users when viewing this incident.
When two or more similar incidents are detected, Kaspersky MLAD automatically combines them into a group. The group name is also automatically assigned in the format Group #N (N is replaced by the sequence number of the group). You can edit the group name, change the status of an incident group, and edit the expert opinion containing recommendations for analyzing similar events, for example.
To add a status and expert opinion to a group of incidents:
- In the main menu, select the Incidents section and click Groups.
- If necessary, change the incident group status by selecting one of the following statuses from the Status drop-down list: Under review, Decision pending, Instructions issued, Problem closed, Cause unknown, Ignore, or False positive.
When changing the status of a group of incidents, Kaspersky MLAD changes the status of the incidents that are part of this group. By default, a group of incidents is assigned the Unknown status.
If necessary, a user with administrator privileges can create, edit, or delete the statuses of incidents.
- In the incident groups table, double-click the row of the incident group.
The Edit group window opens.
You can also change the group on the Incidents tab. To do so, select the required group in the Group filter, and in the expert opinion section for the group, which is displayed above the incidents table, click the Edit button.
- To change the name of the incident group, enter a new name for the group in the Group name field.
- In the Expert opinion field, enter the text of the expert opinion (for example, recommendations for analyzing similar incidents).
- Click the Save button.
The status and expert opinion will be changed for the incident group and can now be viewed by other users in the Groups table in the Incidents section.
Page top
Exporting incidents to a file
Incidents registered for a specific period in Kaspersky MLAD can be exported to an XLSX file.
To save incidents registered for a specific period to a file:
- In the main menu, select the Incidents section.
- In the upper part of the opened page, select the start and end dates of the period.
- Click the Export button.
- Select a folder to save on your local drive, and save the file.
Incidents registered for the selected period in Kaspersky MLAD will be saved to an XLSX file on the local drive. The XLSX file can be opened in Microsoft Excel.
Page top
Working with ML models and templates
The Models section provides data on ML models and on the templates created based on the ML models added to Kaspersky MLAD.
The Models tab displays a table of ML models uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD or added based on the templates by the users with administrator privileges. There is a vertical menu  next to each model in the table that allows you to view detailed information about the model. You can view information about the ML model parameters and parameters of ML model elements, as well as view the diagram of the data flow between ML model elements.
next to each model in the table that allows you to view detailed information about the model. You can view information about the ML model parameters and parameters of ML model elements, as well as view the diagram of the data flow between ML model elements.
The Templates tab provides a table of templates created by the users with administrator privileges based on ML models added to Kaspersky MLAD.
Viewing ML model parameters
To view the parameters of an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the vertical menu
 next to the ML model whose data you need to view.
next to the ML model whose data you need to view. - To view the ML model parameters, select Model details.
The <ML model name> pane opens on the right on the Model parameters tab displaying a list of ML model parameters.
An ML model is characterized by the following parameters:
- ID – automatically assigned short identifier of the ML model.
- Model name – name of the ML model. The parameter can be changed by users with administrator privileges.
- UUID – automatically assigned full identifier of the ML model.
- Description – description of the ML model. The parameter can be changed by users with administrator privileges.
- File name – name of the ML model file.
- Version – version of the ML model.
- Updated by – name of the user who performed the last update of the ML model.
- Updated at – date and time of the last update of the ML model.
- Created by – name of the user who created the ML model.
- Created at – date and time when the ML model was created.
Viewing ML model element parameters
To view the parameters of an ML model element:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the vertical menu
 next to the ML model whose data you need to view, and select Model details.
next to the ML model whose data you need to view, and select Model details.The <ML model name> pane opens on the right showing detailed information on the ML model.
- To view the parameters of an ML model element, select the Model elements tab and click the down arrow (
 ) next to the relevant ML model element.
) next to the relevant ML model element.The <Model name> pane displays a list of the ML model element.parameters.
A list of ML model element parameters and their descriptions are provided in the table below.
ML model element parameters
ML model element parameters |
Description of ML model element parameters |
|---|---|
ID |
Automatically assigned short identifier of the ML model element. |
Element name |
Name of the ML model element. This parameter can be edited. |
UUID |
Automatically assigned full identifier of the ML model element. |
element_path |
Path to the ML model element. |
block_type |
Type of ML model element (for example, neural_forecaster – predictive neural network or rule). |
color |
Color to display the ML model element and indicator points of the incidents registered by the ML model element on the graphs in the Monitoring and History sections. This parameter can be edited. |
alpha |
Parameter for smoothing the cumulative MSE (for an ML model based on the Forecaster detector) or parameter for smoothing the anomaly detection probability (for a model based on the XGBoost detector). This parameter can be edited. |
delta_t |
Parameter that determines the step of the time grid (in nanoseconds). The ML model works with data calculated on a uniform temporal grid. Conversion of the received telemetry data to a uniform temporal grid is performed automatically. |
tag_ids |
List of tag identifiers included in the ML model element. |
in_tags |
List of tags that serve as input data for predicting the values of the output tags (out_tags). |
indicator_tags |
List of output indicator tags included in the ML model element. This parameter is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Rule Detector. |
input_window_size |
Input interval of observations measured by the number of steps of the time grid (size of the input window). |
power |
Power indicator of the cumulative forecast error (MSE). This parameter can be edited and is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Forecaster detector. |
threshold |
Threshold value for an incident registration. This parameter is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Forecaster detector. |
batch_size |
Number of input windows processed by the ML model element in one pass during training. This parameter is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Forecaster detector. |
forecast_shift |
Offset of the forecast window forecast_window_size relative to the start of the input window input_window_size (in time grid steps). |
forecast_window_size |
Size of the output window for which the ML model element determines the values of the output tags out_tags based on the input tags in_tags in the input window input_window_size. The output window size is specified as the number of time grid steps. |
out_tags and mse_weights |
List of output tags and their relative weights. The values of output tags are predicted by the ML model and then compared with the actual values. This parameter can be edited and is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Forecaster detector. |
mode |
MSE calculating method used by the Anomaly Detector service. This parameter is available only in the list of parameters of the ML model based on the Forecaster detector. |
In neural network ML models, the cumulative prediction error denoted by the MSE parameter in the application web interface is usually calculated with exponential smoothing, as the sum of the instantaneous prediction errors at the current and previous points, and the contribution of a point lagging k steps behind decreases with the coefficient (1-alpha)^k. The cumulative error is calculated as the power-th root of the mse_weights-weighted sum of the individual instantaneous prediction errors for each output tag to the specified power. The MSE value is calculated without smoothing when the alpha parameter is set to 1.
Viewing the data flow diagram of an ML model
You can view a diagram showing how data flows between elements of an ML model.
To view the data flow diagram of an ML model:
- In the main menu, select the Models section.
- Click the vertical menu
 next to the ML model whose data you need to view, and select Model details.
next to the ML model whose data you need to view, and select Model details.The <ML model name> pane opens on the right showing detailed information on the ML model.
- Select the Data flow diagram tab.
The <ML model name> pane displays a diagram of the data flow between ML model elements.
- If you need to view the settings of an ML model element, move the mouse cursor over it.
A window listing the values of settings of the selected element will be displayed.
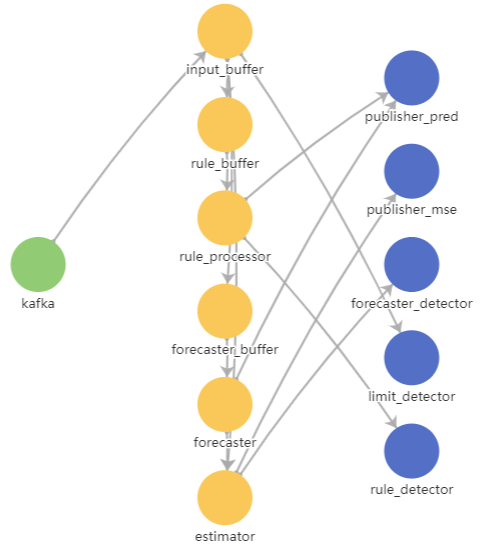
ML model data flow diagram
Managing presets
A preset is a set of tags generated by a user in arbitrary order or created automatically when an incident is registered. A set of tags in a custom preset can correspond to a certain aspect of the technological process or a section of the monitored asset.
In the Presets section, the left side of the window displays a list of available custom presets, and the right side of the window shows a list of tags included in the selected preset.
To view the received data on the graphs in the History and Monitoring sections, upload the preset configuration to Kaspersky MLAD from a JSON file. As part of Kaspersky MLAD deployment, a common preset configuration can be created for all users.
In the Presets section, you can also do the following:
- Create necessary presets that include tags corresponding to the industrial units of the monitored asset. The presets created by you are displayed only for your user account.
- Edit presets (add, group, or delete tags).
- Delete presets.
- Export presets to a JSON file.
You can also specify expressions with simple arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) to calculate derived tag values.

Presets section
Viewing a preset
You can view presets you created or uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD for your monitored asset.
To view a preset:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section.
The list of presets is displayed in the left part of the workspace.
- Click the relevant preset.
The table on the right shows the tags that are included in the selected preset. The following information is displayed for each tag included in the preset:
- ID refers to the tag ID.
- Tag name refers to the tag name.
- Dimension refers to the tag measurement units.
- Limits refers to the limit values for the tag; when these values are reached, incidents are registered if the Limit Detector is enabled.
- Description refers to a description of the tag.
If necessary, you can change the preset or create a new preset.
Page top
Creating a new preset
You can create new presets in Kaspersky MLAD.
When creating a preset, you can specify an expression to use for calculating the values of tags in the preset to display these values on the graph in the Time slice section. For example, you can use the specified expressions to view personal tag errors, predicted tag values, and the values of tags received from the monitored asset's sensors at the same time. You can use the following variables in your expressions:
- $tagValue is the received tag value (based on the results of monitoring).
- $tagError is the personal tag error.
- $tagPrediction is the predicted tag value.
- $tagX is the X coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location specified when creating the tag.
- $tagY is the Y coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location specified when creating the tag.
- $tagZ is the Z coordinate of the monitored asset's sensor location specified when creating the tag.
To create a new preset:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section and click the Create button.
The Create preset window opens.
- Specify the name of the preset in the Preset name field.
- If you need to change the preset icon, click the Choose an icon button and select the appropriate icon in the opened window.
By default, the preset is assigned a sun icon (
 ).
).You can upload a preset icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you want to delete the preset icon, click the preset icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- If you want to add an expression for calculating tag values to display them on a graph in the Time slice section, do the following:
- Turn on the Configure expressions for Time Slice toggle button.
- In the X-axis caption field, enter the caption to be displayed on the x-axis.
- Click the Add expression button and specify the following values in the drop-down section:
- In the Expression name field, enter the name of the expression.
- In the Y-axis caption field, enter the caption to be displayed on the y-axis.
- In the Expression for calculation field, enter an expression for calculating tag values.
You can define expressions with simple arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division). For example, if the sensors are reporting temperature in Fahrenheit, you can use the following expression to display the temperature in Celsius:
5/9 * ($tagValue - 32)
If necessary, you can add multiple expressions for the Time slice section.
- In the Graph color field, select the color of the graph that will be displayed for the preset in the Time slice section.
- If you want to delete an expression from a preset for the Time slice section, click the trash bin icon (
 ) in the lower-right corner of the expression section.
) in the lower-right corner of the expression section.
- If you need to add tags that are part of another preset, select this preset from the Copy tags from selected preset drop-down list.
- Add tags to the preset by selecting the check boxes next to the relevant tags in the list below. You can search for tags by entering the tag name in the Search by tag name field.
- If you need to delete tags from a preset, clear the check boxes next to the tags you want to delete in the list of tags.
- Click the Create button.
The new preset is displayed in the Presets section in the list of presets on the left and in the drop-down list of presets in the History and Monitoring sections. The preset for which step 4 of these instructions was performed will also be displayed in the drop-down list of presets in the Time slice section.
If necessary, you can change the position of presets in the list of presets. To do this, drag the preset up or down in the list by the dots ( ) to the left of its icon.
) to the left of its icon.
Editing a preset
You can edit the presets you created or uploaded.
To edit a preset:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant preset from the list of presets on the left.
The table on the right shows all tags that are included in the selected preset.
If necessary, change the position of the tags in the table. To do this, drag the desired tag up or down in the tag tree by the dots (
 ) to the left of its icon.
) to the left of its icon. - Click the Change preset (
 ) button next to the selected preset.
) button next to the selected preset.The Edit preset window opens.
- If required, enter the new name of the preset in the Preset name field.
You can also modify the preset name in the preset list. To do this, double-click the preset name, in the opened field enter a new preset name, and press ENTER.
- If you need to change the preset icon, click the Choose an icon button and select the appropriate icon in the opened window.
You can upload a preset icon by clicking the Load icon button. Images of any format larger than 128x128 pixels are shrunk to 128x128 while maintaining the aspect ratio. The size of the uploaded image in SVG format must not exceed 200 KB.
If you want to delete the preset icon, click the preset icon and then click Delete in the opened window.
- If you want to add an expression for calculating tag values to display them on a graph in the Time slice section, do the following:
- Turn on the Configure expressions for Time Slice toggle button.
- In the X-axis caption field, enter the caption to be displayed on the x-axis.
- Click the Add expression button and specify the following values in the drop-down section:
- In the Expression name field, enter the name of the expression.
- In the Y-axis caption field, enter the caption to be displayed on the y-axis.
- In the Expression for calculation field, enter an expression for calculating tag values.
You can define expressions with simple arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division). For example, if the sensors are reporting temperature in Fahrenheit, you can use the following expression to display the temperature in Celsius:
5/9 * ($tagValue - 32)
If necessary, you can add multiple expressions for the Time slice section.
- In the Graph color field, select the color of the graph that will be displayed for the preset in the Time slice section.
- To delete an expression from a preset for the Time slice section, click the trash bin icon (
 ) in the lower-right corner of the expression section.
) in the lower-right corner of the expression section.
- If necessary, add tags to the preset by selecting the check boxes next to the relevant tags in the list of tags below. You can search for tags by entering the tag name in the Search by tag name field.
- If necessary, clear the check boxes next to the names of the tags that you want to remove from the preset.
- Click the Save button.
The changed preset will be updated in the list of presets in the Presets section and in the drop-down list of presets in the History and Monitoring sections. The changed preset for which step 6 of these instructions was performed will also be displayed in the drop-down list of presets in the Time slice section.
If necessary, you can change the position of presets in the list of presets. To do this, drag the preset up or down in the list by the dots ( ) to the left of its icon.
) to the left of its icon.
Deleting a preset
You can delete the presets you created or uploaded.
To delete a preset:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section.
- On the opened page, select the relevant preset from the list of presets on the left.
- Click the Delete preset (
 ) button next to the selected preset.
) button next to the selected preset. - In the opened Delete preset window, click Yes to confirm deletion of the preset.
The preset will be deleted from the list of presets.
Page top
Loading a preset configuration from a file
You can load a preset configuration to Kaspersky MLAD from a JSON file. If the file is uploaded by a user with administrator privileges, the tag configuration is uploaded to the application as well.
To upload a preset configuration to Kaspersky MLAD:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section.
- In the upper part of the opened page, click the Import button.
- Select the JSON file containing the preset configuration on your local drive.
The selected file will be loaded into Kaspersky MLAD, and new presets will be displayed in the list of presets.
Page top
Saving a preset configuration to a file
You can save the presets you created and uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD as a JSON file.
To save the presets you created and uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD to a file:
- In the main menu, select the Presets section.
- In the upper part of the opened page, click the Export button.
The presets you created and uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD will be saved to a JSON file on the local drive.
Page top
Viewing the status of a service
The Services section displays a table containing information about services and their statuses. In the Kaspersky MLAD web interface, services are grouped by their functionality, and the following information is displayed for each service:
- Name is the name of the service.
- Status refers to the current status of the service (Started, Stopped, Starting, Unavailable).
- Actions are the available actions (start, stop, and restart). Only a user with administrator privileges can start, stop, or restart Kaspersky MLAD services.
You can view the status of a service to make sure that the service was successfully started or stopped.
Kaspersky MLAD checks the statuses of services every 30 seconds.
To view the status of a service:
In the main menu, select the Services section.
The Services section opens to display a table listing all available services, their statuses, and available actions (start, stop, and restart).
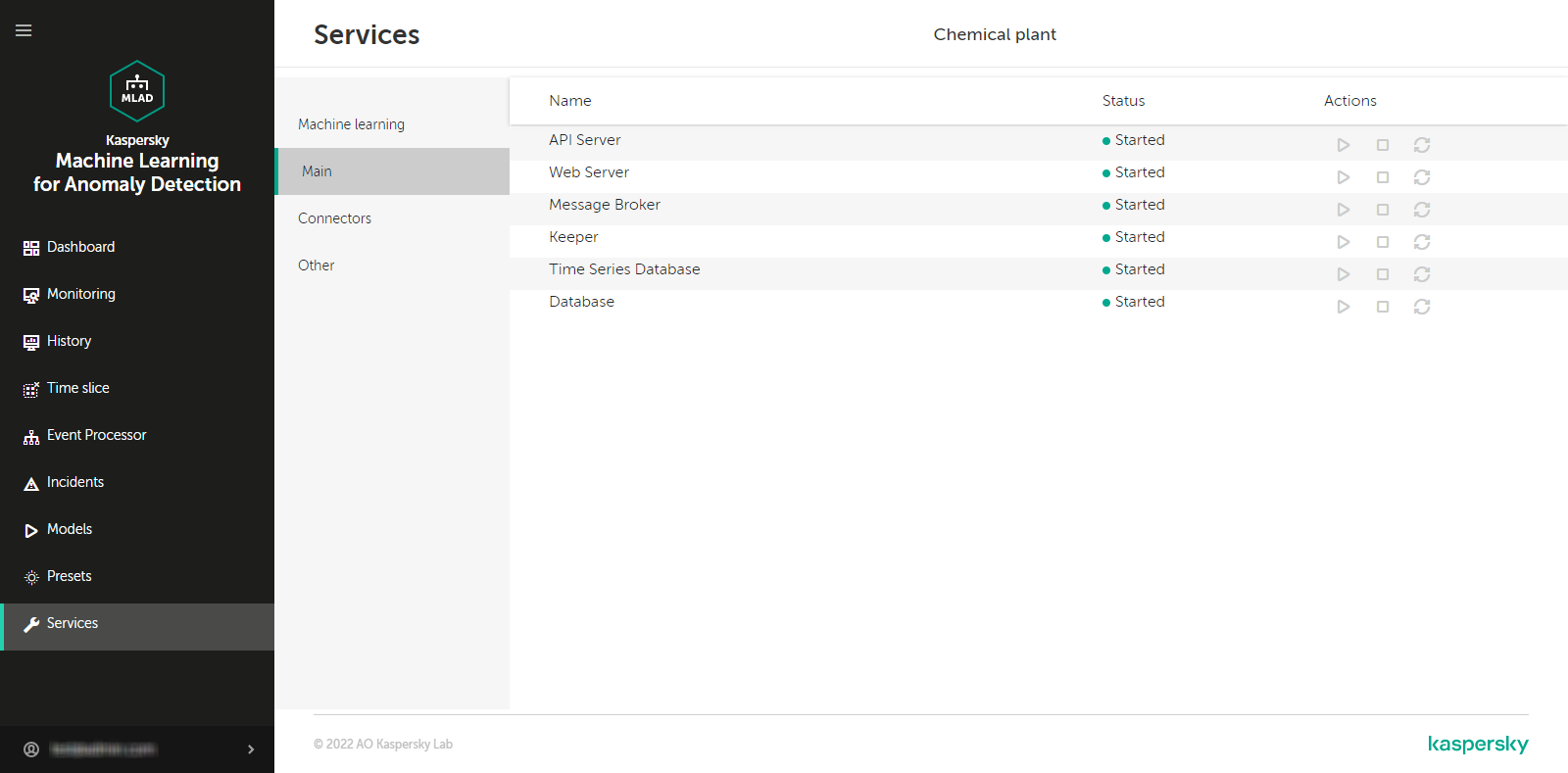
Services section
Page top
Troubleshooting
This section describes possible problems in the operation of Kaspersky MLAD and methods for resolving them.
When connecting to Kaspersky MLAD, the browser displays a certificate warning
Problem
When attempting to connect to Kaspersky MLAD, the browser displays a warning that the security certificate or the established connection is not trusted. The contents of the warning depend on the specific browser being used.
Solution
After Kaspersky MLAD is installed, a self-signed certificate is used by default to connect to the web interface. When using a self-signed certificate, the browser displays a warning that the security certificate or the connection being established is not trusted. To use a trusted certificate, contact a qualified administrator – a Customer employee who has the right to accept the application License Agreement. The administrator can update certificates for connecting to Kaspersky MLAD using the web interface.
You can temporarily use a self-signed certificate to connect to Kaspersky MLAD (for example, during test operation). When using a self-signed certificate, in the browser warning window select the option that lets you continue connecting. After connecting to Kaspersky MLAD, the browser window displays a warning about the certificate. The text of the message depends on the specific browser being used.
If the browser displays a warning after a trusted certificate is installed, then the certificate may have been spoofed by a malicious actor. Contact the Technical Support.
Page top
The hard drive has run out of free space
Problem
The hard drive of the computer on which Kaspersky MLAD is installed has run out of free disk space.
Solution
The computer must meet the hardware and software requirements to ensure proper functioning of the application.
To ensure that the application functions correctly:
On the hard drive of the computer, free up sufficient space to satisfy the minimum free disk space requirements.
Page top
The operating system restarted unexpectedly
Problem
Unexpected restart of a computer with Kaspersky MLAD installed.
Solution
Wait for the computer restart to finish. After the computer has restarted, the following statuses of Kaspersky MLAD are possible:
- Kaspersky MLAD has fully resumed normal operation.
- Kaspersky MLAD has not resumed normal operation.
If the malfunction persists, please contact Kaspersky Technical Support.
Cannot connect to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface
Problem
When connecting to the web interface of Kaspersky MLAD after correct password is entered, the following error is displayed: Error! Invalid server error.
Solution
Often, the error Error! Invalid server error occurs because the server hosting Kaspersky MLAD has run out of free hard drive space.
To restore correct operation of the application:
On the hard drive of the server, free up sufficient space to satisfy the minimum free disk space requirements.
After freeing up disk space, if you still cannot connect to the web interface of Kaspersky MLAD, please contact Technical Support.
Page top
Graphs are not displayed in the History and Monitoring sections
Problem
The History and Monitoring sections are not showing graphs.
This may be caused by the following:
- Presets were not imported into Kaspersky MLAD.
- The selected preset contains no tags.
- Time interval with no data is selected in the History section.
- The connector used to receive data from the monitored asset is not running.
- The monitored asset is powered off.
Solution
Make sure the monitored asset is on. Enable the connector used to receive data from the monitored asset. Import or create presets that contain tags. To display data on the graph, in the History section, select a date, a time interval, and a preset containing tags. To display data in the Monitoring section, select a time interval and a preset containing tags.
Events are not transmitted between Kaspersky MLAD and external systems
Problem
Events are not received by Kaspersky MLAD and/or alerts about the monitor activation are not sent to external systems.
Solution
To restore the exchange of events with external systems:
- Start the Event Processor service and the CEF Connector.
- When configuring the Event Processor service, perform the following steps:
- In the Event processor configuration file field, upload the configuration file describing the event parameters.
- In the Interval for receiving batch events (sec.) field, specify the time interval in seconds required to generate an episode, taking into account the speed of receiving events from the monitored asset.
- To receive events in the .env file, specify the port number used to connect to the external event source.
- To send events, when configuring the CEF Connector, specify the IP address and the port number for connecting to the external system.
Cannot load data to view in the Event Processor section
Problem
After restarting Kaspersky MLAD, it is impossible to upload data for viewing the events history and/or pattern history in the Event Processor section (the Process request button is not available). This problem may also arise after changing the settings of the Event Processor service.
Solution
To resume uploading of data for viewing the events history and/or pattern history in the Event Processor section:
It is recommended to wait for several minutes. After Kaspersky MLAD is restarted, the state of the Event Processor service is restored. It may take several minutes to restore the state of the service if there is a significantly large number of processed events or registered patterns. Until the state of the Event Processor service is restored in the Event Processor section, requests are not fulfilled, data is not updated, and data received from the CEF Connector is not processed. This data is temporarily stored in the system message queue and is processed after the state of the Event Processor service is restored.
Page top
Data is incorrectly processed in the Event Processor section
Problem
A large number of short patterns is being created.
Solution
To reduce the number of short patterns registered:
You must increase the episode length in the Event Processor service settings.
Problem
A large number of monitor activation alerts is being received.
Solution
To reduce the number of monitor activation alerts:
Check the previously created monitors and delete the ones that are no longer needed. It is also recommended to update the following monitor activation parameters: Sliding window and Threshold.
Page top
Events are not displayed in the Event Processor section
Problem
When you make a request to view the event history, the Event Processor section does not display the events that were displayed before.
Solution
Make sure that Kaspersky MLAD saves the state of the Event Processor service to the database table.
If the state of the Event Processor service is saved to a file in bit format, Kaspersky MLAD saves the state of the service with the frequency specified in the Component backup frequency field. When the Event Processor service is restarted, the results of processing of the event stream received by the Event Processor since the last time the service state was saved are lost.
Page top
Previously created monitors and the specified attention settings are not displayed in the Event Processor section
Problem
After restarting or modifying the Event Processor service settings, the Event Processor section does not display previously created monitors and the specified attention settings.
Solution
The Event Processor saves the created monitors and the specified attention settings after saving the state of the Event Processor service to a database table or a file in bit format. If Kaspersky MLAD saves the state of the service to a database table, it is recommended not to restart the Event Processor service or change its settings until the first episode of events from the monitored asset is processed, in order to save the created monitors and the specified attention settings. If the application saves the state of the Event Processor service to a file in bit format, it is recommended not to restart the Event Processor service or change its settings until the first backup of the service, in order to save the created monitors and the defined attention settings. The frequency of the Event Processor service backups depends on the value of the Component backup frequency setting specified by the administrator.
To receive events, configure the settings and start the Event Processor service and the CEF Connector. To process the registered incidents as events, configure and start the Anomaly Detector service and the connector required to receive telemetry data from the monitored asset. Go to the Dashboard section and make sure that events are received by Kaspersky MLAD in the online mode.
If the malfunction persists, please contact Kaspersky Technical Support.
Page top
The localization language for Help needs to be changed before connecting to the application
Problem
The Help localization language must be changed prior to connecting to the Kaspersky MLAD web interface.
Solution
To change the localization language of the application Help Guide without connecting to the application web interface:
- Open the browser installed on your computer.
- In the browser address bar, enter the Kaspersky MLAD web address received from the ICS specialist.
- On the account credentials entry page that opens, click Help (
 ).
). - Specify the necessary localization language in the web address:
- ru – if you want to open Help in Russian (for example, https://<Kaspersky MLAD web address>/help/ru/171583.htm).
- en – if you want to open Help in English (for example, https://<Kaspersky MLAD web address>/help/en/171583.htm).
After connecting to the application, you can change the language of the interface and Help in the user menu.
Page top
Contacting Technical Support
This section describes the ways to receive technical support, and its terms and conditions.
If you cannot find a solution to your problem in the application documentation or in one of the other sources of information about the application, you are advised to contact Technical Support. Technical Support experts will answer your questions about installing and using the application.
Technical support services are provided if you have an active Technical Support Agreement. The scope of provided technical support services is determined by the current Technical Support Agreement.
Before contacting Technical Support, please read the technical support rules.
You can contact Technical Support experts by emailing them at mlad-support@kaspersky.com.
Technical Support experts may request that you provide information from the Kaspersky MLAD logging system.
Page top
Settings of a .env configuration file
The settings of the configuration file can be changed only by a Kaspersky Lab employee or certified integrator.
The .env configuration file is filled in to configure the CEF Connector and has the settings described in the table below.
Settings of a .env configuration file
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
CEF_CONNECTOR_INCOMING_IP |
IP address used to connect the CEF Connector to an external source of events. |
CEF_INCOMING_PORT |
Port number that will be used to connect the CEF Connector to an external source of events. |
To apply changes to the configuration file, restart Kaspersky MLAD.
Page top
Example JSON file containing a tag configuration
Below is an example of a JSON file containing descriptions of tags, their configuration, and presets.
A user with administrator privileges uploads the tag configuration in the Settings → Tags section. The configuration of the presets described in the JSON file is also uploaded to Kaspersky MLAD. A user with operator privileges can upload only preset configurations.
{ "tags": { "1": { "id": 1, "name": "Sep_level_setpoint", "description": "Separator-level setpoint", "tag_type": "", "measurement_units": "%", "plc_id": "TEP", "real_type": "line", "predicted_type": "spline", "max": null, "min": null, "high_limit": null, "low_limit": null, "cls": "level", "type": "SV", "position": [], "icon": null, "expressions": null, "is_virtual": false, "bias": 0, "multiplier": 1, "threshold_lines": null }, ... "121": { "id": 121, "name": "No reactor temperature response", "description": "Rule", "tag_type": "13", "measurement_units": "", "plc_id": "", "real_type": "line", "predicted_type": "spline", "max": null, "min": null, "high_limit": null, "low_limit": null, "cls": "level", "type": "PV", "position": [], "icon": null, "expressions": null, "is_virtual": false, "bias": 0, "multiplier": 1, "threshold_lines": null } }, "tags_structure": [ { "directory_id": "root", "name": "Root", "description": null, "children": [ "tags", "trash_bin" ], "icon": null }, ... { "directory_id": "tags", "name": "Chemical plant", "description": null, "children": [ "Reactor", "Separator", "Stripper", "Product", "Purge", "Cooler", "a5eeb30739a742d3955765608ff73229" ], "icon": null } ], "presets": [ { "name": "Product", "tag_list": [ 51, 52, 53, 49, 50 ], "evaluations": { "axis_x_name": "", "evaluations": [] }, "css_class": null, "icon": "logout-signout" }, ... { "name": "Cooler", "tag_list": [ 64 ], "evaluations": { "axis_x_name": "", "evaluations": [] }, "css_class": null, "icon": "graph" } ], "version": 2 } |
Example JSON file containing a configuration for the Event Processor service
Below is an example of a JSON file containing a configuration for the Event Processor service. The file contains a description of the event parameters for the Event Processor.
The configuration file is created by a Kaspersky expert or a certified integrator. A user with administrator privileges uploads the Event Processor configuration file when configuring the Event Processor service settings.
{ "timestamp_field": "TimeStamp", "timestamp_scale": "ms", "fields": [ "User_Host", "User_Name", "Destination_Host", "Access_Result" ], "groupBy": [ "User_Host", "User_Name", "Destination_Host", "Access_Result" ], "nodes": [ { "name": "User_Name", "depth": 0, "tooltip": { "templates": [ "User: {{User_Name}}" ] } }, { "name": "User_Host", "depth": 1, "tooltip": { "templates": [ "User host: {{User_Host}}" ] } }, { "name": "Destination_Host", "depth": 2, "tooltip": { "templates": [ "Destination: {{Destination_Host}}" ] } } ], "links": [ { "source": "User_Name", "target": "User_Host", "value": "count", "tooltip": { "templates": [ "{{User_Name}} » {{User_Host}}", "Count: {{count}}" ] }, "isGraphGroup": true }, { "source": "User_Host", "target": "Destination_Host", "value": "count", "tooltip": { "templates": [ "{{User_Host}} » {{Destination_Host}}", "DeviceEventClassID: {{Access_Result}}", "Count: {{count}}" ] } } ] }
|
Viewing the Kaspersky MLAD log
The Kaspersky MLAD log stores entries only for the last 48 hours.
Naming Kaspersky MLAD services in the logging subsystem
Kaspersky MLAD services whose states are monitored in the logging subsystem are identified based on the names of their corresponding containers or images in Docker. In most cases, the abbreviated name of the service is used as the name of the image. The container name is formed according to the following template:
<application folder>-<image name>-#,
where # is the number of the Docker container.
By default, Kaspersky MLAD uses the mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number> folder.
The table below presents the correspondence between Kaspersky MLAD services and the names of Docker containers and images.
Correspondence between Kaspersky MLAD services and the names of Docker containers and images
Kaspersky MLAD service |
Image name |
Container name |
|---|---|---|
Anomaly Detector |
anomaly_detector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-anomaly_detector-1 |
Time Series Database |
influxdb |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-influxdb-1 |
Message Broker |
kafka |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-kafka-1 |
Keeper |
keeper |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-keeper-1 |
Logger |
logger |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-logger-1 |
Database |
postgres |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-postgres-1 |
Similar Anomaly |
similar_anomaly |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-similar_anomaly-1 |
Event Processor |
event-processor |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-event-processor-1 |
Stream Processor |
stream-processor |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-stream-processor-1 |
Trainer |
trainer |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-trainer-1 |
Web Server |
nginx-ui |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-nginx-ui-1 |
API Server |
web-server |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-web-server-1 |
Mail Notifier |
postman |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-postman-1 |
OPC UA Connector |
opcua-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-opcua-connector-1 |
MQTT Connector |
mqtt-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-mqtt-connector-1 |
AMQP Connector |
amqp-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-amqp-connector-1 |
HTTP Connector |
gate |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-gate-1 |
KICS Connector |
kics3-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-kics3-connector-1 |
CEF Connector |
cef-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-cef-connector-1 |
WebSocket Connector |
ws-connector |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-ws-connector-1 |
|
webstatic |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-webstatic-1 |
|
migrations |
mlad-release-3.0.0-<installation build number>-migrations-1 |
Scenario: Assessing the main metrics of Kaspersky MLAD
Before starting to work with the logging subsystem, it is recommended to read the Grafana User Guide.
When connecting to the logging subsystem for the first time, you must change the default password.
This subsection provides a sequence of actions that must be performed to assess the health and general state of Kaspersky MLAD.
The scenario for assessing the health and general state of Kaspersky MLAD consists of the following steps:
- Navigating to the logging subsystem
Select the Logging section from the user menu. This opens the Grafana interface in which you need to enter the login and password of the Kaspersky MLAD user.
This is available only for Kaspersky MLAD users with the administrator role.
- Analyzing the main metrics of Kaspersky MLAD
In the Summary docker metrics section, analyze the graphs of the main Kaspersky MLAD metrics for the selected period.
The following metrics are displayed for each container of Kaspersky MLAD services:
- CPU usage – history of central processor workload caused by the container. This is measured as a percentage.
- RAM usage – history of the container's RAM usage. This is measured in bytes.
- Disk usage – history of the container's load on the disk subsystem (read/write operations). This is measured in bytes.
- Network usage – history of the container's use of network resources. This is measured in bytes per second.
Scenario: Viewing container metrics and logs
Before starting to work with the logging subsystem, it is recommended to read the Grafana User Guide.
The Kaspersky MLAD log stores entries only for the last 48 hours.
This subsection provides steps for assessing the performance and viewing the logs of a specific container from the Kaspersky MLAD distribution kit.
The scenario for assessing the performance and viewing the logs of a specific container consists of the following steps:
- Navigating to the logging subsystem
Select the Logging subsection from the user menu. This opens the Grafana interface in which you need to enter the login and password of the Kaspersky MLAD user.
This is available only for Kaspersky MLAD users with the administrator role.
- Navigating to the section with container logs and metrics
Go to the Service detailed monitoring section and select the relevant container from the Container drop-down list.
- Analyzing container metrics
In the Service detailed monitoring section, analyze the graphs of Kaspersky MLAD metrics for the selected container during the relevant period.
The Service detailed monitoring section provides the following metrics:
- Memory – history of the container's RAM usage. This is measured in bytes.
- CPU – history of central processor workload caused by the container. This is measured as a percentage.
- File system – history of the container's load on the disk subsystem (read/write operations). This is measured in bytes.
- Network – history of the container's use of network resources. This is measured in bytes per second.
- Analyzing container logs
Analyze the container log records for the selected period, which are displayed under the metrics dashboard. You can search the container log records. To do so, enter a search query in the Log search field and press the ENTER key. To reset the search results, clear the Log search field and press the ENTER key.
- Exporting container logs
To export container logs for the selected period to a text file, in the Service detailed monitoring section, select Inspect → Data from the Service log drop-down list and click Download CSV in the opened form.
Special characters of regular expressions
You can use regular expressions to search for events, patterns and values of event parameters in the Event Processor section. Kaspersky MLAD supports use of the following special characters in regular expressions:
^– Corresponds to the start of the parameter value. For example,^Аmeans that the event parameter search will look for values beginning with the letter A.$– Corresponds to the end of the parameter value. For example,A$means that the event parameter search will look for values ending with the letter A..– Corresponds to any single character.|– Splits permissible options for characters or a set of characters in a parameter value. For example,c(o|a)tmatches both thecotandcatvalues.\– Indicates that the next character is an ordinary character (not a special character) in the parameter value. You can use the\character to search for special characters in a parameter value. For example,\.describes a dot in the parameter value, while\\describes a backslash.[]– Corresponds to any character from the set of permissible characters. For example,[abc]matches the occurrence of any one of the three specified characters.To search for a range of values, you can use the
-character. To find the characters that are not within the specified range, you can use the^character in the square brackets. For example,[^0-9]means any character except numerals can be present.
You can use the following special characters to indicate the necessary number of repetitions of an expression in the values of event parameters:
?– Character indicating that the preceding expression may occur zero or one time in a parameter value.*– Character indicating that the preceding expression may occur zero or more times in a parameter value.+– Character indicating that the preceding expression may occur one or more times in a parameter value.{}– Character class that lets you indicate the necessary number of repetitions of the preceding expression. You can specify the repetition count in one of the following ways:{n}– The expression preceding the curly brackets occurs in the parameter value exactlyntimes.{m,n}– The expression preceding the curly brackets occurs in the parameter value frommtontimes inclusive.{m,}– The expression preceding the curly brackets occurs in the parameter value at leastmtimes.{,n}– The expression preceding the curly brackets occurs in the parameter value no more thanntimes.
You can also use parentheses () to group elements of an expression. For example, (c[oa]t){2} matches cotcot, catcat, cotcat, and catcot.
Glossary
Account role
Set of access rights that determine the actions available to a user when connected to the application web interface. There are two roles available to users in Kaspersky MLAD: Administrator and Operator.
Anomaly
Any deviation in the behavior of a monitored asset that is abnormal, unexpected, and not prescribed by the industrial process.
Attention
A special configuration of the Event Processor intended to track events and patterns for specific subsets of event history (attention directions). An attention direction is defined by the event parameter value that is common for all events of this direction. The Event Processor detects events and patterns only for the attention directions defined in the attention settings.
Connector
Service that facilitates the exchange of data with external systems.
Event
Set of values describing a change in the state of a monitored asset based on a predefined list of parameters, with the timestamp of the change.
Gradient boosting
Machine learning technique for classification and regression problems that builds a prediction model in the form of an ensemble of prediction models, which are typically decision trees (XGBoost).
ICS
Abbreviation for Industrial Control System. A package of hardware and software designed to automate control of process equipment at industrial enterprises.
Incident
A deviation from the expected (normal) behavior of a monitored asset identified by the anomaly detector.
ML model
Algorithm based on machine learning methods tasked with analyzing the telemetry of the monitored asset and detecting anomalies.
ML model branch
Determines how the predicted tag value, personal tag error and MSE are calculated. For a complex model, the calculation may involve multiple ML model elements that have a different composition of tags and error calculation parameters.
Monitor
Source of notifications about patterns, events, or values of event parameters detected by the Event Processor according to the defined monitoring criteria. The monitoring criteria define a sliding time interval, the number of sequential detections, filters for event parameter values, and the condition for detecting new events, patterns, or event parameter values.
Notification
A message with information about an incident (or incidents), which is sent by the application via notification delivery systems (for example, via email) to the specified addresses.
Pattern
Sequence of events or other patterns identified within the stream of events from the monitored asset.
Preset
Set of tags generated by a user in arbitrary order or created automatically when an incident is registered. A set of tags in a custom preset can correspond to a certain aspect of the technological process or a section of the monitored asset.
Tag
Variable that contains the value of a specific process parameter such as temperature.
Uniform temporal grid (UTG)
An infinite sequence of points in time separated by equal intervals, to which the stream of incoming telemetry data is converted.
Page top
Information about third-party code
Information about third-party code is contained in the file legal_notices.txt located in the application installation folder (in the 'legal' subfolder).
Page top
Trademark notices
Registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Ubuntu is a registered trademark of Canonical Ltd.
The Grafana Word Mark and Grafana Logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of Coding Instinct AB in the United States and other countries and are used with the permission of Coding Instinct. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by Coding Instinct, or the Grafana community.
Docker and the Docker logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Docker, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Docker, Inc. and other parties may also have trademark rights described in other terms used in this document.
Google Chrome is a trademark of Google LLC.
TensorFlow and any related marks are trademarks of Google LLC.
Intel, Core, and Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Microsoft and Excel are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Python is a trademark or registered trademark of Python Software Foundation.
Page top